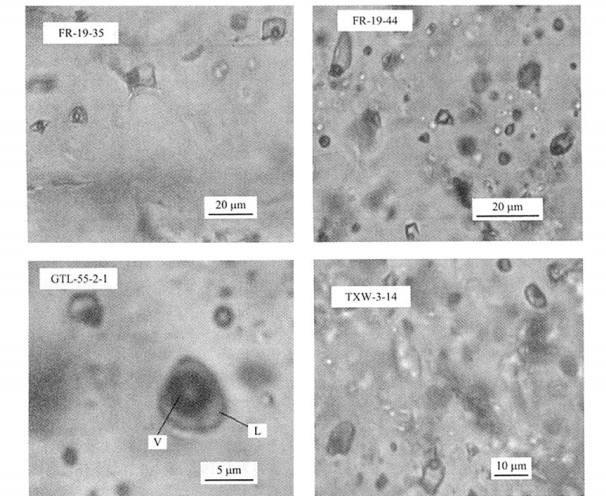
Helium Isotope Composition of Fluid Inclusions and the Origin of Ore-Forming Fluids of Furong Tin Orefield in Hunan Province, China
-
摘要: 芙蓉锡矿田位于湖南省骑田岭花岗岩体的南部, 是一个新近发现的超大型锡矿田.与以往所研究的与S型花岗岩有关的锡矿床明显不同, 这个矿田在时空上都与骑田岭A型花岗岩密切相关.该矿田矿石硫化物流体包裹体的3He/4He测定值为0.14-2.95 Ra, 低于地幔的3He/4He值(6-7 Ra), 且高于地壳的3He/4He值(0.01-0.05 Ra).这表明芙蓉锡矿田成矿流体中的He具壳幔两端元混合的特点.该区一致的硫、锶及其他证据也都表明, 深部地幔物质确实参与了该区锡的成矿.骑田岭岩体属造山期后张性环境下形成的A型花岗岩类.芙蓉锡矿田就产在骑田岭岩体的内外接触带或岩体中, 其主成矿期与骑田岭岩体的形成时间相当吻合, 且两者均具壳幔两端元混合成因的特征, 所以其形成地球动力学背景可能均与中生代华南岩石圈的拉张、伸展作用密切相关.Abstract: The Furong tin orefield, located in southern Hunan, China, is a newly-discovered super-large tin orefield. In contrast to most other tin deposits associated with S-type granites, the Furong tin deposit is spatially and temporally associated with the Qitianling A-type granite. The 3He/4He ratios of fluid inclusions in sulfides from this orefield range from 0. 14 to 2. 95 Ra, which are lower than that of the mantle, and higher than that of the crust, indicating that the helium in ore-forming fluids from this orefield is a mixture of two end-member components, mantle-source He and crust-source He. This conclusion is in accordance with the S isotope, Sr isotope and other results, suggesting that there must be some mantle-source substance in mineralization of this orefield. The Qitianling granite belongs to A-type granite which formed in a post-orogenic extensional settings. The Furong tin orefield is located at the contact zone (outer or inner) or within of Qitianling granite, and its main tin-mineralization time is consistent with the intrusion time of Qitianling granite. The relationship reflects that their forming settings of geodynamics might both be related to the Mesozoic lithospheric extension in South China.
-
Key words:
- Furong tin orefield /
- ore-forming fluid /
- He isotope
-
图 3 芙蓉锡矿田He同位素组成演化(Mamyrin and Tols-tikhin, 1984)
Fig. 3. Helium isotopic composition and evolution in the Furong tin orefield
表 1 芙蓉锡矿田硫化物流体包裹体中的He同位素组成
Table 1. He isotopic composition of fluid inclusions in sulfides from the Furong tin orefield

-
Baptiste, P. J., Fouquet, Y., 1996. Abundance and isotopic composition of helium in hydrothermal sulfides from the East Pacific Rise at 13°N. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60: 87-93. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00357-6 Burnard, P. G., Polya, D. A., 2004. Importance of mantle-derived fluids during granite associated hydrothermal circulation: He and Ar isotopes of ore minerals from Panasqueira. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68 (7): 1607-1615. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.10.008 Cai, J. H., Wei, C. S., Sun, M H., et al., 2004. Genetic study about the Bailashui tin deposits in Qitianling area of Hunan. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 28(1): 45-52 (in Chinese with English abstract). Cai, M. H., Mao, J. W., Liang, T., et al., 2004. Helium and argon isotopic components of fluid inclusions in Dachang tin-polymetallic deposit and their geological implications. Mineral Deposits, 23 (2): 225-231 (in Chinese with English abstract). Craig, H., Lupton, J. E., 1996. Primordial neon, helium and hydrogen in oceanic basalts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 31: 369-385. Dunai, T., Touret, J. L. R., 1995. Helium, neon and argon isotope systematics of European lithospheric mantle xenoliths: Implications for its geochemical evolution. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59: 2767-2783. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00172-V Hu, R. Z., Burnard, P. G., Turner, G., et al., 1998a. Helium and argon isotope systematics in fluid inclusions of Machangqing copper deposit in west Yunnan Province, China. Chemical Geology, 146: 55-63. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00003-5 Hu, R. Z., Burnard, P. G., Bi, X. W., et al., 2004. Helium and argon isotope geochemistry of alkaline intrusion-associated gold and copper deposits along the Red River-Jinshajiang fault belt, SW China. Chemical Geology, 203: 305-317. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.10.006 Hu, R Z., Turner, G., Burnard, P. G., et al., 1998b. Helium isotopic compositions of Machangqing copper deposit in western Yunnan, China Chinese Science Bulletin, 43: 69-72. Huang, G. F., Zeng, Q. W., Wei, S. L., et al., 2001. Geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of the Fu-rong orefield, Qitianling, Hunan. Geology in China, 28 (10): 30-34 (in Chinese with English abstract). Inguaggiato, S., Rizzo, A., 2004. Dissolved helium isotope ratios in ground-waters: A new technique based on gas-water re-equilibration and its application to Stromboli volcanic system. Applied Geochemistry, 19: 665-673. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.10.009 Kurz, M. D., 1986. In situ production of cosmogenic helium and some applications to geochronology. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 50: 2855-2862. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(86)90232-2 Li, Y. H., Li, J. C., Song, H. B., et al., 2002. Helium isotope studies of the mantle xenoliths and megacrysts from the Cenozoic basalts in the eastern China. Science in China (Series D), 45: 174-183. doi: 10.1007/BF02879794 Marty, B., Jambon. A., Sano, Y., 1989. Helium isotopes and CO2 in volcanic gases of Japan. Chemical Geology, 76: 25-40. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(89)90125-3 Mamyrin, B. A., Tolstikhin, I. N., 1984. Helium isotopes in nature. In: Fyfe, W. S., ed., Developments in geochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 273. Mao, J. W., Li, Y. H., Li H. Y., et al., 1997. Helium isotopic evidence on metalgenesis of mantle fluids in the Wangu gold deposit, Hunan Province. Geological Review, 43 (6): 646-649 (in Chinese with English abstract). Mao, J. W., Wei, J. X., 2000. Helium and argon isotopic components of fluid inclusions and tracing to the source of metallogenic fluids in the Dashuigou tellurium deposit of Sichuan Province. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 21(1): 58-61 (in Chinese with English abstract). Park, J., Kazaki, R., Nagao, K., 2003. Noble gas studies of Martian Meteorites: Dar Al Gani 476/489, Sayh Al Uhaymir 005/060, Dhofar 019, Los Angeles 001 and Zagami. Proceeding of Lunar and Planetary Science Conference ⅩⅩⅩⅣ, 1213. Podosek, F. A., Bernatowicz, T. J., Kramer, F. E., 1980. Absorption of xenon and krypton on shales. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 45: 2401-2415. Simmons, S. F., Sawkins, F. J., Schlutter, D. J., 1987. Mantle-derived helium in two Peruvian hydrothermal ore deposits. Nature, 329: 429-432. doi: 10.1038/329429a0 Stuart, F. M., Burnard, P. G., Taylor, R. P., et al., 1995. Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluids: He-Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from DaeHwa W-Mo mineralisation, South Korea. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59: 4663-4673. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00300-2 Stuart, F. M., Turner, G., Duckworth, R. C., et al., 1994. Helium isotopes as tracers of trapped hydrothermal fluids in ocean floor sulfides. Geology, 22: 823-826. Torgersen, T., Jenkins, W. J., 1982. Helium isotopes in geo-thermal systems: Iceland, the Geysers, Raft River and Steamboat Springs. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 46: 739-748. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(82)90025-4 Turner, G., Stuart, F., 1992. Helium/heat rations and deposition temperatures of sulfides from the ocean floor. Nature, 375: 581-583. Trull, T. W., Kurz, M D., Jenkins, W. J., 1991. Diffusion of cosmogenic 3He in olivine and quartz: Implications for surface exposure dating. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 103: 241-251. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(91)90164-D Turner, G., Burnard, P. R, Ford, J. L., et al., 1993. Tracing fluid sources and interactioa Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A., 344: 127-140. doi: 10.1098/rsta.1993.0081 Wang, D. D., 1998. Noble gas isotopic abundance in some chondrites and middle-ferreous aerolites in China. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 18(4): 336-341 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, X. W., Wang, X. D., Liu, J. Q., et al., 2004. Relationship of Qitianling granite to Sn mineralization in Hunan Province. Geological Science and Technology In formation, 23(2): 1-12 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, Y. C., 1997. Helium isotope distribution of natural gases and its structural setting. Earth Science Frontiers, 4(3-4): 185-190 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xue, C. J., Chen, Y. C., Wang, D., et al., 2003. Geology and isotopic composition of helium, neon, xenon and metal-logenic age of the Jinding and Baiyangping ore deposits, northwest Yunnan, China. Science in China (Series D), 46: 789-800. doi: 10.1007/BF02879523 Zhao, K. D., Jiang, & amp; amp; Y., Xiao, H. Q., et al., 2002. Origin of ore-forming fluids of the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore deposit: Evidence from helium isotopes. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47: 1041-1045. Zhao, Z. H., Bao, Z. W., Zhang, R Y., et al., 2001. Crust-mantle interaction and its contribution to the Shizhuyuan superlarge tungsten polymetallic mineralization. Science in China (Series D), 44: 266-276. doi: 10.1007/BF02882261 Zheng, J. J., Jia, R H., 2001. Geological characteristics and related tin-polymetallic mineralization of the Qitianling granite complex in southern Hunan Province. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 9 (4): 50-57 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhu, J. C., Huang, G. F., Zhang, P. H., et al., 2003. On the emplacement age and material sources for the granites of Calling superunit, Qitianling pluton, South Hunan Province. Geological Review, 49(4): 245 - 252 (in Chinese with English abstract). 蔡锦辉, 韦昌山, 孙明慧, 等, 2004. 骑田岭白腊水锡矿床成因探讨. 大地构造与成矿学, 28(1): 45-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2004.01.007 蔡明海, 毛景文, 梁婷, 等, 2004. 广西大厂锡多金属矿床氦、氩同位素特征及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 23(2): 225- 231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2004.02.011 黄革非, 曾钦旺, 魏绍六, 等, 2000. 湖南骑田岭芙蓉矿田锡矿地质特征及控矿因素初步分析. 中国地质, 28(10): 30 -34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6995.2000.10.008 毛景文, 李延河, 李红艳, 等, 1997. 湖南万古金矿床地幔流体成矿的氦同位素证明. 地质论评, 43(6): 646-649. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1997.06.011 毛景文, 魏家秀, 2000. 大水沟碲矿床流体包裹体的He、Ar同位素组成及其示踪成矿流体的来源. 地球学报, 21 (1): 58-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2000.01.009 王道德, 1998. 我国某些球粒陨石及中铁陨石稀有气体的同位素丰度. 空间科学学报, 18(4): 336-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJKB199804008.htm 汪雄武, 王晓地, 刘家齐, 等, 2004. 骑田岭A型花岗岩形成时代及其地球动力学意义. 地球化学, 26(2): 36-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2004.02.008 徐永昌, 1997. 天然气中氦同位素分布及构造环境. 地学前缘, 4(3-4): 185-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY7Z2.031.htm 郑基俭, 贾宝华, 2001. 骑田岭岩体的基本特征及其与锡多金属成矿作用关系. 华南地质与矿产, 9(4): 50-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2001.04.011 朱金初, 黄革非, 张佩华, 等, 2003. 湖南骑田岭岩体菜岭超单元花岗岩侵位年龄和物质来源研究. 地质论评, 49(4): 245-252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200303004.htm -









 下载:
下载: