Geospatial Complex Structure Simulation and Analysis System of Geological Disasters Using Petri Net
-
摘要:
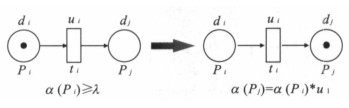
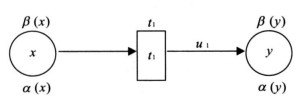
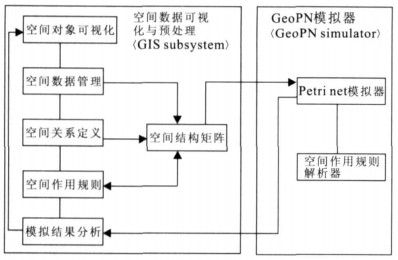
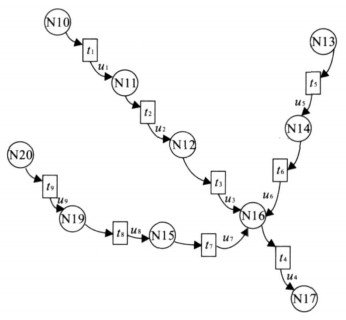
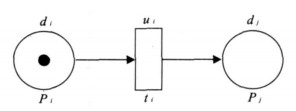
地球系统中各种空间对象在时空及功能上的直接或间接的依赖关系是研究各种复杂问题的出发点, 模拟和分析这些对象之间的直接和间接制约关系往往是认识复杂系统和进行空间决策的基础, 如在地震、洪水、火灾等突发性事件发生过程中各种应急设施和部门的相互影响和制约往往是复杂的、不协调的关系.由此产生的级联效应往往会造成意想不到的严重后果.如何提高对灾害效应的认识, 预警预报灾害的级联效应是提高灾害预防和应急反应能力的重要基础.在研究灾害事件中相关对象之间的空间复杂结构的基础上, 通过建立定量关系来表示对象之间的相互关系, 采用模糊Petri网技术模拟对象之间的级联效应.以四川汶川大地震后堰塞湖的空间复杂结构为例, 动态模拟堰塞湖的潜在级联效应, 推测出易受影响的堰塞湖, 从而为有效防治地震后的次生灾害提供一种理论与技术思路.该方法和技术同样可以用于其他地学复杂系统结构的模拟和分析.
Abstract:In the domain of earth system, temporal-spatial and functional direct or indirect interdependent relationships between geospatial objects provide the clue for the study of complex issues.The simulation and analysis of the direct and indirect dependent relationships between these geospatial objects are always the foundation to know complex systems and make geospatial decisions.For example, in some emergencies, such as earthquakes, floods, and fire disasters, the interrelated effect and dependency among particular infrastructures and departments are usually complicated and inharmonious.Then, the potential cascading effects may cause unexpected serious consequences.Therefore, how to know more about disaster effects, and forecast corresponding cascading effects becomes quite important and fundamental to increase the capability of disaster prevention and emergency response.Based on the study on geospatial complex structure among relative objects in disasters, this paper quantifies the interrelationships between these objects, and then applies fuzzy Petri net to simulate potential cascading effects between them.Finally, an example is included to illustrate geospatial complex structure of barrier lakes coming from the Wenchuan earthquake in Sichuan Province, China.The potential cascading effects among barrier lakes are dynamically simulated, and then the vulnerable barrier lakes can be found out, which provides one specific theory and technical method to efficiently prevent secondary disasters of earthquakes.In the same way, the proposed method and technique would be used to simulate and analyze other geoscientific complex system structures as well.
-
Key words:
- Petri net /
- fuzzy Petri net /
- geospatial complex structure /
- simulation system
-
表 1 关系强度矩阵
Table 1. Matrix of relationship strength

表 2 堰塞湖的风险值
Table 2. Risk values of barrier lakes

-
Chen, S. M., 2000. Fuzzy backward reasoning using fuzzy Petri nets. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics, 30 (6): 846-856. doi: 10.1109/3477.891146 Chen, S. M., 2002. Weighted fuzzy reasoning using weighted fuzzy Petri nets. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 14 (2): 386-397. doi: 10.1109/69.991723 Chen, S. M., Ke, J. S., Chang, J. F., 1990. Knowledge representation using fuzzy Petri nets. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2 (3): 311-319. doi: 10.1109/69.60794 Cheng, Q. M., 2007. A fuzzy relation analysis method implemented in GIS for modeling infrastructure interdependency. In: Lecture notes in geoinformation and cartography. Heidelberg, Springer, Berlin. Dudenhoeffer, D. D., Permann, M. R., Manic, M., 2006. CIMS: A framework for infrastructure interdependency modeling and analysis. IEEE Winter Simulation Conference. USA, IEEE, 478-485. [65] Dunn, M., Wigert, I., 2004. International CIIP handbook 2004: Aninventory and analysis of protection policies infourteen countries. Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich, 243. Levy, S., 1992. Artificial life—A report from the frontier where computers meet biology. Vintage, New York. Li, X., Rosano, F. L., 2000. Adaptive fuzzy Petri nets for dynamic knowledge representation and inference. ExpertSystems with Applications, 19 (3): 235-241. doi: 10.1016/S0957-4174(00)00036-1 Li, X., Yu, W., 2001. Object oriented fuzzy Petri net for complex knowledge system modeling. Proceeding of the IEEE international conference on control applications. September 5-7, 2001. Mexico City, Mexico. Lin, C., 2005. Stochastic Petri nets and system performance evaluation. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, 1-2 (inChinese). Murata, T., 1989. Petri nets: Properties, analysis and applications. Proc. IEEE, 77 (44): 541-580. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/24143 Rinaldi, S. M., Peerenboom, J. P., Kelly, T. K., 2001. Identifying, understanding, and analyzing critical infrastructure interdependencies. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 12 (6): 11-25. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/969131 Schneis, T. D., Collins, L., 2000. Disaster management and preparedness. Lewis Publishers, Washington, D. C., USA. Wu, Z. H., 2006. Petri nets guide. China Machine IndustryPress, Beijing, 1-2, 264-265 (in Chinese). Zadeh, L. A., 1965. Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, 8 (3): 338-353. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/afs/2009/303042/ Zurawski, R., Zhou, M. C., 1994. Petri nets and industrial applications: A tutorial. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 41 (6): 567-583. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/334574 林闯, 2005. 随机Petri网和系统性能评价. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1-2. 吴哲辉, 2006. Petri网导论. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1-2, 264-265. -









 下载:
下载: