Indosinian Orogenesis of the Gangdise Terrane: Evidences from Zircon U-Pb Dating and Petrogenesis of Granitoids
-
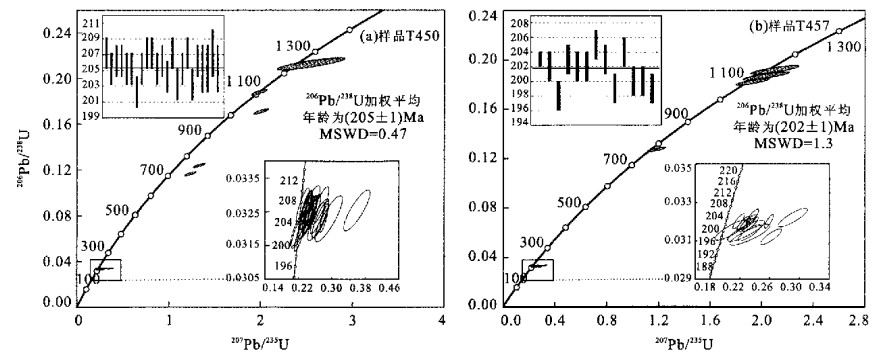
摘要: 对冈底斯中部地区二云母花岗岩和花岗闪长岩进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年、主量元素、微量元素和锆石Hf同位素组成的测定.结果表明, 二云母花岗岩的岩浆结晶年龄为(205± 1)Ma, 岩石属于强过铝质花岗岩, A/CNK= 1.16~ 1.20, K2O/Na2O= 1.67~ 1.95.岩石富Rb、Th和U等元素, Eu/Eu* = 0.29~ 0.41, (La/Yb)N= 22.62~ 35.08.锆石εHf(t)= -12.4~ -1.8.二云母花岗岩的岩浆产生于地壳中泥质岩类在无外来流体加入的情况下云母类矿物脱水反应所诱发的部分熔融作用, 其岩石形成机制类似于喜马拉雅新生代淡色花岗岩.花岗闪长岩的岩浆结晶年龄为(202± 1)Ma, 岩石属于准铝质(A/CNK= 0.96~ 0.98), K2O/Na2O= 1.42~ 1.77, Eu/Eu* = 0.54~ 0.65, (La/Yb)N= 6.76~ 13.35.锆石εHf(t)= -8.2~ -5.5.根据花岗闪长岩的地球化学特征和锆石Hf同位素组成, 花岗闪长岩的岩浆来自于地壳中基性岩类的部分熔融.冈底斯印支晚期强过铝质花岗岩的确定, 表明了冈底斯在印支晚期以前曾发生地壳的缩短与加厚作用, 从而进一步明确了冈底斯印支早期的造山事件及冈底斯经历了多期造山作用的演化.Abstract: This paper reports LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages, whole-rock major and trace element and zircon Hf isotopic com- positions from two-mica granite and granodiorite plutons occurring in the middle part of the Gangdise terrane, Tibet. Magma zircons from the two-mica granite yielded a weighted 206Pb/238 U mean age of(205± 1)Ma(MSWD= 0.47), which is inter- preted as its magma crystallization age(Late Indosinian). The two-mica granite is strongly peraluminous, with Al index(A/ CNK)= 1.16 -1.20 and K2O/Na2O= 1.67 -1.95. The two-mica granite is characterized by enrichments of Rb, Th and U etc. Rare earth element(REE)data display Eu/Eu*= 0.29 -0.41 and(La/Yb)N= 22.62 -35.08.εHf(t)(205 Ma)values from the dated zircons range from -12.4 to -1.8. It is suggested that the magma for the two-mica granite was dominately derived from patial melting of argillaceous rocks in crust, induced by dehydration of mica minerals. The petrogenesis of the two-mica granite is similar to that of the Himalayan Tertiary leucogranites. Magma zircons from the granodiorite yielded a weighted 206Pb/238 U age of(202± 1)Ma, representing its magma crystallization age. The granodiorite is metaluminous, with Al index(A/CNK)= 0.96 -0.98, K2O/Na2O= 1.42 -1.77. REE data show Eu/Eu* = 0.54 -0.65 and(La/Yb)N= 6.76 -13.35. Dated zircon Hf isotopic compositions exhibitεHf(202 Ma)values ranging from -8.2 to -5.5. The geo- chemical signatures and zircon Hf isotopic compositions suggest that the magma of granodiorite formed by partial melting of basaltic rocks in crust. The Late Indosinian stronlgly peralumineous granite is the first report in the Gangdise terrane. The occurring of the stronlgly peralumineous granite reveals Gangdise crustal thickening prior to Late Indosinian, and gives an impelling evidence that the Gangdise terrane took place an Early Indosinian orogenic event.
-
Key words:
- Indosinian granitoids /
- U-Pb zircon dating /
- Hf isotope /
- geochemistry /
- tectonic implication /
- Gangdise terrane /
- Tibet
-
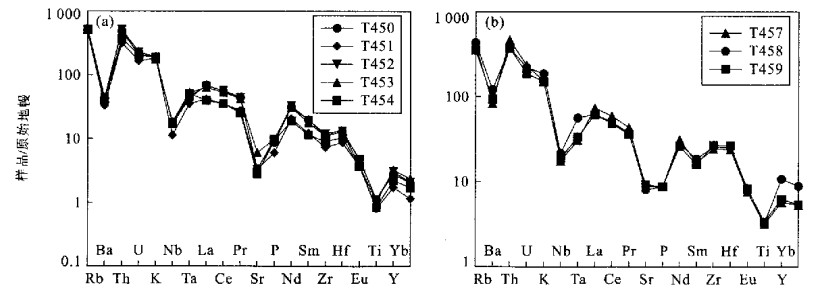
图 4 原始地幔标准化的元素组成模式
a.二云母花岗岩; b.花岗闪长岩; 原始地幔标准化值据Sun and McDonough(1989)
Fig. 4. Primitive mantle normalized elemental compositional patterns of two-mica granite(a) and granodiorite(b)
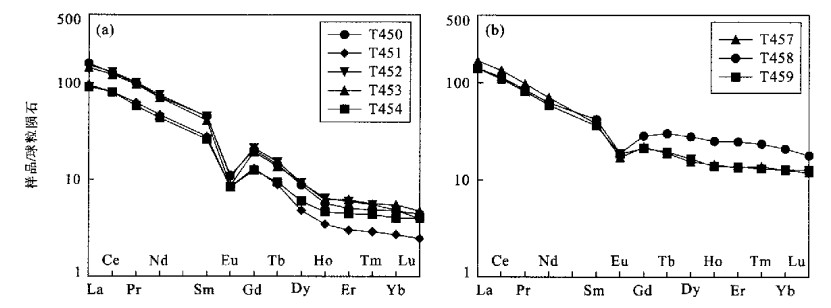
图 5 稀土元素组成模式
a.二云母花岗岩; b.花岗闪长岩; 球粒陨石标准化值据Taylor and McLennan(1985)
Fig. 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of two-mica granite(a) and granodiorite(b)
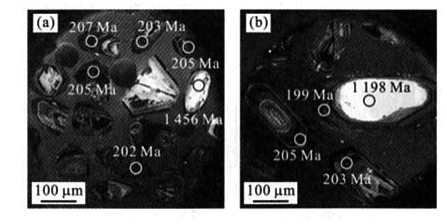
表 1 样晶T450和T457 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素资料
Table 1. U-Pb zircon LA-ICP MS chronoiogical data of samples T450 and T457

表 2 冈底斯印支期花岗岩类主量元素(%)和微量元素(μg/g)资料
Table 2. Major element (%) and Lracc clerment (μg/g) data of Gangdise Indosinian granitoid

表 3 样品T450和T457锆石Lu-Hf同位素资料
Table 3. Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic data of samples T450 and T457

-
Andersen, T., 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chem. Geol. , 192: 59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X Beard, J.S., Lofgren, G.E., 1991. Dehydration melting and water-saturated melting of basaltic and andesitic greenstones and amphibolites at 1.3 and 6.9 kbar. Journal of Petrology, 32: 365-402. doi: 10.1093/petrology/32.2.365 Blichert-Toft, J., Albarede, F., 1997. The Lu-Hf geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. , 148: 243-258. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00040-X Chu, M.F., Chung, S.L., Song, B., et al., 2006. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints on the Mesozoic tectonics and crustal evolution of southern Tibet. Geology, 34: 745-748. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/geology/article-abstract/34/9/745/129621/Zircon-U-Pb-and-Hf-isotope-constraints-on-the Chu, N.C., Taylor, R.N., Chavagnac, V., et al., 2002. Hf isotope ratio analysis using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: An evaluation of isobaric interference corrections. J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. , 17: 1567-1574. doi: 10.1039/b206707b Chung, S.L., Chu, M.F., Zhang, Y.Q., et al., 2005. Tibetan tectonic evolution inferred from spatial and temporal variations in post-collisional magmatism. Earth-Science Reviews, 68: 173-196. Chung, S.L., Dunyi, L., Ji, J., et al., 2003. Adakites from continental collision zones: Melting of thickened lower crust beneath southern Tibet. Geology, 31: 1021-1024. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/geology/article-abstract/31/11/1021/29168/Adakites-from-continental-collision-zones-Melting DeBievre, P., Taylor, P.D. P., 1993. Table of the isotopic composition of the elements. Int. J. Mass. Spectrom. Ion Process, 123: 149. doi: 10.1016/0168-1176(93)87009-H Griffin, W.L., Wang, X., Jackson, S.E., et al., 2002. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes. Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes. Lithos, 61: 237-269. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493702000828 Harris, N., Ayres, M., Massey, J., 1995. Geochemistry of granitic melts produced during the incongruent melting of muscovite: Implication for the extraction of Himalayan leucogranite mamas. Journal of Geophysical Research, 100: 15767-15777. doi: 10.1029/94JB02623 Harris, N., Inger, S., 1992. Trace element modeling of pelitederived granites. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 110: 46-56. doi: 10.1007/BF00310881 Harrison, T.M., Lovera, O.M., Grove, M., 1997. New insights into the origin of two contrasting Himalayan granite belts. Geology, 25: 899-902. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/geology/article/25/10/899/187693/New-insights-into-the-origin-of-two-contrasting He, Z.H., Yang, D.M., Zheng, C.Q., et al., 2006. Isotopic dating of the Mamba granitoid in the Gangdise tectonic belt and its constraint on the subduction time of the Neotethys. Geological Review, 52: 100-106(in Chinese with English abstract). Helz, R.T., 1976. Phase relations of basalts in their melting ranges at pH2O= 5 kar, part II: Melt compositions. Journal of Petrology, 17: 139-193. doi: 10.1093/petrology/17.2.139 Hou, Z.Q., Gao, Y.F., Qu, X.M., et al., 2004. Origin of adakitic intrusives generated during mid-Miocene eastwest extension in southern Tibet. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. , 220: 139-155. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00007-X Inger, S., Harris, N., 1993. Geochemical constrains on leucogranite magmatism in the Langtang Valley, Nepal Himalaya. Journal of Petrology, 34: 345-368. doi: 10.1093/petrology/34.2.345 Kapp, J., Harrison, T.M., Kapp, P., et al., 2005. Nyainqentanglha Shan: A window into the tectonic, thermal, and geochemical evolution of the Lhasa block, southern Tibet. Journal of Geophysical Research, 110: B08413(1-23). doi: 10.1029/2004JB003330 Li, C., Wang, T.W., Li, H.M., et al., 2003. Discovery of Indosinian megaporphyritic granodiorite in the Gangdise area: Evidence for the existence of Paleo-Gangdise. Geological Bulletin of China, 22: 364-366(in Chinese with English abstract). Ludwig, K.R., 2001. Users manual for Isoplot/Ex(rev. 2. 49): A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication No. 1a, 55. Mo, X.X., Dong, G.C., Zhao, Z.D., et al., 2005. Spatial and temporal distribution and characteristics of granitoids in the Gangdise, Tibet and implication for crustal growth and evolution. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11: 281-290(in Chinese with English abstract). https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GXDX200503001.htm Mo, X.X., Hou, Z.Q., Niu, Y.L., et al., 2007. Mantle contributions to crustal thickening during continental collision: Evidence from Cenozoic igneous rocks in southern Tibet. Lithos(in press). Pan, G. T., Mo, X. X., Hou, Z. Q., et al., 2006. Spatialtemporal framework of the Gangdise orogenic belt and its evolution. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22: 521-533(in Chinese with English abstract). https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200603001.htm Patino-Douce, A. E., Harris, N., 1998. Experimental constraints on Himalayan anatexis. Journal of Petrology, 39: 689-710. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.4.689 Rushmer, T., 1991. Partial melting of two amphibolites: Contrasting experimental results under fluid absent conditions. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 107: 41-59. doi: 10.1007/BF00311184 Scherer, E., Munker, C., Mezger, K., 2001. Calibration of the lutetium-hafnium clock. Science, 293: 683-687. doi: 10.1126/science.1061372 Searle, M.P., Parrish, R.R., Hodges, K.V., et al., 1997. Shisha pangma leucogranite, South Tibetan Himalaya: Field relations, geochemistry, age, origin and emplacement. The Journal of Geology, 105: 295-317. doi: 10.1086/515924 Sun, S.S., McDonough, W.F., 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Sunders, A.D., Norry, M.J., eds., Magmatism in the ocean basins. London: Special Publications, 42: 313-345. Sylvester, P.J., 1998. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites. Lithos, 45: 29-44. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00024-3 Taylor, S. R., McLennan, S. M., 1985. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1-132. Tepper, J.H., Nelson, B.K., Bergantz, G.W., 1993. Petrology of the chilliwack batholith, North Cascades, Washington: Generation of calc-alkaline granitoids by melting of mafic lower crust with variable water fugacity. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 113: 333-351. doi: 10.1007/BF00286926 Vervoort, J.D., Blichert-Toft, J., 1999. Evolution of the depleted mantle: Hf isotope evidence from juvenile rocks through time. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 63: 533-556. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00274-9 Visona, D., Lombardo, B., 2002. Two-mica and tourmaline leucogranites from the Everest-Makalu region(NepalTibet): Himalayan leucogranite genesis by isobaric heating. Lithos, 62: 125-150. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00112-3 White, A.J.R., Chappell, B.W., 1977. Ultrametamorphism and granitoid genesis. Tectonophysics, 43: 7-22. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(77)90003-8 Wolf, M.B., Wyllie, P.J., 1992. The formation of tonalitic liquids during the vapor-absent partial melting of amphibolite at 10 kbar. Eos, 70: 506-518. Wu, F.Y., Yang, Y.H., Xie, L.W., et al., 2006. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology. Chem. Geol. , 232: 105-126. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254106002452 Yuan, H.L., Gao, S., Liu, X.M., et al., 2004. Accurate UPb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Geostand. Newsl. , 28: 353-370. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb00755.x Zhai, Q.G., Li, C., Li, H.M., et al., 2005. U-Pb zircon age of leucogranite in the central Gangdise, Tibet, and its geological significance. Geological Bulletin of China, 24: 349-353(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, G. W., Guo, A. L., Yao, A. P., 2004. Western Qinling-Songpan continental tectonic node in China's continental tectonics. Earth Science Frontiers, 11: 23-32(in Chinese with English abstract). https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200403004.htm Zhang, H.F., Gao, S., Zhong, Z.Q., et al., 2002. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of Cretaceous granitoids: Constraints on tectonic framework and crustal structure of the Dabieshan ultrahigh pressure metamorphic belt, China. Chem. Geol. , 186: 281-299. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00006-2 Zhang, H.F., Harris, N., Parrish, R., et al., 2004. Causes and consequences of protracted melting of the mid-crust exposed in the North Himalayan antiform. Earth Planetary Science Letters, 228: 195-212. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2004.09.031 Zhang, H.F., Harris, N., Parrish, R., et al., 2005. Geochemistry of North Himalayan leucogranites: Regional comparison, petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Earth Science— Journal of China University of Geosciences, 30(3): 275-288(in Chinese with English abstract). https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-IGQM200408001058.htm 和钟铧, 杨德明, 郑常青, 等, 2006. 冈底斯带门巴花岗岩同位素测年及其对新特提斯洋俯冲时代的约束. 地质论评, 52: 100-106. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.01.013 李才, 王天武, 李惠民, 等, 2003. 冈底斯地区发现印支期巨斑花岗闪长岩: 古冈底斯造山的存在证据. 地质通报, 22: 364-366. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.05.011 莫宣学, 董国臣, 赵志丹, 等, 2005. 西藏冈底斯带花岗岩的时空分布特征及地壳生长演化信息. 高校地质学报, 11: 281-290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.03.001 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等, 2006. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化. 岩石学报, 22: 521-533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200603001.htm 翟庆国, 李才, 李惠民, 等, 2005. 西藏冈底斯中部淡色花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 地质通报, 24: 349-353. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2005.04.008 张国伟, 郭安林, 姚安平, 2004. 中国大陆构造中的西秦岭松潘大陆构造结. 地学前缘, 11: 23-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.004 张宏飞, Harris, N., Parrish, R., 等, 2005. 北喜马拉雅淡色花岗岩地球化学: 区域对比、岩石成因及其构造意义. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 30(3): 275-288. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200503003.htm -









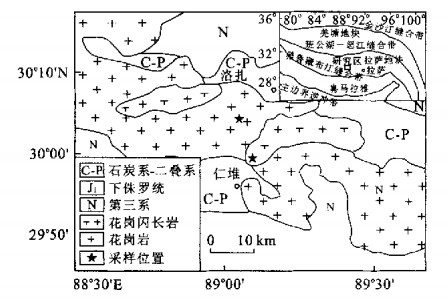
 下载:
下载: