Groundwater Resources Attribute Based on Environmental Isotopes
-
摘要: 从可持续角度提出了区域地下水资源属性的概念; 分析了含水层系统中地下水质点的时间效应; 利用大量同位素资料分析了不同区域含水层系统中的地下水资源属性和人类活动对地下水资源属性的影响.指出利用环境同位素是研究区域地下水资源属性最直接、有效的方法; 正确认识评价区域地下水资源属性对实现地下水资源可持续性具有重要意义.Abstract: The paper put forward a concept of regional groundwater resources attribute from point of sustainability based on isotope information. It analyzed the distribution of groundwater age in the aquifer system, groundwater resources attribute in some regional aquifer systems using isotope data and the effect of human activities (groundwater exploitation) on regional groundwater resources attribute. It point out that the direct and cost effective tool for assessment of regional groundwater resources attribute is environmental isotopes, and correct recognition and estimation of regional groundwater resources attribute will play a very important role on realizing groundwater resources sustainability.
-
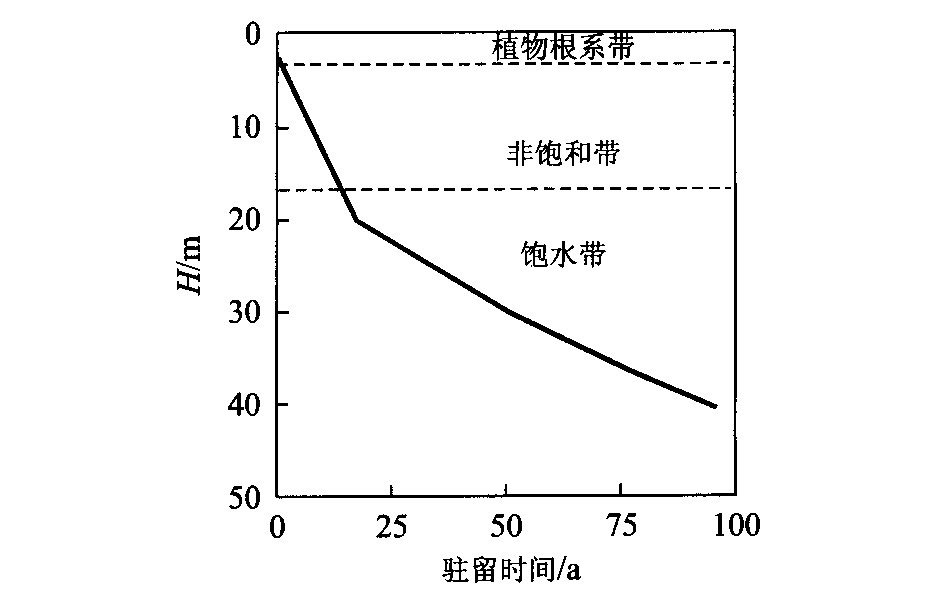
图 1 理想含水层中地下水年龄分布示意图
a.潜水含水层; b.承压含水层.实线为等年龄线, 虚线为地下水流线.据Cook等[2]改编
Fig. 1. Sketch map of groundwater age in an ideal aquifer
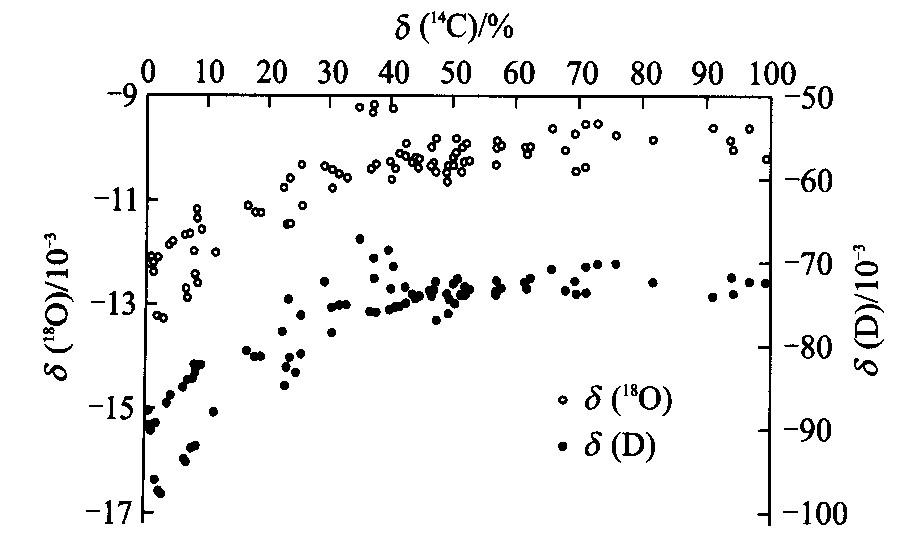
图 3 晚第四纪地下水δ (D), δ (18O) 与δ (14C) 关系[8]
Fig. 3. Relationships between δ (D), δ (18O) and δ (14C) of Upper Quaternary groundwater
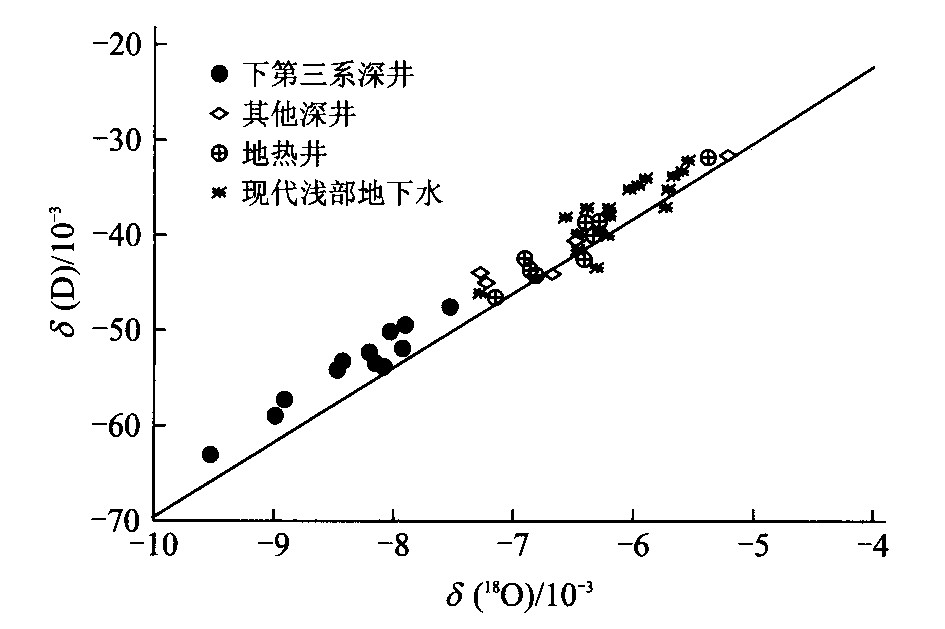
图 4 法国西南部Aquitain盆地地下水δ (D) -δ (18O) 关系[9]
Fig. 4. Relationship between δ (D) and δ (18O) of groundwater in Aquitain basin, southwestern France
图 5 撒哈拉沙漠中部Ahaggar地区地下水δ (D) -δ (18O) 关系(数据引自Saighi等[10])
Fig. 5. Relationship between δ (D) and δ (18O) of groundwater in Ahaggar area, central Sahara
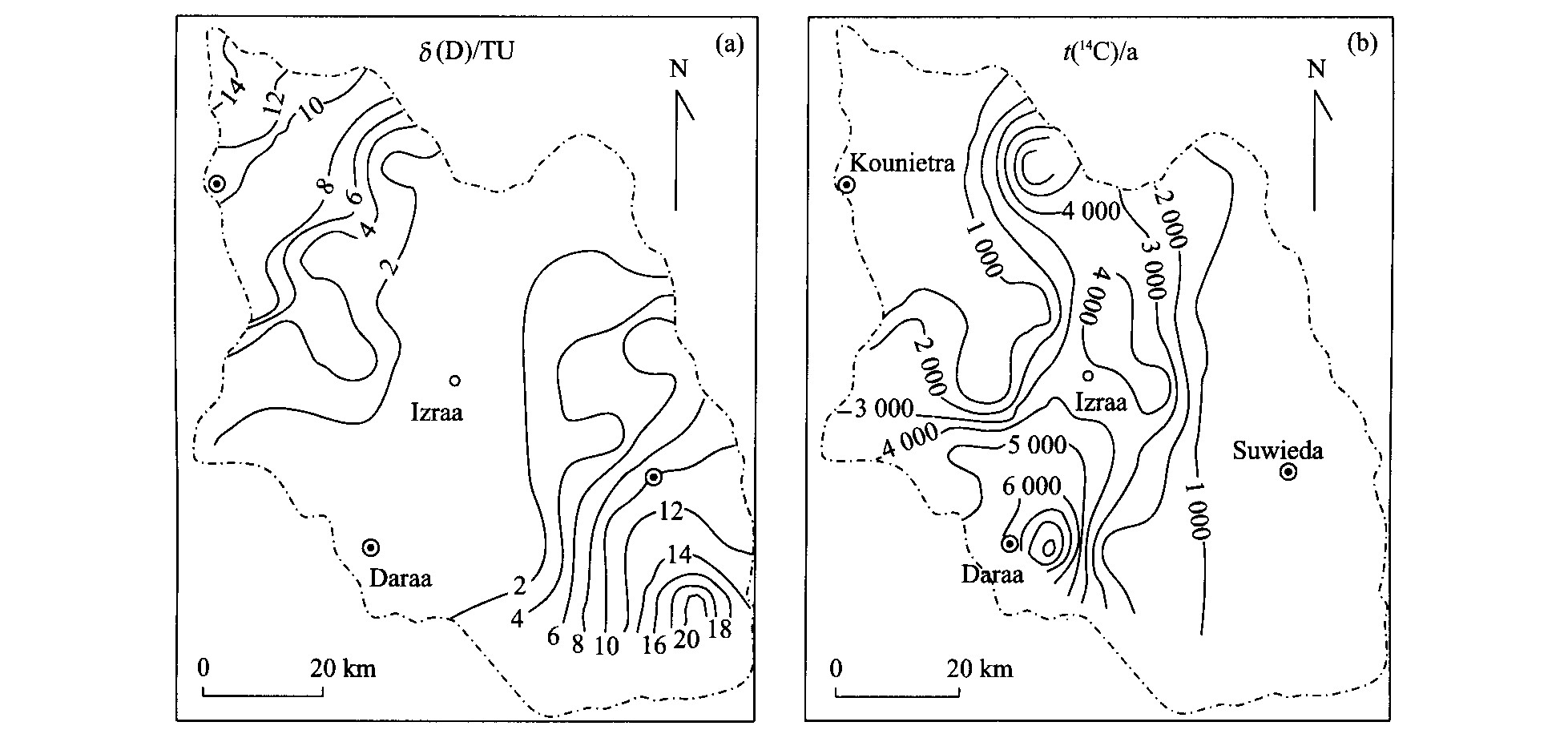
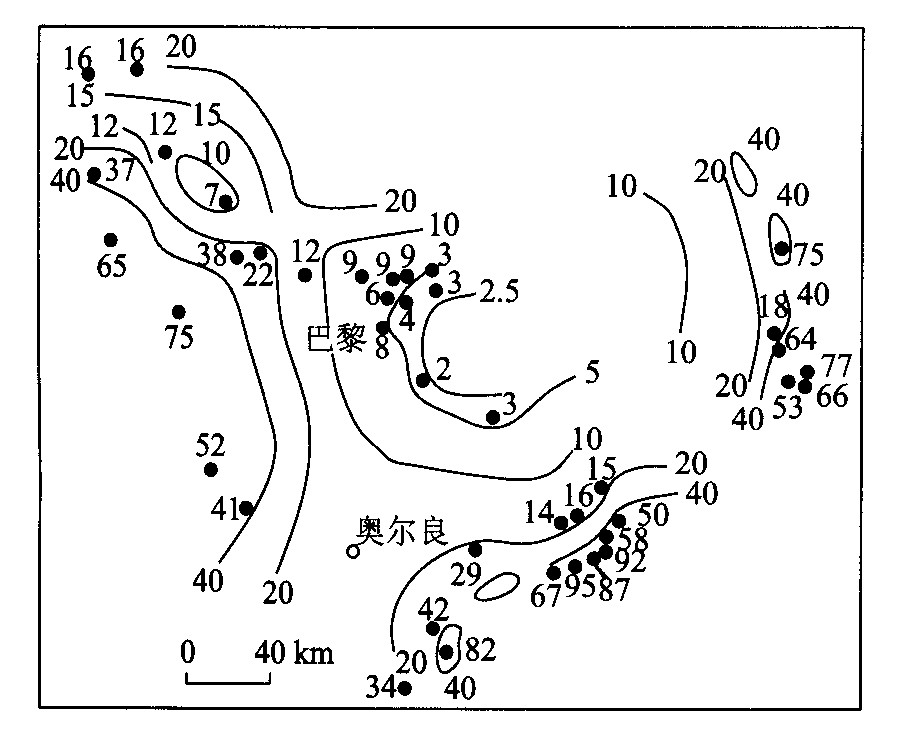
图 7 巴黎盆地地下水δ (14C) 分布[13]
Fig. 7. δ (14C) distribution of groundwater in Paris basin
-
[1] Appelo C A J, Postma D. Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution[M]. Rotterdam: Balkema A A, 1996. [2] Cook P G, John K B. Determining timescale for groundwater flow and solute transport[A]. In: Cook P G, Andrew L H, eds. Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology[C]. Massachusetts: KluwerAcademic Publishers, 2000. 529. [3] IAEA. Proceedings of a regional executive management seminar on isotope techniques in water resources development and management and a regional workshop on isotope hydrology for Asia and the Pacific organized by the IAEA and held in Beijing[R]. Beijing, 15-26 June, 1987. [4] Oliver S. Groundwater: past achievements and future challenges[M]. Rotterdam: Balkema A A, 2000. [5] Eberts S M, George L L. Regional ground-water flow and geochemistry in the Midwestern basins and arches aquifer system in parts of Indiana, Ohio, Michigan, and Illinois [A]. US Geological Survey Professional Paper[C]. http://water.usgs.gov/pubs/pp/, 2000. 103. [6] Mazor E. Applied chemical and isotopic groundwater hydrology[M]. Milton Keynes: Open University Press, 1991. 274. [7] Wang D S, Wang K. Isotopes in precipitation in China (1986-1999)[A]. In: Water Resources Assessment: Isotope Techniques[C]. Technologies Sciences(Series E), 2001, 44(Supplement): 192. [8] Klaus P S. Environmental isotopes in the hydrological cycle: principles and applications. Volume V: man' s impact on groundwater systems[M]. Vienna: IAEA, 2001. [9] Blavoux B, Dray M, Fehri A, et al. Palaeoclimatic and hydrodynamic approach to the Aquitain basin deep aquifer (France) by means of environmental isotopes and noble gases[A]. In: IAEA, ed. Isotope techniques in the study of past and current environmental changes in the hydrosphere and the atmosphere[C]. Vienna: IAEA, 1993. 293-305. [10] Saighi O, Michelot J L, Filly A. Isotopic characteristics of meteoric water and groundwater in Ahaggar Massif (central Sahara)[A]. In: IAEA, ed. Isotope techniques in water resources investigations in arid and semi-arid regions, IAEA-TECDOC-1207[C]. Vienna: IAEA, 2001. 7-26. [11] Coplen T B, Herczeg A L, Barnes C. Isotope engineering — using stable isotopes of the water molecule to solve practical problems[A]. In: Cook P, Herczeg A L, eds. Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology[C]. Massachusetts: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2000. [12] Katten Z. Chemical and environmental isotope study of the fissured basaltic aquifer systems of the Yarmouk basin (Syrian Arab Republic)[A]. In: IAEA, ed. Isotope techniques in water resources development and management[C]. Vienna: IAEA, 1999. 674. [13] Mazor E. Chemical and isotopic groundwater hydrology [M]. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc, 1997. 413. [14] Bentley H W, Phillips F M, Stanley N D, et al. Chlorine-36 dating of very old groundwater, the Great Artesian basin, Australia[J]. Water Resources Research, 1986, 22(13): 1991-2001. doi: 10.1029/WR022i013p01991 [15] Torgersen T, Habermehl M A, Phillips F M, et al. Chlorine-36 dating of very old groundwater 3. Further studies in the Great Artesian basin, Australia[J]. Water Resources Research, 1991, 27(12): 3201-3213. doi: 10.1029/91WR02078 [16] Radke B M, Ferguson J, Cresswell R G, et al. Hydrochemistry and implied hydrodynamics of the Cadna-owie-Hooray aquifer, Great Artesian basin, australia[M]. Canberra: Bureau of Rural Sciences, 2000. 229. [17] Wang K, Zhu J L. A conceptual model of the Tianjin geothermal system based on isotopic studies[J]. Technologies Sciences(Series E), 2001, 44(Supplement): 160-164. doi: 10.1007/BF02916809 [18] Emanuel M. Interrelations between groundwater dating, palaeoclimate and palaeohydrology[A]. In: IAEA, ed. Isotope techniques in the study of past and current environmental changes in the hydrosphere and the atmosphere [C]. Vienna: IAEA, 1993. 621. -










 下载:
下载: