Adsorption of Chromate in System Hydroxy-Fe-montmorillonite
-
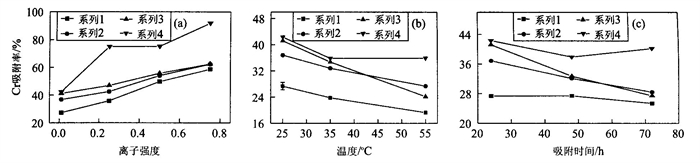
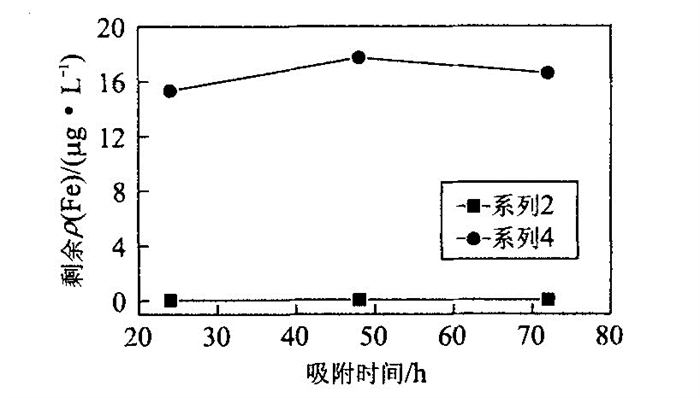
摘要: 采矿、电镀、制革等行业废物排放及含Cr矿物风化可造成一些地区土壤和地下水的Cr污染.Cr主要以三价和六价形式存在, 其中Cr (Ⅵ) 有强的迁移能力, 对动植物均有很强的毒害性.研究了在氧化、酸性条件下, 土壤及土壤溶液中的蒙脱石和羟基铁离子共存时对铬酸根离子(主要以HCrO42-和CrO42-等Cr (Ⅵ) 形式存在) 的吸附行为.进行了蒙脱石、羟基铁离子、Cr (Ⅵ) 离子添加顺序不同的3个系列的实验, 重点研究了Cr的初始质量浓度、溶液pH值、环境温度、吸附时间、溶液离子强度对3个系列Cr吸附行为的影响, 并与羟基铁离子体系进行了对比.结果表明, 蒙脱石-羟基铁离子体系的Cr吸附能力明显强于蒙脱石而低于羟基铁离子, 其Cr吸附率随Cr初始质量浓度、温度的升高和吸附时间的延长而降低, 随离子强度的升高而升高, 而pH值对不同系列的Cr吸附率有不尽相同的影响.Abstract: Chromate ions have high affinity for soluble hydroxy-Fe species and for Fe-oxyhydroxide precipitates. The hydrolysis of Fe (Ⅲ) and the growth of initially precipitated Fe (Ⅲ) phases is, in turn, strongly affected by montmorillonite. In this paper, the adsorption of Cr (Ⅵ) in the system hydroxy-Fe-montmorillonite was studied. Four series of batch experiments were conducted by mixing montmorillonite, hydroxy-Fe and chromate in the following order: (1) Montmorillonite+hydroxy-Fe before addition of chromate; (2) Hydroxy Fe+chromate before addition of montmorillonite; (3) Montmorillonite+chromate before addition of hydroxy-Fe; (4) Hydroxy-Fe+chromate. For each series, the effects of pH, ionic strength, temperature, initial Cr concentration and adsorption duration on the overall uptake of Cr in the system hydroxy-Fe-montmorillonite were studied.Resultsshow that the uptake of Cr increases with the increase in ionic strength and decreases with the increases in temperature, initial Cr concentration and adsorption duration. Optimum pH values exist for Series 2, 3 and 4, but not for Series 1. These effects occur, to different extents, in the four series. On all experimental conditions, the hydroxy-Fe-montmorillonite system displayed very strong affinity for Cr with Series 3 containing the highest Cr adsorption capacity and Series 1 the lowest. The authors attribute this to the difference in mixing order adopted, resulting in more hydroxy-Fe (the main adsorbent for Cr) being adsorbed onto montmorillonite for Series 1 before the hydroxy-Fe is able to adsorb Cr, that is the case for Series 2 and 3. Discussions and explanations have been given to these experimental phenomena.
-
Key words:
- hydroxy-Fe /
- montmorillonite /
- chromate /
- adsorption.
-
表 1 蒙脱石用量对羟基离子-蒙脱石体系Cr吸附率的影响
Table 1. Influence of montmorillonite dosage on the percentage adsorption of Cr in hydroxy-Fe-montmorillonite system

-
[1] Rai D, Eary L E, Zachara J M. Environmental chemistry of chromium[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 1989, 86(1-2): 15-23. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(89)90189-7 [2] Brigatti M F, Franchini G, Lugli C, et al. Interaction between aqueous chromium solutions and layer silicates[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 15(9): 1307-1316. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00120-1 [3] Bartlett R J, James B. Mobility and bioavailability of chromium in soils[A]. In: Nriagu J O, Nieboer E, eds. Chromium in natural and human environments[C]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1988. 267-304. [4] Weerasooriya R, Tobschall H J. Mechanistic modelling of chromate adsorption onto goethite[J]. Colloids and Surfaces: A Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2000, 162: 167-175. [5] Buerge I J, Hug S J. Influence of mineral surfaces on chromium(Ⅵ) reduction by iron(Ⅱ)[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1999, 33: 4285-4291. doi: 10.1021/es981297s [6] Taylor R W, Shen S Y, Bleam W F, et al. Chromate removal by dithionite-reduced clays: evidence from direct X-ray adsorption near edge spectroscopy(XANES) of chromate reduction at clay surfaces[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2000, 48(6): 648-654. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.2000.0480606 [7] Brigatti M F, Lugli C, Cibin G, et al. Reduction and sorption of chromium by Fe(Ⅱ)-bearing phyllosilicates: chemical treatments and X-ray adsorption spectroscopy (XAS) studies[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2000, 48 (2): 272-281. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.2000.0480214 [8] Abdel-Samad H, Watson P R. An XPS study of the adsorption of chromate on goethite(α-FeOOH)[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1997, 108: 371-377. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(96)00609-5 [9] Khan S A, Rehman U R, Khan M A. Adsorption of chromium(Ⅲ), chromium (Ⅵ) and silver (Ⅰ) on bentonite[J]. Waste Management, 1995, 15(4): 271-282. doi: 10.1016/0956-053X(95)00025-U [10] Ding M, de Jong B H W S, Roosendaal S J, et al. XPS studies on the electronic structure of bonding between solid and solutes: adsorption of arsenate, chromate, phosphate, Pb2+, and Zn2+ ions on amorphous black ferric oxyhydroxide[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64: 1209-1219. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00386-5 [11] Vujaković A D, Tomašević-Čanović M R, Daković A S, et al. The adsorption of sulphate, hydrogenchromate and dihydrogenphosphate anions on surfactant-modified clinoptilolite[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2000, 17: 265-277. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1317(00)00019-3 [12] Ainsworth C C, Girvin D C, Zachara J M, et al. Chromate adsorption on goethite-effects of aluminium substitution[J]. Soil Sci Soc Am J, 1989, 53(2): 411-418. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1989.03615995005300020017x [13] Zachara J M, Ainsworth C C, Cowan C E, et al. Adsorption of chromate by subsurface soil horizons[J]. Soil Sci Soc Am J, 1989, 53(2): 418-428. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1989.03615995005300020018x [14] Karel M, William F. Chromate and oxalate adsorption on goethite. 1. Calibration of surface complexation models [J]. En Sci Technol, 1992, 26(12): 2357-2364. doi: 10.1021/es00036a004 [15] Criscenti L J, Sverjensky D A. The role of electrolyte anions(ClO4-, NO3-, and Cl-)in divalent metal(M2+) adsorption on oxide and hydroxide surfaces in salt solution [J]. Am J Sci, 1999, 299: 828-899. doi: 10.2475/ajs.299.10.828 [16] Gao Y, Mucci A. Acid base reactions, phosphate and arsenate complexation, and their competitive adsorption at the surface of goethite in 0.7 mol/ L NaCl solution[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65: 2361-2378. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00589-0 [17] Sylva R N. The hydrolysis of iron(Ⅲ)[J]. Rev Pure and Appl Chem, 1972, 22: 115-132. [18] Byrne R H, Luo Y R, Young R W. Iron hydrolysis and solubility revisited: observations and comments on iron hydrolysis characterizations [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2000, 70: 23-35. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4203(00)00012-8 [19] Cornell R M, Giovanoli R, Schneider W. Review of the hydrolysis of iron (Ⅲ) and the crystallization of amorphous iron (Ⅲ) hydroxide hydrate[J]. Chem Tech Biotechnol, 1989, 46: 115-134. [20] Van Geen A, Robertson A P, Leckie J O. Complexation of carbonate species at the goethite surface: implication for adsorption of metal ions in natural waters[J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1994, 58: 2073-2086. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90286-0 [21] Papassiopi N, Virčíková E, Nenov V, et al. Removal and fixation of arsenic in the form of ferric arsenates: three parallel experimental studies [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1996, 41: 867-873. [22] Meyer W R, Pulcinelli S H, Santilli C V, et al. Formation of colloidal particles of hydrous iron oxide by forced hydrolysis[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2000, 273: 41-47. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3093(00)00142-3 [23] SchneiderW, Schwyn W. The hydrolysis of iron in synthetic, biological and aquatic media[A]. In: Stumm W, ed. Aquatic surface chemistry[C]. New York: Wiley Interscience, 1987. 167-188. [24] Kraepiel A M L, Keller K, Morel F M M. A model for metal adsorption on montmorillonite[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1999, 210: 43-54. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1998.5947 [25] Ferreiro E A, Helmy A K, de Bussetti S G. Interaction of Fe-oxyhydroxide colloidal particles with montmorillonite[J]. Clay Minerals, 1995, 30: 195-200. doi: 10.1180/claymin.1995.030.3.03 [26] Thompson D W, Tahir N M. The influence of a smectite clay on the hydrolysis of iron(Ⅲ)[J]. Colloids and Surfaces, 1991, 60: 369-398. doi: 10.1016/0166-6622(91)80288-Y -










 下载:
下载: