Effects of Bimetal Ni/Fe on Dechlorination of PCE
-
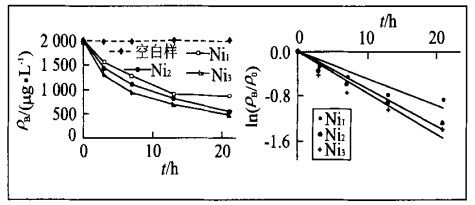
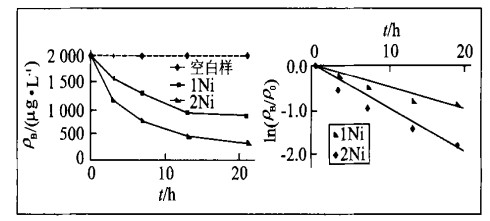
摘要: 以四氯乙烯(PCE)为目标污染物, 利用批试验研究Ni/Fe双金属对氯代烃脱氯的影响因素.结果表明: (1)当参加反应的Ni/Fe双金属分别为10 g和20 g时, 反应速率常数kobs分别为0.047 7 h-1和0.097 0 h-1, 说明增加参加反应的Ni/Fe双金属的质量可提高脱氯速率; (2)当粒度分别为20~ 40目、40~ 65目和80~ 100目时, kobs分别为0.047 7 h-1, 0.059‥ 8 h-1和0.088 6 h-1, 说明选用Ni/Fe双金属颗粒越小脱氯速率越快; (3)当Ni/Fe质量比分别为0.024%, 0.048%和0.072%时, 所得kobs分别为0.047 7 h-1, 0.066 2 h-1和0.073 4 h-1, 说明Ni/Fe双金属系统中Ni/Fe质量比越高脱氯效果越好, 但最优Ni/Fe质量比还有待于进一步研究.Abstract: In order to study the affecting factors in the degradation of chlorinated hydrocarbon, tetrachlrethene (PCE) was selected as target contaminant and Ni/Fe bimetal was used as reactants in batch experiments. The results show: (1) When the mass of Ni/Fe bimetal used in batch experiment was 10 g and 20 g, the reaction rates (kobs) were 0.047 7 h-1 and 0.09 7 h-1, respectively. The more the Ni/Fe bimetal used in PCE degradation, the faster the reaction. (2) The reaction rates (kobs) were 0.047 7 h-1, 0.059 8 h-1 and 0.088 6 h-1 when Ni/Fe bimetal was 20-40 mesh, 40-65 mesh and 80-100 mesh, respectively. The finer the metal, the faster the reaction. (3) The reaction rates (kobs) were 0.047 7 h-1, 0.066 2 h-1 and 0.073 4 h-1 when the Ni/Fe mass ratio was 0.024%, 0.048% and 0.072%, respectively. The higher the Ni/Fe mass ratio, the faster the reaction. Further study of the optimum Ni/Fe mass ratio is needed.
-
Key words:
- Ni/Fe bimetal /
- tetrachlrethene (PCE) /
- mass /
- grain level /
- Ni/Fe mass ratio
-
表 1 Ni/Fe双金属降解PCE结果
Table 1. PCE degradation using Ni/Fe
(μg·L-1) 
-
[1] Sivavec T M, Mackenzie P D, Horney D P, et al. Redoxactive media for permeable reactive barriers[A]. International containment technology conference[C]. St Petersburg, Florida: [s. n. ], 1997. 753- 759. [2] 李海明, 陈鸿汉, 钟佐燊, 等. 垃圾堆放场氯代脂肪烃对浅层地下水的污染特征初步分析[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2002, 27(2): 227- 230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200202024.htmLI HM, CHEN HH, ZHONG Z S, et al. Characteristics of chlorocaliphatic hydrocarbons in shallow groundwater contaminated from landfill leachates[J]. Earth Science— Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2002, 27(2): 227- 230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200202024.htm [3] Gillham R W, Blowes D W, Ptacek C J, et al. Use of zero-valent metals in in-situ remediation of contaminated ground water[A]. In: Glendo W G, et al, eds. In-situ remediation: scientific basis for current and future technologies, part 2[C]. Columbus: Battelle Press, 1994.913 - 930. [4] Gillham R W, O'Hannesin S F. Enhanced degradation of halogenated alphatics by zero-valent iron[J]. Ground Water, 1994, 32(6): 958- 967. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1994.tb00935.x [5] Johnson T J, Fish W, Gorby Y A, et al. Degradation of carbon tetrachloride by iron metal: complexation effects on the oxide surface[J]. J Contam Hydrol, 1998, 29: 379- 398. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7722(97)00063-6 [6] Matheson J L, Tratnyek P G. Reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated methanes by iron metal[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1994, 28(12): 2045- 2053. doi: 10.1021/es00061a012 [7] 刘菲, 汤鸣皋, 何小娟, 等. 零价铁降解水中氯代烃的实验室研究[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2002, 27(2): 186- 188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200202015.htmLIU F, TANG M G, HE X J, et al. Study of chlorinated hydrocarbons in drinking water using Fe0 in lab[J]. Earth Science— Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2002, 27(2): 186- 188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200202015.htm [8] 何小娟, 刘菲, 黄园英, 等. 利用零价铁去除挥发性氯代脂肪烃的试验[J]. 环境科学, 2003, 24(1): 139- 142. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2003.01.025HE X J, LIU F, HUANG Y Y, et al. Degradation of volatile chlorinated aliphatics by zero-valent iron[J]. Environmental Science, 2003, 24(1): 139- 142. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2003.01.025 [9] Kober R, Schlicker O, Ebert M, et al. Degradation of chlorinated ethylenes by Fe0: inhibition processes and mineral precipitation[J]. Environmental Geology, 2002, 41: 644- 652. doi: 10.1007/s00254-001-0443-5 [10] Mallat T, Bodnar Z, Petro J. Reduction by dissolving bimetals[J]. Tetrahedron, 1991, 47(3): 441- 446. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)90501-0 [11] Zhang W X, Wang C B, Lien H L. Treatment of chlorinated organic contaminants with nanoscale bimetallic particles[J]. Catalysis Today, 1998, 40: 387- 395. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00067-4 [12] 何小娟, 汤鸣皋, 李旭东, 等. 利用镍/铁和铜/铁双金属降解四氯乙烯的试验研究[J]. 环境化学, 2003(待刊).HE X J, TANG M G, LI X D, et al. Degradation of PCE using Ni/Fe and Cu/Fe bimetal systems[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2003(in press). [13] 章安安. 挥发性卤代烃、水和废水监测分析方法指南(中册)[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1997. 270- 286.ZHANG A A. Direction of analysis method for water and waste water(Middle Volume)[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1997. 270- 286. -









 下载:
下载: