Characteristics of Soil Salinity Profiles and Relationship between Salinity and Soil Particle Composition in Yanqi Basin of Xinjiang, China
-
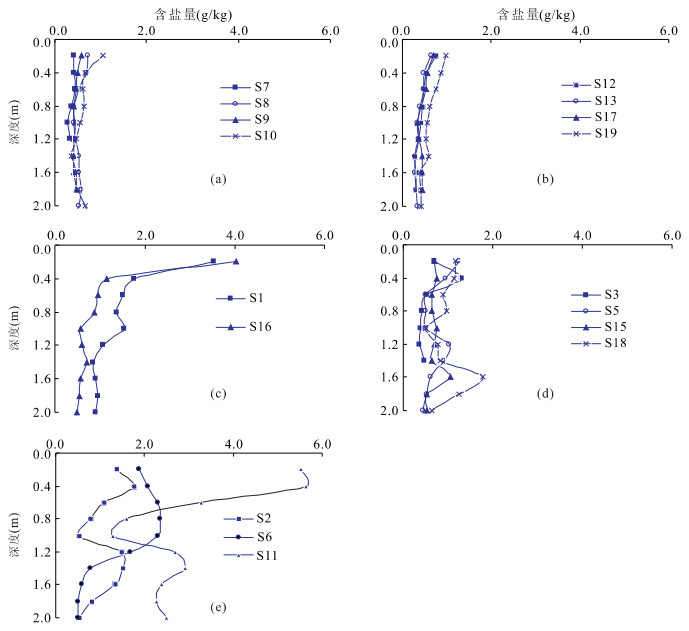
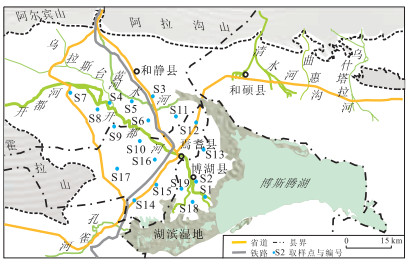
摘要: 为查明焉耆盆地土壤盐分剖面特征及其影响因素, 进行土壤样本含盐量及颗粒组成测试, 利用Spearman等级相关分析两者关系.结果表明: 土壤盐分剖面分为3种类型——均布型、表聚型和振荡型, 均布型剖面含盐量最低且分布均匀, 表聚型剖面盐分表聚特征最明显(表聚系数4.20), 振荡型剖面含盐量高且变异程度大(变异系数82.4%); 土样类型中粉质壤土最多(占70.8%), 颗粒组成中粉粒平均含量最高(57.1%); 均布型剖面盐分与粘粒含量相关程度最高(相关系数0.560), 为极显著正相关; 振荡型剖面盐分与砂粒含量相关程度最高(相关系数-0.639), 呈极显著负相关; 表聚型剖面盐分与颗粒组成无明显关系.结合各类剖面分布区域可知, 在砂粒含量与盐分含量较低的非盐渍化地带, 土壤盐分分布主要受粘粒含量影响; 砂粒含量与盐分含量较高的盐渍化地带, 土壤盐分分布主要受砂粒含量影响.
-
关键词:
- 土壤盐分剖面 /
- 颗粒组成 /
- Spearman等级相关 /
- 焉耆盆地
Abstract: To understand the distribution pattern of salinity in soil profiles and factors influenced, soil samples were collected from irrigated areas of Yanqi basin and tested for total salinity and soil particle composition, and then the relationship between salinity and particle composition was studied using the Spearman rank correlation analysis. Based on the analysis, soil salinity profiles in the area are classified into three types: equably distribution profiles (EDP), surface accumulation profiles (SAP) and oscillation profiles (OP). EDP are featured with the lowest and equal distribution of salinity; SAP are characterized by the most obvious soil surface salinity accumulation (accumulation coefficient is 4.20), OP by the highest salinity and the largest coefficient of variation (82.4%). Silty loam is the most common textural class (70.8% in all soil samples) and silt is the highest particle-size fraction of soil samples (mean content is 57.1%). In EDP the correlation coefficient of salinity with clay content (0.560) is the highest, and the positive correlation of them is extremely significant. In OP the correlation coefficient of salinity with sand content (-0.639) is the highest, and the negative correlation of them is extremely significant. In SAP the salinity is not obviously correlated with soil particle composition. Considering the existing areas of EDP and OP, it is found that soil salinity is mainly affected by the clay content in the non-salinization area with relatively lower salinity and sand content, and whereas it is mainly affected by the sand content in the salinization area with relatively higher salinity and sand content. -
表 1 焉耆盆地不同类型盐分剖面土样点分布状况
Table 1. Spatial distribution of soil sampling holes for different kinds of profiles in Yanqi basin

表 2 焉耆盆地不同类型盐分剖面土壤样本盐分统计值
Table 2. Statistical characteristics of soil samples for different kinds of profiles in Yanqi basin

表 3 焉耆盆地土壤类型分布
Table 3. Distribution of soil textural classes in Yanqi basin

表 4 焉耆盆地土样颗粒组成百分含量统计特征值
Table 4. Statistical characteristics of sand, silt and clay fractions in Yanqi basin

表 5 各类盐分剖面土样颗粒组成百分含量平均值
Table 5. Average content of sand, silt and clay in soil samples for different kinds of profiles

表 6 各类盐分剖面土壤含盐量与土壤粒度组分含量间关系(Spearman系数)
Table 6. Relationship between soil salinity and content of sand, silt and clay for different kinds of profiles

-
Chen, M., Yang, S. B., 1992. Formation and improvement of saltaffected soil in Yanqi basin, Xinjiang, China. Territory & Natural Resources Study, (3): 46-49 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jacobsen, O. H., Leij, F. J., Van Genuchten, M. Th., 1992. Lysimeter study of an ion transport through layered coarse-textured soil profiles. Soil Sci. , 154 (3): 196-205. doi: 10.1097/00010694-199209000-00003 Jin, M. G., Liu, Y. F., Dong, X. G., et al., 2002. Water saving irrigation and control of agricultural pollution: Acase study in Yanqi basin, Xinjiang, China. Geological Science and Technology Information, 21 (1): 51-54 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, H. T., Brunner, P., Li, W. P., et al., 2006a. Application of ASTER image to soil salinization assessment. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 33 (5): 75-79 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200605018.htm Li, H. T., Li, X. M., Philip, B., et al., 2006b. Application of electromagnetic method to soil salinization assessment. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 33 (1): 95-98 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Y. Z., Hu, K. L., 2004. Simulationfor the effect of claylayer on the transport of soil water and solutes under evaporation. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 28 (3): 105-106 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB200404000.htm Liu, F. H., Wang, Z. Q., 1993. Salt-water dynamics in soilprofiles of different texture under groundwater evaporation condition. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 30 (2): 173-181 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, S. Y., Wei, Y. Q., 1988. Study on the factors affecting salinization of soils in the Majia river valley. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 25 (2): 110-118 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB198802001.htm Liu, Y. F., Jin, M. G., Jin, Y. C., 2004a. Principal componentanalysis of soil salinizationin Yanqi basin. Agricultural Researchin the Arid Area, 24 (1): 165-171 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, Y. F., Jin, M. G., Jin, Y. C., et al., 2004b. Characteristics analysis of soil salinization in Yanqi basin of Xinjiang Wei Autonomous region. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 24 (1): 49-52 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-STTB200401015.htm Ministry of Water Ressources of P. R. C., 1999. Standard of geotechnical test methods (GB/T50123-1999). China Planning Press, Beijing, 315 (in Chinese). Porro, I., Wierenga, P. J., Hills, R. G., 1993. Solute transport through large unform and layered soil columns. Water Resour. Res. , 29 (4): 1321-1330. doi: 10.1029/92WR02528 Shi, W. J., Shen, B., Wang, Z. R., 2005. Reviews on transport of water and salt inlayered soil. Agricultural Research in the Arid Area, 23 (5): 250-254 (in Chinese with English abstract). USDA-SCS, 1975. Soil taxonomy: Abasic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys. U. S. Gov. Print. Office, Washington, D. C., 436. Wen, Y. H., 2002. Influence of texture and bulk density on the transport's law of Clin soils. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 9 (1): 73-75 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, M. D., Ernest, K. Y., 2002. Water balance duringevaporation and drainage in cover soils under differentwater table conditions. Advances in Environmental Research, 6: 505-521. doi: 10.1016/S1093-0191(01)00077-6 Zhao, F. Y., 1997. Permutation and combination of soil layers and differences in crop production. Chinese Journal of Soil Scienc, 28 (3): 105-106 (in Chinese with English abstract). 陈模, 杨绍斌, 1992. 焉耆盆地盐渍化土壤的形成与改良. 国土与自然资源研究, (3): 46-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTZY199203009.htm 靳孟贵, 刘延锋, 董新光, 等, 2002. 节水灌溉与农业面源污染控制研究—以新疆焉耆盆地为例. 地质科技情报, 21 (1): 51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2002.01.012 李海涛, Brunner, P., 李文鹏, 等, 2006a. ASTER遥感影像数据在土壤盐渍化评价中的应用. 水文地质工程地质, 33 (5): 75-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200605018.htm 李海涛, 李小梅, Philip, B., 等, 2006b. 电磁感应方法在土壤盐渍化评价中的应用研究. 水文地质工程地质, 33 (1): 95-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200601026.htm 李韵珠, 胡克林, 2004. 蒸发条件下粘土层对土壤水和溶质运移影响的模拟. 土壤学报, 41 (4): 493-502. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2004.04.001 刘福汉, 王遵亲, 1993. 潜水蒸发条件下不同质地剖面的土壤水运动. 土壤学报, 30 (2): 173-181. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.1993.02.003 刘思义, 魏由庆, 1988. 马颊河流域影响土壤盐渍化的几个因素的研究. 土壤学报, 25 (2): 110-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB198802001.htm 刘延锋, 靳孟贵, 金英春, 2004a. 焉耆盆地土壤盐渍化状况的主成分分析. 干旱地区农业研究, 24 (1): 165-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDQ200401036.htm 刘延锋, 靳孟贵, 金英春, 等, 2004b. 新疆焉耆盆地土壤盐渍化特征分析. 水土保持通报, 24 (1): 49-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB200401015.htm 史文娟, 沈冰, 汪志荣, 2005. 层状土壤水盐动态研究与分析. 干旱地区农业研究, 23 (5): 250-254. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7601.2005.05.049 温以华, 2002. 不同质地和容重对Cl-在土壤中运移规律的影响. 水土保持研究, 9 (1): 73-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2002.01.018 赵风岩, 1997. 土层排列组合与作物产量差异. 土壤通报, 28 (3): 105-106. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.1997.03.004 中华人民共和国水利部, 1999. 土工试验方法标准(GB/T50123-1999). 北京: 中国计划出版社, 315. -









 下载:
下载: