Water Contents in Peridotite Xenoliths from Subei Basin, Eastern China
-
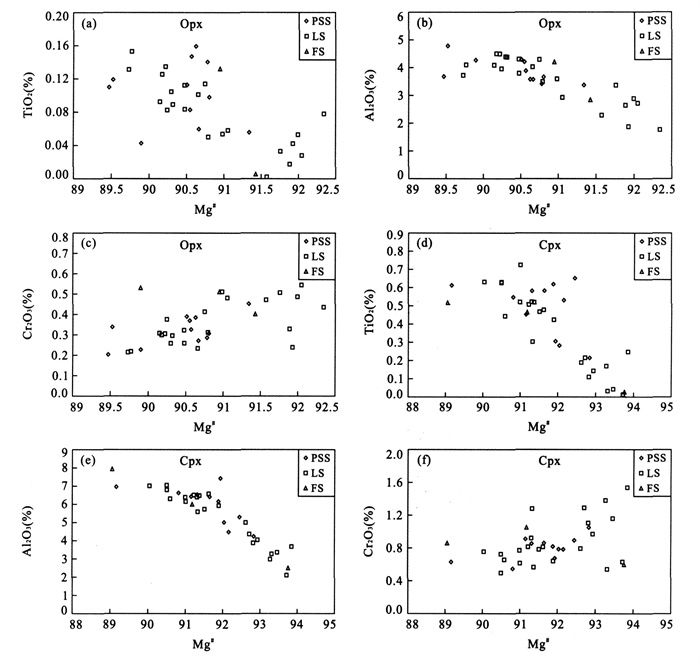
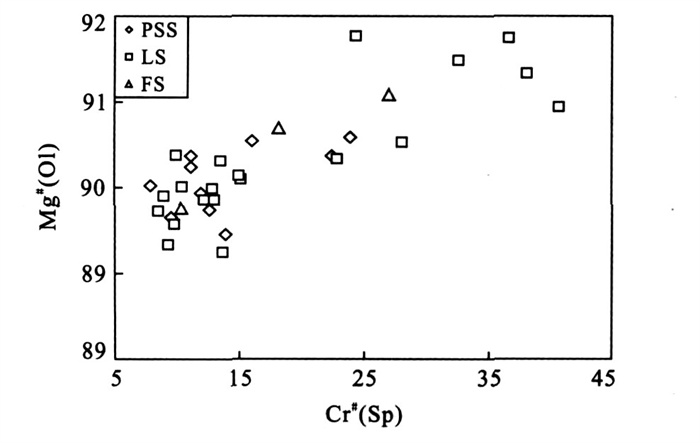
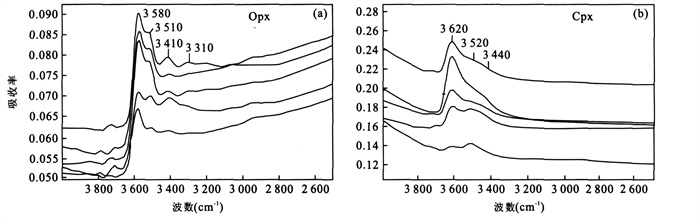
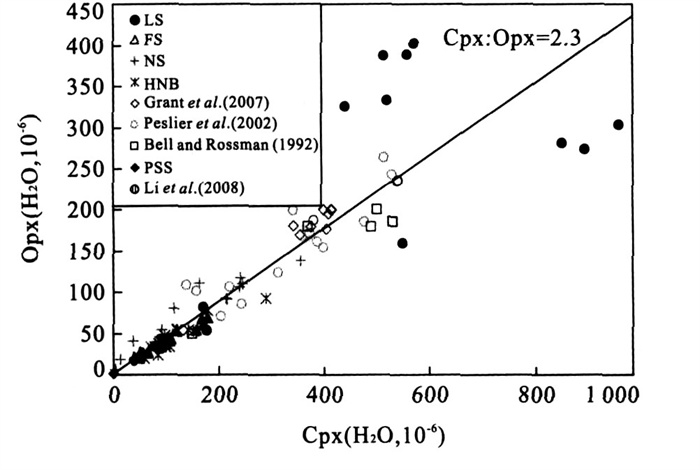
摘要: 对来自苏北盆地盘石山、练山和方山地区新生代玄武岩中的50个橄榄岩包体矿物进行了系统的微区傅立叶变换红外光谱(Micro-FTIR) 分析.结果显示, 所有的单斜辉石和斜方辉石颗粒都含有以OH形式存在的结构水, 盘石山、练山和方山橄榄岩的单斜辉石水含量分别为64×10-6~183×10-6、37×10-6~102×10-6和41×10-6~177×10-6; 斜方辉石水含量分别为16×10-6~61×10-6、13×10-6~45×10-6和21×10-6~74×10-6.几乎所有的橄榄石都没有检测到明显的OH吸收峰, 暗示其水含量低于仪器的检出限(~2×10-6).根据矿物水含量(假设橄榄石的水含量为2×10-6) 和它们的体积分数计算的盘石山、练山和方山橄榄岩全岩的水含量分别为12×10-6~52×10-6、7×10-6~25×10-6和13×10-6~44×10-6.结合已经发表的橄榄岩包体的数据来看, 在岩石圈地幔的物理化学条件下, 单斜辉石与斜方辉石之间水的平衡分配系数大约为2.2±0.4.结合已经发表的安徽女山和河北汉诺坝的橄榄岩数据, 对比世界上其他地区橄榄岩的数据来看, 华北的岩石圈地幔具有低的水含量: 华北橄榄岩的单斜辉石水含量多 < 200×10-6, 而世界上其他地区(包括南非克拉通、美国新墨西哥地区、美国Colorado高原、美国盆岭省地区、墨西哥南部、法国中央地体以及加拿大WestKettle地区) 橄榄岩的单斜辉石水含量多 > 200×10-6; 华北的斜方辉石水含量多 < 100×10-6, 而世界上其他地区多 > 100×10-6; 华北的橄榄岩全岩水含量多 < 50×10-6, 而世界上其他地区多 > 100×10-6.华北岩石圈地幔的低水含量有可能是由于上升软流圈的热侵蚀造成的, 因此目前的华北岩石圈地幔可能大部分都是中生代岩石圈减薄后的残余, 而不是新生地幔.Abstract: Nominally anhydrous minerals, clinopyroxene (Cpx), orthopyroxene (Opx) and olivine (Ol), in peridotite xenoliths hosted by Cenozoic basalts from Panshishan, Lianshan and Fangshan of the Subei basin, eastern China have been investigated by Micro-FTIR for their water contents.All Cpx and Opx grains contain a certain amount of "water" as hydroxyl defect in the crystal structure.Water contents (expressed as H2O wt.) of Cpx and Opx from Panshishan, Lianshan and Fangshan peridotites are 64×10-6-183×10-6, 37×10-6-102×10-6, 41×10-6-177×10-6 and 16×10-6-61×10-6, 13×10-6-45×10-6, 21×10-6-74×10-6, respectively.OH peaks can not be detected for almost all olivine grains, indicating that the water content is below the detection limit (~2×10-6) of FTIR.The whole rock water contents calculated according to the water contents of minerals and their volume proportions are 12×10-6-52×10-6, 7×10-6-25×10-6 and 13×10-6-44×10-6 for Panshishan, Lianshan and Fangshan respectively.Based on the new results from the Subei basin and the data reported in literatures, the partition coefficient of H2O between Cpx and Opx in the continental lithosphere mantle is estimated to be 2.2±0.4.Peridotite xenoliths from Nüshan, Hannuoba and the Subei basin of the North China block have much lower water contents than those from other localities of the world (South Africa craton, New Mexico, Colorado plateau and basin and Range province of USA, South Mexico, French Central Massif and West Kettle of Canada).This difference is probably induced by the thermal erosion of asthenosphere during Mesozoic-Cenozoic period in the North China block.If this explanation is correct, the present lithosphere mantle in the North China block is mainly the relict after the Mesozoic lithospheric thinning, rather than the new accreted mantle.
-
Key words:
- micro-FTIR /
- water /
- peridotite xenoliths /
- Subei basin /
- North China craton
-
图 5 橄榄岩中两种辉石水含量的相关性图解
NS.女山; HNB.汉诺坝, 引自Yang et al. (2008); Bell and Rossman (1992a).样品来自Bell and Rossman (1992b); Peslier et al. (1992).样品来自Peslier et al (2002); Grant (2007).样品来自Grant et al. (2007); Li (2008).样品来自Li et al. (2008)
Fig. 5. Diagram showing the correcation of water contents of clinopyroxene and orthopyroxene from peridotite xenoliths
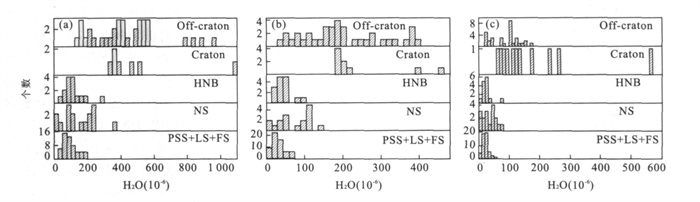
图 6 华北橄榄岩水含量与世界其他各地橄榄岩的对比
Off-craton和Craton的数据引自Bell and Rossman (1992); Peslier et al. (2002); Grant et al. (2007)和Li et al. (2008); 3个图依次为单斜辉石、斜方辉石和全岩水含量的对比
Fig. 6. Comparison of the water content of peridotites from the North China block with other localities in the world
表 1 苏北盆地橄榄岩包体中橄榄石的主要元素组成
Table 1. Olivine compositions of peridotite xenoliths from the Subei basin

表 2 苏北盆地橄榄岩包体中单斜辉石的主要元素组成
Table 2. Clinoproxene compositions of peridotite xenoliths from the Subei basin

表 3 苏北盆地橄榄岩包体中斜方辉石的主要元素组成
Table 3. Orthopyroxene compositions of peridotite xenoliths from the Subei basin

表 4 苏北盆地橄榄岩包体中尖晶石的主要元素组成
Table 4. Spinel compositions of peridotite xenoliths from the Subei basin

表 5 苏北盆地橄榄岩包体矿物和全岩的水含量
Table 5. Water content of minerals and whole-rocks of peridotite xenoliths from the Subei basin

-
Aubaud, C., Withers, M., Hirschmann, M., et al., 2007. In-tercalibration of FTIRand SI MSfor hydrogen measure-ments in glasses and nominally anhydrous minerals. Am. Mineral., 92 (5-6): 811-828. doi: 10.2138/am.2007.2248 Bell, D. R., Ihinger, P. D., Rossman, G. R., 1995. Quantita-tive analysis of hydroxyl in garnet and pyroxene. Am. Mineral., 80: 465-474. doi: 10.2138/am-1995-5-607 Bell, D. R., Rossman, G. R., 1992a. Water in the earth'smantle: The role of nominally anhydrous minerals. Sci-ence, 255 (5050): 1391-1397. doi: 10.1126/science.255.5050.1391 Bell, D. R., Rossman, G. R., 1992b. The distribution of hydroxylin garnets fromthe subcontinental mantle of southern Afri-ca. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 111: 161-178. doi: 10.1007/BF00348949 Bell, D. R., Rossman, G. R., Moore, R. O., 2004. Abundanceand partitioning of OH in a high-presssure magmaticsystem: Megacrysts from the Monastery kimberlite, South Africa. J. Petrol., 45 (8): 1539-1564. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egh015 Brey, G. P., Kohler, T., 1990. Geothermobarometry in fourphase lherzolitesⅡ: Newthermo-barometers and practical assessment of existing thermobarmeters. J. Petrol., 31: 1353-1378. doi: 10.1093/petrology/31.6.1353 Carpenter, W. S., Mackwell, S., Dyar, D., 2000. Hydrogen indiopside: Diffusion profiles. Am. Mineral., 85: 480-487. doi: 10.2138/am-2000-0409 Chen, D. G., Li, B. X., Zhi, X. C., 1994. Geneitic geochemis-try of mantle-derived peridotite xenolith from Panshis-han, Jiangsu. Geochimica, 23 (1): 13-24 (in Chinesewith English abstract). Chen, D. G., Peng, Z. C., 1988. K-Ar ages and Pb, Sr isotopic characteristics of some Cenozoic volcanic rocks fromAnhui and Jiangsu provinces, China. Acta PetrologicaSinica, 4 (2): 3-12 (in Chinese with English abstract). Demouchy, S., Jacobsen, S. D., Gaillard, F., et al., 2006. Rapid magma ascent recorded by water diffusion pro-files in mantle olivine fromearth's mantle. Geology, 34 (6): 429-432. doi: 10.1130/G22386.1 Fan, Q. C., Hooper, P. R., 1989. The mineral chemistry ofultramafic xenoliths of eastern China—implications forupper mantle composition and paleogeotherms. J. Pet-rol., 30 (5): 1117-1158. doi: 10.1093/petrology/30.5.1117 Fan, W. M., Zhang, H. F., Baker, J., et al., 2000. On and offthe North China craton: Whereis the Archaean keel? J. Petrol., 41 (3): 933-950. http://petrology.oxfordjournals.org/content/41/7/933.full Gao, S., Rudnick, R. L., Carlson, R. W., et al., 2002. Re-Osevidence for replacement of ancient mantle lithospherebeneath the North China craton. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 198: 307-322. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00489-2 Grant, K., Ingrin, J., Lorland, J. P., et al., 2007. Water par-tition between mantle minerals from peridotite xeno-liths. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 154 (1): 25-34. Guo, L. H., Lin, X. Y., Xie, M. Z., et al., 1998. Water in theperidotite xenoliths from Hannuoba, Hebei. Acta Geo-logical Sinica, 72 (2): 138-143 (in Chinese with Eng-lish abstract). Hauri, E. H., Gaetani, G. A., Green, T. H., 2006. Partitio-ning of water during melting of the earth's upper man-tle at H2O-undersaturated conditions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 248 (3-4): 715-734. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.06.014 Hercule, S., Ingrin, J., 1999. Hydrogen in diopside: Diffu-sion, kinetics of extraction-incorporation, and solubility. Am. Mineral., 84 (10): 1577-1587. doi: 10.2138/am-1999-1011 Ingrin, J., Skogby, H., 2000. Hydrogen in nominally anhy-drous upper-mantle minerals: Concentration levels andimplications. Eur. J. Mineral., 12: 543-570. doi: 10.1127/ejm/12/3/0543 Keppler, H., Bolfan-Casanova, N., 2006. Thermodynamics ofwater solubility and partitioning. In: Keppler, H., Smyth, J. R., eds., Water in nominally anhydrous Min-erals. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington D. C., 193-230. Kohlstedt, D. L., Mackwell, S. J., 1998. Diffusion of hydro-gen andintrinsic point defects in olivine. Zeitschrift forPhysikalische Chemie, 307: 147-162. Kovacs, I., Hermann, J., O'Neill, H. S. C., et al., 2008. Quantitative absorbance spectroscopy with unpolarizedlight: Part Ⅱ. Experimental evaluation and developmentof a protocol for quantitative analysis of mineral IRspectra. Am. Mineral., 93 (5-6): 765-778. doi: 10.2138/am.2008.2656 Li, Z. X., 1994. Collision between the North and South Chinablocks: A crust-detachment model for suturing in theregion east of the Tanlu fault. Geology, 22: 739-742. Li, Z. X., Lee, C. A., Peslier, A. H., et al., 2008. Water con-tents in mantle xenoliths fromthe Colorado Plateau andvicinity: Implications for the mantle rheology and hydra-tion-induced thinning of continental lithosphere. J. Geo-phy. Res., 113, B09210, doi: 10.1029/2007JB005540. Libowitzky, E., Rossman, G. R., 1996. Principles of quanti-tative absorbance measurements in anisotropic crystals. Phy. Chem. Mineral., 23 (6): 319-327. Liu, J. H., Yan, J., 2007. Peridotitic xenoliths in the Cenozo-ic basalts fromthe Subei basin. Journal of Mineralogyand Petrology, 27 (2): 39-46 (in Chinese with Englishabstract). Meisel, T., Walker, R. J., Irving, A. J., 2001. Osmiumiso-topic compositions of mantle xenoliths: A global per-spective. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 65 (8): 1311-1323. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00566-4 Michael, P., 1995. Regionally distinctive sources of depletedMORB: Evidence from trace elements and H2O. EarthPlanet. Sci. Lett., 131 (3-4): 301-320. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(95)00023-6 Paterson, M. S., 1982. The determination of hydroxyl by in-frared-absorption in quartz, silicate-glasses and similarmaterials. Bulletine de Mineralogie, 105: 20-29. Peslier, A. H., Luhr, J. F., 2006. Hydrogen loss from oli-vines in mantle xenoliths from Simcoe (USA) andMexico: Mafic alkalic magma ascent rates and waterbudget of the sub-continental lithosphere. Earth Plan-et. Sci. Lett., 242 (3-4): 302-319. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.12.019 Peslier, A. H., Luhr, J. F., Post, J., 2002. Low water con-tents on pyroxenes from spinel-peridotite of the oxi-dized, sub-arc mantle wedge. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 201: 69-86. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00663-5 Reisberg, L., Zhi, X. C., Lorang, J. P., et al., 2005. Re-Osand S systematics of spinel peridotite xenoliths fromeast Central China: Evidence for contrasting effects ofmelt percolation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 239 (3-4): 286-308. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.09.010 Skogby, H., Bell, D. R., Rossman, G. R., 1990. Hydroxide inpyroxene: Variations in the natural environment. Am. Mineral., 75 (7-8): 764-774. Skogby, H., Rossman, G. R., 1989. OHin pyroxene: An ex-perimental study of incorporation mechanisms and sta-bility. Am. Mineral. , 74: 1059-1069. Stalder, R., Skogby, H., 2003. Hydrogen diffusion in naturaland synthetic orthopyroxene. Phy. Chem. Mineral., 30: 12-19. doi: 10.1007/s00269-002-0285-z Wu, F. Y., Walker, R. J., Yang, Y. H., et al., 2006. Thechemical-temporal evolution of lithospheric mantle un-derlying the North China craton. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 70: 5013-5034. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.07.014 Xia, Q. K., Dallai, L., Deloule, E., 2004. Oxygen and hydro-gen isotope heterogeneity of clinopyroxene megacrystsfrom Nushan volcano, SE China. Chem. Geol., 209 (1-2): 137-151. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.04.028 Xia, Q. X., Zhi, X. C., Meng, Q., et al., 2004. The trace elementand Re-Os isotopic geochemistry of mantle-derived perido-tite xenoliths from Hannuoba: Nature and age of SCLMbe-neath the area. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20 (5): 1215-1224 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, X. S., Griffin, W. L., O'Reilly, S. Y., et al., 2008. Re-Osisotopes of sulfides in mantle xenoliths from easternChina: Progressine modification of lithospheric mantle. Lithos, 102: 43-64. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.06.010 Xu, Y. G., Blusztajn, J., Ma, J. L., et al., 2008. Late Archeanto Early Proterozoic lithospheric mantle beneath thewestern North China craton: Sr-Nd-Os isotopes of peri-dotite xenoliths from Yangyan and Fansi. Lithos, 102: 25-42. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.04.005 Yang, X. Z., Xia, Q. K., Deloule, E., et al., 2008. Water inminerals of the continental lithospheric mantle and o-verlying lower crust: A comparative study of peridotiteand granulite xenoliths from the North China craton. Chem. Geol., 256 (1-2): 33-45. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.07.020 Yu, H. M., Xia, Q. K., Deloule, E., 2005. Hydrogen isotopic compositions of pyroxenes in Nushan peridotite xeno-liths, SE China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79 (3): 801-807. Zheng, J. P., Griffin, W. L., O'Reilly, S. Y., et al., 2006. Mineral chemistry of peridotites from Paleozoic, Meso-zoic and Cenozoic lithosphere: Constraints on mantle e-volution beneath eastern China. J. Petrol., 47 (1): 2233-2256. Zhi, X. C., Peng, Z. C., Chen, D. G., et al., 2001. The lon-gevity of subcontinental lithospheric mantle beneathJiangsu-Anhui region: The Os isotope model age ofmantle-derived peridotite xenoliths. Science in China (Ser. D), 44 (12): 1110-1118. doi: 10.1007/BF02906867 Zhi, X. C., Reisberg, L., Xu, X. S., 2007. Re-Os geochemis-try of mantle peridotite xenoliths from Nushan. Journalof University of Science and Technology of China, 37 (8): 945-952 (in Chinese with English abstract). 陈道公, 李彬贤, 支霞臣, 1994. 江苏盘石山幔源橄榄岩包体成因的地球化学. 地球化学, 23 (1): 13-24. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1994.01.002 陈道公, 彭子成, 1988. 皖苏若干新生代火山岩的钾氩年龄和铅锶同位素特征. 岩石学报, 4 (2): 3-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1988.02.002 郭立鹤, 林兴源, 谢漫泽, 等, 1998. 河北汉诺坝玄武岩幔源捕虏体中的水. 地质学报, 72 (2): 138-143. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1998.02.005 刘建宏, 闫峻, 2007. 苏北盆地新生代玄武岩中的地幔橄榄岩包体. 矿物岩石, 27 (2): 39-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2007.02.007 夏琼霞, 支霞臣, 孟庆, 等, 2004. 汉诺坝幔源橄榄岩包体的Re-Os同位素地球化学: ScLm的性质和形成时代. 岩石学报, 20 (5): 1215-1224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200405016.htm 支霞臣, Reisberg, L., 徐夕生, 2007. 安徽女山幔源橄榄岩捕虏体Re-Os同位素地球化学. 中国科学技术大学学报, 37 (8): 945-952. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2778.2007.08.020 -









 下载:
下载: