Effect of Annual Precipitation to Geotherm of Ore-Forming Fluid: A Case of Antimony Deposits in Xikuangshan
-
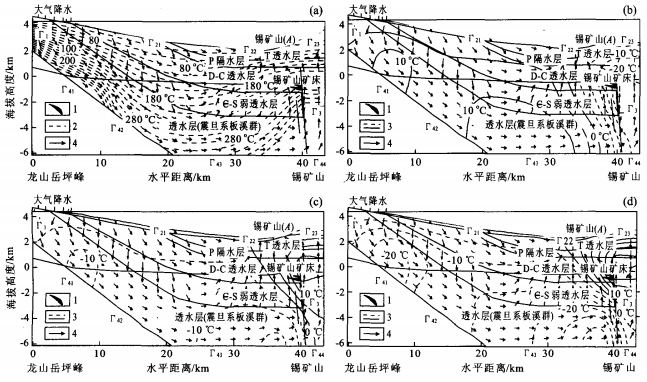
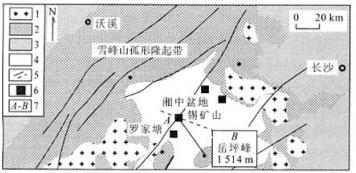
摘要: 成矿流体热场直接影响矿床的成矿作用.依据湘中盆地的水文地质特征, 以锡矿山锑矿床成矿流体为例, 利用热-重力驱动型流体运移模型, 选择具有代表性的龙山岳坪峰-锡矿山(AB)剖面, 研究大气年降水量的大小对成矿流体热场的影响.首先选取一个对比降水量1200 mm/a, 计算出区域的温度场分布, 然后分别取年平均大气降水量为600、1800和2400 mm/a与对比降水量的温度场进行对比, 得出2种温度场的差值图.模拟结果表明: 大气降水的水量大小对区域流场影响较大, 而对区域温度场的影响不大, 在不同降水量条件下, 其对温度的影响在5%~20%之间.研究结论认为, 大气降水量对成矿流体的热场影响不大.Abstract: The geotherm of ore-forming fluid affects ore formation directly. This article studies the effect of annual precipitation on the geotherm of ore-forming fluid, according to the geohydrologic conditions of the central Hunan basin. Ore-forming fluid in antimony deposits in Xikuangshan was taken as an example and a representative section of Xikuangshan-Yuepingfeng was chosen. Heat and gravity driven modes of fluid movement were considered. A contrastive rainfall Q=1 200 mm/a was chosen, the distribution of the area temperature field was calculated, and the difference of two temperature fields was obtained by taking the annual precipitation of 600 mm/a, 1 800 mm/a and 2 400 mm/a compared with the temperature field of the contrastive rainfall. The simulation result shows that precipitation affects the fluid field more than the temperature field. The effect of precipitation on the temperature stays between 5%-20%. The effect of precipitation on the geotherm of ore-forming fluid is negligible.
-
Key words:
- ore-forming fluid /
- simulation /
- geotherm /
- annual precipitation /
- antimony deposits /
- Xikuangshan.
-
表 1 不同降水量下流体的流速
Table 1. Velocity of flow at various rainfalls

-
Bear, J., 1972. Dynamics of fluids in porous media. Dover, New York, 1-764. Deming, D., 1994. Fluid flow and heat transport in the upper continental crust. In: Parnell, J., ed., Geofluids: Origin, migration and evolution of fluids in sedimentary basins. Geological Society Special Publication, 78: 27-42. Forster, C., Smith, L., 1988a. Groundwater flow systems in mountainous terrain: 1. Numerical modeling technique. Water Resour. Res., 24: 999-1010. doi: 10.1029/WR024i007p00999 Forster, C., Smith, L., 1988b. Groundwater flow systems in mountainous terrain: 2. Controlling factors. Water Resour. Res., 24: 1011-1023. doi: 10.1029/WR024i007p01011 Forster, C., Smith, L., 1989. The influence of groundwater flow on thermal regimes in mountainous terrain: A model study. J. Geophys. Res., B94;9439-9451. Garven, G., Freeze, R. A., 1984a. Theoretic analysis of the role of groundwater flow in the genesis of stratabound ore deposits. 1. Mathematical and numerical model. Am. J. Sci., 284: 1085-1124. doi: 10.2475/ajs.284.10.1085 Garven, G., Freeze, R. A., 1984b. Theoretic analysis of the role of groundwater flow in the genesis of stratabound ore deposits. 2. Quantitative results. Am. J. Sci., 284: 1125-1174. doi: 10.2475/ajs.284.10.1125 Garven, G., De, S., Person, M. A., et al., 1993. Genesis of stratabound ore deposits in the Midcontinent basins of North America. 1. The role of regional groundwater flow. Am. J. Sci., 293: 497-568. doi: 10.2475/ajs.293.6.497 Ma, D. S., Pan, J. Y., Xie, Q. L., 2003. Ore source of Xiang-zhong Sb(Au) deposits: Ⅱ. Evidences of isotopic geochemistry. Mineral Deposits, 22 (1): 78-87 (in Chinese with English abstract). Oliver, J., 1992. The spots and stains of plate tectonic. Earth Sci. Reviews, 32: 77-106. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(92)90013-J Pei, R. F., Wu, L. S., Xiong, Q. Y., et al., 1998. The deflection of ore genesis and structure assembling field of mineralization abnormality on super-large deposits in China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, 202-223 (in Chinese). Peng, J. T., Hu, R. Z., Ling, Y. X., et al., 2002a. Sm-Nd isotopic dating of epithermal calcite for the Xikuangshan antimony deposit. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47 (10): 789-792 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2002-47-10-789 Peng, J. T., Hu, R. Z., Zou, L. Q., et al., 2002b. Isotope tracing of ore-forming materials of the Xikuangshan antimony deposit, central Hunan. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 22 (2): 155-159 (in Chinese with English abstract). Peng, J. T., Hu, R. Z., Deng, H. L., et al., 2001. Strontium isotope geochemistry of the Xikuangshan antimony deposit, central Hunara. Geochimica. 30 (3): 248-256 (in Chinese with English abstract). Person, M., Raffensperger, J. F., Ge, S., et al., 1996. Basinscale hydrogeologic modeling. Reviews of Geophysics, 34: 61-87. doi: 10.1029/95RG03286 Rabinowicz, M., Sempere, J. C., Genthon, P., 1999. Thermal convection in a vertical permeable slot: Implications for hydrothermal circulation along mid-ocean ridges. J. Geophys. Res. , 104 (B12): 29275-29292. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900259 Rao, J. R., Luo, J. L., Yi, Z. J., 1999. The mantle. crustal tectonic metallogenic model and ore. prospecting prognosis in the Xikuangshan antimony ore field. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 23 (4): 241-249 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, R. Y., Ma, D. S., Pan, J. Y., 2003. Study on the paleogeothermal field of ore-forming fluid to form Xikuang shan Sb deposit. Geochimica, 32 (6): 509-519 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yu, C. W., Cen, K., Bao, Z. Y., et al., 1993. Dynamics of the hydrothermal ore-forming processes. China University of Geosciences Press, Wuhan, 1-189 (in Chinese). 马东升, 潘家永, 解庆林, 2003. 湘中锑(金)矿床成矿物质来源——Ⅱ. 同位素地球化学证据. 矿床地质, 22 (1): 78-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200301011.htm 裴荣富, 吴良士, 熊群尧, 等, 1998. 中国特大型矿床成矿偏在性与异常成矿构造聚敛场. 北京: 地质出版社, 202-223. 彭建堂, 胡瑞忠, 林源贤, 等, 2002a. 锡矿山锑矿床热液方解石的Sm-Nd同位素定年. 科学通报, 47 (10): 789-792. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200210015.htm 彭建堂, 胡瑞忠, 邹利群, 等, 2002b. 湘中锡矿山锑矿床成矿物质来源的同位素示踪. 矿物学报, 22 (2): 155-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200202009.htm 彭建堂, 胡瑞忠, 邓海琳, 等, 2001. 湘中锡矿山锑矿床的Sr同位素地球化学. 地球化学, 30 (3): 248-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2001.03.008 饶家荣, 骆检兰, 易志军, 1999. 锡矿山锑矿田幔-壳构造成矿模型及找矿预测. 物探与化探, 23 (4): 241-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH904.000.htm 杨瑞琰, 马东升, 潘家永, 2003. 锡矿山锑矿床成矿流体的热场研究. 地球化学, 32 (6): 509-519. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2003.06.001 於崇文, 岑况, 鲍征宇, 等, 1993. 热液成矿作用动力学. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1-189. -









 下载:
下载: