Iron Biomineralization and Biometallogenesis in the Ancient-Wood Buried Zone from Coast of Zhoushan Island, Zhejiang Province
-
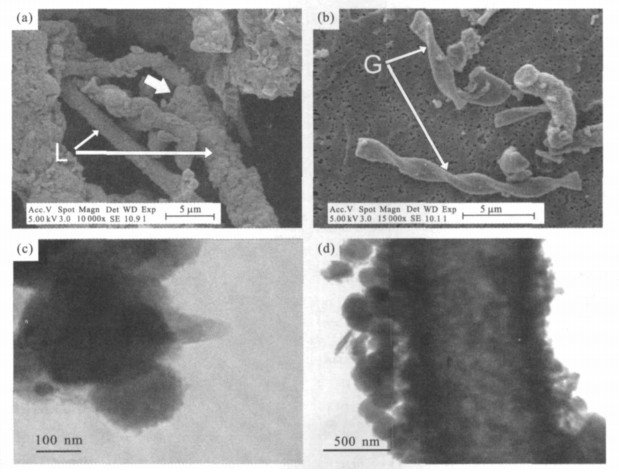
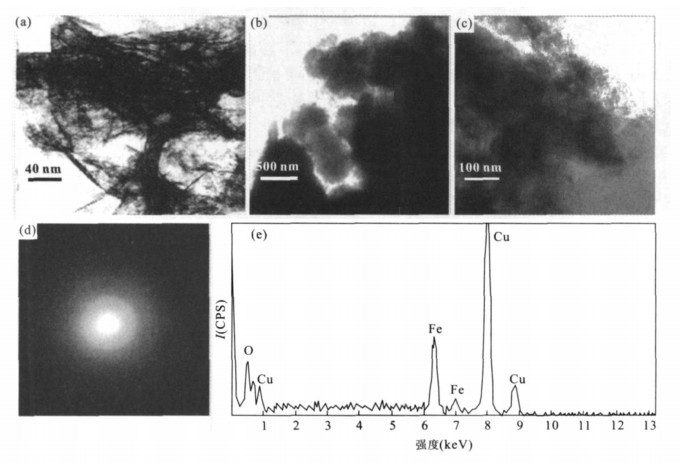
摘要: 以浙江舟山海岸带铁矿石为研究对象, 通过对铁矿石及其周围环境背景样品的形态学显微观察、矿物学及地球化学分析, 结果显示渗漏水沉淀铁泥中存在大量形貌与Leptothrix ochracea和Gallionella ferruginea中性铁氧化菌极为相似的微生物鞘, 该微生物可促进Fe2+的氧化和Fe3+的快速沉淀, 并且细胞最终被完全矿化后将永久保存起来.与此相对应的是: 在铁矿石内部存在大量的似球形和丝杆状的针铁矿, 并且还保留了死亡的铁细菌外鞘, 这些特征揭示该铁矿石与微生物历史活动密切相关.将现代渗漏水铁泥中铁细菌的矿化作用和铁矿石中保留的微生物活动记录相对比, 为该环境下的铁矿石生物成矿作用及其成因机制提供了良好的佐证.铁矿石的形成与古木堆积密切相关, 古木埋藏腐烂过程产生的腐植酸加剧了基岩及其周围土壤中的铁淋滤进入到潮间带, 从而为铁矿石形成提供充足的铁来源.该研究有助于更好理解和认识地史时期腐植质及微生物在铁矿床形成中的作用.Abstract: In the present study, we describe the formation of iron ores collected in the intertidal zone of the Zhoushan Island in Zhejiang Province in the East China Sea, where ancient-wood layers were buried.Morphological, mineralogical and geochemical analyses were performed on the iron ores and the surrounding geological material.The results show that the iron ores are not only composed of spherical and fibre-like aggregates of goethite, but also contain the dead bacterial sheaths, which present morphological characteristics reminiscent of bacterial activity.Similar present-day biomineralization characteristics were also observed in an iron seepage system near the studied intertidal zone.The presence of Leptothrix-like sheaths and Gallionella-like stalks in the present-day environment promoted the oxidization of Fe2+ to Fe3+ and the rapid precipitation of biogenic iron oxides around the bacteria.The role of bacteria in mineral formation in the seepage area is believed to represent an analogue mechanism for the formation of the iron ores.It is hypothesized that the degradation of the ancient wood provided humic substances which accelerated the leaching process of iron from the surrounding bedrock and soils, and then created local biogeochemical conditions which led to the biomineralization of the iron ores.The present findings help elucidate the role of bacteria and humic substances in the formation of iron ores in the history time.
-
Key words:
- ancient woods buried /
- seepage water /
- iron ores /
- iron-oxidizing bacteria /
- biomineralization
-
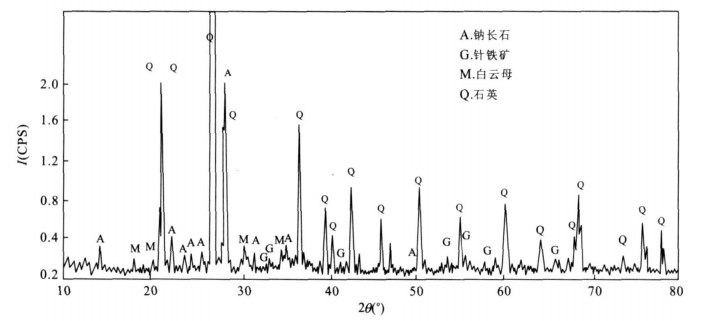
表 1 铁矿石及其相关环境样品化学组成(%)
Table 1. The chemical composition of iron ore and the surrounding geological material (%)

表 2 采样点水体物理化学组成
Table 2. The physical and chemical composition of water for sampling sites

-
Akai, J., Akai, K., Ito, M., et al., 1999. Biologically induced iron ore at Gunmairon mine, Japan. Am. Mineral. , 84 (1-2): 171-182. doi: 10.2138/am-1999-1-219 Allwood, A. C., Walter, M. R., Kamber, B. S., et al., 2006. Stromatolite reef fromthe Early Archaean era of Australia. Nature, 441: 714-718. doi: 10.1038/nature04764 Beard, B. L., Johnson, C. M., Cox, L., et al., 1999. Iron isotope biosignatures. Science, 285 (5435): 1889-1892. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5435.1889 Brown, D. A., Sherriff, B. L., Sawicki, J. A., et al., 1999. Precipitation of iron minerals by a natural microbial consortium. Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 63 (15): 2163-2169. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00188-X Chan, C. S., De Stasio, G., Welch, S. A., et al., 2004. Microbial polysaccharides template assembly of nanocrystalfibers. Science, 303 (5664): 1656-1658. doi: 10.1126/science.1092098 Che, Y., Sun, Z. Y., Chen, J. Z., 2000. Microbial mineralizations of ironin modern sedimentation environments. Geological Journal of China Universities, 6 (2): 278-281 (in Chinese with English abstract). Croal, L. R., Johnson, C. M., Beard, B. L., et al., 2004. Iron isotope fractionation by Fe (Ⅱ) -oxidizing photoautotrophic bacteria. Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 68: 1227-1242. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.09.011 Dai, Y. D., Song, H. M., Shen, J. Y., 2003. Fossil bacteria in Xuanlong iron ore deposits of Hebei Province. Science in China (Series D), 33 (8): 751-759 (in Chinese). Edwards, K. J., Bach, W., McCollom, T. M., et al., 2004. Neutrophilic iron oxidizing bacteria in the ocean: Their habitats, diversity, and roles in mineral deposition, rock alteration, and biomass production in the deep-sea. Geomicrobiology Journal, 21 (6): 393-404. doi: 10.1080/01490450490485863 Ehrlich, H. L., 2002. Geomicrobiology of iron. In: Ehrlich, H. L., ed., Geomicrobiology. Marcel Dekker, Inc, New York, 345-428. Emerson, D., Weiss, J. V., 2004. Bacterial iron oxidation in circumneutral freshwater habitats: Findings from the field and laboratory. Geomicrobiology Journal, 21 (6): 405-414. doi: 10.1080/01490450490485881 Ferris, F. G., 2005. Biogeochemical properties of bacteriogenic iron oxides. Geomicrobiology Journal, 22 (3-4): 79-85. doi: 10.1080/01490450590945861 Ferris, F. G., Fyfe, W. S., Beveridge, T. J., 1988. Metallic ion binding by Bacillus Subtilis: Implications for the fossilization of microorganisms. Geology, 16 (2): 149-152. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0149:MIBBBS>2.3.CO;2 Ferris, F. G., Konhauser, K. O., Lyven, B., et al., 1999. Accumulation of metals by bacteriogenic iron oxides in a subterranean environment. Geomicrobiology Journal, 16 (2): 181-192. doi: 10.1080/014904599270677 Fortin, D., Langley, S., 2005. Formation and occurrence of biogenic iron-rich minerals. Earth-Science Reviews, 72 (1-2): 1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2005.03.002 Hallberg, R., Ferris, F. G., 2004. Biomineralization by Gallionella. Geomicrobiology Journal, 21 (5): 325-330. doi: 10.1080/01490450490454001 Hu, M. A., 2000. Metallogenic significance of organisms and organic matters in low temperature mineralization system. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 25 (4): 375-379 (in Chinese with English abstract). James, R. E., Ferris, F. G., 2004. Evidence for microbial-mediated iron oxidation at a neutrophilic groundwater spring. Chem. Geol. , 212 (3-4): 301-311. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.08.020 Kennedy, C. B., Martinez, R. E., Scott, S. D., et al., 2003a. Surface chemistry and reactivity of bacteriogenic iron oxides from Axial Volcano, Juan de Fuca Ridge, Northeast Pacific Ocean. Geobiology, 1: 59-66. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-4669.2003.00001.x Kennedy, C. B., Scott, S. D., Ferris, F. G., 2003b. Characterization of bacteriogenic iron oxide deposits from Axial Volcano, Juan de Fuca Ridge, Northeast Pacific Ocean. Geomicrobiology Journal, 20 (3): 199-214. doi: 10.1080/01490450303873 Kennedy, C. B., Scott, S. D., Ferris, F. G., 2004. Hydrothermal phase stabilization of2-line ferrihydrite by bacteria. Chem. Geol. , 212: 269-277. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.08.017 Konhauser, K. O., Hamade, T., Raiswell, R., et al., 2002. Could bacteria have formed the Precambrian banded iron formations? Geology, 30 (12): 1079-1082. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1079:CBHFTP>2.0.CO;2 Lizasa, K., Kawasaki, K., Maeda, K., et al., 1998. Hydrothermal sulfide-bearing Fe-Si oxyhydroxide deposits from the Coriohs Thoughs, Vanuatu backarc, southwestern Pacific. Marine Geology, 145: 1-21. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(97)00112-6 Martinez, R. E., Smith, D. S., Pedersen, K., et al., 2003. Surface chemical heterogeneity of bacteriogenic iron oxides from a subterranean environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 37 (24): 5671-5677. doi: 10.1021/es0342603 McKay, D. S., Gibson, E. K. J., Thomas-Keprta, K. L., et al., 1996. Search for past life on Mars: Possible relic biogenic activity in Martian meteorite ALH84001. Science, 273 (5277): 924-930. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5277.924 Peng, X. T., Zhou, H. Y., Wu, Z. J., et al., 2007. Biomineralization phototrophic microbes in silica-enriched hot springs in South China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52 (3): 367-379. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0042-2 Pierson, B. K., Parenteau, M. N., Griffin, B. M., 1999. Phototrophs in high-iron-concentration microbial mats: Physiological ecology of phototrophs in an iron-depositing hot spring. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. , 65 (12): 5474-5483. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.12.5474-5483.1999 Roden, E. E., Sobolev, D., Glazer, B., et al., 2004. Potential for microscale bacterial Fe redox cycling at the aerobicanaerobic interface. Geomicrobiol. J. , 21: 379-391. doi: 10.1080/01490450490485872 Sun, L. G., Xie, Z. Q., Shen, X. S., et al., 2000. Ancientwood layer at Guanyin Bayin Zhujiajian, Zhejiang Province being discovered and its significance. Ziran Zazhi, 22 (6): 354-358 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tazaki, K., 2000. Formation of bandediron-manganese structures by natural microbial communities. Clays and Clay Minerals, 48 (5): 511-520. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.2000.0480503 Xie, S. C., Yin, H. F., Xie, X. N., et al., 2007. On the geobiological evaluation of hydrocarbon source rocks. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 32 (6): 727-740 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yin, H. F., Xie, S. C., Zhou, X. G., 1994. Advances and trends on the study of microbial metallogenesis. Earth Science Frontiers, 1 (3-4): 148-156 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Z., Zhang, B. G., Hu, J., et al., 2006. A preliminary discussion on the bio-metallogenesis of Tl deposits in the low-temperature minerogenetic province of southwestern China. Science in China (Series D), 36 (10): 894-904 (in Chinese). 车遥, 孙振亚, 陈敬中, 2000. 现代沉积环境中铁的微生物矿化作用. 高校地质学报, 6 (2): 278-281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2000.02.027 戴永定, 宋海明, 沈继英, 2003. 河北宣龙铁矿化石细菌. 中国科学(D辑), 33 (8): 751-759. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200308005.htm 胡明安, 2000. 低温成矿系列中生物有机质的矿床学意义. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 25 (4): 375-379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200004007.htm 彭晓彤, 周怀阳, 吴自军, 等, 2007. 热泉微生物的矿化作用和机制: 来自华南富硅热泉光合自养微生物席中的证据. 科学通报, 52 (1): 89-99. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.01.016 孙立广, 谢周清, 沈显生, 等, 2000. 浙江朱家尖观音湾古木层的发现及其意义. 自然杂志, 22 (6): 354-358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2000.06.011 谢树成, 殷鸿福, 解习农, 等, 2007. 地球生物学方法与海相优质烃源岩形成过程的正演和评价. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 32 (6): 727-740. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200706002.htm 殷鸿福, 谢树成, 周修高, 1994. 微生物成矿作用研究的新进展和新动向. 地学前缘, 1 (3-4): 148-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY404.004.htm 张忠, 张宝贵, 胡静, 等, 2006. 中国西南低温成矿域铊矿床生物成矿初步研究. 中国科学(D辑), 36 (10): 894-904. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200610002.htm -










 下载:
下载: