Low-Temperature Hot-Water in Xiangshan Orefield and Its Relation with Uranium Mineralization
-
摘要: 从矿田现代温热水入手, 运用水文地球化学、同位素水文地质等手段, 结合地热基础理论与方法, 剖析了典型矿床地温特征, 对温热水的补给源、热源进行了研究; 结合铀成矿机理分析, 探讨了热水与铀成矿作用的关系.认为相山矿田温热水属隆起断裂型热水, 大气降水为温热水的主要补给源, 地下水深循环及放射性生热为温热水获得热量的主要途径, 热水活动对铀成矿作出了重要贡献, 铀源主要来自水-岩作用, 形成了受基底构造和火山盖层构造联合控制的地温高场、温热水及铀矿化于一体的空间组合.Abstract: Xiangshan uranium orefield is one of the largest volcanic rock type hydrothermal uranium orefield in China. Beginning with modern warm hot-water in the orefield, and applying hydrogeochemistry and isotopic hydrogeology, this paper (analyzes) the geothermal characteristics of typical deposits, studies supply and heat sources of warm hot-water, and discusses the relation between hot-water and uranium mineralization according to the mechanism of uranium metallogenesis. The warm hot-water in Xiangshan orefield is hot-water of uplift fault type, meteoric water is the major supply source of warm hot- (water); deep circulation of groundwater and radioactive heat are the main channels for warm hot-water to obtain heat energy; hot-water activity made an important contribution to uranium metallogenesis; the uranium source mainly comes from water-rock interaction; a space unit is formed on integration with geothermal high field, warm hot-water and uranium mineralization which are controlled by base tectonics and volcano cover structure.
-
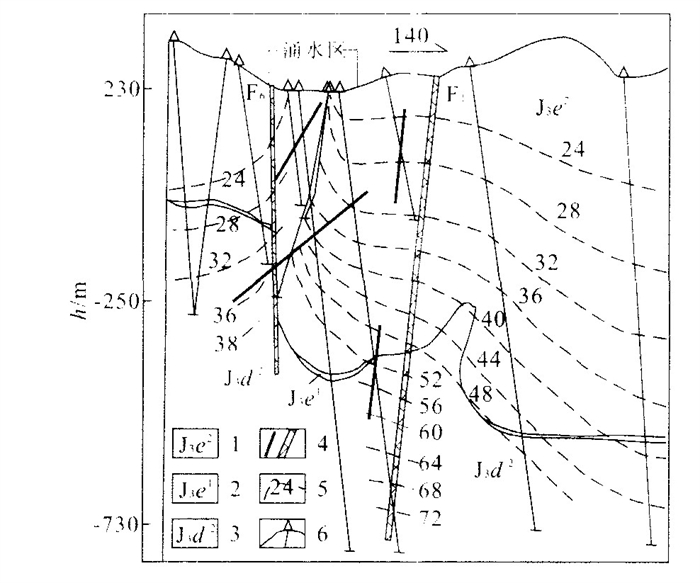
表 1 相山矿田若干铀矿床地温梯度值
Table 1. Geothermic gradie nt of several ur anium deposits in Xiangshan orefield

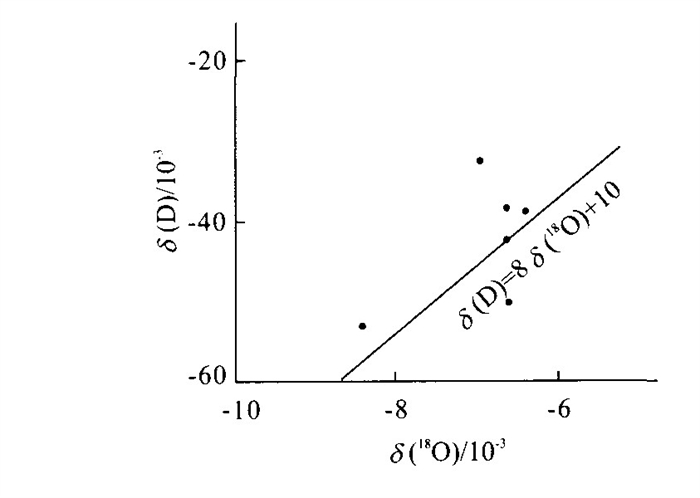
表 2 温热水的铀同位素比值
Table 2. Ratio of uranium isotope in warm hot-water

表 3 相山矿田GDCC矿床蚀变岩石的微量元素(据黄志章等,1999)
Table 3. Content of trace elements in altered rock of No.6122 deposit in Xiangshan orefield wB/10-6

-
Fan, H. H., Ling, H. F., Wang, D. Z., etal., 2003. Study on metallogenetic mechanism of Xiangshan uranium orefield. Uranium Geology, 19 (4): 208-213 (in Chinese with English abstract). Fei, H. C., Xiao, R. G., 2000. Ore forming fluid evolution and metallogenetic phy sical chemistry. Bulletin of Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 21 (2): 139-144 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huang, Z. Z., Li, X. Z., Cai, G. Q., 1999. Alteration field and type in hydrothermal uranium deposits. Atomic Energy Press, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Jia, L. X., 1992. Geophysical and geochemical investigation methods for geothemal water. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Li, J. W., Li, Z. J., Fu, Z. R., etal., 2000. Heat sources and hydrothermal uranium mineralization in the SuichuanReshui strike-slip fault zone. Geological Science and Technology In formation, 19 (3): 39-43 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, X. L., 1992. On the mineralization model of"there sources—Heat, water and uranium". Journal of East China Geological Institute, 15 (2): 101-112 (in Chinese with English abstract). Osmond, J. K., Cowart, J. B., Kaufman, M, I., 1983. Urani-um isotopic disequilibrium in groundwater as an indicator of anomalies. Int. J. Appl. Isot., 34 (1): 283-308. doi: 10.1016/0020-708X(83)90132-1 Qiu, A. J., Guo, L. Z., Zheng, D. Y., etal., 2002. Continental tectonic constraint on formation of Xiangshan largescale uranium deposits with high grade. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Shao, F., 2000. Genesis of low-thermal water and its relation with uranium mineralizalion in Zoujiashan deposit. Journal of East China Geological Institute, 23 (1): 24-27 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, R. H., Hu, S. M., Wang, J., etal., 2002. Water-rock interaction in typical volcanic rock areas in middle-lower Yangtze valley. China Dadi Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Zhao, T. F., Yuan, F., Yue, S. C., etal., 2002. Water-rock interaction during formation of skarn-type deposits in Yueshan orefield, Anhui Province. Mineral Deposits, 21 (1): 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, W. B., Sun, Z. X., Li, X. L., 2000. Fossil hydrothermal system and uranium metallogenesis. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). 范洪海, 凌洪飞, 王德滋, 等, 2003. 相山铀矿田成矿机理研究. 铀矿地质, 19 (4): 208-213. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2003.04.003 费红彩, 肖荣阁, 2002. 成矿流体溶化与成矿物理化学. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 21 (2): 139-144. 黄志章, 李秀珍, 蔡根庆, 1999. 热液铀矿床蚀变场及蚀变类型. 北京: 原子能出版社. 贾苓希, 1992. 地下热水调查的物探化探方法. 北京: 地质出版社. 李建威, 李紫金, 傅昭仁, 等, 2000. 遂川-热水走滑断裂带热异常与热液铀成矿作用. 地质科技情报, 19 (3): 39-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2000.03.008 李学礼, 1992. 论热源、水源、矿(铀) 源三源成矿问题. 华东地质学院学报, 15 (2): 101-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ199202000.htm 邱爱金, 郭令智, 郑大瑜, 等, 2002. 大陆构造作用对相山富大铀矿形成的制约. 北京: 地质出版社. 邵飞, 2000. 邹家山矿床低温热水成因及其与铀矿化关系. 华东地质学院学报, 23 (1): 24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2000.01.005 张荣华, 胡书敏, 王军, 等, 2002. 长江中下游典型火山岩区水-岩相互作用. 北京: 中国大地出版社. 周涛发, 袁峰, 岳书仓, 等, 2002. 安徽月山矿田矽卡岩型矿床形成的水岩作用. 矿床地质, 21 (1): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2002.01.001 周文斌, 孙占学, 李学礼, 2000. 古水热系统与铀成矿作用. 北京: 地质出版社. -









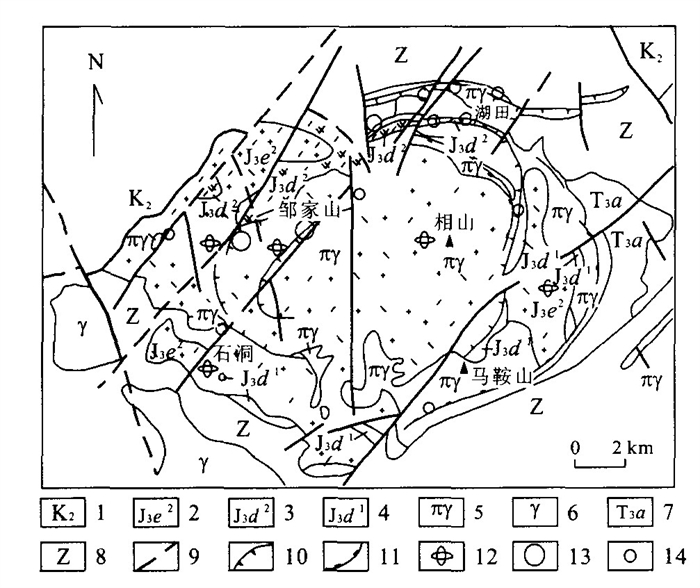
 下载:
下载: