Tectonic Styles and Kinematic Characteristics of Negative Inversion Structure in Dongying Depression
-
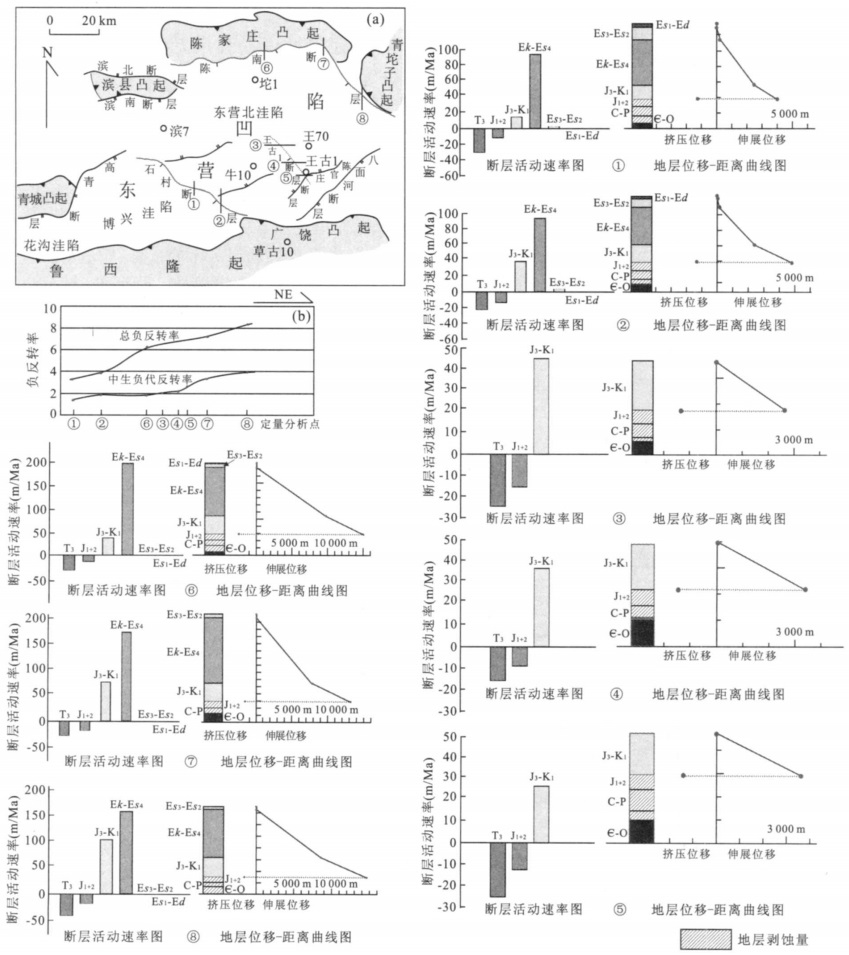
摘要: 中、新生代强烈的负反转作用是东营凹陷构造演化的一个重要特色.为了解负反转构造对东营凹陷中、新生代盆地形成过程中的意义, 以高分辨率三维地震资料解释为基础, 详细刻画了东营凹陷负反转构造几何学样式, 并综合运用计算断层活动速率和负反转率以及编制地层位移-距离曲线等方法, 对东营凹陷负反转断层运动学特征进行了系统的定量研究.结果表明, 东营凹陷J3-K1和Ek-Es4两期盆地的主体均是印支期逆冲断层发生负反转作用所致, 总的负反转率约为3.367~8.3, 其中J3-K1时期负反转率为1.388~3.904;负反转构造最终定型于Es3-Es2时期; 负反转作用在空间上呈现出SW至NE逐渐增强的演变规律.东营凹陷负反转构造的研究对于盆地内部深层油气藏的勘探具有重要的理论意义和实际应用价值.Abstract: The strong negative inversion structure in Mesozoic-Cenozoic is a prominent characteristic during the tectonic evolution of Dongying depression.In order to understand the significance of the negative inversion structure in the process of Mesozoic-Cenozoic basin formation in Dongying depression, this paper describes in detail the geometry styles of negative inversion structures in Dongying depression on the basis of the interpretation of the new high resolution 3D seismic profiles.And by utilizing the methods of calculating the fault activity velocity, negative inversion ratio, and displacement-distance curve, the authors quantitatively analyse the kinematic characteristics of the negative inversion structures in Dongying depression.The result indicates that in the Dongying depression, the extension basins developed in J3-K1 and Ek-Es4 stages were mainly controlled by the negative inversion of the thrust faults formed in Indo-Chinese epoch.The total negative inversion ratio is 3.367-8.3, and the ratio in J3-K1 stage is 1.388-3.904.The negative inversion structures accomplished ultimately in the Es3-Es2 stage.The distribution of the negative inversion ratios indicates an increase in deformational degree from SW to NE in the whole region.The research of negative inversion structures in Dongying depression has important theoretic and practical significance in the exploration of the deep hydrocarbon reservoirs.
-
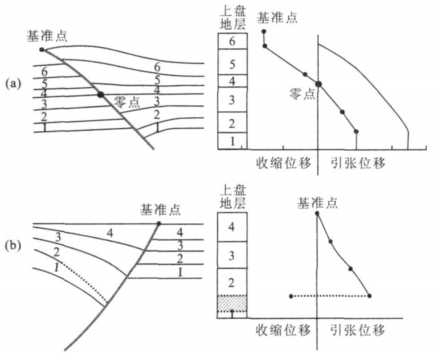
图 3 (a) 正反转断层位移-距离曲线示意图(Williams et al., 1989)和(b)负反转断层位移-距离曲线示意图
Fig. 3. Sketch of displacement-distance curve of inversion fault suggested by Williams et al. (1989) and (b) sketch of displacement distance curve of negative inversion fault
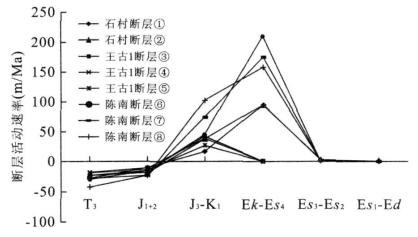
表 1 东营凹陷负反转断层负反转率统计表
Table 1. Calculation result of the negative inversion ratio in Dongying depression

-
Buchanan, P. G., McClay, K. R., 1991. Sandbox experiments of inverted listric and planar fault systems. Tectonophysics, 188 (1-2): 97-115. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(91)90317-L Chang, G. Z., Bi, C. Q., Lin, H. M., 2002. Reverse tectonic evolution, reservoir-forming system and exploration oflow buried-hill—Taking Gubei low buried-hill, Shengli oilfield as an example. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 9 (5): 19-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, F. J., Wang, X. Q., Zhang, G. Y., et al., 1992. Structure and geodynamic setting of oil and gas basins in the People's Republic of China. Geoscience, 6 (3): 317-327 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, J., Dong, D., Qiu, M. W., 1999. Negative inversion structure in the Jiyang depression andits petroleum geological significance. Geology & Experimental Petroleum, 21 (3): 201-206 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, Z. N., Chen, F. J., 1995. Inversion structures and their relationship to traps of oil and gas. Earth Science Frontiers, 2 (3-4): 96-102 (in Chinese with English abstract). Cooper, M. A., Williams, G. D., 1989. Inversion tectonics—Adiscussion. In: Copper, M. A., Williams, G. D., eds., Inversion tectonics. Geological Society, Special Publications, London, (44): 335-347. Glennie, K. W., Boegner, P. L. E., 1981. Sole pit inversiontectonics. In: Illing, L. V., Hobson, G. D., eds., Petroleum geology of the continental shelf of northwest Europe. Institute of Petroleum, London, 110-120. Hao, X. F., Zong, G. H., Li, C. H., et al., 2001. Preli minaryanalysis of the positive-reversal structure in Jiyang depression. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 8 (3): 8-10 (in Chinese). Harding, T. P., 1985. Seismic characteristics and identification of negative flower structures, positive flower structures, and positive structural inversion. AAPG Bulletin, 69: 582-600. Lamplyugh, G. W., 1920. Structure of the weald and ana-logues tracts. Quarterly Journal Geological Society, 75: LXXIII-XCT (Anniversary Address of the President). Letozey, J., 1990. Fault reactivation and structural inversion, backarc and intraplate compressive deformations—Example of the eastern Sunda shelf (Indonesia). Tectonophysics, 183 (1-4): 341-362. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(90)90425-8 Li, P. L., Zhang, S. W., Qu, S. L., et al. , 2003. Tectonic evolution and tectonic patterns of ontinental fault basin—volume1of petroleumgeology and exploration of continental fault basin. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Mitra, S., 1993. Geometry and kinematic evolution of inversion structures. AAPG Bulletin, 77 (7): 1159-1191. Mu, Z. H., Lu, T. Q., Xie, G. S., et al., 2001. Restoration of the denueed thicknesses of Permian in the southwest part of Talimu basin. Natural Gas Industry, 21 (2): 41-43 (in Chinese with English abstract). Pang, X. Q., 2003. Modeling of geologic processes. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Ren, J. Y., 2004. Tectonic significance of S6' boundary in Dongying depression, Bohai Gulf basin. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 29 (1): 69-76, 92 (in Chinese with English abstract). Song, T. G., 1997. Inversion styles in the Songliao basin (northeast China) and esti mation of the degree of inversion. Tectonophysics, 283 (1-4): 173-188. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00147-9 Su, J. B., Zhu, W. B., Lu, H. F., et al., 2009. Geometrystyles and quantification of inversion structures in the Jiyang depression, Bohai Bay basin, eastern China. Marine and Petroleun Geology, 26 (1): 25-38. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2007.08.003 Tan, M. Y., Bing, J. Y., Jin, X. X., et al., 1996. Origin analyses of both negative inversion faults and negative inversion structures in Palaeozoic Group in coastal region of North Shandong Province. OGP, 31 (6): 844-850 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, X. P., Fei, Q., Zhang, J. H., et al. , 1990. Tectonic analysis in oil exploration. China University of Geosciences press, Wuhan (in Chinese). Wei, W. B., Ye, G. F., Jin, S., et al., 2007. Three dimensional P-wave velocity structure of the crust of North China. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 32 (4): 441-452 (in Chinese with English abstract). Williams, G. D., Powell, C. M., Cooper, M. A., 1989. Geometry and kinematics of inversion tectonics. In: Cooper, M. A., Williams, G. D., eds., Inversion tectonics. Geological Society, Sepcial Publications, London, (44): 3-15. Yao, C., Jiao, G. H., Wang, T. H., et al. , 2004. The structures of oil and gas-bearing basins of China. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Ye, X. S., Wang, W. F., 2008. Plate subduction contrains on the formation of Jiyang depression. Earth Science—Journal of China Unversity of Geosciences, 33 (2): 235-242 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2008.031 Zhai, M. G., Meng, Q. R., Liu, J. M., et al., 2004. Geological features of Mesczoic tectonic regime inversionin eastern North China and implication for geodynamics. Earth Science Frontiers, 11 (3): 285-297 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, G. C., Jin, L., 1997. On inversion tectonics and structures. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 17 (4): 83-90 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zheng, D. S., Wu, Z. P., Li, W., et al., 2005. Faults and their control on the basin during the transfer stage of the Jiyang depression in the Mesozoic-Cenozoic. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79 (3): 386-394 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhu, Y. M., Qin, Y., Fan, B. H., et al., 2001. Restoration and significance of the original thickness of Triassic system in Baohai wan Bay basin. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 30 (2): 195-200 (in Chinese with English abstract). 常国贞, 毕彩芹, 林红梅, 2002. 低潜山反转构造演化、成熟体系与勘探——以胜利油区孤北低潜山为例. 断块油气田, 9 (5): 19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8907.2002.05.006 陈发景, 汪新文, 张光亚, 等, 1992. 中国中、新生代含油气盆地构造和动力学背景, 现代地质, 6 (3): 317-327. 陈洁, 董冬, 邱明文, 1999. 济阳坳陷内的负反转构造及其石油地质意义. 石油实验地质, 21 (3): 201-206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.1999.03.003 陈昭年, 陈发景, 1995. 反转构造与油气圈闭. 地学前缘, 2 (3-4): 96-102. 郝雪峰, 宗国洪, 李传华, 等, 2001. 济阳坳陷正反转构造初步分析. 油气地质与采收率, 8 (3): 8-10. 李丕龙, 张善文, 曲寿利, 等, 2003. 陆相断陷盆地油气地质与勘探(卷一)——陆相断陷盆地构造演化与构造样式. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 148-158. 牟中海, 陆廷清, 谢桂生, 等, 2001. 塔西南地区二叠系剥蚀厚度恢复. 天然气工业, 21 (2): 41-43. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2001.02.009 庞雄奇, 2003. 地质过程定量模拟. 北京: 石油工业出版社. 任建业, 2004. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷S6'界面的构造变革意义. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 29 (1): 69-76, 92. 谭明友, 邴进营, 金学新, 等, 1996. 山东北部滨海地区负反转断层及古生界负反转结构成因分析. 石油地球物理勘探, 31 (6): 844-850. 王燮培, 费琪, 张家骅, 等, 1990. 石油勘探构造分析. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社. 魏文博, 叶高峰, 金胜, 等, 2007. 华北地区地壳P波三维速度结构. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 32 (4): 441-452. 姚超, 焦贵浩, 王同和, 等, 2004. 中国含油气构造样式. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 318-403. 叶兴树, 王伟锋, 2008. 板块俯冲对济阳坳陷形成的制约. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 33 (2): 235-242. 翟明国, 孟庆任, 刘建明, 等, 2004. 华北东部中生代构造体制转折峰期的主要地质效应和形成动力学探讨. 地学前缘, 11 (3): 285-297. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.027 张功成, 金利, 1997. 论反转构造. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 17 (4): 83-90. 郑德顺, 吴智平, 李伟, 等, 2005. 济阳坳陷中、新生代盆地转型期断裂特征及其对盆地的控制作用. 地质学报, 79 (3): 386-394. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.03.010 朱炎铭, 秦勇, 范炳恒, 等, 2001. 渤海湾盆地三叠系沉积厚度恢复及其意义. 中国矿业大学学报, 30 (2): 195-200. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2001.02.022 -










 下载:
下载: