Incline of the 21st Century's Mining Industry to Developing State of Post-Industry: Survival of the Fittest and Sustainable Development
-
摘要: “后工业”(post-industry)是知识经济或曰“新经济”的发展时代.这个时代的自然资源和一般劳动力资源, 包括矿产资源在国民经济和社会发展中的基础地位逐渐为知识产权、市场网络、信息、创新环境等后天获得性资源, 以及为创新人才的新“认知”(recognized intellect, RI)所代替.然而, 据矿产资源分布及其成矿既具有一定的全球统一性又有区域的特殊性, 以及不同国家(地区)对矿产资源勘查程度的不均衡性, 特别是矿业活动与其他产业性质的不同, 如何能按不同国家(地区)的具体发展状况, 做好21世纪矿业向“后工业”发展势态的倾斜, 达到适者生存和矿业可持续发展的目标是当代探讨的重大问题.在概括阐述了21世纪矿业发展势态、矿业活动特点及其自然属性的基础上, 提出了矿业可持续发展的地质勘查和矿业活动决策支持系统的模拟, 以及对当前紧缺铜矿资源可持续发展的新“认知”.Abstract: Post industry is a developing epoch regarded as "intellectual economy" or "new economy". In these years, natural resources, common (general) labour resources and mineral resources' basic status in national economy and social development has gradually been replaced by acquired resources, such as: information property right, marketing network, information and innovative environment and new "recognized intellect" for persons with innovative ability. However, the distribution and metallogeny of mineral resources possess certain global uniformity and regional exceptionality as well as inhomogeneity of exploring extent of different countries to mineral resources, especially to the difference of mining activities and other industry, so if we can, in term of different developing conditions of different countries, manage the 21st century's mining industry to incline to developing states of "post industry", trying to make it realize the survival of the fittest and sustainable development - obviously, it is also an important project expecting to be discussed. In this paper, on the basis of the general discussion for developing state of the 21st century's mining industry, the characteristics of mining activities and its natural property, the author proposes a modeling of geological exploration for sustainable development of mining industry and decision making system for mining activity, as well as the new "recognized intellect" for sustainable development of very shortage copper deposits.
-
图 1 矿产勘查评价模拟设想
Ⅰ.矿产普查; Ⅱ.矿床勘探(初步); Ⅲ.矿床勘探(详细); Ⅳ.矿山建设可行性研究; Ⅴ.矿山建设; Ⅵ.矿山基础建设矿床地质研究; Ⅶ.矿山生产矿床地质研究.1.可进行勘探(初步) 矿床; 2.工业远景不明矿床; 3.无地质和工业远景矿床; 4.可进行勘探(详细) 矿床; 5.成矿复杂但具开采技术经济条件初步可行矿床; 6.成矿基本查明但具未来开采技术经济条件可行矿床; 7.成矿复杂不具开采技术经济条件可行矿床; 8.可进行初步矿山建设设计矿床; 9.按计划任务进行建设设计矿山; 10.达到最终开采技术经济条件可行研究的技术储备矿山(暂不建设); 11.投资单位基建矿山; 12.已建成矿山; 13.已投产和持续扩大远景矿山; (1-3) /5.0表示工作周期(月或年) /投资百分比
Fig. 1. Assessment modeling of mineral exploration
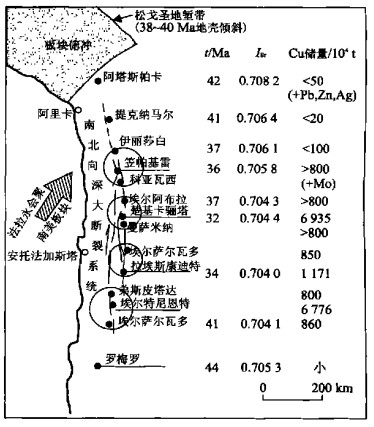
表 1 世界铜金属储量大于500万t的铜矿床
Table 1. More than 5 million tons of metals for copper deposits in the world

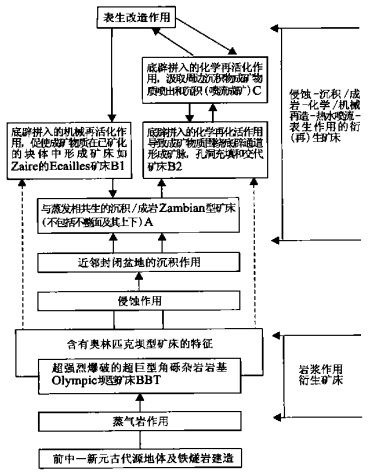
表 2 澳林匹克坝铜金矿和沉积岩容矿型铁铜钴矿衍生成矿变异相及演化
Table 2. Derivative heteromorphic phase deposit and its evolution of Olympic Dam Cu-Au-U-La-Ce deposit and sedimentary-hosted Fe-Cu-Co-Ag-Zn deposit

-
[1] 宋瑞祥. 中国矿产资源报告[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997.43-52.Song R X. Mineral resources report of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1997. 43-52. [2] 裴荣富, 熊群尧. 金属成矿省等级体制成矿与矿产勘查评价: 当代矿产资源勘查评价的理论与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999. 134-141.Pei R F, Xiong Q Y. Hierarchical systematic metallogeny and assessment of mineral exploration in metallogenic province: theory and method for assessment of mineral exploration[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1999. 134-141. [3] 裴荣富, 熊群尧, 沈保丰. 难识别及隐伏大矿、富矿资源潜力的地质评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2001. 72-75.Pei R F, Xiong Q Y, Shen B F. Geological assessment of mineral resources potential for hard-identified concealed large rich ore deposits[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2001. 72-75. [4] 裴荣富, 吴良士, 熊群尧, 等. 中国特大型矿床成矿偏在性与异常成矿构造聚敛场[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998. 262-284, 312-364.Pei R F, Wu LS, Xong Q Y, et al. Preferentially of exceptional ore deposits and its metallotect convergence [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1998. 262-284, 312-364. [5] 李朝阳, 徐贵忠, 胡瑞忠, 等. 中国铜矿主要类型特征及其成矿远景[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000.1-10.Li C Y, Xiu G Z, Hu RZ. Characteristics of major types of copper deposits and its metallogenic potential of China [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2000. 1-10. [6] 戴自希. 国外铜矿地质概况[M]. 北京: 地矿部地质矿产司, 1983. 36-87.Dai Z X. General geological situation of copper ore in foreign countries[M]. Beijing: Geological Mineral Department of the Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources, 1983. 36-87. [7] Goldfarb R J, Groves D I. Orogenic gold and geologic time: a global synthesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2001. 18: 1-13. [8] 赵鹏大. 矿产勘查理论与方法[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2000.5-7, 24-25.Zhao P D. Mineral exploration theory and method[M]. Wuhan: China Geological University of Geoscience Press, 2000. 5-7, 24-25. [9] Kirkham R V. Sediment hosted stratiform copper(SSC) other stratabound base metal deposits and the importance of basinal brines and/or evaporites, halotectonics and halokinesis[A]. Proceedings of the joint sixth SGA-SEG [C]. Lisse: Swets & Zeitlinger Publishers, 2001. 15-18. [10] 裴荣富, 吴良士, 熊群尧, 等. 找寻特大型隐伏矿床的衍生矿床导向和成矿轨迹追踪研究[J]. 矿床地质, 1994, 13(4): 380-382. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ404.009.htmPei R F, Wu LS, Xiong Q Y, et al. Derivative deposits as a guide and metallogenetic path for prospecting concealed ore deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1994, 13 (4): 380-382. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ404.009.htm [11] Bogacz W V. Metalliferous deposits: tectogenesis and mineralization at the beginning of the 21st century[A]. Proceedings of the joint sixth SGA-SEG[C]. Lisse: Swets & Zeitlinger Publishers, 2001. 7-13. -










 下载:
下载: