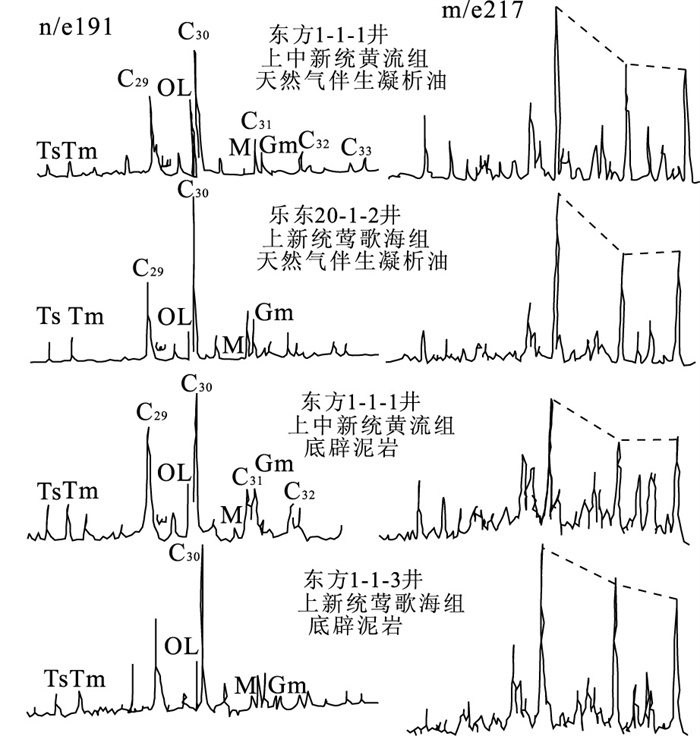
|
Cao, C.R., Liu, Z.H., 2005. Petroliferous basin analysis theory and method. Jilin University Press, Jilin (in Chinese). |
|
Chiu, J.K., Tseng, W.H., Liu, C.S., 2006. Distribution of gassy sediments and mud volcanoes offshore southwestern Taiwan. Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 17(4): 703-722. doi: 10.3319/TAO.2006.17.4.703(GH) |
|
Ding, W.W., Wang, Y.M., Chen, H.L., et al., 2004. Deformation characters and its tectonic evolution of the Southwest Taiwan basin. Journal of Zhejiang University (Sciences Edition), 31 (2): 216-220 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285075351_Deformation_characters_and_its_tectonic_evolution_of_the_Southwest_Taiwan_Basin |
|
Du, D.L., 1991. Characteristics of geologic structure and hydrocarbon potential of the Southwest Taiwan basin. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 11(3): 21-33 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ199103003.htm |
|
Fan, W.P., Zheng, L.Q., Gong, J.H., et al., 2007. Forming of mud volcano and relation with hydrocarbon. Turpan-Hami Oil and Gas, 12(1): 43-47 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-THYQ200701010.htm |
|
Gong, Z.S., Li, S.T., 1997. Northern South China Sea continental margin basin analysis and hydrocarbon accumulation. Science Press, Beijing, 1-178 (in Chinese). |
|
Gong, Z.S., Li, S.T., Yang, J.M., et al., 2004. The South China Sea basin, forming the northern continental margin dynamics. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese). |
|
Hao, F., Li, S.T., Dong, W.L., et al., 1998. Abnormal organic-matter maturation in the Yinggehai basin, South China Sea: implications for hydrocarbon expulsion and fluid migration from overpressured systems. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 21(4): 427-444. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-5457.1998.tb00794.x |
|
Hao, F., Li, S.T., Gong, Z.S., et al., 2001. Yingge Sea basin diapiric development of mechanisms and episodic fluid injection. Science in China (Ser. D), 31(6): 471-476 (in Chinese). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zgkx-cd200106005 |
|
He, J.X., Chen, H.L., Chen, G., et al., 1995. Gas reservoir and exploration targets of mud diapir belt, Yinggehai basin. China's Offshore Oil and Gas, 9(3): 157-163 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199503001.htm |
|
He, J.X., Chen, S.H., Yao, Y.J., et al., 2008b. Main genetic types of oil & gas and characteristics of their accumulation and distribution in North Marginal basins, South China Sea. Natural Gas Geoscience, 19(1): 34-40 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
He, J.X., Chen, W.H., Zhong, Q.X., et al., 1994. Yingge Sea basin, mud diapir characteristics and gas exploration orientation. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 21(6): 6-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
He, J.X., Huang, H.Y., Chen, L.C., 1994a. Origin and distribution of mud diapirs in the Yinggehai basin and their relation to the migration and accumulation of natural gas. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 12(3): 120-129 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/289802278_Origin_and_distribution_of_mud_diapirs_in_the_Yinggehai_basin_and_their_relation_to_the_migration_and_accumulation_of_natural_gas |
|
He, J.X., Li, M.X., Chen, W.H., et al., 2000a. Geotemperature field and up-welling action of hot flow body and its relationship with natural gas migration and accumulation in Yinggehai basin. Natural Gas Geoscience, 11(6): 29-43 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
He, J.X., Li, M.X., Huang, B.J., et al., 2000b. The analysis of the oil and gas exploration prospect and the distribution of outflow of oil and gas in the northern slope of the Yinggehai basin. Natural Gas Geoscience, 11(2): 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
He, J.X., Liu, H.L., Yao, Y.J., et al., 2008d. Northern South China Sea marginal basin geology and resources of oil and gas prospects. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing, 1-178 (in Chinese). |
|
He, J.X., Xia, B., Liu, B.M., et al., 2004. Analysis on the upintrusion of thermal fluid and the migration and accumulation rules of natura gas and CO2 in the mud diapirs of the yinggehai basin. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 26(4): 349-358 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_petroleum-geology-experiment_thesis/0201218261633.html |
|
He, J.X., Xia, B., Liu, B.M., et al., 2005b. Origin, migration and accumulation of CO2 in East China and offshore shelf basins. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 32(4): 42-49 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
He, J.X., Xia, B., Wang, Z.X., et al., 2006b. Petroleum geologic characteristics and exploration base of Southwest Taiwan basin in eastern area of continental shelf in northern of the South China Sea. Natural Gas Geoscience, 17(3): 344-350 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
He, J.X., Xia, B., Zhang, S.L., et al., 2005a. Genetic types of carbon dioxide in the terrestrial faulted basins and offshore continental shelf basins in East China. Natural Gas Industry, 25(8): 21-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-TRQG200508006.htm |
|
He, J.X., Xia, B., Zhang, S.L., et al., 2006a. Origin and distribution of mud diapirs in the Yinggehai basin and their relation to the migration and accumulation of natural gas. Geology in China, 33(6): 1336-1344 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/289802278_Origin_and_distribution_of_mud_diapirs_in_the_Yinggehai_basin_and_their_relation_to_the_migration_and_accumulation_of_natural_gas |
|
He, J.X., Xu, R.S., Liu, Q.W., et al., 2008a. Development and evolution of mud diapir and migration and accumulation of natural gas and CO2 in Yinggehai basin. Quaternary Geology & Marine Geology, 28(1): 91-98 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
He, J.X., Yao, Y.J., Liu, H.L., et al., 2008c. Genetic types of natural gas and characteristic of the gas source composition in marginal basins of the northern South China Sea. Chinese Geology, 35(5): 997-1006 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.mendeley.com/catalog/genetic-types-natural-gas-characteristics-gas-source-composition-marginal-basins-northern-south-chin/ |
|
He, J.X., Zan, L.S., Chen, L.C., et al., 1990. Characteristics of mud-mount evolution and oil potential in Yinggehai basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 11(4): 436-445 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199004012.htm |
|
He, J.X., Zan, L.S., Huang, H.Y., et al., 1989. Yinggehai basin, due to their distribution patterns in soil Qiu Cheng. The South China Sea Oil, 6(4): 24-30 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
He, J.X., Zhu, Y.H., Chen, S.H., et al., 2009. Genetic types and mineralization characteristics of gas hydrate and resources potential of northern South China Sea. Natural Gas Geoscience, 20(2): 237-243 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200902013.htm |
|
Sha, Z.B., Zhang, G.X., L, J.Q., et al., 2005. Mud volcano-one live evidence of the existence of gas hydrates. Geological South China Sea, 17(1): 48-56 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-NHDZ200500006.htm |
|
Sun, J.Z., Li, L.B., Yang, S.G., et al., 1995. Evolution of transform-extension Yinggehai basin. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 20(3): 243-249 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX503.001.htm |
|
Sun, Z., Zhong, Z.H., Zhou, D., 2007. The analysis and analogue modeling of the tectonic evolution and strong subsidence in the Yinggehai basin. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 32(3): 347-356 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200703006.htm |
|
Wang, Z.F., He, J.X., Xie, X.N., et al., 2004. Heat flow action and its control on natural gas migration and accumulation in mud-fluid diapir areas in Yinggehai basin. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 29(2): 203-210 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/283411174_Heat_flow_action_and_its_control_on_natural_gas_migration_and_accumulation_in_mud-fluid_diapir_areas_in_Yinggehai_basin |
|
Wang, Z.F., Huang, B.J., 2008. Dongfang 1-1 gas field in the mud diapir belt of the Yinggehai basin, South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 25(4/5): 445-455. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.01.004 |
|
Xie, X.N., Li, S.T., Dong, W.L., et al., 1999. Trace marker of hot fluid flow and their geological implications, a case study of Yinggehai basin. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 24 (2): 183-188 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX902.016.htm |
|
Zeng, W.H., Liu, J.X., 2007. The mud volcano off southwestern Taiwan. Scientific Development, 4(412): 18-25 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2006AGUFMOS33B1705C |
|
Zhang, Q.M., Liu, F.N., Yang, J.H., 1996. Overpressure system and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Yinggehai basin. Chinese offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 10(2): 65-75 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199602000.htm |
|
曹成润, 刘志宏, 2005. 含油气盆地构造分析原理及方法. 吉林: 吉林大学出版社. |
|
丁巍伟, 王渝明, 陈汉林, 等, 2004. 台西南盆地构造特征与演化. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 31(2): 216-220. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-9497.2004.02.023 |
|
杜德莉, 1991. 台西南盆地地质构造特征及油气远景. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 11(3): 21-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ199103003.htm |
|
范卫平, 郑雷清, 龚建华, 等, 2007. 泥火山的形成及其与油气的关系. 吐哈油气, 12(1): 43-47. |
|
龚再升, 李思田, 等, 1997. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地分析与油气聚集. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-178. |
|
龚再升, 李思田, 杨甲明, 等, 2004. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地成藏动力学研究. 北京: 科学出版社. |
|
郝芳, 李思田, 龚再升, 等, 2001. 莺歌海盆地底辟发育机理与流体幕式充注. 中国科学(D辑), 31(6): 471-476. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200106004.htm |
|
何家雄, 陈红莲, 陈刚, 等, 1994b. 莺歌海盆地泥底辟带天然气成藏条件及勘探方向. 中国海上油气(地质), 9(3): 157-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199503001.htm |
|
何家雄, 陈胜红, 姚永坚, 等, 2008b. 南海北部边缘盆地油气主要成因类型及运聚分布特征. 天然气地球科学, 19(1): 34-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200801011.htm |
|
何家雄, 陈伟煌, 钟启祥, 等, 1994b. 莺歌海盆地泥底辟特征及天然气勘探方向. 石油勘探与开发, 21(6): 6-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK406.001.htm |
|
何家雄, 黄火尧, 陈龙操, 1994a. 莺歌海盆地泥底辟发育演化与油气运聚机制. 沉积学报, 12(3): 120-129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB403.014.htm |
|
何家雄, 李明兴, 陈伟煌, 等, 2000a. 莺歌海盆地热流体上侵活动与天然气运聚富集关系探讨. 天然气地球科学, 11(6): 29-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200006005.htm |
|
何家雄, 李明兴, 黄保家, 等, 2000b. 莺歌海盆地北部斜坡带油气苗分布与油气勘探前景剖析. 天然气地球科学, 11(2): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200002000.htm |
|
何家雄, 刘海龄, 姚永坚, 等, 2008d. 南海北部边缘盆地油气地质及资源前景, 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1-178. |
|
何家雄, 夏斌, 刘宝明, 等, 2004. 莺歌海盆地泥底辟热流体上侵活动与天然气及CO2运聚规律剖析. 石油实验地质, 26(4): 349-358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2004.04.008 |
|
何家雄, 夏斌, 刘宝明, 等, 2005b. 中国东部及近海陆架盆地CO2成因及运聚规律与控制因素研究. 石油勘探与开发, 32(4): 42-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200504009.htm |
|
何家雄, 夏斌, 王志欣, 等, 2006b. 南海北部大陆架东区台西南盆地石油地质特征与勘探前景分析. 天然气地球科学, 17(3): 344-350. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200603013.htm |
|
何家雄, 夏斌, 张树林, 等, 2005a. 东部陆相断陷盆地及近海陆架盆地CO2成因类型. 天然气工业, 25(8): 21-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200508006.htm |
|
何家雄, 夏斌, 张树林, 等, 2006a. 莺歌海盆地泥底辟成因、展布特征及其与天然气运聚成藏关系. 中国地质, 33(6): 1336-1344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200606018.htm |
|
何家雄, 徐瑞松, 刘全稳, 等, 2008a. 莺歌海盆地泥底辟发育演化与天然气及CO2运聚成藏规律研究. 第四纪地质与海洋地质, 28(1): 91-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200801015.htm |
|
何家雄, 姚永坚, 刘海龄, 等, 2008c. 南海北部边缘盆地天然气成因类型及气源构成特点. 中国地质, 35(5): 997-1006. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200805021.htm |
|
何家雄, 昝立声, 陈龙操, 等, 1990. 莺歌海盆地泥丘发育特征与油气远景. 石油与天然气地质, 11(4): 436-445. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199004012.htm |
|
何家雄, 昝立声, 黄火尧, 等, 1989. 莺歌海盆地泥丘成因及其分布特征. 南海石油, 6(4): 24-30. |
|
何家雄, 祝有海, 陈胜红, 等, 2009. 天然气水合物成因类型及成矿特征与南海北部资源前景. 天然气地球科学, 20(2): 237-243. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200902013.htm |
|
解习农, 李思田, 董伟良, 等, 1999. 热流体活动示踪标志及其地质意义——以莺歌海盆地为例. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 24(2): 183-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX902.016.htm |
|
沙志彬, 张光学, 梁金强, 等, 2005. 泥火山——天然气水合物存在的活证据. 南海地质研究, 17(1): 48-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHDZ200500006.htm |
|
孙家振, 李兰斌, 杨士恭, 等, 1995. 转换-伸展盆地-莺歌海的演化. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 20(3): 243-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX503.001.htm |
|
孙珍, 钟志洪, 周蒂, 2007. 莺歌海盆地构造演化与强烈沉降机制的分析和模拟. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 32(3): 347-356. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200703006.htm |
|
王振峰, 何家雄, 解习农, 2004. 莺歌海盆地泥-流体底辟带热流体活动对天然气运聚成藏的控制作用. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 29(2): 203-210. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200402013.htm |
|
曾威豪, 刘家瑄, 2007. 台湾西南海域的泥火山. 科学发展, 4(412): 18-25. |
|
张启明, 刘福宁, 杨计海, 1996. 莺歌海盆地超压体系与油气聚集. 中国海上油气(地质), 10(2): 65-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199602000.htm |









 下载:
下载: