Formational Mechanisms of Homogeneous Fluid and Boiling Fluid: Evidences from Synthetic Fluid Inclusions
-
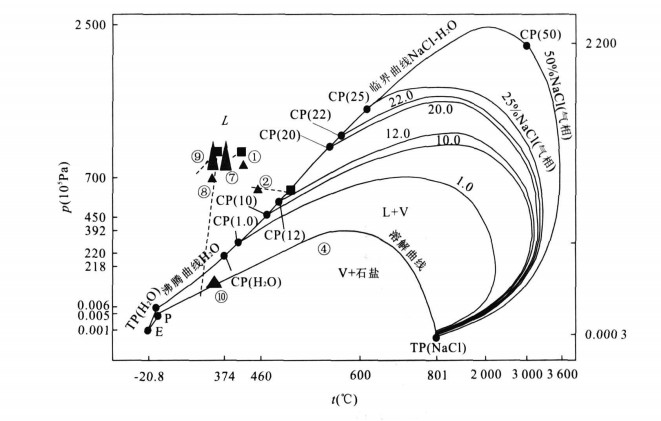
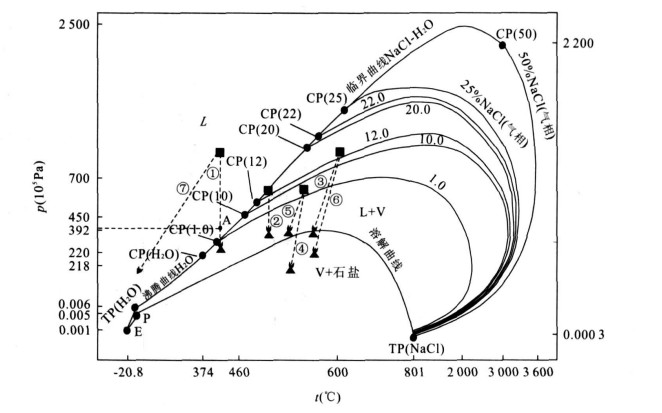
摘要: 为详细了解流体的形成机制, 对系统的流体包裹体合成实验进行研究.研究表明, 在合成流体包裹体实验中, 广泛存在流体的均一化和沸腾作用; 流体的均匀与否, 与流体p-t轨迹在TP (H2O)-CP(H2O)-CP(NaCl-H2O) 曲线的部位有密切的关系.p-t轨迹在曲线上部的流体为均匀流体, 反之则为沸腾流体.但也有例外, 如在溶解曲线上被主矿物捕获的流体.这为本次研究一定条件下流体的形成机制、探讨成矿作用提供了理论依据.Abstract: Synthetic fluid inclusions were studied in order to discuss formational mechanisms of homogeneous fluid and boiling fluid in detail.The results of experiments of fluid inclusion synthesizing show frequent occurrences of homogeneous fluid and boiling fluid, was closely in relation to the position of its p-t locus in TP (H2O)-CP(H2O)-CP(NaCl-H2O) curve of p-t phase diagram of NaCl-H2O system determined whether the fluid was homogeneous.If it was at the upper zone of TP (H2O)-CP(H2O)-CP(NaCl-H2O) curve, then the fluid was homogeneous, otherwise, the fluid was boiling.But the fluid trapped on the solution curve of NaCl in water was an exception, for example No.10 experiment.This was very beneficial for us to study on the formation mechanism of fluid and mineralization in the ore deposit.
-
Key words:
- synthetic fluid inclusion /
- homogeneous fluid /
- boiling fluid /
- formational mechanism
-
表 1 合成流体包裹体实验条件
Table 1. The experimental conditions of synthetic fluid inclusions

表 2 合成流体包裹体的测试结果
Table 2. The measurements of synthetic fluid inclusions

-
Bakker, R. J., Diamond, L. W., 2000. Determination of thecomposition and molar volume of H2O-CO2 fluid inclu-sions by microthermometry. Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 64 (10): 1753-1764. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00334-8 Bischoff, J. L., 1991. Densities of liquids and vapors in boil-ing NaCl-H2O solutions: A PVTX summary from300℃to500℃. Amer. J. Sci., 291: 309-338. doi: 10.2475/ajs.291.4.309 Chen, J. Y., Zheng, H. F., Zeng, Y. S., 2002. Raman spectro-scopic study on hydrogen bond of water molecules insynthetic inclusions under high temperature. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 21 (3): 166-170 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, Z. L., Xu, J. Y., 2007. Dip of the oil (gas) -water inter-faces in anticline-hydrodynamic oil (gas) pools. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 32 (1): 89-92 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hoffmann, M. M., Conradi, S., 1997. Are there hydrogenbonds in supercritical water. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119 (16): 3811-3817. doi: 10.1021/ja964331g Ikushi ma, Y., Hatakeda, K., Soito, N., 1998. An in-situ Ra-man spectroscopy studies of subcritical and supercriticalwater: The peculiarity of hydrogen bonding near thecritical point. J. Chem. Phys., 108 (14): 5855-5860. doi: 10.1063/1.475996 Kendrich, M. A., Burgess, R., Pattrich, R. A. D., et al., 2001. Fluid inclusion noble gas and halogen evidence onthe origin of Cu-porphyry mineralizingfluids. Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 65 (16): 2651-2668. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00618-4 Liu, B., Shen, K., 1995. Formulae for calculating oxygen fugacities of fluid inclusions and their applications. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 15 (3): 291-302 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, B., Shen, K., 1999. Thermodynamics of fluidinclusion. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, 119-140 (in Chinese). Philippot, P., 1996. The chemistry of high-pressure fluids (1 to3 GPa): Natural observations vs. experi mental constraints. Earth Sciences Frontiers, 3 (3): 39-48 (in Chinese with English abstract). Roedder, E., Kopp, O. C., 1975. Acheck on the validity of thepressure correction in inclusion geothermometry, using hydrothermally grown quartz. Fortschr. Mineral., 52: 431. Schmidt, C., Rosso, K. M., Bodnar, R. J., 1995. Syntheticfluid inclusions: XIII. Experimental determination of thePVT properties in the system H2O+40% NaCl+5mol% CO2 at elevated temperature and pressure. Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 59: 3953-3959. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00258-2 Spycher, N. F., Reed, M. H., 1989. Evolution of a broad lands-type epithermal orefluid along alternative P-Tpaths: Impli-cations for the transport and deposition of base, precious, and volatile metals. Econ. Geol., 84: 328-359. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.84.2.328 Sterner, S. M., Bodnar, R. J., 1984. Synthetic fluid inclusionsin natural quartz: I. Compositional types synthesized andapplications to experi mental geochemistry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 48: 2659-2668. Xiao, X. J., Gu, L. X., Ni, P., et al., 2004. Esti mation of gas-escaping amount during ore-formation originated fromfluid boiling at massive sulfide deposits, Tongling re-gion. Uranium Geology, 20 (4): 91-98 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, W. R., Zhang, W. H., 1996. Character of fault proper-ty and combination of fluid inclusions. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 21 (3): 285-290 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, D. H., 1997. Some new advances in ore-forming fluidgeochemistry on boiling and mixing of fluids during theprocesses of hydrothermal deposits. Advances in Earth Science, 12 (6): 546-552 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, W. H., Chen, Z. Y., 1993. Geology of fluid inclusion. China University of Geosciences Press, Wuhan, 108-112 (in Chinese). Zhang, Y. G., Frantz, J. D., 1989. Experimental determination of the compositional limits of immiscibility in thesystem CaCl2-H2O-CO2at high temperatures and pres-sures using synthetic fluid inclusions. Chemical Geology, 74: 289-308. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(89)90039-9 Zhang, Z. L., Huang, Z. L., Rao, B., et al., 2005. Concentration mechanism of ore-forming fluid in Huize lead-zincdeposits, Yunnan Province. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 30 (4): 443-450 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zheng, Y. Y., Gao, S. B., Zhang, D. Q., et al., 2006. Ore-forming fluid controlling mineralization in Qulongsuper-large porphyry copper deposit, Tibet. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 31 (3): 349-354 (in Chinese with English abstract). 陈晋阳, 郑海飞, 曾贻善, 2002. 高温下合成包裹体中流体水分子氢键的拉曼光谱分析. 岩矿测试, 21 (3): 166-170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2002.03.002 陈振林, 许浚远, 2007. 背斜-水动力复合油(气) 藏油(气) 水界面产状. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 32 (1): 89-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200701012.htm 刘斌, 沈昆, 1995. 流体包裹体的氧逸度计算公式及其应用. 矿物学报, 15 (3): 291-302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1995.03.009 刘斌, 沈昆, 1999. 流体包裹体热力学. 北京: 地质出版社, 119-140. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1012365217.htm Philippot, P., 1996. 高压流体(1-3GPa) 的化学组成: 自然观察与实验对比. 地学前缘, 3 (3): 39-48. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1996.03.004 肖新建, 顾连兴, 倪培, 等, 2004. 铜陵地区金属硫化物矿床沸腾流体成矿过程中气体逸失量的估算. 铀矿地质, 20 (2): 91-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200402004.htm 杨巍然, 张文淮, 1996. 断裂性质与流体包裹体组合特征. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 21 (3): 285-290. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX603.009.htm 张德会, 1997. 流体的沸腾和混合在热液成矿中的意义. 地球科学进展, 12 (6): 546-552. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ706.006.htm 张文淮, 陈紫英, 1993. 流体包裹体地质学. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 108-112. 张振亮, 黄智龙, 饶冰, 等, 2005. 会泽铅锌矿床成矿流体浓缩机制探讨. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 30 (4): 443-450. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200504008.htm 郑有业, 高顺宝, 张大权, 等, 2006. 西藏驱龙超大型斑岩铜矿床成矿流体对成矿的控制. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 31 (3): 349-354. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200603009.htm -









 下载:
下载: