Shear Wave Velocity Inversion with Routine Well Logs Based on Rock Physics and Multi-Mineral Analysis
-
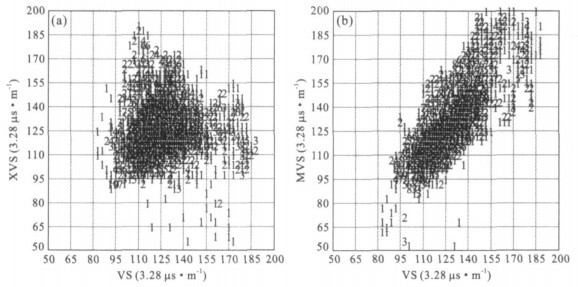
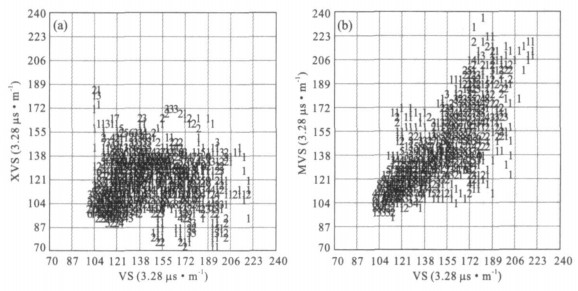
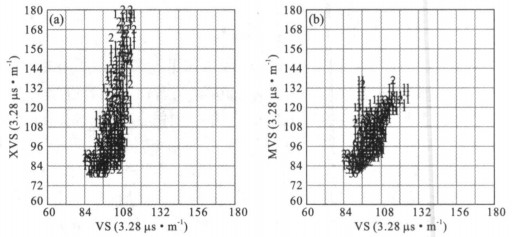
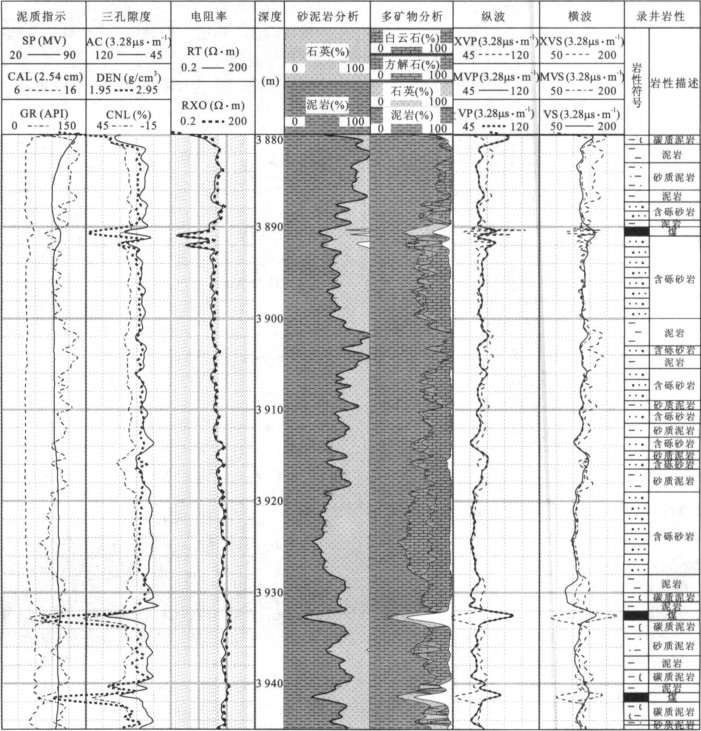
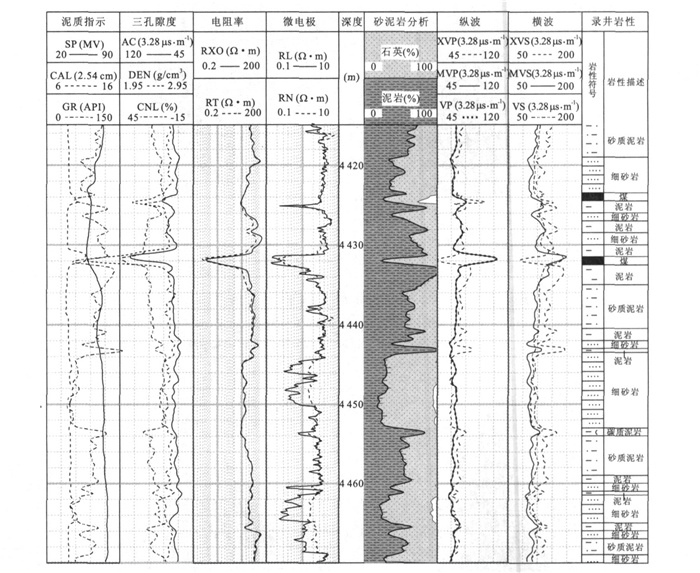
摘要: 测井横波速度是测井地震联合反演的重要标定参数.为克服大量老井缺少横波速度资料和现有横波速度估算方法的不足, 基于孔隙介质岩石物理理论, 通过常规测井资料求取多矿物组分, 利用VRH模型求得地层的等效弹性模量; 最后利用纵波速度作为约束条件, 根据Biot-Gassmann方程得到地层横波速度.计算结果与实测结果对比表明, 平均相对误差限在5%左右, 与Xu-White模型相比, 该方法物理意义更为明确, 使用更简便, 计算精度提高一倍左右.Abstract: The shear wave velocity of well log is an important parameter for mutual inversion, but lots of wells are short of this value.As present estimation method can't calculate the shear velocity precisely, based on rock physics, using VRH model this paper firstly calculates the equivalent elastic modulus via multi-mineral analysis from routine well logs, and then by taking compressional velocity as a constraint, calculates the shear wave velocity based on Biot-Gassmann equations.The method has clearer physics meaning, and practice results show that this method is much more convenient, economic and precise than Xu-White methods, and the error between computational value and measured value is less than 5 percent.
-
Key words:
- rock physics /
- well logs data /
- multi-mineral analysis /
- Biot-Gassmann equation /
- shear wave velocity /
- geophysics.
-
表 1 多矿物地层组分体积模型
Table 1. Multi-mineral mode of formation

表 2 计算地层波速所用矿物组分参数
Table 2. Parameters for formation velocity calculation

表 3 单矿物砂泥组分模型不同方法平均相对误差限比较
Table 3. Average relative error band comparison of different method under sand-shale mode

表 4 多矿物组分析法与Xu-White砂泥模型平均相对误差限比较
Table 4. Average relative error band comparison of multi-mineral mode and Xu-White sand-shale mode

-
Berryman, J. G., 1980a. Long-wavelength propagation incomposite elastic media. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. , 68 (6): 1809-1831. doi: 10.1121/1.385171 Berryman, J. G., 1980b. Confirmation of Biot's theory. Ap-pl. Phys Lett. , 37 (4): 382-384. doi: 10.1063/1.91951 Biot, M. A., 1956a. Theory of propagation of elastic waves ina fluid-saturated porous solid, Ⅰ: Low-frequency range. Acoust. Soc. Amer. , 28: 168-178. doi: 10.1121/1.1908239 Biot, M. A., 1956b. Theory of propagation of elastic waves ina fluid-saturated porous solid, Ⅱ: High-frequencyrange. Acoust. Soc. Amer. , 28: 179-191. doi: 10.1121/1.1908241 Biot, M. A., 1962. Mechanics of deformation and acousticpropagation in porous media. J. Appl. Phys. , 33 (4): 1482-1498. doi: 10.1063/1.1728759 Castagna, J. P., Batzle, M. L., Eastwood, R. L., et al., 1985. Relationship between compressional-wave and shear-wave velocities in clastic silicate rock. Geophysics, 50, 571-581. doi: 10.1190/1.1441933 Castagna, J. P., Batzle, M. L., Kan, T. K., et al., 1993. Rockphysics: The link between rock properties and AVOre-sponse. In: Castagna, J. P., Backus, M. M., eds., Offsetdependent reflectivity-theory and practice of AVOanal-ysis. SEG Investigations in Geophysics Series, 8: 135-171. Chen, Y., Huang, T. F., 2001. Rock physics. Peking Univer-sity Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Chu, Z. H., 1987. Theory of acoustic logging. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Dvorkin, J., Mavko, G., Nur, A., et al., 1995. Squirt flowinfully saturated rocks. Geophysics, 60 (1): 97-107. doi: 10.1190/1.1443767 Faust, L. Y., 1953. A velocity function including lithologicvariation. Geophysics, 18 (2): 271-288. doi: 10.1190/1.1437869 Gardner, G. H. F., Gardner, L. W., Gregory, A. R., et al., 1974. Formation velocity and density: The diagnosticbasics for stratigraphic traps. Geophysics, 39 (6): 770-780. doi: 10.1190/1.1440465 Gassmann, F., 1951. ber die elastizitat por ser Medien. Vi-erteljahrsschrift der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft in Zürich, 96: 1-23. Hill, R., 1952. The elastic behavior of crystalling aggregate. Proc. Physical Soc. , A65: 349-354. Krief, M., Garat, J., Stellingwerff, J., et al., 1990. A petro-physical interpretation using the velocities of P and Swaves (full-wave formsonic). The Log Analyst, 31 (6): 355-369. Kuster, G. T., Toksöz, M. N., 1974. Velocity and attenuationof seismic waves in two-phase media, partⅠ: Theoreti-cal formulations. Geophysics, 39 (5): 587-606. doi: 10.1190/1.1440450 Mavko, G., Mukerji, T., Dvorkin, J., et al., 2003. The rockphysics handbook. Cambridge University Press, Cam-bridge. Milholland, P., Manghnani, M. H., Schlanger, S. O., et al., 1980. Geoacoustic modeling of deep-sea carbonate sedi-ments. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. , 68 (5): 1351-1360. doi: 10.1121/1.385102 Pickett, G. R., 1963. Acoustic character logs and their appli-cations information evaluation. J. Petrol. Tech. , 15 (6): 659-667. doi: 10.2118/452-PA Reuss, A., 1929. Berechnung der Fliegrenze Von Misch Kristallen. Angew. Mathem. U. Mech. , 9 (1): 49-58. doi: 10.1002/zamm.19290090104 Voight, W., 1910. Lehrbuch der Kristallphysik, Teunber-Verlag, Leipzig. Wang, Y. M., Miao, Y. K., Meng, X. J., et al., 2006. Calcu-lation procedure of shear velocity curve on petrophys-ics. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 13 (4): 58-61 (in Chinese). Winkler, K. W., 1983. Frequency dependent ultrasonic prop-erties of high porosity sandstone. Journal of Geophysi-cal Research, 88 (B11): 9493-9499. doi: 10.1029/JB088iB11p09493 Xie, J. Z., Chu, Z. H., Li, Y. H., et al., 2003. On the methodto determine residual oil saturation from acoustic com-pression coefficient. Well Logging Technology, 27 (3): 181-184 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, S., White, R. E., 1995. A new velocity model for clay-sand mixtures. Geophys. Prospecting, 43 (1): 91-118. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.1995.tb00126.x Yong, S. H., Zhang, C. M., 1996. Digital processing and in-terpretation of well-logging. China University of Petro-leum Press, Dongying, 313-316 (in Chinese). 陈颙, 黄庭芳, 2001. 岩石物理学. 北京: 北京大学出版社. 楚泽涵, 1987. 声波测井原理. 北京: 石油工业出版社. 王玉梅, 苗永康, 孟宪军, 等, 2006. 岩石物理横波速度曲线计算技术. 油气地质与采收率, 13 (4): 58-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2006.04.018 谢进庄, 楚泽涵, 李艳华, 等, 2003. 用声波弹性参数确定剩余油饱和度的方法探讨. 测井技术, 27 (3): 181-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS200303002.htm 雍世和, 张超谟, 1996. 测井数据处理与综合解释. 东营: 中国石油大学出版社, 313-316. -









 下载:
下载: