Permian Radiolarians, Chert and Basalt from the Nan Suture Zone, Northern Thailand
-
摘要: 在泰国北部难河构造带Pha Som变质杂岩中发现保存很好的放射虫硅质岩、玄武岩地层层序.层状硅质岩含放射虫化石Follicucullus porrectus, 地质时代为中二叠世晚期至晚二叠世早期.其硅质岩SiO2含量均在92.5%以上, Al/ (Al+Fe+Mn) 平均比值为0.51, Ce/Ce*比值为1.14, 为大陆边缘型硅质岩.玄武岩具有富集大离子亲石元素与高场强元素以及轻稀土富集等洋岛玄武岩的特点.说明难河构造带中-晚二叠世之交存在洋岛型火山岩和靠近大陆边缘的深海盆地硅质岩, 代表了小洋盆的沉积组合.该构造带闭合时间应在晚二叠世与晚三叠世之间.Abstract: Well-preserved stratigraphic sequences composed of radiolarian chert and basalt were found in Pha Som metamorphic complex in Nan suture zone, northern Thailand.Bedded chert contains Follicucullus porrectus, fossils from late Middle Permian to early Late Permian.These cherts have high SiO2 (> 92.5%), low Al/ (Al+Fe+Mn) ratio (0.51 on average), and high Ce/Ce ratio (1.14 on average).These geochemical characteristics mentioned above indicate that the cherts deposited on continental margins.The basalt has high abundances of large ion lithophile elements (LILE), high field strength elements (HFSE), and light rare earth lements (LREE), suggesting characteristics of oceanic island basalt (OIB).The OIB characteristics of basalts and deep-sea-basin chert imply that the Nan suture zone was a small oceanic basin, which is similar to modern Southwest Pacific.The Nan Ocean presumably closed during the period from Late Permian to Late Triassic.
-
Key words:
- Permian /
- radiolaria /
- chert /
- oceanic island basalt /
- Nan suture zone
-
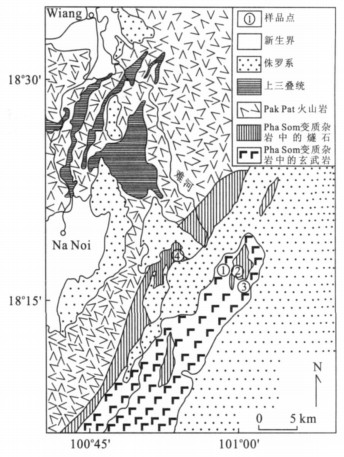
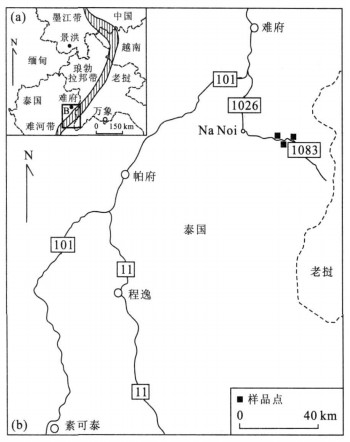
图 1 研究区大地构造位置(a) 及地理位置图(b) (Hada et al., 1999; Mantajit, 1999)
Fig. 1. Tectonic location (a) and geographical map (b) of study area
图 2 研究区地质简图及采样位置(Hess and Koch, 1975)
Fig. 2. Geological sketch map of study area and sampling sites
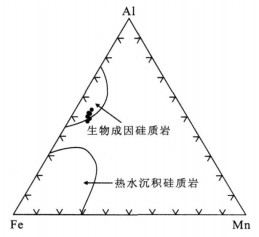
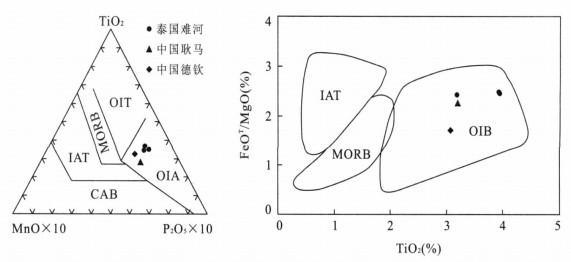
图 4 难河构造带硅质岩Al-Fe-Mn图解(Adachi et al., 1986)
Fig. 4. Al-Fe-Mn discrimination diagram for chert in the Nan suture zone
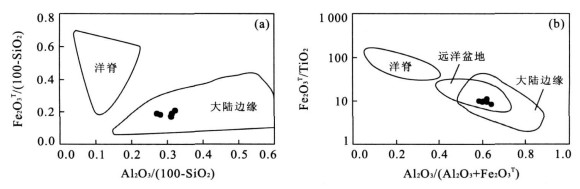
图 5 难河构造带硅质岩形成环境判别图(据Murray, 1994)
Fig. 5. Tectonic setting discrimination diagram for cherts in the Nan suture zone
图 6 难河构造带硅质岩北美页岩(NASC) 标准化的REE分布形式(北美页岩REE值引自Gromet, 1984)
Fig. 6. NASC-normalized REE distribution patterns for cherts in the Nan suture zone
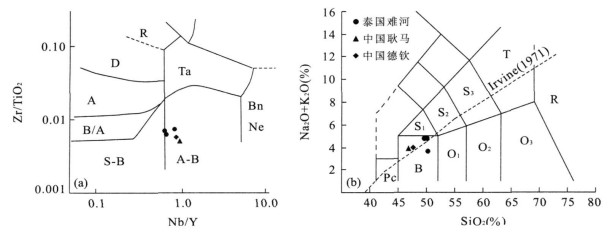
图 7 难河构造带火山岩Zr/TiO2-Nb/Y图解(a) (据Winchester et al., 1977) 和难河构造带火山岩TAS图解(b) (据Le Bas et al., 1986)
S-B.亚碱性玄武岩; A-B.碱性玄武岩; B/A.玄武岩-玄武质安山岩; A.安山岩; D.英安岩; R.流纹岩; Ta.粗安岩; Bn.碧玄岩; Ne.霞石岩; Pc.苦橄玄武岩; B.玄武岩; O1.玄武安山岩; O2.安山岩; O3.英安岩; S1.夏威夷岩(Na质)、钾质粗面玄武岩(K质); S2.橄榄粗面岩(Na质)、钾玄岩(K质); S3.长粗面岩(Na质)、安粗岩(K质); T.粗面岩(Na质)、粗面英安岩
Fig. 7. Zr/TiO2-Nb/Y (a) and TAS (b) diagrams for the basalt in the Nan suture zone
图 9 难河构造带洋中脊玄武岩(MORB)标准化的微量元素丰度型式(a)图(MORB数据引自Pearce, 1982) 和难河构造带球粒陨石标准化的稀土元素配分模式图(b)(球粒陨石REE值引自Boynton, 1984)
Fig. 9. MORB normalized trace element (a) and chondrite normalized REE distribution (b) patterns for basalts in Nan suture zone
表 1 泰国北部难河构造带硅质岩和玄武岩的主量元素(%) 和微量元素(μg/g) 分析结果a
Table 1. Major element (%) and trace element (μg/g) contents in cherts and basalts from the Nan suture zone, northern Thailand

-
Adachi, M., Yamamoto, K., Sugisaki, R., 1986. Hydrother-mal chert and associated siliceous rocks fromthe north-ern Pacific; their geological significance as indication of ocean ridge activity. Sedimentary Geology, 47 (1-2): 125-148. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(86)90075-8 Asnachinda, P., 1978. The mineralisation in the Burmese-Malayan Peninsula—A plate tectonic model. In: Nuta-laya, P., ed., Proceedings of the third regional confer-ence on geology and mineral resources of Southeast Asia, Bangkok, 293-299. Baltuck, M., 1982. Provenance and distribution of Tethyan pelagic and hemipelagic siliceous sediments, Pindos Mountains, Greece. Sedimentary Geology, 31 (1): 63-88. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(82)90008-2 Barr, S. M., MacDonald, A. S., 1987. Nan River suture zone, northern Thailand. Geology, 15: 907-910. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1987)15<907:NRSZNT>2.0.CO;2 Barr, S. M., MacDonald, A. S., 1991. Toward a Late Paleozo-ic Early Mesozoic tectonic model for Thailand. Journal of Thai Geosciences, 1 (1): 11-22. Barr, S. M., MacDonald, A. S., Dunning, G. R., et al., 2000. Petrochemistry, U-Pb (zircon) age, and palaeotectonic set-ting of the Lampang volcanic belt, northern Thailand. Jour-nal ofthe Geological Society, 157 (3): 553-563. Bostrom, K., Peterson, M. N. A., 1969. The origin of aluminum-poor ferromanganoan sediments in areas of high heat flow on the East Pacific rise. Marine Geolo-gy, 7 (5): 427-447. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(69)90016-4 Boynton, W. V., 1984. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth ele-ments; meteorite studies. In: Henderson, P., ed., Rare earth element geochemistry, Elsevier Science Publishing Company, Amsterdam, 63-114. Bunopas, S., 1981. Paleogeographic history of western Thai-land and adjacent parts of Southeast Asia: A plate tec-tonics interpretation [Dissertation]. Victoria University of Wellington, New Zealand, 810. Bunopas, S., Vella, P., 1978. Late Palaeozoic and Mesozoic structural evolution of northern Thailand: A plate tec-tonics model. In: Nutalaya, P., ed., Proceedings of the third regional conference on geology and mineral re-sources of Southeast Asia, Bangkok, 133-140. Bunopas, S., Vella, P., 1983. Tectonic and geologic evolution of Thailand. In: Nutalaya, P., ed., Proceedings of the workshop on stratigraphic correlation of Thailand and Malaysia, Haad Yai, 307-322. Burton, C. K., 1984. The tectonic framework of mainland Southeast Asia. In: Proceedings of the conference on ap-plications of geology and the national development. Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, 255-266. Chantaramee, S., 1978. Tectonic synthesis of Lansang area and discussion of regional tectonic evolution. In: Nuta-laya, P., ed., Proceedings of the third regional confer-ence on geology and mineral resources of Southeast Asia, Bangkok, 177-186. Cooper, M. A., Herbert, R., Hill, G. S., 1989. The structural evolution of Triassic intermontane basins in northeast-ern Thailand. In: Thanasuthipitak, T., Ounchanum, P., eds., Proceedings of the international symposiumonin-termontane basin: Geology and Resources, Chiang Mai, 231-242. Feng, Q. L., 1992. Permian and Triassic radiolarian bios-tratigraphy in South and Southwest China. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 3 (1): 51-62. Feng, Q. L., Liu, B. P., 1993. Permian radiolarias on south-west Yunnan. Earth Science—Journal of China Uni-versity of Geosciences, 18 (5): 553-564 (in Chinesewith English abstract). Gatinsky, Y. G., Mischina, A. V., Vinogradov, I. V., et al., 1978. The main metallogenic belts of Southeast Asia as the result of different geodynamic conditions interfer-ence. In: Nutalaya, P., ed., Proceedings of the third re-gional conference on geology and mineral resources of Southeast Asia, Bangkok, 313-318. Gromet, L. P., Dymek, R. F., Haskin, L. A., et al., 1984. The "North American shale composite": its compilation, major and trace element characteristics. Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 48 (12): 2469-2482. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90298-9 Hada, S., Bunopas, S., Ishii, K., et al., 1999. Rift-drift histo-ry and the amalgamation of Shan-Thai and Indochina/East Malaya blocks. In: Metcalfe, I., ed., Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion, 67-87. Hahn, L., 1985. The Indosinian orogeny in Thailand and ad-jacent areas. Memoires de la Societe Geologique de France, 147: 71-82. Hayashi, M., 1988. The hydrocarbon potential and tectonics of Indochina. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 11 (2): 219-231. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-5457.1988.tb00815.x Helmcke, D., 1982. On the Variscan evolution of central ma-inland Southeast Asia. Earth Evolution Science, 2 (4): 309-319. Helmcke, D., 1985. The Permo-Triassic "Paleotethys" in mainland Southeast Asia and adjacent parts of China. Geologische Rundschau, 74: 215-228. doi: 10.1007/BF01824893 Helmcke, D., 1986. On the geology of the Petchabun fold belt (Central Thailand) —Implications for the geody-namic evolution of Mainland SE Asia. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia, 19: 79-85. doi: 10.7186/bgsm19198607 Helmcke, D., Kraikhong, C., 1982. On the geosynclinal and geological evolution of central and northeastern Thai-land. Journal of the Geological Society of Thailand, 5: 52-74. Helmcke, D., Lindenberg, H. G., 1983. New data on the In-dosinian orogeny from Central Thailand. Geologische Rundschau, 72 (1): 317-328. doi: 10.1007/BF01765912 Hess, A., Koch, K. E., 1975. Geological map of Nan (1∶250, 000). Federal Institute of Geosciences and NaturalResources, Hannover. Hou, Z. Q., Mo, X. X., Zhu, Q. W., et al., 1996. Mantle plumein the Sanjiang paleo-Tethyan region, China: Evidence fromo cean-island basalts. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 17 (4): 343-361 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hutchison, C. S., 1975. Ophiolite in southeast Asia. Geolog-ical Society of America Bulletin, 86 (6): 797-806. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1975)86<797:OISA>2.0.CO;2 Hutchison, C. S., 1983. Multiple Mesozoic Sn-W-Sb granit-oids of Southeast Asia. In: Roddick, J. A., ed., Circum-Pacific plutonic terranes. Geological Society of America Memoir, 35-60. Hutchison, C. S., 1989. Geological evolution of Southeast Asia. Clarendon Press, Oxford. Ishiga, H., 1990. Paleozoic radiolarians. In: Ichikawa, K., Mi-zutani, S., Hara, I., et al., eds., Pre-Cretaceous terra-nes of Japan. Nippon Insatsu Shuppan Co. Ltd., Osaka, 285-295. Le Bas, M. J., Le Maitre, R. W., Streckeisen, A., et al., 1986. Chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram. Journal of Petrology, 27 (3): 745-750. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745 Macdonald, A. S., Barr, S. M., 1978. Tectonic significance ofa Late Carboniferous volcanic arc in northern Thailand. In: Nutalaya, P., ed., Proceedings of the third regionalconference on geology and mineral resources of South-east Asia, Bangkok, 151-156. MacDonald, A. S., Barr, S. M., 1984. The Nan River mafic-ultramafic belt, northern Thailand: Geochemistry and tectonic significance. Buletin Persatuan Geologi Malay-sia, 17: 209-224. Mantajit, N., 1999. Thailand and Tethys Sea. In: Ratanas-thien, B., Rieb, S. L., eds., International symposium on shallow Tethys, 5, Chiang Mai, Ⅸ-ⅩⅩⅦ. Metcalfe, I., 1986. Late Palaeozoic palaeogeography ofSoutheast Asia: Some stratigraphical, palaeontological and palaeomagnetic constraints. Bulletin Geological So-ciety of Malaysia, 19: 153-164. doi: 10.7186/bgsm19198612 Mitchell, A. H. G., 1977. Tectonic settings for emplacement of Southeast Asian tin granites. Bulletin Geological So-ciety of Malaysia, 9: 123-140. doi: 10.7186/bgsm09197710 Mitchell, A. H. G., 1986. Mesozoic and Cenozoic regional tectonics and metallogenesis in mainland SE Asia. Bul-letin Geological Society of Malaysia, 20: 221-239. doi: 10.7186/bgsm20198612 Mitchell, A. H. G., 1992. Late Permian-Mesozoic events andthe Mergui Group nappe in Myanmar and Thailand. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 7 (2-3): 165-178. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(92)90051-C Mo, X. X., Shen, S. Y., Zhu, Q. W., 1998. Volcanics-ophiolites and related mineralization in the middle southern segment of Sanjiang region. Geological Pub-lishing House, Beijing, 1-128 (in Chinese). Murray, R. W., 1994. Chemical criteria to identify the depo-sitional environment of chert: General principles and ap-plications. Sedimentary Geology, 90 (3-4): 213-232. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(94)90039-6 Murray, R. W., Buchholtz ten Brink, M. R., Gerlach, D. C., et al., 1992a. Rare earth, major, and trace element com-position of Monterey and DSDP chert and associated host sediment: Assessing the influence of chemical frac-tionation during diagenesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimi-ca Acta, 56 (7): 2657-2671. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(92)90351-I Murray, R. W., Buchholtz ten Brink, M. R., Gerlach, D. C., et al., 1991. Rare earth, major, and trace elements inchert from the Franciscan complex and Monterey Group, California: Assessing REE sources to fine-grained marine sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 55 (7): 1875-1895. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(91)90030-9 Murray, R. W., Buchholtz ten Brink, M. R., Jones, D. L., et al., 1990. Rare earth elements as indicators of different marine depositional environments in chert and shale. Geology, 18 (3): 268-271. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<0268:REEAIO>2.3.CO;2 Murray, R. W., Jones, D. L., Buchholtz ten Brink, M. R., 1992b. Diagenetic formation of bedded chert: Evidence from chemistry of the chert-shale couplet. Geology, 20 (3): 271-274. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0271:DFOBCE>2.3.CO;2 Panjasawatwong, Y., 1991. Petrology, geochemistry and tectonicimplications of igneous rocks in the Nan suture zone, Thai-land and an empirical study of the effects of Ca/Na, Al/Siand H2O on plagioclase-melt equilibria at5-10kb pres-sure. University of Tasmania, Hobart, 239. Pearce, J. A., 1982. Trace element characteristics of lavafrom destructive plate boundaries. In: Thorpe, R. S., ed., Orogenic Andesites. John Wiley & Sons, Chiches-ter, 525-548. Ridd, M. F., 1980. Possible Palaeozoic drift of SE Asia and Triassic collision with China. Journal of the Geological Society of London, 137: 635-640. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.137.5.0635 Sengör, A. M. C., 1984. The Cimmeride orogenic systemandthe tectonics of Eurasia. Geological Society of Ameri-ca, Special Paper, 195: 82. Shen, S. Y., Feng, Q. L., Liu, B. P., et al., 2002. Study on oceanridge, ocean island volcanic rocks of Changning-Menglianbelt. Geological Science and Technology Information, 21 (3): 13-17 (in Chinese with English abstract). Shen, S. Y., Zhang, B. M., Wei, Q. R., et al., 1994. Charac-teristics of oceanic and para-oceanic ridge volcanic rocksin Jinshajiang belt. Tethyan Geology, 18: 130-142 (in Chinese with English abstract). Singharaj warapan, S., Berry, R., Panjasawatwong, Y., 2000. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance ofthe Permo-Triassic Pak Pat volcanics, Uttaradit, north-ern Thailand. Journal of the Geological Society of Thailand, 2000 (1): 1-7. Stauffer, P. H., 1974. Malaya and Southeast Asia in the pat-tern of continental drift. Bulletin Geological Society of Malaysia, 7: 89-138. doi: 10.7186/bgsm07197405 Thanasuthipitak, T., 1978. Geology of Uttaradit area and itsimplications on tectonic history of Thailand. In: Nuta-laya, P., ed., Proceedings of the third regional confer-ence on geology and mineral resources of SoutheastAsia, Bangkok, 187-197. Wang, D. A., Chen, R. J., 1995. Geochemically genetic crite-ria of silicolites in Yaluzangbu suture belt and their geo-logical significance. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 13 (1): 27-31 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Y. J., 1994. Cherts and radiolarian assemblage zonesof Qinzhou area, Guangxi. Chinese Science Bulletin, 39 (13): 1208-1210 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1994-39-13-1208 Wang, Y. Z., Li, X. L., Duan, L. L., et al., 2000. Geotecton-ics and metallogenyin the south Nujiang-Lancangjiang-Jinsha rivers area. Geological Publishing House, Bei-jing, 1-122 (in Chinese). Winchester, J. A., Floyd, P. A., 1977. Geochemical discrimi-nation of different magma series and their differentiationproducts using immobile elements. Chemical Geology, 20 (4): 325-343. Wu, H. R., Boulter, C. A., Ke, B. J., et al., 1995. TheChangning-Menglian suture zone: Asegment of the ma-jor Cathaysian-Gondwana dividein Southeast Asia. Tec-tonophysics, 242 (3-4): 267-280. Wu, H. R., Xian, X. Y., 1994. Late Paleozoic radiolarian as-semblages of southern Guangxi andits geological signif-icance. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 29 (4): 339-345 (inChinese with English abstract). Yamamoto, K., 1987. Geochemical characteristics and depo-sitional environments of cherts and associated rocks inthe Franciscan and Shimanto terranes. Sedimentary Ge-ology, 52 (1-2): 65-108. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(87)90017-0 Zhong, D. L., 1998. Paleotethysides in west Yunnan and Si-chuan, China. Science Press, Beijing, 1-248 (in Chinese). 冯庆来, 刘本培, 1993. 滇西南二叠纪放射虫化石. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 18 (5): 553-564. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199305002.htm 侯增谦, 莫宣学, 朱勤文, 等, 1996. "三江"古特提斯地幔热柱——洋岛玄武岩证据. 地球学报, 17 (4): 343-361. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB604.001.htm 莫宣学, 沈上越, 朱勤文, 1998. 三江中南段火山岩-蛇绿岩与成矿. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-128. 沈上越, 冯庆来, 刘本培, 等, 2002. 昌宁-孟连带洋脊、洋岛型火山岩研究地质科技情报, 21 (3): 13-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2002.03.003 沈上越, 张保民, 魏启荣, 等, 1994. 金沙江洋脊-准洋脊火山岩特征研究. 特提斯地质, 18: 130-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD400.009.htm 王东安, 陈瑞君, 1995. 雅鲁藏布缝合带硅岩的地球化学成因标志及其地质意义. 沉积学报, 13 (1): 27-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB501.003.htm 王义昭, 李兴林, 段丽兰, 等, 2000. 三江地区南段大地构造与成矿. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-122. 王玉净, 1994. 广西钦州地区硅质岩及其放射虫化石组合带. 科学通报, 39 (13): 1208-1210. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199413015.htm 吴浩若, 咸向阳, 1994. 广西南部晚古生代放射虫组合及其地质意义. 地质科学, 29 (4): 339-345. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.1994.04.002 钟大赉, 1998. 滇川西部古特提斯造山带. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-231. -









 下载:
下载: