Mesozoic Zonal Lithosphere beneath the Southern Margin of the North China: Significance for Continental Formation and Evolution
-
摘要: 大陆岩石圈根的形成与破坏是当前固体地球科学的重大研究课题之一.对独具时空特色的华北东部地块南缘信阳中生代火山岩中一系列包括下地壳镁铁质-长英质的麻粒岩、榴辉岩、变辉长岩、辉石岩和上地幔橄榄岩等岩石包体进行了系统的定深、定年研究, 建立了华北中生代(~160Ma) 多块体结合部位的组成和年龄呈带状结构的岩石圈几何模型, 并在此基础上分析了形成的动力学过程.在华北南缘地表出露最老~2.85Ga的岩石之下的30km处(上部下地壳), 由年龄为3.6~3.4Ga的长英质麻粒岩和辉石岩组成; 更深处30~40km位置, 则由具古元古代年龄(2.0~1.8Ga) 的镁铁质-长英质麻粒岩和变辉长岩构成, 其形成过程与华北东部地块与西部地块的碰撞有关, 记录着全球性的哥伦比亚超大陆汇聚事件.Hf同位素数据显示在这次重要事件里, 既有新生地幔物质加入, 也有古老地壳(3.8~3.0Ga) 组分的再熔融作用.在来自下地壳更深处的榴辉岩(40~45km) 和上地幔橄榄岩(> 45km), 它们的主要年龄分别是古生代(440~260Ma) 和早中生代(228~219Ma), 记录着在显生宙不同时期扬子与华北碰撞的动力学过程.Abstract: The formation and destruction of the continental root is one of the most important going topics on the solid earth sciences.A series of deep-seated xenoliths, including mafic to felsic granulite, eclogite, metagabbro, pyroxenite and peridotite, from the Xinyang area with unique temporal and spatial meaning, at southern margin of the North China, were used to dating in ages and properties.The geometrical model of the zonal lithosphere structure in age and composition were suggested for the conjoint position of multi-blocks in Mesozoic (~160Ma).Basing on the zonal lithosphere, the authors also discussed the dynamic processes for its formation.The exposed rocks up to ca.2.85Ga old are underlain by felsic granulites and rare pyroxenites with zircon ages of 3.6-3.4Ga (to ca.30km depth).Deeper (ca.30-45km) parts of the lower crust consist of high-pressure mafic to felsic granulite and meta-gabbro, which give Paleoproterozoic (2.0-1.8Ga) zircon ages.Our data show the significance of underplating and vertical crustal growth in the Paleoproterozoic, which was related to the amalgamation of the eastern and western block of this craton and a global (Columbia) supercontinent assembly.Hf-isotope data indicate that both juvenile material and remelting of older (3.8-3.0Ga) crustal rocks were involved in this important event.Paleozoic (440-260Ma) and Early Mesozoic (228-219Ma) zircons are also found in xenoliths from the deeper part of the lower crust and the uppermost mantle (i.e., eclogite and peridotite).They are interpreted as reflecting geodynamic processes related to the continental collision between this craton and the Yangtze craton, respectively.The xenoliths from Xinyang diatremes thus record the growth and modification of the old (Paleo-Mesoarchean?) continental lithosphere by magma underplating during several tectonic events: assembly of the southern and northern parts of the Eastern Block in Neoarchean time, collision of the western and eastern blocks along the Trans-China orogen in the Paleoproterozoic, and subduction and collision of the Yangtze craton with the North China craton in early Paleozoic and Triassic times, respectively.
-
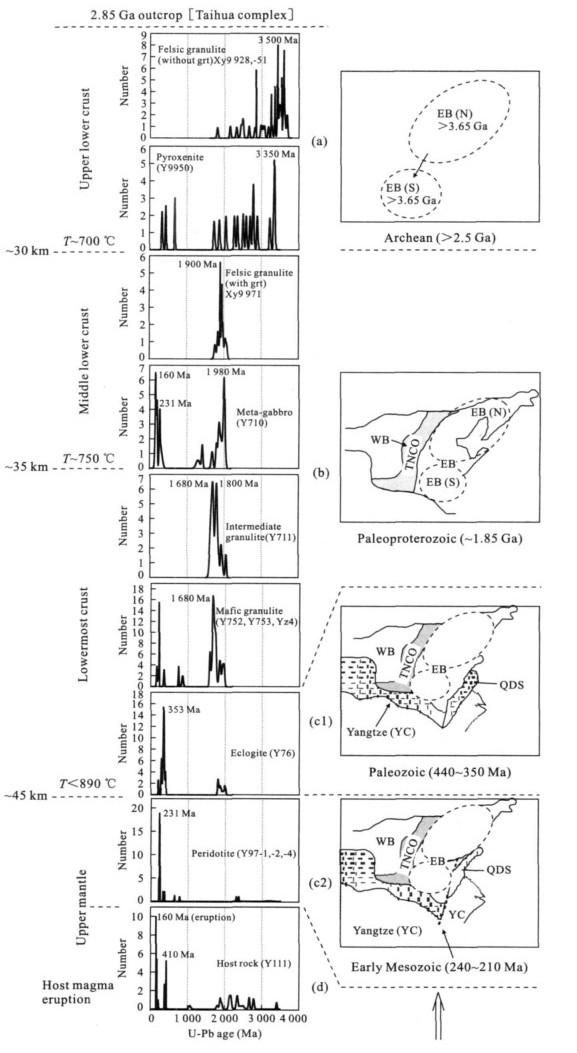
图 1 信阳中生代火山岩形成年龄及捕虏晶锆石其所揭示的岩石圈热事件
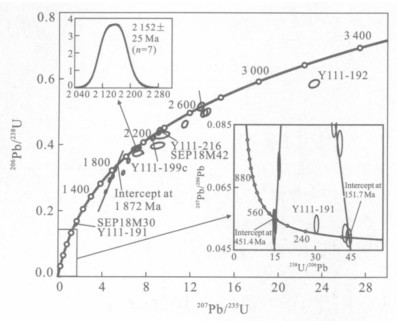
部分原始数据引自Zheng et al. (2008b); 最小年龄(协和的下交点,151.7 Ma)代表信阳火山岩的喷发年龄; 其他年龄包括: 208 Ma(1个颗粒的协和年龄); 451 Ma(8个颗粒的协和下交点); 1000 Ma(2个颗粒的协和年龄); 1 872 Ma(4个颗粒的协和上交点); 2152士25 Ma(7个协和点平均); 2 355 Ma(1个协和点); 2416 Ma(2个协和点); 2 670 Ma(1协和点)和~3404 Ma(1个近谐和点), 这些年龄基本上都可以在相应的岩石包体(Zheng et al.,2004a, 2008b)中找到对应记录
Fig. 1. Eruption age of the Xinyang igneous rocks and the lithos-pheric thermal events rllcted by zircon xenocrysts
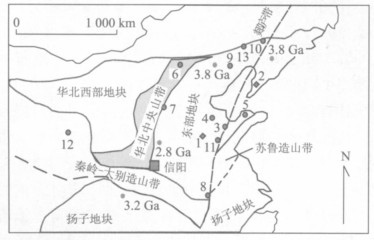
图 2 多块体结合部早中生代火山岩(信阳)及华北东部相关岩石包体出露点
图中年龄数据(Ga)代表出露的古老岩石; 其他1~13代表其他主要的包体出露点: 古生代金伯利岩: 1.山东蒙阴; 2.辽宁复县; 新生代玄武岩: 3~5.山东山旺、无棣,栖霞; 6.河北汉诺坝; 7.河南鹤壁; 8.安徽女山: 9.河北平泉; 10.辽宁阜新; 11.山东方城; 早中生代闪长岩: 12.甘肃礼县; 晚中生代玄武岩: 13.内蒙古咯喇沁旗
Fig. 2. Major tectonice units, ages of some outcropping Ar-chean rocks and xenolith positions in the North China Craton
图 3 华北南缘岩石圈带状结构及所记录的动力学过程(Zheng et al., 2008b)
Fig. 3. Cartoon showing the continental collision and accretion events recorded in the deep lithosphere
-
Condie, K. C., 2000. Episodic continental growth models: Af-ferthoughts and extensions. Tectonophysics, 322: 153-162. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00061-5 Deng, J. F., Mo, X. X., Zhao, H. L., et al., 2004. A newmodel for the dynamics evolution of Chinese lithosphere continental roots-plume tectonics. Earth Science Re-view, 65: 223-275. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2003.08.001 Deng, J. F., Zhao, H. L., Mo, X. X., et al., 1996. Continentalroots-plume tectonics of China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Fan, W. M., Menzies, M. A., 1994. Sr and Nd isotopic com-position of the ultramafic xenoliths fromeastern China: Inferences about the structure of the subcontinental lithosphere mantle and the origin of basaltic magmas. Geotectonicaet Metallogenia, 18: 39-50. Gao, S., Rudnick, R. L., Carlson, R. W., et al., 2002. Re-Osevidence for replacement of ancient mantle lithospherebeneath the North China craton. Earth. Planet. Sci. Lett., 198: 307-322. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00489-2 Griffin, W. L., Zhang, A., O'Reilly, S. Y., et al., 1998. Phanerozoic evolution of the lithosphere beneath theSino-Korean craton. In: Flower, M., Chung, S. L., Lo, C. H., et al., eds., Mantle dynamics and plate interac-tions in East Asia. American Geophysical Union, Wash-ington D. C., 27: 107-126. Guan, H., Sun, M., Wilde, S. A., et al., 2002. SHRI MPU-Pb zircon geochronology of the Fuping complex: Implications for formation and assembly of the NorthChina craton. Precambrian Research, 113: 1-18. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(01)00197-8 Jahn, B. M., 1998. Geochemical andisotopic characteristics ofUHP eclogites and ultramafic rocks of the Dabie oro-gen: Implications for continental subduction and colli-sional tectonics. In: Hacker, B. R., Liou, J. G., eds., When continental collide: Geodynamics and geochemis-try of Ultrahigh-Pressure rocks. Kluwer Academic Pub-lishers, Netherlands, 203-239. Kröner, A., Compston, W., Zhang, G., et al., 1988. Age andtectonic setting of Late Archean greenstone-gneiss ter-rain in Henan Province, China, as revealed by single-grain zircon dating. Geology, 16: 211-215. Li, S. G., Xiao, T. L., Liou, D. L., et al., 1993. Collision ofthe North China and Yangtze blocks and formation ofcoesite-bearing eclogites: Timing and processes. Chem. Geol., 109: 89-111. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(93)90063-O Liou, J. G., Hacker, B. R., Zhang, R. Y., 2000. Into the for-bidden zone. Science, 287: 1215-1216. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5456.1215 Liu, D. Y., Nut man, A. P., Compston, W., et al., 1992. Remnants of3800Ma crust in Chinese part of the Sino-Korean craton. Geology, 20: 339-342. Liu, Y. S., Gao, S., Jin, S. Y., et al., 2001. Geochemistry oflower crustal xenoliths from Neogene Hannuoba basalt, North China craton: Implications for petrogenesis andlower crustal composition. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 65 (15): 2589-2604. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00609-3 Menzies, M. A., Fan, W. M., Zhang, M., 1993. Paleozoic andCenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of & 120km of Ar-chaean lithosphere, Sino-Korean craton, China. Geol. Soc. Spec. Pub., 71-81. Pearson, D. G., 1999. The age of continental roots. Lithos, 48: 171-194. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00026-2 Rudnick, R. L., 1995. Making continental crust. Nature, 378: 571-578. doi: 10.1038/378571a0 Shao, J. A., Han, Q. J., Li, H. M., 2000. Discover of theEarly Mesozoic granulitic xenoliths in North China cra-ton. Science in China (Ser. D), 30 (Suppl. ): 149-153 (in Chinese). Shen, Q. H., Xu, H. F., Zhang, Z. Q., et al., 1992. Precam-brian granulite in China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, 192 (in Chinese). Song, B., Nut man, A. P., Liu, D. Y., et al, 1996.3800to2500Ma crustal evolutionin the Anshan area of Liaon-ing Province, northeastern China. Precambrian Res., 78: 79-94. doi: 10.1016/0301-9268(95)00070-4 Wei, C. J., Wu, Y. X., Ni, Y. Y., et al., 1999. Character andimplication of eclogite from the Tongbai area, HenanProvince. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44: 1882-1885 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1999-44-17-1882 Wilde, S. A., Zhou, X. H., Nechin, A. A., et al., 2003. Meso-zoic crust-mantle interaction beneath the North Chinacraton: Aconsequence of the dispersal of Gondwanalandand accretion of Asia. Geology, 31: 817-820. Wu, F. Y., Yang, J. H., Liu, X. M., et al., 2005.3. 8Ga zir-con Hf isotope and the dating of the early crust of theNorth China craton. Chin. Sci. Bull., 50: 1996-2003. doi: 10.1360/csb2005-50-18-1996 Xu, W. L., Zheng, C. Q., Wang, D. Y., 1999. Discover andimplication of the upper mantle and lower crust xeno-liths in basalts fromthe western Liaoning Province. Ge-ological Review, 45 (Suppl. ) 444-449 (in Chinese withEnglish abstract). Xu, X. S., O'Reilly, S. Y., Griffin, W. L., et al., 1998. Thenature of the Cenozoic lithosphere at Nushan, easternChina. In: Flower, M., Chung, S. L., Lo, C. H., eds., Mantle dynamics and plate interactions in East Asia. Geodynamics Series, Amer. Geophys. Union, Washing-ton, D. C., 27: 167-196. Xu, Y. G., 2001. Thermo-tectonic destruction of the Archeanlithospheric keel beneath the Sino-Korean craton inChina: Evidence, timing and mechanism. Phys. Chem. Earth (A), 26: 747-757. Xu, Y. G., 2002. Evidence for crustal components in themantle and constraints on crustal recycling mecha-nisms: Pyroxenite xenoliths from Hannuoba, NorthChina. Chemical Geology, 182: 301-322. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00300-X Yan, J., Chen, J. F., Xie, Z., et al., 2003. Mantle xenoliths inK1basalts fromeastern Shandong Province: Constrainton the time of the lithospheric thinning beneath theeastern China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48: 1570-1574 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2003-48-14-1570 Yang, J. S., Xu, Z. Q., Pei, X. Z., et al., 2002. Discovery ofdiamond in North Qinling: Evidence for a giant UHPMbelt across Central China and recognition of Paleozoicand Mesozoic dual deep subduction between North Chi-na and Yangtze plates. Acta Geologica Sinica, 4: 169-178. Ye, K., Cong, B. L., Ye, D. N., 2000. The possible subduc-tion of continental materials to depth greater than200km. Nature, 407: 334-336. Yu, J. H., Xu, X. S., O'Reilly, S. Y., et al., 2003. Granulitexenoliths from Cenozoic basalts in SE China provide ge-ochemical fingerprints to distinguish lower crust terra-nes from the North and South China tectonic blocks. Lithos, 67: 77-102. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00253-0 Zhai, M. G., Bian, A. G., Zhao, T. P., 2000. The amalgama-tion of the supercontinent of North China craton at theend of the Neoarchean and its break up during lateProterozoic and Mesoproterozoic. Sci. in China (Ser. D), 43: 219-232. doi: 10.1007/BF02911947 Zhai, M. G., Fan, Q. C., 2002. Mesozoic lower crustal re-placement beneath the North China craton: Non-orogen-ic crust-mantle interaction. Acra Petrologica Sinica, 18: 1-18 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhai, M. G., Guo, J. H., Liu, W. J., 2005. Neoarchean to Pal-eoproterozoic continental evolution and tectonic historyof the North China craton: A review. J. Asian EarthSci., 24: 547-561. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.01.018 Zhang, H. F., Sun, M., Zhou, X. H., et al., 2002. Mesozoiclithosphere destruction beneaththe North China craton: Evidence from major, trace-element and Sr-Nd-Pb iso-tope studies of Fangcheng basalts. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 144: 241-253. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0395-0 Zhang, H. F., Sun, M., Zhou, X. H., et al., 2003. Secularevolution of thelithosphere beneaththe eastern North Chi-na craton: Evidence from Mesozoic basalts and high-Mg an-desites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 15: 4373-4387. Zhang, H. F., Ying, J. F., Xu, P., 2004. Mantle olivine xeno-crysts in the Mesozoic basalts from the North China: Revelation for the lithospheric mantle replacement. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49: 784-789 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-8-784 Zhang, H. F., Zheng, J. P., 2003. Character and petrogenetic processes of the Mesozoic basalts from the NorthChina: Take Fuxin of Liaoning Province as an example. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48: 603-609 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2003-48-6-603 Zhao, G. C., Cawood, P. A., Wilde, S. A., et al., 2000. Meta-morphismof basement rocks in the Central Zone of theNorth China craton: Implications for Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution. Precambrian Research, 103: 55-88. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00076-0 Zhao, G. C., Sun, M., Wilde, S. A., et al., 2003. Assembly, accretion and breakup of the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic Columbia supercontinent: Records in the North Chinacraton. Gondwana Res., 6: 417-434. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70996-5 Zhao, G. C., Sun, M., Wilde, S. A., et al., 2004. APaleo-Me-soproterozoic supercontinent: Assembly, growth andbreakup. Earth Sci. Rev., 67: 91-123. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.02.003 Zhao, G. C., Sun, M., Wilde, S. A., et al., 2005. Late Arche-an to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China cra-ton: Key issues revisited. Precam. Res., 136: 177-202. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002 Zhao, G. C., Wilde, S. A., Cawood, P. A., et al., 1999. Ther-mal evolution of two textural types of mafic granulitesin the North China craton: Evidence for both mantleplume and collisional tectonics. Geol. Mag., 136 (3): 223-240. doi: 10.1017/S001675689900254X Zhao, T. P., Zhou, M. F., Zhai, M. G., et al., 2002. Paleo-proterozoic rifting-related volcanism of the Xiong'erGroup, North China craton: Implications for the breakupof Columbia. Int. Geol. Rev., 44: 336-351. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.44.4.336 Zheng, J. P., 1999. Mesozoic-Cenozoic mantle replacementand lithospheric thinning beneath the eastern China. China University of Geosciences Press, Wuhan, 126 (inChinese). Zheng, J. P., Griffin, W. L., O'Reilly, S. Y., et al., 2004a. 3.6Ga lower crust in Central China: New evidence onthe assembly of the North China craton. Geology, 32: 229-232. Zheng, J. P., Griffin, W. L., O'Reilly, S. Y., et al., 2004b. U-Pb and Hf-Isotope analysis of zircons in mafic xeno-liths from Fuxian kimberlites: Evolution of the lowercrust beneath the North China craton. Contrib. Miner-al. Petrol., 148: 79-103. doi: 10.1007/s00410-004-0587-x Zheng, J. P., Lu, F. X., Yu, C. M., 2004c. An in situ zirconHf isotope, U-Pb age and trace element study of bandedgranulite xenoliths from Hannuoba basalt: Tracking theearly evolution of the lower crust in the North Chinacraton. Chin. Sci. Bull., 49: 277-285. Zheng, J. P., Griffin, W. L., O'Reilly, S. Y., et al., 2006a. Arefractory mantle protolith in younger continentalcrust, East-Central China: Age and composition of zir-conin the Sulu UHP peridotite. Geology, 34: 705-708. Zheng, J. P., Griffin, W. L., O'Reilly, S. Y., et al., 2006b. Zircons in peridotite xenoliths record the Triassic Yan-gtze-North China continental collision. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 247: 130-142. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.05.011 Zheng, J. P., Griffin, W. L., O'Reilly, S. Y., et al., 2007. Mechanismand timing of lithospheric modification andreplacement beneath the eastern North China craton: Peridotitic xenoliths fromthe100Ma Fuxin basalts anda regional synthesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 71: 5203-5225. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.07.028 Zheng, J. P., Lu, F. X., 1999. Heterogeneity of the Paleozoic lithospheric mantle beneaththe North China craton: Ev-idences fromthe peridotitic xenoliths in Jiao-Liao kim-berlites. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15 (1): 65-74 (inChinese with English abstract). Zheng, J. P., O'Reilly, S. Y., Griffin, W. L., et al., 1998. Nature and evolution of Cenozoic lithospheric mantlebeneath Shandong Peninsula, North China platform. Int. Geol. Rev., 40: 471-499. doi: 10.1080/00206819809465220 Zheng, J. P., O'Reilly, S. Y., Griffin, W. L., et al., 2001. Relics of refractory mantle beneath the eastern NorthChina block: Significance for lithosphere evolution. Lithos, 57: 43-66. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00073-6 Zheng, J. P., Sun, M., Griffin, W. L., et al., 2008a. Age andgeochemistry of contrasting peridotite types in the Da-bie UHP belt, eastern China: Petrogenetic and geody-namic implications. Chemical Geology, 247: 282-304. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.023 Zheng, J. P., Sun, M., Griffin, W. L., et al., 2008b. Age andgeochemistry of contrasting peridotite types in the Da-bie UHP belt, eastern China: Petrogenetic and geody-namic implications. Chem. Geol., 247: 282-304. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.023 Zheng, J. P., Sun, M., Lu, F. X., et al., 2003. Mesozoic lowercrustal xenoliths and their significance in lithospheric evolution beneaththe Sino-Korean craton. Tectonophys-ics, 361: 37-60. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(02)00537-1 Zheng, J. P., Sun, M., Zhou, M. F., et al., 2005. Trace ele-mental and PGE geochemical constraints of Mesozoicand Cenozoic peridotitic xenoliths onlithospheric evolu-tion of the North China craton. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 69: 3401-3418. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.03.020 Zhou, X. H., Sun, M., Zhang, G. H., et al., 2002. Continen-tal crust and lithospheric mantle interaction beneathNorth China: Isotopic evidence from granulite xenolithsin Hannuoba, Sino-Korean craton. Lithos, 62: 111-124. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00110-X Zhou, X. M., Yu, J. H., Xu, X. S., et al., 1992. Discover andim-plication of granulitic xenoliths fromthe Nushan basalts. Chinese Science Bulletin, 13: 1198-1201 (in Chinese). 邓晋福, 赵海玲, 莫宣学, 等, 1996. 中国大陆根-柱构造: 大陆动力学的钥匙. 北京: 地质出版社. 邵济安, 韩庆军, 李惠民, 2000. 华北克拉通早中生代麻粒岩捕虏体的发现. 中国科学(D辑), 30 (增刊): 149-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2000S1018.htm 沈其韩, 徐惠芬, 张宗清, 等, 1992. 中国前寒武纪麻粒岩. 北京: 地质出版社, 198. 魏春景, 吴玉新, 倪云燕, 等, 1999. 河南桐柏地区榴辉岩特征及其地质意义. 科学通报, 44: 1882-1885. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.17.020 许文良, 郑常青, 王东艳, 1999. 辽西中生代粗面玄武岩中地幔和下地壳捕虏体的发现及意义. 地质论评, 45 (增刊): 444-449. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP1999S1061.htm 闫峻, 陈江峰, 谢智, 等, 2003. 鲁东晚白垩世玄武岩中的幔源捕虏体: 对中国东部岩石圈减薄时间制约的新证据. 科学通报, 48 (14): 1570-1574. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.14.018 翟明国, 樊棋诚, 2002. 华北克拉通中生代下地壳置换: 非造山过程的壳幔交换. 岩石学报, 18: 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200201000.htm 张宏福, 英基丰, 徐平, 2004. 华北中生代玄武岩中地幔橄榄石捕虏晶: 对岩石圈地幔置换过程的启示. 科学通报, 49: 784-789. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.08.015 张宏福, 郑建平, 2003. 华北中生代玄武岩的地球化学特征与岩石成因: 以辽宁阜新为例. 科学通报, 48: 603-609. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.06.016 郑建平, 1999. 中国东部地幔置换作用与中新生代岩石圈减薄. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 126. 郑建平, 路凤香, 1999. 胶辽半岛金伯利岩中地幔捕虏体岩石学特征: 古生代岩石圈地幔不均一性. 岩石学报, 15 (1): 65-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB901.006.htm 周新民, 于津海, 徐夕生, 等, 1992. 女山玄武岩中的麻粒岩捕虏体的发现和意义. 科学通报, 13: 1198-1201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199213013.htm -









 下载:
下载: