Groundwater Isotopic Stratification and Its Implications in Northern China
-
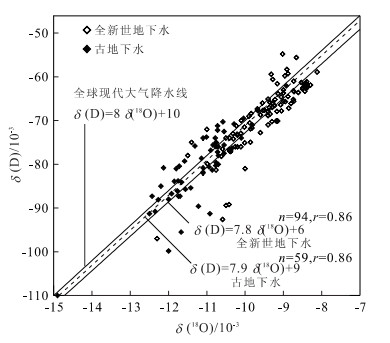
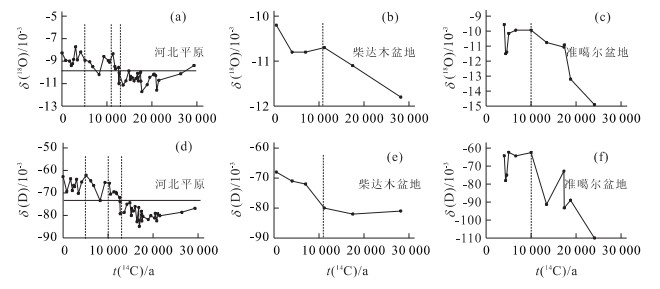
摘要: 中国北方第四系地下水中的D, 18O, 3H和14C含量存在明显的分层现象, 这种现象与末次冰期以来的古气候变化有着较好的对应性, 反映了全新世和末次冰期气候条件的差别以及地下水不同的形成机制.深层地下水为晚更新世末次冰期时期形成, 其δ(D) 和δ(18O) 值与全新世补给形成的浅层地下水相比, 分别贫4× 10-3~ 16× 10-3和1× 10-3~ 2× 10-3, 说明末次冰期时期年均气温较低.古地下水中D和18O的大陆梯度与全新世以来地下水中的梯度基本相同, 说明在过去30000a来尽管气温发生变化, 但中国北方大陆的大气循环模式没有发生实质性的改变.地下水同位素分层现象反映了3种不同的补给机制及参与现代水循环程度.这些信息对大陆尺度上的水循环研究和地下水的可持续开发利用有着重要的意义.Abstract: The underground water compositions of δ(D), δ(18O), 3H and 14C are distinct in shallow and deep Quaternary aquifers in northern China and reflect differences in average paleoclimatic conditions between the Holocene and the last glacial period of Pleistocene. The recharge of the groundwater in deep confined aquifer during the last glacial period caused δ(D) and δ(18O) to deplete by 4×10-3-16×10-3 and 1×10-3 -2×10-3 when compared to shallow aquifer recharged in Holocene, which suggests that annual mean temperature was lower in the last glacial period than that in the Holocene. While the similarity of the continental gradient of δ(D) and δ(18O) found in old groundwater to that in Holocene suggests that atmospheric circulation may not have gone substantial changes over northern China for the past 30 000 years even though the temperature had changed. The fact that groundwater isotopic stratification implies three different recharge mechanisms and influence of modern hydrological circulation is very important for understanding the continental hydrological circulation and sustaining development for groundwater resources.
-
表 1 地下水同位素测试结果
Table 1. Summary of isotopic compositions for groundwater in northern China

表 2 中国北方地下水同位素统计特征
Table 2. Statistical characteristics of isotopic compositions for groundwater in northern China

-
[1] 李文鹏, 周宏春, 周仰效, 等. 中国西北典型干旱区地下水流系统[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1995.Li W P, Zhou H C, Zhou Y X. et al. Groundwaterflow system in typical arid area, of northwestern China[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1995. [2] 邵益生. 内蒙古呼和浩特盆地地下水的环境同位素地球化学[J]. 工程勘察, 1989, (4): 41-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC198904011.htmShao Y S. Geochemistry of environmental isotopes of groundwater in Hohhot basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Engineering Reconnaissance, 1989, 4: 41-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC198904011.htm [3] 张茂生, 齐加林. 环境同位素方法在白杨水源地勘探中的应用[A]. 见: 王东生, 徐乃安, 主编. 中国同位素水文地质学之进展(1988-1993)[C]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 1993.174-179.Zhang M S, Qi J L. Application of environmental isotopes on exploration of groundwater resources in Baiyang [A]. In: Wang D S, Xu N A, eds. Advance on isotope hydrogeology in China[C]. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press, 1993.174-179. [4] 黎兴国, 常丕兴, 高文义, 等. 渭河平原地下水分布特征与环境同位素研究——以白杨水源地为例[J]. 地球学报, 1994年, (1-2): 177-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB4Z1.024.htmLi X G, Chang P X, Gao W Y. A study on the distribution and environment isotope of underground water in the Weihe plain-evidence from Baiying sources region of water[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 1994, (1 -2): 177 -188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB4Z1.024.htm [5] 张之淦, 张洪平, 孙继朝, 等. 河北平原第四系地下水年龄、水流系统及咸水成因初探[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1987, (4): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG198704001.htmZhang Z G, Zhang H P, Sun J C, et al. Environmental isotope study relatedto groundwaterage, flow system and saline water origin in Quaternary aquifer of Hebei plain [J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1987, (4): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG198704001.htm [6] 刘存富, 王佩仪, 周炼. 河北平原地下水氢、氧、碳、氯同位素组成的环境意义[J]. 地学前缘, 1997, 4 (1 -2): 267-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY7Z1.042.htmLiu C F, Wang P Y, Zhou L. The environment significance of H, O, C and Cl isotopic composition in groundwater of Hebei plain[J]. Earth ScienceFrontiers, 1997, 4(1-2): 267-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY7Z1.042.htm [7] 陈宗宇, 张光辉, 徐家明. 华北地下水古环境意义及古气候变化对地下水形成的影响[J]. 地球学报, 1998, 19 (4): 338-345.Chen Z Y, Zhang G H, Xu J M. Paleoclimate record deduced from groundwater and climate change implications of groundwater resources in North China[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 1998, 19(4): 338-345. [8] Dansgaard W. Stable isotopes in precipitation[J]. Tellus, 1964, 16: 436-468. [9] Rozanski K, Arans-Aragnas L, Gonfiantini R. Relation between long-term trends of oxygen-18 isotope composition of precipitation and climates[J]. Science, 1992, 258: 981-984. doi: 10.1126/science.258.5084.981 [10] Fontes J C, Stute M, Schiosser P, et al. Aquifers as archives of paleoclimate[J]. EOS Trans AGU, 1993, 74: 21-22. doi: 10.1029/93EO00212 [11] 王东生. 中国大气降水氢氧同位素浓度场和环境效应[A]. 见: 曲焕林, 徐乃安, 主编. 环境地学问题论文集[C]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1996.200-207.Wang D S. Temporal-spatial distribution and environmental effect ofδ(D)andδ(18O)in precipitation of China[A]. In: Qu H L, Xu N A, eds. Proceedings of environmental geoscience facing the twenty-first century[C]. Beijing: Petroleum Industrial Press, 1996.200-207. [12] 安芷生, 吴锡浩, 卢演俦, 等. 最近2万年中国环境变迁研究[A]. 见: 刘东生, 主编. 黄土·第四纪地质·全球变化[C]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990.1-26.An Z S, Wu X H, Lu Y C, et al. A preliminary study on the paleoenvironment change of China during the last 20 000 years[A]. In: Liu D S, ed. Loss, quaternary geology and global change[C]. Beijing: Science Press, 1990.1-26. [13] 黄春长. 环境变迁[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998.209.Huang C C. Changes of environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998.209. [14] Davidson M R, Airey P L. The effect of dispersion on the establishment of a palaeoclimatic record from groundwater[J]. J Hydrol, 1982, 58: 131-147. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(82)90074-9 [15] Stute M, Schlosser P. Principles and applications of the noble gas paleothermometer[A]. In: Swart P K, Lohmann K C, Mckenzie J, et al, eds. Climate change incontinental isotopic records[C]. Geophysical Monograph, 1993, 78: 89-100. [16] Kendall C, McDonnell J J. Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science BV, 1998.839. [17] Allison G B, Barnes C J, Hughes M W, et al. The effect ofclimate and vegetation on oxygen-18 and deuterium profiles insoils[A]. Isotopehydrology1983[C]. Vienna: Int At Energy Agency, 1984.105-125. [18] Rozanski K. Deuterium and oxygen-18 in European groundwaters-links to atmospheric circulation in the past[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, 52: 349-363. [19] Shi Y F, Kong Z Z, Wang S M, et al. Climaticfluctuation and important events of Holocene megathermal in China[J]. Science in China (Series B), 1994, 37 (3): 353-365. [20] 陈梦雄. 西北干旱区水资源与第四纪盆地系统[J]. 第四纪研究, 1997, (2): 97-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1997.02.001Chen M X. The waterresources related with Quaternary basin systemsinaridareaof Northwest China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1997, (2): 97-104. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1997.02.001 -









 下载:
下载: