Nanoscale Fluid-Rock Interaction in CO2 Geological Storage
-
摘要: 大气中持续增长的CO2是引起"温室效应"的主要原因, 并给全球带来越来越严重的环境问题.消减CO2是人类共同面临的生存挑战, 也是技术难题.在全球碳循环过程中, 有多种调节方法可以减少大气中CO2含量, 但目前只有地质储存被认为是可快速实施、见效明显的CO2减排方式.CO2流体-岩石相互作用是地质储存的核心科学问题, 其直接影响CO2灌注效率、储存容量和效率、储存安全性和稳定性.纳米尺度的物质拥有奇异特性, 具有很大的表面原子数和表面能.CO2流体-岩石相互作用存在多种尺度变化, 由于微纳岩矿的表面原子数和表面能与离子、晶体之间的巨大差异, 纳米尺度的CO2流体-岩石相互作用的速度和效率远远大于其他尺度.因此, 急需开展CO2流体-岩石相互作用纳米尺度变化的主要控制因素与变化机理的研究; 通过CO2地质储存研究, 寻找、制备天然微纳岩矿以用于经济高效地捕获、储存和转化CO2, 推动CO2减排理论和技术的发展.Abstract: Continuous growth of atmospheric CO2 concentration believed to be the major reason for "greenhouse effect", has become a global environmental issue in recent years. CO2 reduction is a challenge not only for the survival of human society, but also for the development of geosciences and technology. Although there are a variety of approaches to reduce atmospheric CO2, geological storage is considered as an effective way to reduce CO2. Understanding CO2 fluid-rock interaction is the key to successful geological storage of CO2, because of its effects on CO2 injection efficiency, and storage capacity, efficiency, safety and stability of the reservoir. Nanoscale materials have extraordinary properties with their abnormally huge amount of surface atoms and surface energy. CO2 fluid-rock interaction has multi-scale effect, with much higher rate and efficiency at nanoscale than those at other scales, due to substantial differences in surface atoms and surface energy. Therefore, it is critical to reveal the major factors and mechanisms of nanoscale interaction between CO2 fluid and rock to find some natural cost-effective nano-minerals for capture, storage and conversion of CO2.
-
Key words:
- CO2 /
- geological storage /
- nanoscale /
- fluid-rock interaction /
- environmental engineering
-
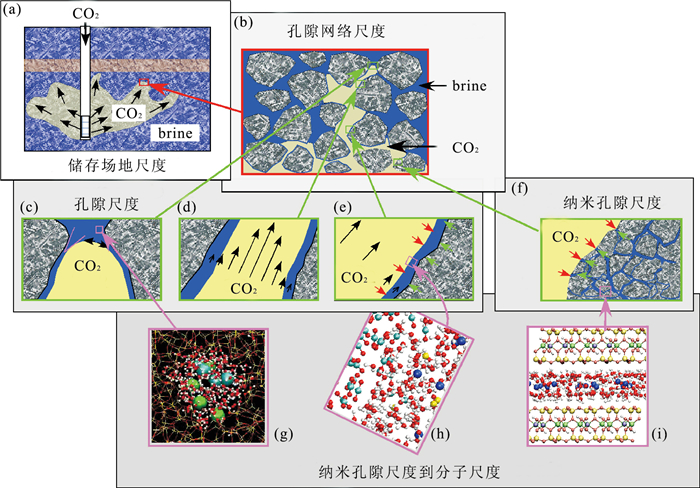
图 1 地质储存中CO2流体-岩石相互作用示意(据Tokunaga and Wan, 2001)
a.储存场地尺度CO2的分布;b.孔隙网络尺度CO2的扩散;c.孔尺度的毛细作用;d.多相流;e.CO2-H2O界面的扩散和反应;f、g、h、i.纳米孔隙和分子尺度CO2流体-岩石相互作用
Fig. 1. CO2-fluid and rock interaction in geologic storage
表 1 挪威、美国和加拿大主要CO2地质储存实际工程
Table 1. The main projects of geologic storage of carbon dioxide in different reservoirs in Norway, USA and Canada
储存类型 工程起始时间 储存地点 储存效果 深层含水层 1996年8月 挪威北海海床 年注入量100万t,占挪威CO2年排放量的3%,目前正在开展对储存容量、储存机制的评估,以及储层中CO2的运移模拟和相关的监测方法研究 2002年11月 美国西维吉尼亚 该项目最需要解决的问题是咸水层以上的岩石是否足够结实,从而保证CO2不会逐渐泄漏 CO2-EOR 2000年10月 加拿大维宾油田 可储存未来25年加拿大所有省份所排放的二氧化碳,同时油田产油量也可增加50% CO2-ECBM 2004年 美国San Juan盆地 初期结果表明这一工艺可以使甲烷回收率增加约75% 表 2 目前各国开展的CO2地质储存系统研究工作
Table 2. The systems researches of CO2 geologic storage in some countries
国家 资助者 主要研究者 主要目的 欧洲各国 欧盟“GESTCO”计划 欧洲的8个地质调查部门(丹麦、英国、荷兰、挪威、德国、希腊、比利时和法国) 对全欧的潜在储存量进行评估 丹麦等4个国家 欧盟“CO2STORE”研究项目 开展CO2储集区地质特征、地球化学模拟、CO2在储层长期储存的行为等研究 美国 美国能源部 Sandia、Lawrence Berkeley等国家实验室及犹他州大学等多家高校联合开展研究 通过试验、模拟和工程等方面的实际工作对CO2地下储存技术在实施过程中可能遇到的问题开展全面的研究 加拿大 加拿大政府,国际能源署“SACS”,国际合作研究计划 阿尔伯达研究院国际共同研究体 通过计算机模拟分析了二氧化碳在含水层的流动、扩散及其与矿物的化学反应过程,明确了二氧化碳的储存机制;采用多种物理和地球化学探查方法在加拿大的维宾油田监测二氧化碳促进石油开采的过程 澳大利亚 “GEODISC”计划 澳大利亚联邦科学和工业组织石油资源研究院及多家大学和研究机构共同参与 寻找适合的储存场所和开发相关的调查评价技术 日本 经济产业省和新能源技术综合开发机构 地球环境产业技术研究机构会同十几所大学共同实施 通过综合研究确立适合日本自然和经济技术条件的分离概念 -
Albritton, D.L., Meira Filho, L.G., Cubasch, U., et al., 2001. Climate change 2001: the scientific basis, contributions of working group Ⅰ to the third assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, UK. Bachu, S., 2002. Sequestration of CO2 in geological media in response to climate change: road map for site selection using the transform of the geological space into the CO2 phase space. Energy Conversion and Management, 43(1): 87-102. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(01)00009-7 Bachu, S., Gunter, W.D., Perkins, E.H., 1996. Carbon dioxide disposal. In: Hitchon, B., ed., Aquifer disposal of carbon dioxide: hydrodynamic and mineral trapping-proof on concept. Geosciences Publishing Ltd. Sherwood Park, Alberta, Canada. Baker, J.C., Bai, G.P., Hamilton, P.J., et al., 1995. Continental scale magmatic carbon dioxide seepage recorded by dawsonite in the Bowen-Gunnedah-Sydney basin system, eastern Australia. Journal of Sediment Research, 65(3): 522-530. doi: 10.1306/D4268117-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D Blunt, M., Fayers, F.J., Orr Jr, F.M., 1993. Carbon dioxide in enhanced oil-recovery. Energy Conversion and Management, 34(9-11): 1197-1204. doi: 10.1016/0196-8904(93)90069-M Bruant, R.G. Jr., Guswa, A.J., Celia, M.A., et al., 2002. Safe storage of CO2 in deep saline aquifers. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(11): 240-245. doi: 10.1021/es0223325 Celia, M.A., 2002. How hydrogeology can save the world. Ground Water, 40(2): 113. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2002.tb02495.x Chesworth, W., 1971. Laboratory synthesis of dawsonite and its natural occurrences. National Physical Science, 231: 40-41. doi: 10.1038/physci231040a0 Chiquet, P., Daridon, J.L., Broseta, D., et al., 2007. CO2/water interfacial tensions under pressure and temperature conditions of CO2 geological storage. Energy Conversion and Management, 48(3): 736-744. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2006.09.011 Chudaev, O.V., Schartzev, S.L., Chudaeva, V.A., et al., 2003. Hydrogeology and water chemistry of folded areas in the Siberia and the Far East. Vladivostok: Dalnauka. Davison, J., Freund, P., Smith, A., 2001. Putting carbon back in the ground. IEA greenhouse gas R & D programme, Cheltenham, United Kingdom. Falkowski, P., Scholes, R.J., Boyle, E., et al., 2000. The global carbon cycle: a test of our knowledge of earth as a system. Science, 290(5490): 291-296. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5490.291 Gale, J., 2004. Geological storage of CO2: what do we know, where are the gaps and what more needs to be done?Energy, 29(9-10): 1329-1338. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2004.03.068 Gao, Y.Q., Liu, L., 2007. Basic characteristics of dawsonite-bearing sandstone and its geologic significance. Geological Review, 53(1): 104-110 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313749939_Basic_characteristics_of_dawsonite-bearing_sandstone_and_its_geologic_significance Gentzis, T., 2000. Subsurface sequestration of carbon dioxide—an overview from an Alberta (Canada) perspective. International Journal of Coal Geology, 43(1-4): 287-305. doi: 10.1016/S0166-5162(99)00064-6 Gherardi, F., Xu, T.F., Pruess, K., 2007. Numerical modeling of self-limiting and self-enhancing caprock alteration induced by CO2 storage in a depleted gas reservoir. Chemical Geology, 244(1-2): 103-129. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.06.009 Goldberg, P., Chen, Z.Y., O'Connor, W., et al., 2001. CO2 mineral sequestration studies in US. Journal of Energy and Environmental Research, 1(1): 117-126. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284697539_CO2_mineral_sequestration_studies_in_US Grimston, M.C., Karakoussis, V., Fouquet, R., et al., 2001. The European and global potential of carbon dioxide sequestration in tackling climate change. Climate Policy, 1(2): 155-171. doi: 10.1016/S1469-3062(01)00002-X Gu, L.B., Li, Z.P., Hou, X.L., 2008. Existing state about geological storage of carbon dioxide. Geological Science and Technology Information, 27(4): 80-84 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200804015.htm Hendriks, C.A., Blok, K., 1993. Underground storage of carbon dioxide. Energy Conversion and Management, 34(9-11): 949-957. doi: 10.1016/0196-8904(93)90041-8 Hendriks, C.A., Blok, K., 1995. Underground storage of carbon dioxide. Energy Conversion and Management, 36(6-9): 539-542. doi: 10.1016/0196-8904(95)00062-1 Hitchon, B., 1996. Aquifer disposal of carbon dioxide: hydrodynamic and mineral trapping-proof of concept. Geoscience Publishing Ltd., Sherwood Park, Alberta. Holloway, S., 1997. An overview of the underground disposal of carbon dioxide. Energy Conversion and Management, 38(Suppl. ): 193-198. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(96)00268-3 Holloway, S., 2005. Underground sequestration of carbon dioxide—a viable greenhouse gas mitigation option. Energy, 30(11-12): 2318-2333. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2003.10.023 Huggins, C.W., Green, T.E., Turner, T.L., 1973. Evaluation of methods for determining nahcolite and dawsonite in oil shales. Report of investigations (United States, Bureau of Mines), 25. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/236363438_Evaluation_of_methods_for_determining_nahcolite_and_dawsonite_in_oil_shales IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), 2005. Special report on carbon dioxide capture and storage. http//www. ipcc. ch. Juanes, R., Spiteri, E.J., Orr Jr, F.M., et al., 2006. Impact of relative permeability hysteresis on geological CO2 storage. Water Resources Research, 42, W12418. doi: 10.1029/2005WR004806 Kaszuba, J.P., Janecky, D.R., Snow, M.G., 2003. Carbon dioxide reaction processes in a model brine aquifer at 200 ℃ and 200 bars: implications for geologic sequestration of carbon. Applied Geochemistry, 18(7): 1065-1080. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00239-1 Kaszuba, J.P., Williams, L.L., Janecky, D.R., et al., 2006. Immiscible CO2-H2O fluids in the shallow crust. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 7(10), Q100003. doi: 10.1029/2005GC001107 Ketzer, J.M., Carpentier, B., Le Gallo, Y., et al., 2005. Geological sequestration of CO2 in mature hydrocarbon fields. Basin and reservoir numerical modeling of the forties field, North Sea. Oil & Gas Science and Technology-Rev. IFP, 60(2): 259-273. doi: 10.2516/ogst:2005016 Kharaka, Y.K., Thordsen, J.J., Hovorka, S.D., et al., 2009. Potential environmental issues of CO2 storage in deep saline aquifers: geochemial results from the Frio-Ⅰ Brine Pilot test, Texas, USA. Applied Geochemistry, 24(6): 1106-1112. doi: 10.1016/j.apgechem.2009.02.010 Li, X.C., Liu, Y.F., Bai, B., et al., 2006. Ranking and screening of CO2 saline aquifer storage zones in China. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 25(5): 963-968 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&cmd=prlinks&retmode=ref&id=21866545 Liu, L.H., Suto, Y., Bignall, G., et al., 2003. CO2 injection to granite and sandstone in experimental rock/hot water systems. Energy Conversion and Management, 44(9): 1399-1410. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(02)00160-7 Liu, Y.F., Li, X.C., Bai, B., 2005. Preliminary estimation of CO2 storage capacity of coalbeds in China. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 24(16): 2947-2952 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=18046691 Liu, Y.F., Li, X.C., Fang, Z.M., et al., 2006. Preliminary estimation of CO2 storage capacity in gas fields in China. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 27(12): 2277-2281 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTLX200612036.htm Mao, X.M., Wang, Y.X., Chudaev, O.V., et al., 2009. Geochemical evidences of gas sources of CO2-rich cold springs from Wudalianchi, northeastern China. Journal of Earth Science, 20(6): 959-970. doi: 10.1007/s12583-009-0081-5 Pruess, K., Spycher, N., 2007. ECO2N—a fluid property module for the TOUGH2 code for studies of CO2 storage in saline aquifers. Energy Conversion and Management, 48(6): 1761-1767. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2007.01.016 Sun, S., 2006. Geological problems of CO2 underground storage and its significance on mitigation climate change. China Basic Science, 3: 17-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJB200603007.htm Tokunaga, T.K., Wan, J.M., 1997. Water film flow along fracture surfaces of porous rock. Water Resources Research, 33(6): 1287-1295. doi: 10.1029/97WR00473 Tokunaga, T.K., Wan, J.M., 2001. Approximate boundaries between different flow regimes in fractured rocks. Water Resources Research, 37(8), 2103-2111. doi: 10.1029/2001WR000245 U.S. Department of Energy, 1999. Carbon sequestration research and development. National Technical Information, 1: 1-24. http://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc739790/ Wigley, T.M.L., Richels, R., Edmonds, J.A., 1996. Economic and environmental choices in the stabilization of atmospheric CO2 concentrations. Nature, 379: 240-243. doi: 10.1038/379240a0 Xu, T.F., Apps, J.A., Pruess, K., 2004. Numerical simulation of CO2 disposal by mineral trapping in deep aquifers. Applied Geochemistry, 19(6): 917-936. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.11.003 Xu, T.F., Apps, J.A., Pruess, K., 2005. Mineral sequestration of carbon dioxide in a sandstone-shale system. Chemical Geology, 217(3-4): 295-318. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.12.015 Zerai, B., Saylor, B.Z., Matisoff, G., 2006. Computer simulation of CO2 trapped through mineral precipitation in the Rose Run Sandstone, Ohio. Applied Geochemistry, 21(2): 223-240. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.11.002 Zhang, H.T., Wen, D.G., Li, Y.L., et al., 2005. Conditions for CO2 geological sequestration in China and some suggestions. Regional Geology of China, 24(12): 1107-1110 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=20885238 Zhang, X.F., Wen, Z.Y., Gu, Z.H., et al., 2004. Hydrothermal synthesis and thermodynamic analysis of dawsonite-type compounds. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 177(3): 849-855. doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2003.09.019 高玉巧, 刘立, 2007. 含片钠铝石砂岩的基本特征及地质意义. 地质论评, 53(1): 104-110. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2007.01.014 谷丽冰, 李治平, 侯秀林, 2008. 二氧化碳地质埋存研究进展. 地质科技情报, 27(4): 80-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2008.04.014 李小春, 刘延锋, 白冰, 等, 2006. 中国深部咸水含水层CO2储存优先区域选择. 岩石力学与工程学报, 25(5): 963-968. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.05.015 刘延锋, 李小春, 白冰, 2005. 中国CO2煤层储存容量初步评价. 岩石力学与工程学报, 24(16): 2947-2952. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.16.023 刘延锋, 李小春, 方志明, 等, 2006. 中国天然气田CO2储存容量初步评估. 岩土力学, 27(12): 2277-2281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.12.037 孙枢, 2006. CO2地下封存的地质学问题及其对减缓气候变化的意义. 中国基础科学, 3: 17-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJB200603007.htm 张洪涛, 文冬光, 李义连, 等, 2005. 中国CO2地质埋存条件分析及有关建议. 地质通报, 24(12): 1107-1110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2005.12.004 -









 下载:
下载:

