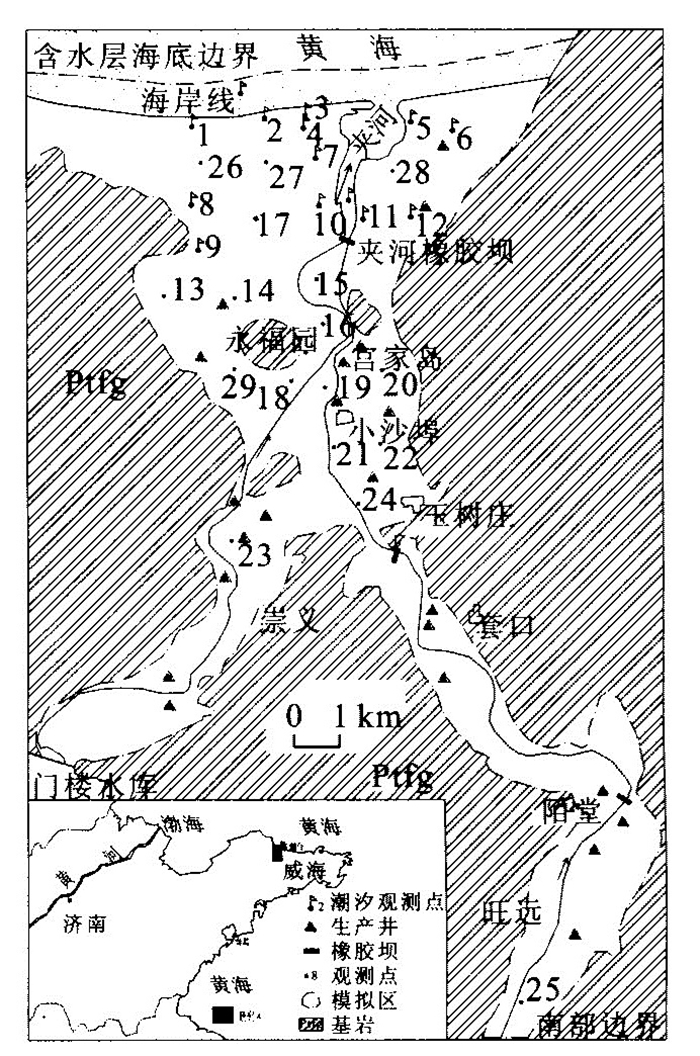
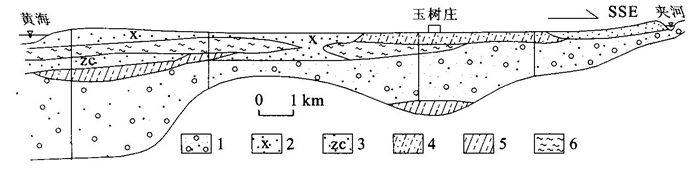
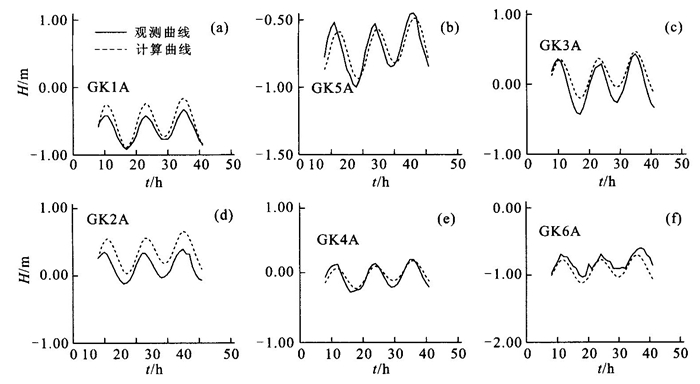
| [1] |
陈崇希, 万军伟. 地下水水平井流的模型及数值模拟方法——考虑井管内不同流态[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2002, 27 (2): 135-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200202004.htmCHEN C X, WAN J W. A New model of groundwater flowing to horizontal well and the numerical simulation approach[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2002, 27 (2): 135-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200202004.htm |
| [2] |
陈崇希, 黎明, 刘文波. 单斜含水层-泉流系统概念模型研究[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2002, 27 (2): 140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200202005.htmCHEN C X, LI M, LIU W B. Study on conceptional model for monocline aquifer-spring system[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2002, 27 (2): 140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200202005.htm |
| [3] |
马腾, 王焰新. U (Ⅵ) 在浅层地下水系统中迁移的反应—输运耦合模拟——以我国南方核工业某尾矿库为例[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2000, 25 (5): 456-461. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200005002.htmMA T, WANG Y X. Coupled reaction-transport modeling of migration of uranium (Ⅵ) in shallow ground-system: a case study of uranium grngue site in southern China[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geoscicnces, 2000, 25 (5): 456-461. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200005002.htm |
| [4] |
梁杏, 王旭升, 张人权, 等. 珠江口盆地东部第三纪沉积环境与古地下水流模式[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2000, 25 (5): 542-546. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200005022.htmLIAN G X, WANG X S, ZHANG R Q, et al. Tertiary sedimentary environments and palaeo-groundwater flow patterns in eastern Pearl River Mouth basin[J]. Earth Science—China University of Geosciences, 2000, 25 (5): 542-546. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200005022.htm |
| [5] |
Chin-Fu Tsang. 非均质介质中地下水流动与溶质运移模拟——问题与挑战[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2000, 25 (5): 443-450. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200005000.htmChin-Fu Tsang. Modeling groundwater flow and mass transport in heterogeneous media: issues and challenges[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2000, 25 (5): 443-450. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200005000.htm |
| [6] |
Ferris J G. Cyclic fluctuation of water level as a basis for determining aquifer transmissibility[J]. IAHS Publ, 1951, 33: 148-155. |
| [7] |
Carr P A, Van der Kamp G. Determining aquifer characteristics by the tidal method[J]. Water Resources Research, 1969, 5 (5): 1023-1031. doi: 10.1029/WR005i005p01023 |
| [8] |
Sun H. A two-dimensional analytical solution of groundwater response to tidal loading in an estuary[J]. Water Resources Research, 1997, 33 (6): 1429-1435. doi: 10.1029/97WR00482 |
| [9] |
Jiao J, Tang Z. An analytical solution of groundwaterre sponse to tidal fluctuation in a leaky confined aquifer[J]. Water Resources Research, 1999, 35 (3): 747-751. doi: 10.1029/1998WR900075 |
| [10] |
Li G M, Chen C X. Determining the length of confined aquifer roof extending under the sea by the tidal method[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1991, 123: 97-104. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(91)90071-O |
| [11] |
Nawang W M, Kishi Y. Modelling of saltwater movement in multilayered coastal aquifer at Tanjuang Mas, Malaysia[A]. In: Proc of international conference on calibration and reliability in groundwater modelling[C]. Hague: IAHS Publ, 1990, 3-6: 112-119. |
| [12] |
陈崇希, 林敏, 舒本媛. 滨海承压含水层等效边界——以北海禾塘水源地为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1990, (4): 2-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG199004002.htmCHEN C X, LIN M, SU B Y. Determination of equivalent boundary in coastal confined aquifer—by example of Hetang pumping area in Beihai[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1990, (4): 2-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG199004002.htm |
| [13] |
Chen C X, Lin M, Li G M, et al. Modelling of quasi-3D groundwater flow and studying of equivalent drainage boundary in Beihai Peninsula, Guangxi[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1992, 3 (1): 105-115. |
| [14] |
Chen C X, Jiao J. Numerical simulation of pumping tests in multilayer wells with non-darcian flow in the wellbore[J]. Ground Water, 1999, 37 (3): 465-474. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1999.tb01126.x |
| [15] |
Cheng J M, Chen C X. Three-dimensional modeling of density-dependent salt water intrusion in multi-layered coastal aquifers in Jahe River basin, Shandong Province, China[J]. Ground Water, 2001, 39 (1): 137-143. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2001.tb00359.x |
| [16] |
Galeati G G, Gambolati G, Neuman S P. Coupled and partially coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian model of freshwater-saltwater mixing[J]. Water Resources Research, 1992, 28 (1): 149-165. doi: 10.1029/91WR01927 |
| [17] |
成建梅. 滨海多层含水系统海水入侵三维水质模型及应用[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 1999.CHENG J M. Three-dimensional seawater intrusion in multi-layered aquifer system: formulation and application[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 1999. |
| [18] |
Huyakorn P S, Anderson P F, Mercer J W, et al. Saltwater intrusion in aquifers: development and testing of a three-dimensional finite element model[J]. Water Resources Research, 1987, 23 (2): 293-312. doi: 10.1029/WR023i002p00293 |









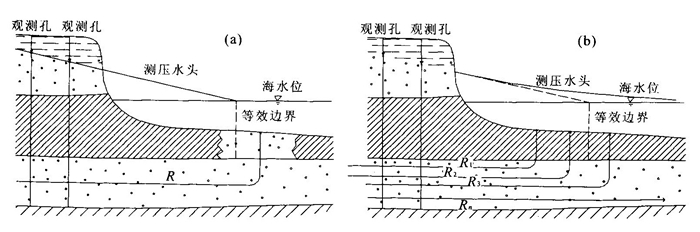
 下载:
下载: