Effects of High Temperature and Overpressure on Reservoir Quality in the Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea
-
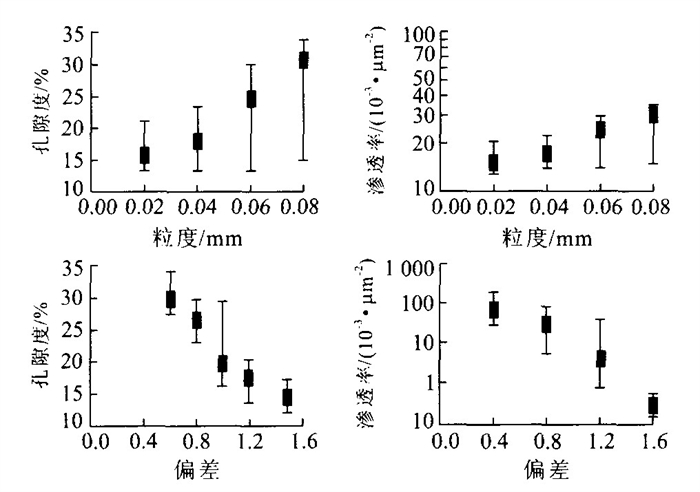
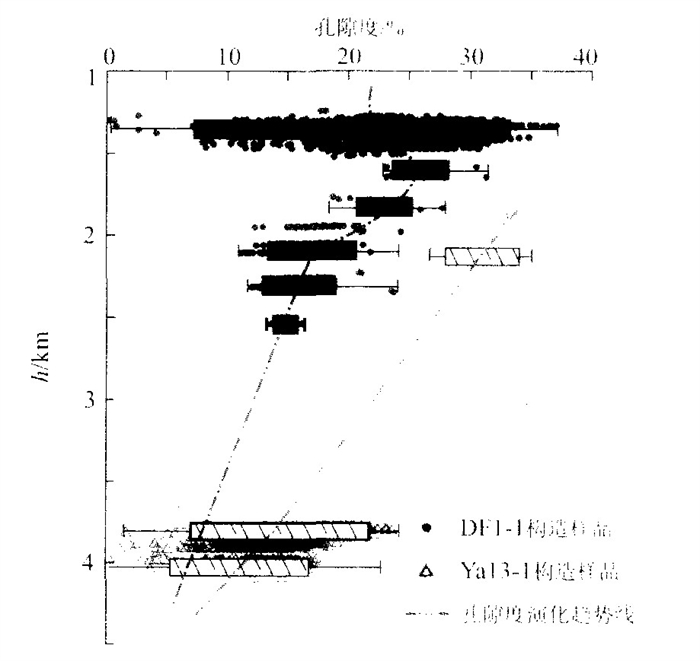
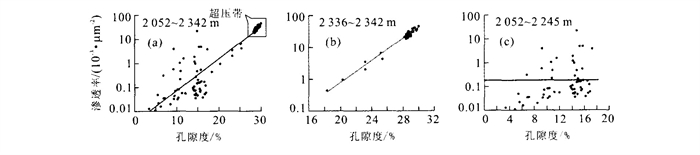
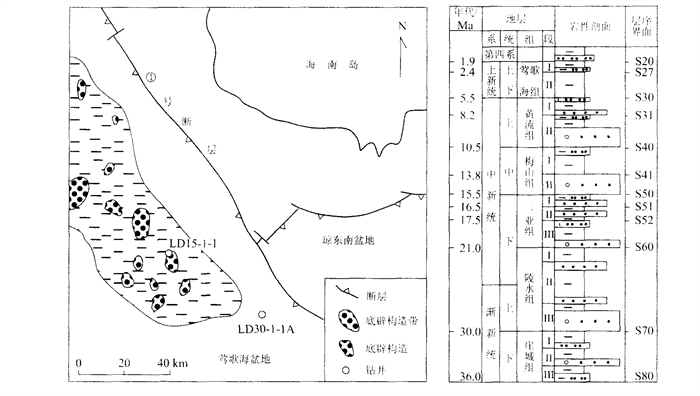
摘要: 莺歌海盆地由于独特的沉积地层和温压场特征, 使得盆地内的储层成岩演化也具有了与众不同的过程和特点.通过对莺歌海盆地内有钻井证实的两种超压体系类型(自源型和传导型) 的对比研究, 阐明了其成因差别及其石油地质意义, 并详细论述了高温超压环境下储层物性的影响因素: (1) 储层物性主要受沉积环境和成岩作用控制; (2) 高地温梯度使砂岩的孔隙度衰减较快; (3) 超压保存了一部分原生孔隙, 这是深部储层还具有高孔隙度的最主要原因; (4) 超压通过溶解等成岩作用产生了一些次生孔隙; (5) 流体压裂突破过程中产生了大量的裂缝, 有效地提高了储层渗透性.Abstract: Research into hydrocarbon basins around the world has shown that overpressure is closely connected with hydrocarbon generation and distribution. Because of unique sedimentary sequences and temperature-pressure characteristics, reservoir diagenesis has larruping processes and traits. Through comparing two types of overpressure systems (self-source type and conduction type), confirmed by core and log, this paper illustrates their origin and hydrocarbon value, and sets forth the effects of high temperature and overpressure on reservoir qualities, which include: ① reservoir characteristics are mainly determined by sedimentary environment and diagenesis; ② high geotemperature gradient decreases sandstone porosity; ③ (overpressure) conserves parts of original porosity, which causes high porosity in a deep reservoir; ④ overpressure brings out much of secondary porosity in the processes of diagenesis; ⑤ fluid breakthrough causes cracks, which effectively increase reservoir permeability.
-
Key words:
- anomalous pressure /
- reservoir characteristics /
- overpressure type /
- Yinggehai basin
-
表 1 不同沉积环境下的碎屑岩物性
Table 1. Clast reservoir qualities in different sedimentary environments

表 2 LG20-1-1井沿岸砂坝岩石学特征
Table 2. Lithologic characteristics of shore sandstones in LG20-1-1 well

-
Chi, G., Giles, P.S., Williamson, M.A., et al., 2003. Diage- netic history and porosity evolution of Upper Carbonif- erous sandstones from the Spring Valley#1 well, mari- times basin, Canada— Implications for reservoir devel- opment. Journal o f Geochemical Exploration, 80: 171 -191. doi: 10.1016/S0375-6742(03)00190-0 Du, X., Zheng, H.Y., Jiao, X.Q., 1995. Abnormal pressure and hydrocarbon accumulation. Earth Science Frontiers, 3(2): 137 -147(in Chinese with English abstract). Gong, Z.S., Li, S. T., Xie, T.J., et al., 1997. Continental margin basin analysis and hydrocarbon accumulation of the northern South China Sea. Science Press, Beijing(in Chinese). Hunt, J., 1990. Generation and migration of petroleum from abnormally pressured fluid compartments. AAPG Bulletin, 74(1): 1 -12. Jiang, J.Q., Hu, J.W., Li, M.K., 2000. Thermal evolution and hydrocarbon generating model of organic matter in high temperature and overpressure setting of Yingqiong basin. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 7(2): 4 -7(in Chinese with English abstract). Lima, R.D., De Ros, L.F., 2002. The role of depositional setting and diagenesis on the reservoir quality of Devonian sandstones from the Solimoes basin, Brazilian Amazonia. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 19: 1047 - 1071. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(03)00002-3 Lü, M., 1999. Reservoir characteristics of the gas bearing area in Yingqiong basin. Natural Gas Industry, 19(1): 20 -24(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.1999.01.006 Ma, Q.F., Chen, S.Z., Zhang, Q.M., et al., 2000. Overpres- sured basins and hydrocarbon accumulations. Geological Publishing House, Beijing(in Chinese). Scherer, M., 1987. Parameters influencing porosity in sand- stone: A model for sandstone porosity prediction. AAPG Bulletin, 71(5): 485 -491. Wang, Z.F., Hu, D.S., 1999. Prospecting for giant gas fields in the central mud diapir structure belt in Yinggehai basin. Natural Gas Industry, 19(1): 7 -11(in Chinese with English abstract). Worden, R.H., Mayall, M., Evans, I.J., 2000. The Effect of Ductile-lithic sand grains and quartz cement on porosity and permeability in Oligocene and Lower Miocene clas- tics, South China Sea: Prediction of reservoir quality. AAPG Bulletin, 84(3): 345 -359. Xie, X.N., 2001. Evolution of overpressure systems and hydrocarbon accumulation in Yinggehai basin. The 2nd national sedimentary conference abstracts in 2001.183(in Chinese with English abstract). Xie, X.N., Li, S.T., Hu, X.Y., et al., 1999a. Conduit system and formation mechanism of heat fluids in diapiric belt of Yinggehai basin, China. Science in China(Series D), 42(6): 561 -571(in Chinese). doi: 10.1007/BF02877783 Xie, X.N., Li, S.T., Dong W.L., et al., 1999b. Overpres- sure development and hydrofracturing in the Yinggehai basin, South China Sea. Journalo f Petroleum Geology, 22(4): 437 -454. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-5457.1999.tb00478.x Yao, G.Q., Li, H.S., 1991. A preliminary investigation on carbonate cements and their origin in sandstones of Hetaoyuan Formation, Nanyang depression. Earth Science—Journal o f China University of Geosciences, 16 (5): 549 -556(in Chinese with English abstract). Zha, M., Qu, J.X., Zhang, W.H., 2002. The relationship between overpressure and reservoir forming mechanism. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 29(1): 19 - 23(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] Zhang, L.X., Li, J., Liu, S.Z., et al., 2000. The control of abnormal pressure on deep oil/gas pool formation in Qi- bei sag. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 27 (5): 19 -21(in Chinese with English abstract). [18] 杜栩, 郑洪印, 焦秀琼, 1995. 异常压力与油气分布. 地学前缘, 3 (2): 137-147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1995.02.016 龚再生, 李思田, 谢泰俊, 等, 1997. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地分析与油气聚集. 北京: 科学出版社. 姜建群, 胡建武, 李明葵, 2000. 莺琼盆地高温超压环境有机质热演化及成烃模式探讨. 特种油气藏, 7 (2): 4-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ200002001.htm 吕明, 1999. 莺琼盆地含气区储层特征. 天然气工业, 19 (1): 20-24. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.1999.01.006 马启富, 陈斯忠, 张启明, 等, 2000. 超压盆地与油气分布. 北京: 地质出版社. 王振峰, 胡代圣, 1999. 莺歌海盆地中央泥拱构造带大气田勘探方向. 天然气工业, 19 (1): 7-11. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.1999.01.003 解习农, 2001. 莺歌海盆地超压体系演化及油气成藏模式. 2001年全国沉积学大会摘要论文集. 武汉. 183. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ200110001121.htm 解习农, 李思田, 胡祥云, 等, 1999a. 莺歌海盆地中央底辟带热流体疏导系统及其成因机制. 中国科学(D辑), 42 (6): 561-571. 姚光庆, 李惠生, 1991. 南阳凹陷下第三系核桃源组砂岩中碳酸岩胶结物及其成因的初步探讨. 地球科学———中国地质大学学报, 16 (5): 549-556. 查明, 曲江秀, 张为海, 2002. 异常超压与油气成藏机理. 石油勘探与开发, 29 (1): 19-23. 张立新, 李军, 刘淑芝, 等, 2000. 试析歧北凹陷异常压力在深层油气藏成藏过程中的控制作用. 石油勘探与开发, 27 (5): 19-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200005005.htm -









 下载:
下载: