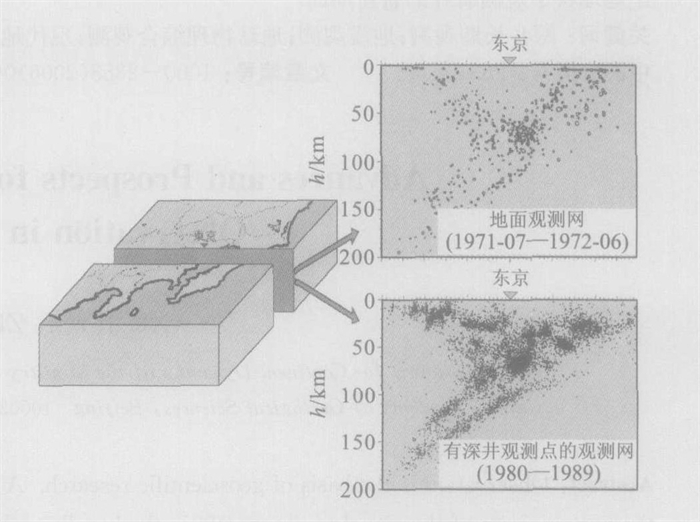
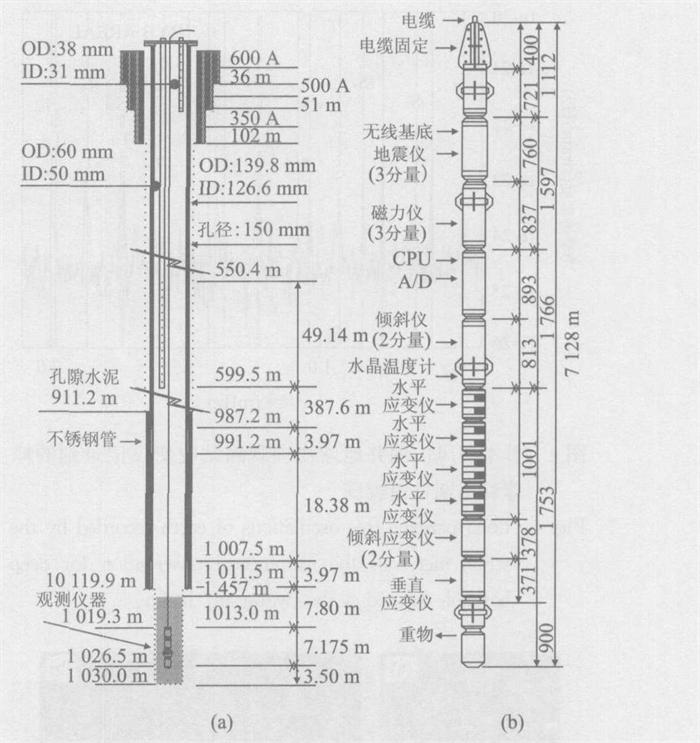
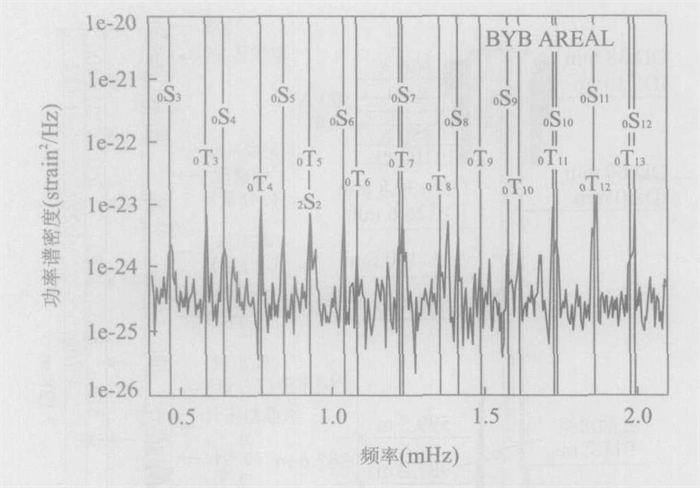
Advances and Prospects for Long-Term Geophysical Observation in Deep Borehole
-
摘要: 地球科学是以观测为基础的科学.当前, 如何克服城市化、工业化、现代化发展带来的噪音干扰, 提高观测的信噪比, 成为地球科学发展的重要课题之一.开展深井观测是解决地面噪音干扰的主要途径.近年来, 随着地球系统科学研究的深入以及解决环境、资源、防灾等科学问题的需求, 世界大陆、大洋科学钻探工程研究以及在钻孔深井内进行的地球物理长期观测得到飞速发展, 并取得了初步的观测研究成果.本文介绍了世界各国在深井长期观测方面的最新进展, 展示了中国大陆科学钻探工程在江苏东海现场开展深井地球物理综合观测的方案及其观测研究前景.东海深井长期观测站将成为中国第一个无地面干扰的综合性深井地震、地球物理实验观测站, 它是实现我国“入地”科学计划的重要基础, 将开创我国21世纪地球科学观测研究的崭新局面.Abstract: Observation is the basis of geoscientific research. A significant project in the development of geoscientific study is the improvement of the signal to noise ratio in the heavily ambient noise of industrialization and urban expansion. Observation in a deep borehole is one way to restrain the noise. Recently, scientific drilling and the long-term multi-component geophysical observations in deep boreholes have been speedily developed on the continent as well as in the ocean. Many observations and studies have been reported. In the present analysis, we provide an overview of geophysical observation achievements in deep boreholes worldwide. A plan for observation in the borehole in Donghai, Jiangsu of the Chinese Continent Scientific Drilling (CCSD) project is discussed and the bright future for the deep borehole geophysical observation is clarified. The long-tem borehole observatory in Donghai will be the first noiseless multi-geophysical observatory in China. The observatory is a significant study base for researching the inner earth. The deep borehole observation will enrich geoscientific knowledge and benefit areas such as resource prospecting, environmental protection and disaster prevention.
-
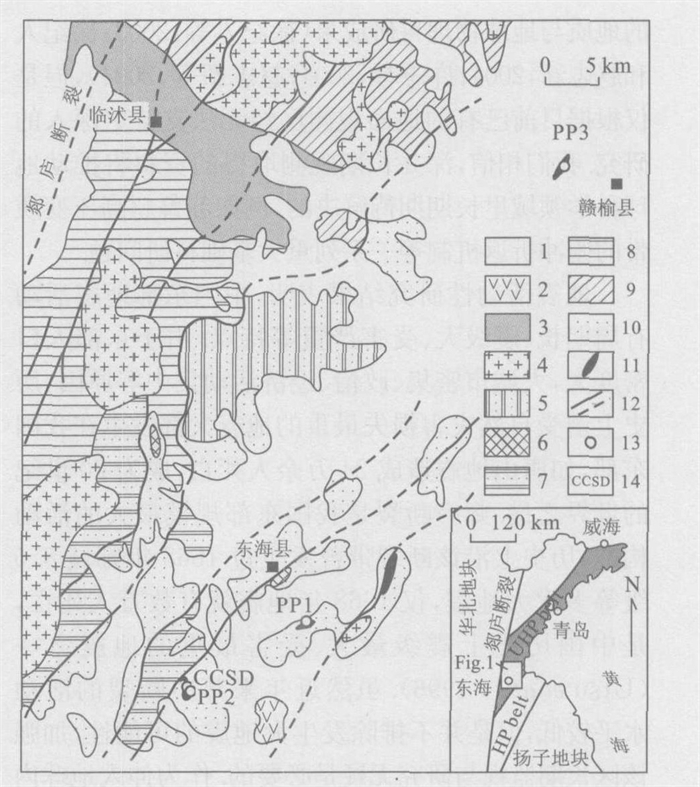
图 6 中国大陆科学钻探(CCSD) 现场地质构造分布
图中PP1、PP2、PP3分别为卫星孔的位置; 1.第四系; 2.第三纪玄武岩; 3.白垩纪盆地沉淀; 4.造山后未变质花岗岩; 5.含霓石角闪石二长花岗质片麻岩; 6.角闪黑云斜长花岗质片麻岩; 7.斜长(二长) 花岗质片麻岩; 8.含黑云母二长花岗质片麻岩; 9.钾长花岗质片麻岩; 10.表壳岩系; 11.榴辉岩和超基性岩; 12.剪切带或断层; 13.卫星孔; 14.主孔; HP belt.高压变质带; UHP belt.超高压变质带
Fig. 6. Simplified geological and tectonic map of the site of the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling (CCSD)
-
Araya, A., Takamori, A., Otake, Y., etal., 2005. Perform-ance of an optically-linked broadband seismometer for borehole observations. Abstracts of 2005 Japan Earth and Planetary Science Joint Meeting. S048-005. Asai, Y., Okubo, M., Ishii, H., etal., 2005. Co-seismic strain-steps associated with the 2004 off the Kii Penin-sula earthquakes—Observed with Ishii-type borehole strainmeters and quartz-tube extensometers. Earth Planets Space, 57: 309-314. Chavarria, J. A., Malin, P., Catchings, R. D., etal., 2003. A look inside the Andreas fault at Parkfield through verti-cal seismic profiling. Science, 302: 1746-1748. Fukao, Y., Ishibashi, K., 1996. Damages caused by Osaka-Kobe-Awaji large earthquake and earthquake predic-tion. Iwanami Press, Tokyo (in Japanese). Ishii, H., Asai, Y., Okubo, M., etal., 2005a. Development of deep borehole instruments for both multi-component obser-vation and in situ stress measurement, and some in teresting results obtained, 2005, Zisin 2. J. Seismo. Soc. Japan, 58: 1-14 (in Japanese with English abstract). Ishii, H., Okubo, M., Asai, Y., etal., 2005b. New develop-ment of seismology by deep strain observations. Ab-stracts of 2005 Japan Earth and Planetary Science Joint Meeting, S098-005. Ishii, H., Yamauchi, T., Asai, Y., etal., 2003. Continuous multi-component monitoring of crustal activities by anewly developed instrument installed in a 1200 m depthborehole—The deepest multiple observation in the world consisting of stress, strain, tilt, seismicwave, geomegnetism, temperature. IUGG2003Poster, Sappo-ro, Japan. Katao, H., Ando, M., 1996. Crustal movement before and af-ter the Hyogo-ken Nanbu earthquake. Science, 66: 78-85 (in Japanese with English abstract). Ogasawara, H., Sato, S., Nishii, N., etal., 2000. Semi-controlled seismogenic experiments in South African deep gold mines. The South African Institute of Min-ing and Metallurgy Symposium Series, s27: 293-300. Okubo, M., Asai, Y., Aoki, H., etal., 2005. The seismologi-cal and geodetical roles of strain seismogram suggested from the 2004 off the Kii peninsula earthquakes. Earth Planets Space, 57: 303-308. Okubo, M., Ishii, H., Yamauchi, T., 2004. The 2003 Yoca-chi-oki Earthquake, observed by borehole strainmeterarray—Comparison with broadband seismogram, Zisin2. J. Seismo. Soc. Japan, 57: 105-113 (in Japanese with Englishabstract). Tu, Y. M., Chen, Y. T., 2002. The accurate location of the injection-induced microearthquakes in German Continental Deep Drilling Program. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 15 (6): 616-627 (in Chinese with English abstract). Utsu, T., Shima, E., Yoshii, K., 1996. Encyclopaedia of earthquakes. Asakura Press, Tokyo, 456-466. Wang, Z. W., Liu, J. H., Li, Z. B., etal., 1999. KTB deep crustal Lab. World Geology, 18 (4): 96-99. Xu, J. R., Yang, W. C., Zhao, Z. X., etal., 2003. Three-dimensional velocity structures of the Sulu-Dabie orogenbelt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77 (4): 577-582 (in Chinese with English abstract). [16] Xu, J. R., Zhao, Z. X., 2004. Regional structure characteristics of crustal root of mountain beneath the Sulu orogenic belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20 (1): 149-156 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, J. R., Zhao, Z. X., Ishii, H., etal., 2006. Multiple geophysical observations by a newly developed multi-component borehole instrument at the Continental Deep Drilling Site of the CCSD, Donghai, China. Aproposal to ICDP. Xu, Z. Q., 2004. The scientific goals and investigation progresses of the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling Project. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20 (1): 1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, Z. Q., Yang, W. C., Cong, B. L., etal., 1998. Drilling operations in the Dabie-Sulu UHPM Belt, East China. Aproposal to ICDP. Zhao, Z. X., Xu, J. R., Yang, W. C., etal., 2004. Simulations of reflection seismic profile of borehole area of Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20 (1): 139-148 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zoback, M. D., Apel, R., Baumgartner, J., etal., 1993. Uppercrustal strength inferred from stress measurements to 6 km depthin the KTB borehole. Nature, 365: 633-634. Zoback, M. D., Hickman, S. H., Ellsworth, W. L., 1998. Scientific Drilling into the San Andreas fault at Parkfield, CA: Project overview and operational plan. A proposal to National Science Foundation. Zoback, M. D., Hickman, S. H., Ellsworth, W. L., 2004. SanAndreas fault observatory at depth (SAFOD). A proposal to ICD. 涂毅敏, 陈运泰, 2002. 德国大陆超深钻井注水诱发地震的精确定位. 地震学报, 24 (6): 587-598. 王祝文, 刘菁华, 李舟波, 等, 1999. KTB深部地壳实验室. 世界地质, 18 (4): 96-99. 徐纪人, 杨文采, 赵志新, 等, 2003. 苏鲁大别造山带岩石圈三维P波速度结构特征. 地质学报, 77 (4): 577-582. 徐纪人, 赵志新, 2004. 苏鲁造山带区域地壳山根结构特征. 岩石学报, 20 (1): 149-156. 许志琴, 2004. 中国大陆科学钻探工程的科学目标及初步成果. 岩石学报, 20 (1): 1-8. 赵志新, 徐纪人, 杨文采, 等, 2004. 中国大陆科学钻探孔区反射地震剖面的数值模拟与分析. 岩石学报, 20 (1): 139-148. -









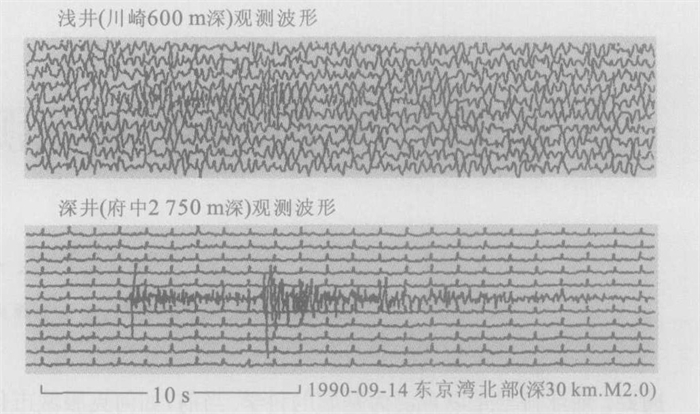
 下载:
下载: