Thermal Stresses and Their Effects during the Deep Hot Fluids Penetrating upward in DF 1-1 Diapiric Area, Yinggehai Basin
-
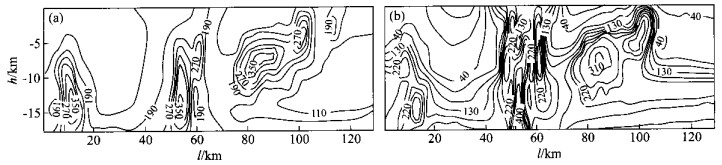
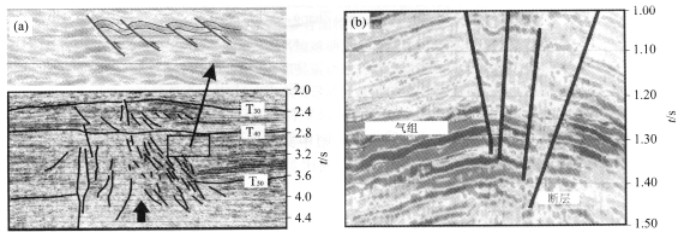
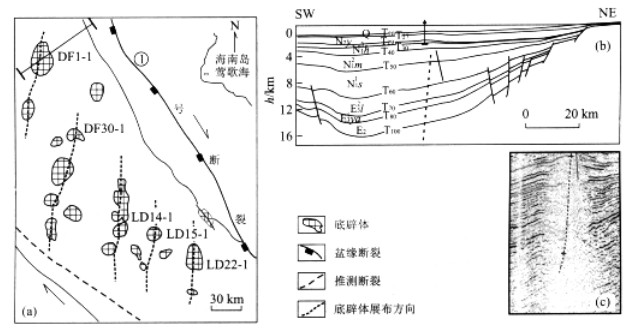
摘要: 东方1 - 1底辟区的热流体活动相当强烈和频繁.深部热流体的穿层上涌产生热应力造成了局部的应力场状况的变化, 形成了特征性的构造和断裂系统, 水力破裂、热流体拱张形成褶皱和局部破裂等, 这些褶皱和断裂共同构成了底辟带热流体活动中垂向输导的主要通道之一.由于热流体穿层活动不仅携带了大量的烃类气和CO2等非烃气, 而且具极强的热力作用, 引起了强烈的热异常, 导致所穿入的浅部地层中的热力学参数, 如粘土矿物的演化、储层中流体包裹体以及岩石所含有机质的镜质体反射率等发生一系列的异常变化, 致使底辟作用前后底辟体内部及其围岩的特征具有非常显著的差别.本次研究对热流体穿层所引起的热应力效应和温度异常采用Field模型进行了定量动力学模拟, 结果显示应力场和温度场的分布随着时间不断向上迁移, 使各小断裂和裂隙连通形成流体的良好的垂向运移通道, 在热流体活动的通道附近热应力的影响十分明显, 致使局部应力急剧增高Abstract: The hot fluids are intensive and frequent in the DF1-1 diapiric area, Yinggehai basin, South China Sea. Thermal fluids penetrating the strata from the deep belt generated thermal stress, which resulted in changes to the local stress field. Moving thermal fluids are capable of transporting a large amount of heat from the deep part of the basin, resulting in thermal anomalies, which heat and expand adjacent sediments to form local thermal stress. Thermal stresses controlled the stress patterns and direction of overpressure fluid migration in some locations. The structural stress associated with thermal stress induced the fluid migration system including fractures, faults and sand folds. On the other hand, because the fluids have had thermal energy and hydrocarbon or CO2 when penetrating strata from the deep, the obvious temperature differentia caused abnormal phenomena in a series of geochemical parameters, including transferring from smectite to illite, vitrinite reflectance rate, the temperature of fluid inclusions etc.. All those processes mean that the characteristics of the diapiric body and its surrounding rock are extremely different before diapirism and after diapirism. This research also demonstrates and analyzes the evolutional process of the thermal stress field and temperature field by comparing a quantitative dynamic simulation with field analysis. The results show that stress fields and temperature fields moved upwards over time. The thermal stress field also promoted the episodic opening of faults, and accelerated the hydrocarbon-bearing fluid flow upwards. The extent of the effect of thermal fluids depends on the proportion between thermal stress and tectonic stress.
-
Key words:
- DF1-1 diapir /
- deep hot fluid /
- strata penetration /
- thermal stress /
- effect
-
表 1 DF1-1流体包裹体温度测试结果
Table 1. Ranges of homogenization temperatures of the fluid inclusions in DF1-1 diapir

-
Bjorlykke, K., 1994. Fluid-flow processes and diagenesis in sedimentary basins. In: Parnell, J., ed., Geofluids: Origin, migration and evolution of fluids in sedimentary basins. Geological Society Special Publication, 78: 127-140. Collett, T. S., 2002. Energy resource potential of natural gas hydrates. AAPG Bulletin, 86(11): 1971-1992 Cosgrove, J. W., 2001. Hydraulic fracturing during the formation and deformation of a basin: A factor in the dewatering of low-permeability sediments. AAPG Bulletin, 85(4): 737-748. Dong, W. L., Huang, B. J., 1999. Heterogeneity of natural gases and the episodic charging process: A case study for Dongfang 1-1 gas field, Yinggehai basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 26(15): 15-18 (in Chinese with English abstract). Gao, B., Tao, M. X., Wang, W. C., 2001. Influences of deeply sourced thermal fluid on the formation of hydrocarbon reservoirs. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemisty, 20(1): 30-34 (in Chinese with English abstract). Gibson, R. G., Bentham, P. A., 2003. Use of fault-seal analysis in understanding petroleum migration in a complexly faulted anticlinal trap, Columbus basin, offshore Trinidad. AAPG Bulletin, 87(3): 465-478. doi: 10.1306/08010201132 Hao, F., Li, S. T., Gong, Z. S., et al., 2001. The mechanism of diapirs developing and episodic expulsing in Yinggehai basin. Science in China (Series D), 31(6): 471-476 (in Chinese). Huang, B. J., Xiao, X. M., Dong, W. L., 2002. Source rocks and generation & evolution model of natural gas in Yinggehai basin. Natural Gas Industry, 22(1): 26-30(in Chinese with English abstract). Huang, C. J., Chen, K. Y., Li, S. T., 2002. Periodicities of diapiric rise in the Yinggehai basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 29(4): 44-46 (in Chinese with English abstract). Larue, D. K., Legarre, H., 2004. Flow units, conductivity, and reservoir characterization in a wave-dominated deltaic reservoir: Meren reservoir, Nigeria. AAPG Bulletin, 88(3): 303-324. doi: 10.1306/10100303043 Lawrence, S. R., Cornford, C., 1995. Basin geofluids. Basin Research, 57: 1-7. Li, S. T., 1992. To get the giant achievements in oil/gas field-The synopsis of the history in researching active hot fluid. China Of fshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 6(6): 69-70(in Chinese with English abstract). Makhous, M., Galushkin, Y. I., 2003. Burial history and thermal evolution of the northern and eastern Saharan basins. AAPG Bulletin, 87(10): 1623-1652. doi: 10.1306/04300301122 Nordgard, B. H. M., Hermanrud, C., Teige, G. M. G., 2004. Origin of overpressures in shales: Constraints from basin modeling. AAPG Bulletin, 88(2): 193-212. doi: 10.1306/10060302042 Sibson, R. H., 2003. Brittle-failure controls on maximum sustainable overpressure in different tectonic regimes. AAPG Bulletin, 87(6): 901-908. doi: 10.1306/01290300181 Xie, X. N., Li, S. T., Dong, W. L., et al., 1999. Trace marker of hot fluid flow and their geological implications-A case study of Yinggehai basin. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 24(2): 183-188 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yin, X. L., Li, S. T., Yang, J. H., 2003. Study on the digital simulation of structural stress field and flow field in DF1-1 diapir. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 28(3): 268-274 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, M. Q., 2000. Migration accumulation characteristics of natural gas in the diapir structure belt of Yinggehai basin. Journal of University of Petroleum, 24(4): 39-42 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Q. M., Liu, F. N., Yang, J. H., 1996. Overpressure system and oil/gas accumulation. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 10(2): 65-75 (in Chinese with English abstract). 董伟良, 黄保家, 1999. 东方1-1气田天然气组成的不均一性与幕式充注. 石油勘探与开发, 26 (15): 15-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK902.004.htm 高波, 陶明信, 王万春, 2001. 深部热流体对油气成藏的影响. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 20 (1): 30-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2001.01.007 郝芳, 李思田, 龚再升, 等, 2001. 莺歌海盆地底辟发育机理与流体幕式充注. 中国科学(D辑), 31 (6): 471-476. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200106004.htm 黄保家, 肖贤明, 董伟良, 2002. 莺歌海盆地烃源岩特征及天然气生成演化模式. 天然气工业, 22 (1): 26-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2002.01.007 黄春菊, 陈开远, 李思田, 2002. 莺歌海盆地泥底辟活动期次分析. 石油勘探与开发, 29 (4): 44-46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2002.04.013 李思田, 1992. 为实现油气领域的重大突破———活动热流体的历史研究简介. 中国海上油气(地质), 6 (6): 69-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199206019.htm 解习农, 李思田, 董伟良, 等, 1999. 热流体活动示踪标志及其地质意义———以莺歌海盆地为例. 地球科学———中国地质大学学报, 24 (2): 183-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX902.016.htm 殷秀兰, 李思田, 杨计海, 2003. DF1-1底辟区构造应力场及渗流场演化的数值模拟研究. 地球科学———中国地质大学学报, 28 (3): 268-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200303005.htm 张敏强, 2000. 莺歌海盆地底辟构造带天然气运聚特征. 石油大学学报, 24 (4): 39-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200004009.htm 张启明, 刘福宁, 杨计海, 1996. 莺歌海盆地超压体系与油气聚集. 中国海上油气(地质), 10 (2): 65-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199602000.htm -









 下载:
下载: