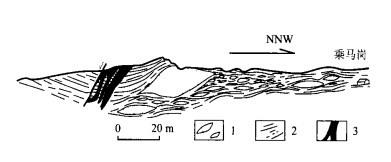
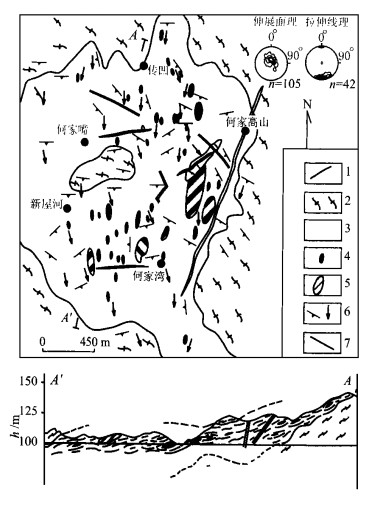
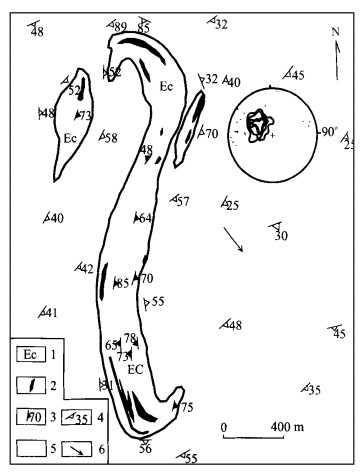
| [1] |
Cong B, Wang Q, Zhai M, et al. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocksin the Dabie-Su-Lu region, China: their formation and exhumation[J]. The Island Arc, 1994, 3: 135~150. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.1994.tb00103.x |
| [2] |
Liou J G, Zhang R Y, Wang X, et al. Metamorphism and tectonics of high-pressure and ultra-high-pressure belts in the Dabie-Sulu region, China[A]. In: Yin A, Harrison M T, eds. Rubey Volume Ⅷ, Tectonic development of Asia[C]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996. 300~344. |
| [3] |
Hacker B R, Wang X, Eide E A, et al. The QinlingDabie ultrahigh-pressure collisional orogen[A]. In: Yin A, Harrison M T, eds. Rubey Volume Ⅷ, Tectonic development of Asia[C]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996. 345~370. |
| [4] |
Ernst W G, Liou J G. Overview of UHP metamorphism and tectonics in well-studied collisional orogens[J]. International Geology Review, 1999, 41: 477~493. doi: 10.1080/00206819909465153 |
| [5] |
Wallis S, Enami M, Banno S. The Sulu UHP terrane: a review of the petrology and structural geology[J]. International Geology Review, 1999, 41: 906~920. doi: 10.1080/00206819909465178 |
| [6] |
Jahn B M. Sm-Nd isotope tracer study of UHP metamorphic rocks: implications for continental subduction and collisional tectonics[J]. International Geology Review, 1999, 41: 859~885. doi: 10.1080/00206819909465175 |
| [7] |
Webb L E, Hacker B R, Ratschbacher L, et al. Thermochronologic constraints on deformation and cooling history of high- and ultrahigh-pressure rocks in the Qinling-Dabie orogen, eastern China[J]. Tectonics, 1999, 18: 621~638. doi: 10.1029/1999TC900012 |
| [8] |
索书田. 大别地块超高压变质省的构造变形研究[J]. 地学前缘, 1999, 6: 255~262. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.04.008 |
| [9] |
索书田, 钟增球, 游振东. 大别地块超高压变质期后伸展变形及超高压变质岩石折返过程[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2000, 30: 9~17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200001001.htm |
| [10] |
Zhong Z, Suo S, You Z. Regional-scale extensional tectonic pattern of ultrahigh-pressure and high-pressure metamorphic belts from the Dabie massif, China[J]. International Geology Review, 1999, 41: 1033~1041. doi: 10.1080/00206819909465188 |
| [11] |
Zhang R Y, Liou J G, Cong B. Petrogenesis of garnetbearing ultramafic rocks and associated eclogites in the SuLu ultrahigh-p metamorphic terrane, eastern China[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 1994, 12: 169~186. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.1994.tb00012.x |
| [12] |
Zhang R Y, Hirajima T, Banno S, et al. Petrology of ultrahigh-pressure rocks from the southern Su-Lu region, eastern China[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 1995, 13: 659~675. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.1995.tb00250.x |
| [13] |
李曙光, 李惠民, 陈移之, 等. 大别山—苏鲁地体超高压变质年代学—Ⅱ. 锆石U-Pb同位素体系[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1997, 27: 200~206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199703001.htm |
| [14] |
Hacker B R, Wang Q. Ar/Ar geochronology of ultrahighpressure metamorphism[J]. Tectonics, 1995, 14: 994 ~1006. doi: 10.1029/95TC00932 |
| [15] |
Hacker B R, Ratschbacher L, Webb L, et al. U/Pb zircon ages constrain the architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure Qinling-Dabie orogen, China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 161: 215~230. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00152-6 |
| [16] |
Wang Q, Cong B. Exhumation of UHP terrane: a case study from the Dabie Mountains, eastern China[J]. International Geology Review, 1999, 41: 994~1004. doi: 10.1080/00206819909465185 |
| [17] |
Ree J H, Cho M, Kwon S T, et al. Possible eastward extension of Chinese collision belt in South Korea: the Imjingang belt[J]. Geology, 1996, 24: 1071~1074. |
| [18] |
朱光, 徐嘉炜. 郯庐断裂带与大别—胶南造山带的构造关系[A]. 见: 马宗晋, 杨主恩, 吴正文, 编. 构造地质学-岩石圈动力学研究进展[C]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1999. 164~170. |
| [19] |
Suo S, Zhong Z. Multi-layered low-angle ductile detachment system in Dabie-Sulu UHPM and HPM belts, China [J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1999, 10: 187~193. |
| [20] |
Meng Q R, Zhang G W. Timing of collision of the North and South China block: controversy and reconciliation [J]. Geology, 1999, 27: 123~126. |
| [21] |
Wang Q, Liu X, Maruyama S, et al. Top boundary of the Dabie UHPM rocks, central China[J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1995, 11: 295~300. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(94)00035-D |
| [22] |
Xu S, Okay A I, Ji S, et al. Diamond from the Dabie Shan metamorphic rocks and its implication for tectonic setting[J]. Science, 1992, 256: 80~82. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5053.80 |
| [23] |
徐树桐, 刘贻灿, 苏文, 等. 大别山超高压变质带面理化榴辉岩中变形石榴石的几何学和运动学特征及其大地构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1999, 15: 321~337. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199903000.htm |
| [24] |
Li S, Xiao Y, Liu D, et al. Collision of the North China and Yangtze block and formation of coesite-bearing eclogites: timing and processes[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 109: 89~111. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(93)90063-O |
| [25] |
Ames L, Tilton, G R, Zhou G. Timing of collision of the Sino-Korean and Yangtse cratons: U-Pb dating of coesitebearing eclogites[J]. Geology, 1993, 21: 339~342. |
| [26] |
Ames L, Zhou G. Xiong B. Geochronology and isotopic character of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism with implications for collision of the Sino-Korean and Yangtze cratons, central China[J]. Tectonics, 1996, 15: 472~489. doi: 10.1029/95TC02552 |
| [27] |
Eide E A, McWilliams M O, Liou J G. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology and exhumation of high-pressure to ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in east-central China [J]. Geology, 1994, 22: 601~604. |
| [28] |
Chavagnac V, Jahn B M. Coesite-bearing eclogites from the Bixiling complex, Dabie Mountains, China: Sm-Nd ages, geochemical characteristics and tectonic implications [J]. Chemical Geology, 1996, 133: 29~51. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00068-X |
| [29] |
Carswell D A, O'brien P J, Wilson R N, et al. Thermobarometry of phengite-bearing eclogites in the Dabie Mountains of central China[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 1997, 15: 239~252. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.1997.00014.x |
| [30] |
Liou J G, Zhang R Y, Jahn B M. Petrology, geochemistry and isotope data on a ultrahigh-pressure jadeite quartzite from Shuanghe, Dabie Mountains, east-central China[J]. Lithos, 1997, 41: 59~78. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(97)82005-1 |
| [31] |
刘景波, 国连杰, 吴颖. 豫南—鄂北大别山北部高压角闪石榴辉岩的研究[J]. 地质科学, 1997, 32: 409~422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX704.000.htm |
| [32] |
Suo S, Zhong Z. Sequence of ductile shear zone in UHP metamorphic province within Dabie massif, China[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1998, 9: 189 ~195. |
| [33] |
Henry C, Michard A, Chopin C. Geometry and structural evolution of ultra-high-pressure and high-pressure rocks from the Dora-Maira massif, Western Alps, Italy [J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1993, 15: 965~981. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(93)90170-F |
| [34] |
Andersen T B, Osmundsen P T. Deep crustal fabrics and a model for the extensional collapse of the southwest Norwegian Caledonides[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1994, 16: 1191~1203. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(94)90063-9 |
| [35] |
Moller C. Decompressed eclogites in the Sveconorwegian (-Grenvillian)orogen of SW Sweden: petrology and tectonic implications[J]. Journal Metamorphic Geology, 1998, 16: 641~656. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.1998.00160.x |
| [36] |
Simpson C, Schmid S. An evaluation of criteria to deduce the sense of movement in sheared rocks[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1983, 94: 1281~1288. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1983)94<1281:AEOCTD>2.0.CO;2 |
| [37] |
Schmid S M, Zingg A, Handy M. The kinematics of movements along the insubric line and the emplacement of the Ivrea zone[J]. Tectonophysics, 1987, 135: 47~66. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(87)90151-X |
| [38] |
Ellis M, Watkinson A J. Orogen-parallel extension and oblique tectonics: the relation between stretching lineations and relative plate motions[J]. Geology, 1987, 15: 1022~1026. |









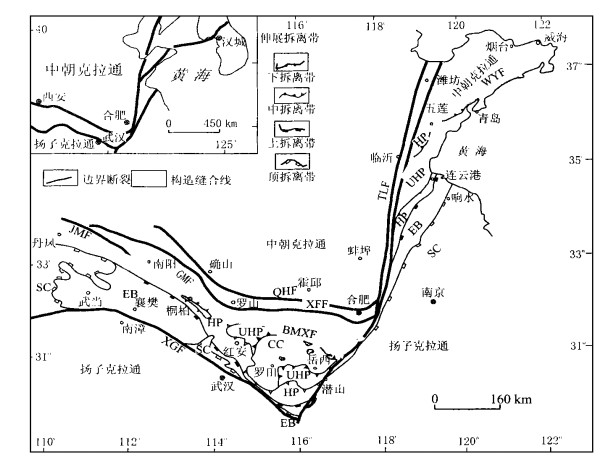
 下载:
下载: