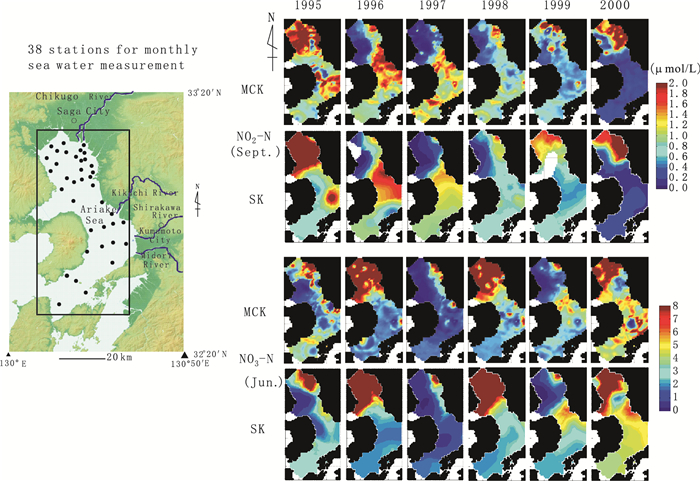
Spatial Modeling Techniques for Characterizing Geomaterials: Deterministic vs.Stochastic Modeling for Single-Variable and Multivariate Analyses
-
-
关键词:
Abstract: Sample data in the Earth and environmental sciences are limited in quantity and sampling location and therefore, sophisticated spatial modeling techniques are indispensable for accurate imaging of complicated structures and properties of geomaterials. This paper presents several effective methods that are grouped into two categories depending on the nature of regionalized data used. Type I data originate from plural populations and type II data satisfy the prerequisite of stationarity and have distinct spatial correlations. For the type I data, three methods are shown to be effective and demonstrated to produce plausible results: (1) a spline-based method, (2) a combination of a spline-based method with a stochastic simulation, and (3) a neural network method. Geostatistics proves to be a powerful tool for type II data. Three new approaches of geostatistics are presented with case studies: an application to directional data such as fracture, multi-scale modeling that incorporates a scaling law, and space-time joint analysis for multivariate data. Methods for improving the contribution of such spatial modeling to Earth and environmental sciences are also discussed and future important problems to be solved are summarized.-
Key words:
- geostatistics /
- spline /
- neural network /
- geological modeling /
- mineral resources /
- fracture distribution /
- water environment
-
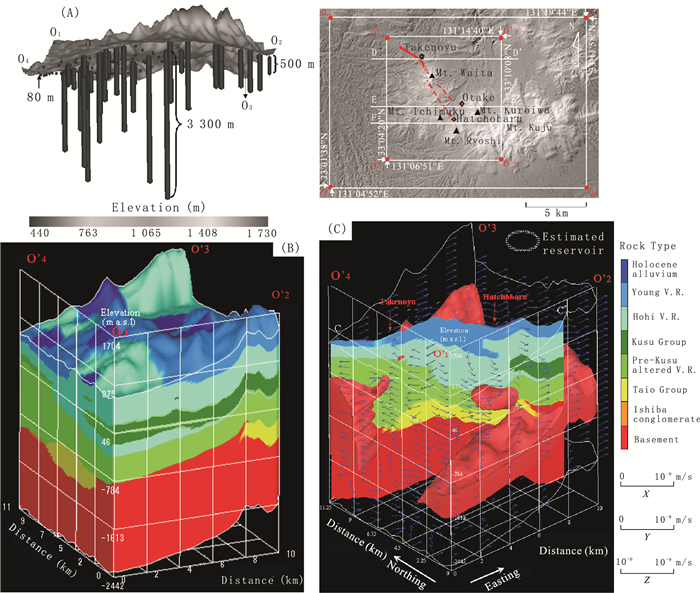
Fig. 1. (A) Hohi geothermal region in central Kyushu, Southwest Japan, showing topography, location of wells, and the lengths of the downhole logs used in the study.Depths range from 80 to 3 300 m. (B) Three-dimensional geological model of the Hohi geothermal region constructed using the OPTSIM method and showing the eight main rock types.The topography of the ground surface is shown.V.R.: volcanic rock. (C) Integration of the temperature model, geological model, and large-magnitude fluid flow velocity vectors.The geological model and vectors are overlaid onto the high-temperature zones (>150 ℃).Two ovals circled represent the geothermal reservoirs inferred from the relationship between the temperature and the geological models
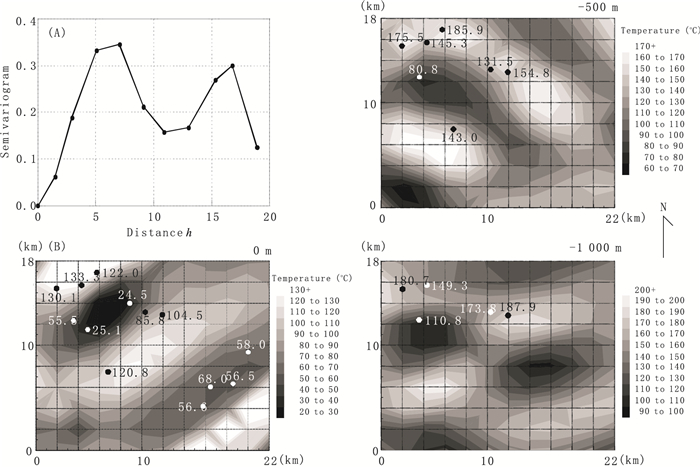
Fig. 2. (A) Semivariogram constructed from the indicator values, 0 for conductive type and 1 for convective type, assigned to each borehole site depending on the temperature profile in the Hohi geothermal region.(B) Horizontal temperature-distributions estimated by neural kriging at 0 m, -500 m, and -1 000 m levels.Values indicate temperatures retrieved at each borehole site
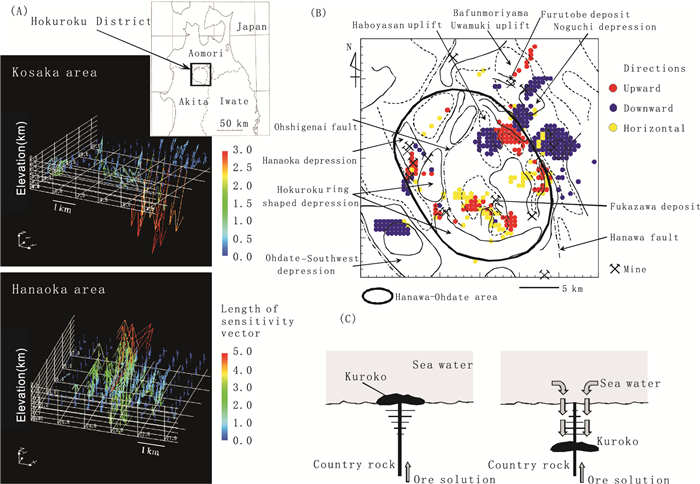
Fig. 3. (A) Distributions of sensitivity vectors for Zn in the Kuroko-mine areas in the Hokuroku District, northern Japan.(B) Distribution of estimation points with large sensitivity vectors.The colors of the points represent the directions of the sensitivity vectors.(C) Schematic model of the occurrence of Kuroko ores, by mixing ore solutions with sea water, for upward vector (left) and downward vector (right)
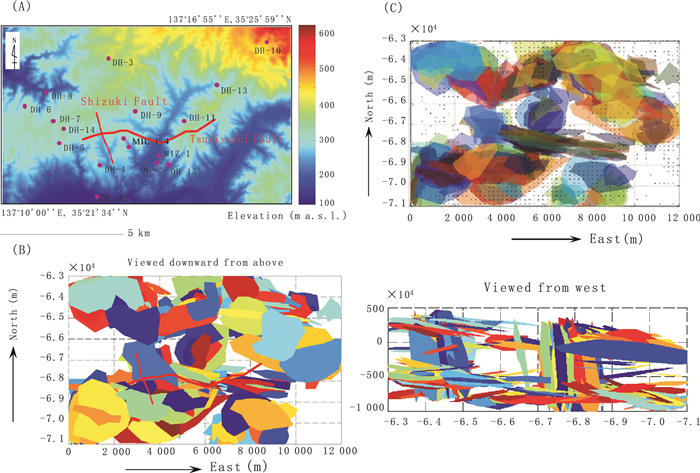
Fig. 4. (A) Topography of the study area (Tono District, central Japan) and the arrangement of 19 sites of deep boreholes ranging 500 to 1 000 m depth.(B) Perspective views showing the distribution pattern of simulated continuous fractures composed of fifty or more facets.(C) Superimposition of the zones of large hydraulic conductivity of more than 10-5 cm/s onto the continuous simulated fractures
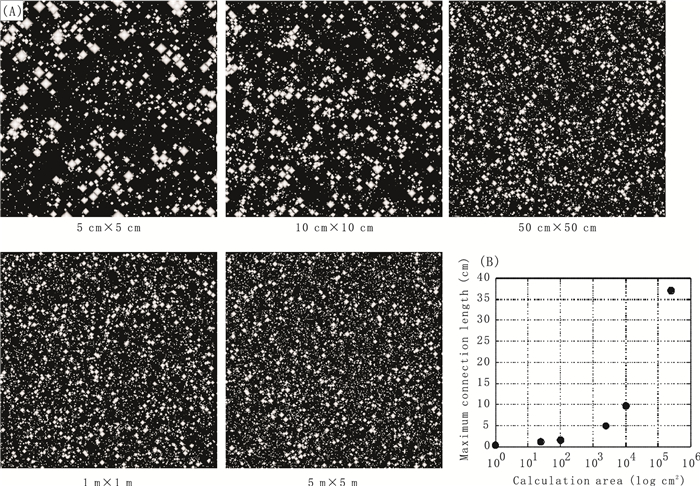
Fig. 5. (A) Pore simulation results for different area sizes under conditions of porosity 40% by simulated annealing with scaling laws on size and the spatial correlation of pores.(B) Relationship between the calculation of area size and the maximum connection length of pores from pore simulation results for porosity 40%
-
Ahmed, S., Marsily, G.D., 1987. Comparison of geostatistical methods for estimating transmissivity using data on transmissivity and specific capacity. Water Resources Research, 23(9): 1717-1737. doi: 10.1029/WR023i009p01717 Bonnet, E., Bour, O., Odling, N.E., et al., 2001. Scaling of fracture systems in geological media. Reviews of Geophysics, 39(3): 347-383. doi: 10.1029/1999RG000074 Briggs, I.C., 1974. Machine contouring using minimum curvature. Geophysics, 39(1): 39-48. doi: 10.1190/1.1440410 Cacas, M.C., Ledoux, E., DeMarsily, G., et al., 1990. Modelling fracture flow with a stochastic discrete fracture network: calibration and validation: 1. The flow model. Water Resources Research, 26(3): 479-489. doi: 10.1029/WR026i003p00491/pdf Caers, J., Zhang, T., 2005. Multiple-point geostatistics: a quantitative vehicle for integrating geological analogs into multiple reservoir model. AAPG Memoir, 80: 383-394. Casanova, P.G., Alvarez, R., 1985. Splines in geophysics. Geophysics, 50(12): 2831-2848. doi: 10.1190/1.1441903 Chaplot, V., Darboux, F., Bourennane, H., et al., 2006. Accuracy of interpolation techniques for the derivation of digital elevation models in relation to landform types and data density. Geomorphology, 77(1-2): 126-141. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2005.12.010 Chilès, J.P., 1988. Fractal and geostatistical methods for modeling of a fracture network. Mathematical Geology, 20(6): 631-654. doi: 10.1007/BF00890581 Costa, J.F., Zingano, A.C., Koppe, J.C., 2000. Simulation—an approach to risk analysis in coal mining. Exploration and Mining Geology, 9(1): 43-49. doi: 10.2113/0090043 Cressie, N., Huang, H., 1999. Classes of nonseparable, spatial-temporal stationary covariance functions. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 94(448): 1330-1340. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1999.10473885 Daïan, J.F., Fernandes, C.P., Philippi, P.C., et al., 2004.3D reconstitution of porous media from image processing data using a multiscale percolation system. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 42(1): 15-28. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920410503002031 de Kemp, E.A., 2000.3-D visualization of structural field data: examples from the Archean Caopatina Formation. Computers & Geosciences, 26 (5): 509-530. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300499001429 de Iaco, S., Myers, E.D., Posa, D., 2002. Nonseparable space-time covariance models: some parametric families. Mathematical Geology, 34(1): 23-42. doi: 10.1023/A:1014075310344 de Iaco, S., Myers, E.D., Posa, D., 2003. The linear coregionalization model and the product-sum space-time variogram. Mathematical Geology, 35(1): 25-38. doi: 10.1023/A:1022425111459 Dekking, M., Elfeki, A., Kraaikamp, C., et al., 2001. Multi-scale and multi-resolution stochastic modeling of subsurface heterogeneity by tree-indexed Markov Chains. Computational Geosciences, 5(1): 47-60. doi: 10.1023/A:1011610003277 Gatrell, A., L?y?nen, M., 1998. GIS and health. Taylor & Francis, London, 230. Gómez-Hernández, J.J., Srivastava, R.M., 1990. ISIM3D: an ANSI-C three-dimensional multiple indicator conditional simulation program. Computers & Geosciences, 16(4): 395-440. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=84572 Heriawan, M.N., Koike, K., 2008a. Identifying spatial heterogeneity of coal resource quality in a multilayer coal deposit by multivariate geostatistics. International Journal of Coal Geology, 73(3-4): 307-330. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2007.07.005 Heriawan, M.N., Koike, K., 2008b. Uncertainty assessment of coal tonnage by spatial modeling of seam structure and coal quality. International Journal of Coal Geology, 76(3): 217-226. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2008.07.014 Journel, A.G., 1989. Fundamentals of geostatistics in five lessons: short course in geology, Vol. 8. American Geophysical Union, 40, Washington D.C. . Kay, M., Dimitrakopoulos, R., 2000. Integrated interpolation methods for geophysical data: applications to mineral exploration. Natural Resources Research, 9(1): 53-63. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/klu/narr/2000/00000009/00000001/00224167 Kirkpatrick, S., Gelatt, C.D., Vecchi, M.P., 1983. Optimization by simulated annealing. Science, 4598: 671-680. http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/open-access_resources_thesis/0100057209782.html Koike, K., Gu, B., Ohmi, M., 1998a. Three-dimensional distribution analysis of phosphorus content of limestone through a combination of geostatistics and artificial neural network. Nonrenewable Resources, 7(3): 197-210. doi: 10.1007/BF02767670 Koike, K., Shiraishi, Y., Verdeja, E., et al., 1998b. Three-dimensional interpolation and lithofacies analysis of granular composition data for earthquake-engineering characterization of shallow soil. Mathematical Geology, 30(6): 733-759. doi: 10.1023/A:1022473320050 Koike, K., Matsuda, S., Gu, B., 2001a. Evaluation of interpolation accuracy of neural kriging with application to temperature-distribution analysis. Mathematical Geology, 33(4): 421-448. doi: 10.1023/A:1011084812324 Koike, K., Sakamoto, H., Ohmi, M., 2001b. Detection and hydrologic modeling of aquifers in unconsolidated alluvial plains through combination of borehole data sets: a case study of the Arao area, Southwest Japan. Engineering Geology, 62(4): 301-317. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00031-X Koike, K., Matsuda, S., Suzuki, T., et al., 2002. Neural network-based estimation of principal metal contents in the Hokuroku district, northern Japan, for exploring Kuroko-type deposits. Natural Resources Research, 11(2): 135-156. doi: 10.1023/A:1015520204066 Koike, K., Fujiyoshi, H., 2003. Spatial modeling of pore distribution in porous media using geostatistics for detecting hydraulic property. In: Saito, T., Murata, S., eds., Environmental rock engineering. A.A. Balkema Publishers, Lisse, 259-264. Koike, K., Matsuda, S., 2005. Spatial modeling of discontinuous geological attributes with geotechnical applications. Engineering Geology, 78(1-2): 143-161. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2004.12.004 Koike, K., Ichikawa, Y., 2006. Spatial correlation structures of fracture systems for identifying a scaling law and modeling fracture distributions. Computers & Geosciences, 32(8): 1079-1095. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300406000318 Koike, K., Matsuda, S., 2006. New indices for characterizing spatial models of ore deposits by the use of a sensitivity vector and influence factor. Mathematical Geology, 38(5): 541-564. doi: 10.1007/s11004-006-9030-3 Koike, K., Liu, C., 2007. Spatial modeling method considering scaling-law with application to pore simulation in porous media. Geoinformatics, 18(3): 159-175 (in Japanese with English abstract). Koike, K., Liu, C., Masoud, A.A., et al., 2009. Large-scale modeling of 3D fracture distributions for hydrogeological characterization. Proceedings iamg09. Stanford Univ., CA, USA. Liu, C., Koike, K., 2007. Extending multivariate space-time geostatistics for environmental data analysis. Mathematical Geology, 39(3): 289-305. doi: 10.1007/s11004-007-9085-9 Long, J.C.S., Gilmour, P., Witherspoon, P.A., 1985. A model for steady fluid flow in random three-dimensional networks of disc-shaped fractures. Water Resources Research, 21(8): 1105-1115. doi: 10.1029/WR021i008p01105 Lu, S., Molz, F.J., Liu, H.H., 2003. An efficient, three-dimensional, anisotropic, fractional Brownian motion and truncated fractional Levy motion simulation algorithm based on successive random additions. Computers & Geosciences, 29(1): 15-25. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300402000730 Magnussen, S., N?sset, E., Wulder, M.A., 2007. Efficient multiresolution spatial predictions for large data arrays. Remote Sensing of Environment, 109(4): 451-463. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2007.01.018 Masoud, A.A., Koike, K., 2009. Spatial quality modeling of the Kaolin resources integrating GIS and geostatistics. Proc. MMIJ Annual Meeting (2009), Vol. I: 125-126. Matías, J.M., Vaamonde, A., Taboada, J., et al., 2004. Support vector machines and gradient boosting for graphical estimation of a slate deposit. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 18(5): 309-323. doi: 10.1007/s00477-004-0185-5 Matsuda, S., Koike, K., 2003. Sensitivity analysis of a feedforward neural network for considering genetic mechanisms of Kuroko deposits. Natural Resources Research, 12(4): 291-301. doi: 10.1023/B:NARR.0000007807.14126.a2 Merwade, V., 2009. Effect of spatial trends on interpolation of river bathymetry. Journal of Hydrology, 371(1-4): 169-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.03.026 Mitasova, H., Mitas, L., 1993. Interpolation by regularized spline with tension: I. theory and implementation. Mathematical Geology, 25(6): 641-655. doi: 10.1007/BF00893171 Palmer, D.J., H?ck, B.K., Kimberley, M.O., et al., 2009. Comparison of spatial prediction techniques for developing Pinus radiata productivity surfaces across New Zealand. Forest Ecology and Management, 258(9): 2046-2055. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2009.07.057 Pardo-Igúzquiza, E., Dowd, P.A., 2002. FACTOR2D: a computer program for factorial cokriging. Computers & Geosciences, 28(8): 857-875. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300402000031 Pardo-Igúzquiza, E., Atkinson, P.M., 2007. Modelling the semivariograms and cross-semivariograms required in downscaling cokriging by numerical convolution-deconvolution. Computers & Geosciences, 33(10): 1273-1284. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2007.05.004 Rizzo, D.M., Dougherty, D.E., 1994. Characterization of aquifer properties using artificial neural networks: neural kriging. Water Resources Research, 30 (2): 483-497. doi: 10.1029/93WR02477 Robinson, T.P., Metternicht, G., 2005. Comparing the performance of techniques to improve the quality of yield maps. Agricultural Systems, 85(1): 19-41. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2004.07.010 Robinson, T.P., Metternicht, G., 2006. Testing the performance of spatial interpolation techniques for mapping soil properties. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 50(2): 97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2005.07.003 Saepuloh, A., Koike, K., 2009. Detailed mapping of pyroclastic flow deposits by SAR data processing for an active volcano in the Torrid zone. In: Proceeding of International Conference on Earth and Space Sciences and Engineering 2009 (ICESSE 2009). Tokyo, Japan, 270-274. Sahimi, M., Mehrabi, A.R., 1999. Percolation and flow in geological formations: upscaling from microscopic to megascopic scales. Physica A, 266(1-4): 136-152. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4371(98)00586-X Sahimi, M., 2000. Fractal-wavelet neural-network approach to characterization and upscaling of fractured reservoirs. Computers & Geosciences, 26(8): 877-905. doi: 10.5555/351914.351917 Salu, Y., Tilton, J., 1993. Classification of miltispectal image data by the binary diamond neural network and by nonparametric, pixel-by-pixel-methods. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 31(3): 606-617. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/30019684845 Samanta, B., Ganguli, R., Bandopadhyay, S., 2005. Comparing the predictive performance of neural networks with ordinary kriging in a bauxite deposit. Transactions of the Institutions of Mining and Metallurgy, Section A: Mining Technology, 114(3): A129-A139. doi: 10.1179/037178405X53980 Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., et al., eds., 2007. Climate change 2007—the physical science basis, contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC. Cambridge University Press, New York, 996. Strebelle, S., 2002. Conditional simulation of complex geological structures using multiple-point statistics. Mathematical Geology, 34(1): 1-21. doi: 10.1023/A:1014009426274 Sun, Y., Kang, S., Li, F., et al., 2009. Comparison of interpolation methods for depth to groundwater and its temporal and spatial variations in the Minqin oasis of Northwest China. Environmental Modelling & Software, 24(10): 1163-1170. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20133063655.html Tadakuma, N., Koike, K., Asaue, H., 2010.3D temperature modeling over Kyushu Island (SW Japan) and its characterization from geological structures. Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2010, Bali, Indonesia. Paper Number 1539. Teng, Y., Koike, K., 2007. Three-dimensional imaging of a geothermal system using temperature and geological models derived from a well-log dataset. Geothermics, 36(6): 518-538. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2007.07.006 Tran, N.H., Chen, Z., Rahman, S.S., 2006. Integrated conditional global optimisation for discrete fracture network modeling. Computers & Geosciences, 32(1): 17-27. van der Meer, F., 1994. Sequential indicator conditional simulation and indicator kriging applied to discrimination of dolomitization in GER 63-channel imaging spectrometer data. Nonrenewable Resources, 3(2): 146-164. doi: 10.1007/BF02286439 Weissmann, G.S., Carle, S.F., Fogg, G.E., 1999. Three-dimensional hydrofacies modeling based on soil surveys and transition probability geostatistics. Water Resources Research, 35: 1761-1770. doi: 10.1029/1999WR900048 Wolf, D.J., Withers, K.D., Burnaman, M.D., 1994. Integration of well and seismic data using geostatistics. In: Yarus, J.M., Chambers, R.L., eds., Stochastic modeling and geostatistics. AAPG, Tulsa, 177-199. Yamamoto, J.K., 2005. Correcting the smoothing effect of ordinary kriging estimates. Mathematical Geology, 37(1): 69-94. doi: 10.1007/s11004-005-8748-7 Zimmerman, D., Pavlik, C., Ruggles, A., et al., 1999. An experimental comparison of ordinary and universal kriging and inverse distance weighting. Mathematical Geology, 31(4): 375-390. doi: 10.1023/A:1007586507433 Zhu, H., Journel, A., 1993. Formatting and integrating soft data: stochastic imaging via the Markov-Bayes algorithm. In: Soares A., ed., Geostatistics Toria'92. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1-12. -









 下载:
下载: