Porphyry Ore Deposits: Important Study Subjects of Nontraditional Mineral Resources
-
摘要: 多年来, 斑岩型矿床在传统意义上被认为是铜和钼的主要来源.然而, 斑岩型矿床成岩成矿地质条件复杂, 矿化类型丰富, 尤其是对一些大型-超大型斑岩矿床, 均为多元素综合性的巨型矿床, 除传统意义上的铜、钼等矿产外, 非传统矿产的成矿-找矿潜力巨大, 包括: 金、银、锡、钨、铋、铅、锌、铼、铀、钴、硫、硒、碲、铂族元素、磁铁矿等, 金红石和稀有金属如钽、铌等也值得关注.开展斑岩型矿床成岩成矿地质背景、矿床地质特征与非传统矿产矿化富集分布规律研究, 总结斑岩型矿床非传统矿产资源潜力预测评价标志, 指导找矿预测与资源潜力评价, 具有重要的理论价值和现实意义.Abstract: For many years, porphyry ore deposits have been regarded as the primary sources of the Cu and Mo in a traditional way. However, the geologic conditions of the diagenesis and metallogenesis of the porphyry ore deposits are complex with various mineralization types. Some of the large-superlarge deposits are multielemental and comprehensive. In addition to the Cu, Mo porphyry ore deposits, the metallogenesis and prospecting on nontraditional resources have great potential, including Au, Ag, Sn, W, Bi, Pb, Zn, Re, U, Co, S, Se, Te, PGE, magnetite, etc; rutile and rare metals, such as Ta, Nb are also worth paying attention to. It is of important theoretical value and practical significance to study the diagenesis and metallogenesis of geological background, geological characteristics, mineralization of distribution and the enrichment of a nontraditional view on the porphyry ore deposits; it is meaningful to summarize the indicator of prognosis and assessment on the nontraditional mineral resources, and to guide the prospecting and resource potential assessment on the porphyry ore deposits.
-
表 1 多宝山等斑岩型矿床中辉钼矿的Re、Os含量
Table 1. Re, Os contents in the porphyry deposits of Duobaoshan etc.
矿床 样号 样重(mg) Re(μg/g) 187Re(μg/g) 187Os(ng/g) 资料来源 多宝山铜矿 Du-9 9 567±19 355±12 3 044±47 赵一鸣等(1997) Du-20 13.8 537.9±25 336.74±1.59 2 824±26 D865 18.6 303.2±1.5 189.81±0.95 1 586.6±7.1 铜山铜矿 832~860 9 822±21 515±13 4 288±50 832~2 11.3 497±6 311±4 2 434±67 乌奴格吐山铜矿 W-48 12.46 50.9±0.4 31.9±0.3 81±9 金堆城钼矿 J82-1 85 12.9±0.4 8.1±0.3 17.2±0.7 黄典豪等(1994) J82-9 150 19.7±0.5 12.3±0.3 26.4±0.4 J82-0 498~512 15.8±0.5 9.9±0.3 22.6±0.4 表 2 滇西北喜山期富碱斑岩成矿专属性与成矿多样性特征
Table 2. The metallogenic relation and mineralizing diversity of alkali rich porphyry in Xishan period in Northwest of Yunnan Province, China
系列 亚系列 矿床类型 矿产组合 典例 喜山期富碱斑岩成矿系列 花岗斑岩类成矿亚系列 斑岩型、矽卡岩-角岩型、热液(脉)型 主要Cu-Mo-(Au)次要:Pb-Zn-Ag 马厂箐矿区 二长斑岩类成矿亚系列 斑岩型、矽卡岩-角岩型、热液(脉)型 主要:Cu-Au-(Mo)次要:Pb-Zn-Ag 西范坪-罗卜地矿区 正长斑岩类成矿亚系列 斑岩型、矽卡岩-角岩型、热液(脉)型 主要:Pb-Zn-Ag-Au次要:Cu-Mo-W-Fe 北衙矿区、姚安矿区 富钾煌斑岩类成矿亚系列 热液型 主要:Au 老王寨矿区、姚安矿区 碱性杂岩成矿亚系列 岩浆型、热液型 主要:霞石正长岩-磷灰石-稀土-Au 卓潘矿区 -
Armstrong, F.C., 1974. Uranium resources of the future-porphyry uranium depsits, formation of uranium ore deposits. International Atomic Energy Agecy, Vienna, 625-634. Babcock, R.C., Ballantyne, G.H., Phillips, C.H., 1995. Summary of the geology of the Bingham district, Utah. In: Pierce, F.W., Bolm, J.G., eds., Porphyry copper deposits of the American Cordillera. Arizona Geological Society Digest, 20: 316-335. Clark, G.H., 1990. Panguna copper-gold deposit. In: Hughes, F.E., ed., Geology of the mineral deposits of Australia and Papua New Guinea. Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, Australian, 1807-1816. Desborough, G.A., Mihalik, P., 1980. Accessory minerals in the igneous host of molybdenum ore, Henderson Mine, Colorado. US Geological Survey, Open-File Report, 80-661. Desbomugh, G.A., Sharp, W.N., 1978. Tantalum, uranium, and scandium in heavy accessory oxides, Climax molybdenum mine, Climax, Colorado. Economic Geology, 73(8): 1749-1751. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.73.8.1749 Du, Q., Zhao, Y.M., Lu, B.G., et al., 1988. Porphyry Cu (Mo) deposits in Duobaoshan. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, 225-247 (in Chinese). Halter, W., E., Pettke, T., Heinrich, C.A., 2002. The origin of Cu/Au ratios in porphyry-type ore deposits. Science, 296(5574): 1844-1846. doi: 10.1126/science.1070139 Hou, Z.Q., 2004. Porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposits: some new insights and advances. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(1): 131-144 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200401014.htm Hou, Z.Q., Ma, H.W., Za, W.K., et al., 2003. The Himalayan Yulong porphyry copper belt: product of large-scale strike-slip faulting in eastern Tibet. Economic Geology, 98: 125-145. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/247864181_The_Himalayan_Yulong_Porphyry_Copper_Belt_Product_of_Large-Scale_Strike-Slip_Faulting_in_Eastern_Tibet Huang, C.K., Bai, Y., Zhu, Y.S., et al., 2001. Copper deposits in China (Rudin). Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Huang, D.H., Wu, C.Y., Du, A.D., et al., 1994. Re-Os isotope ages of molybdenum deposits in East Qinling and their significance. Mineral Deposits, 12(3): 221-230 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jr, A.A., Hedenquist, J.W., Itaya, T., et al., 1995. Contemporaneous formation of adjacent porphyry and epithermal Cu-Au deposits over 300 ka in northern Luzon, Philippines. Geology, 23(4): 337-340. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1995)?023<0337:CFOAPA>?2.3.CO;2 Li, J.X., Qin, K.Z., Li, G.M., 2006. Basic characteristics of gold-rich porphyry copper deposits and their ore sources and evolving processes of high oxidation magma and ore-forming fluid. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3): 678-688. Li, W.C., Pan, G.T., Hou, Z.Q., et al., 2010. Metallogenic theory and prospecting technology in the polyarc-basin series of "Three-River" region in Southwest China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Macdonald, G.D., Amold, L.C., 1994. Geological and geochemical zoning of the Grasberg igneous complex, Irian Jaya, Indonesia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 50(1-3): 143-178. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(94)90023-X Meldrum, S.J., Aquino, R.S., Gonzales, R.I., et al., 1994. The Batu Hijau porphyry copper-gold deposit, Sumbawa Island, Indonesia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 50(1-3): 203-220. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(94)90025-6 Qu, X.M., Hou, Z.Q., Huang, W., 2001. Is Gangdese porphyry copper belt the second "Yulong" copper belt?Mineral Deposits, 20(4): 355-366 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284665935_Is_Gangdese_porphyry_copper_belt_the_second_Yulong_copper_belt Richard, J.P., Boyce, A.J., Pringle, M.S., 2001. Geologic evolution of the Escondia area, northern Chile: a model for spatial and temporal localization of porphyry Cu mineralization. Economic Geology, 96(2): 271-305. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.96.2.271 Rui, Z.Y., Huang, C.K., Qi, G.M., et al., 1984. Porphyry Cu(Mo) deposits in China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, 242-272 (in Chinese). Rush, P.M., Seegers, H.J., 1990. Ok Tedi copper-gold deposits. In: Hughes, F.E., ed., Geology of the mineral deposits of Australia and Papua New Guinea. Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, Australian, 1747-1754. Sillitoe, R.H., 1983. Unconventional metals in porphyry deposits. In: Shanks, W.C., III, ed., Society of mining engineers. Am. Inst. of Mining, Metallurg. & Petrol. Eng., New York, 207-221. Titey, S.R., Beane, R.E., 1981. Porphyry copper deposits, PartⅠ: Geologic settings, petrology, and tectogensis. Economic Geology, 75: 214-235. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/20000481718 Tooker, E.W., 1990. Gold in the Bingham district, Utah. U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin, 1857 E: 1-16. Wang, D.H., Chen, Y.C., Xu, Y., et al., 2005. Cenozoic mineralization in China (Rudin). Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Xia, B., Chen, G.W., Wang, H., 2003. Analysis of tectonic settings of global superlarge porphyry copper deposits. Science in China (Series D), 46(Suppl. ): 110-122. Zhang, Y.Q., Xie, Y.W., Qiu, H.N., et al., 1998. Shoshonitic series: Sr, Nd, and Pb isotopic compositions of ore bearing porphyry for Yulong copper ore belt in the eastern Xizang (Tibet). Chinese Journal of Geology, 33(3): 359-366 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, P.D., 2003. An introduction to nontraditional mineral resources. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Zhao, Y.M., Zhang, D.Q., 1997. Metallogeny and evaluation of copper-polymetallic deposits in the Dahinggan Mountains and its adjacent regions. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Zheng, M.H., et al., 1993. Principle of ore geology. Press of Chengdu University of Science and Technology, Chengdu (in Chinese). 杜琦, 赵玉明, 卢秉刚, 等, 1988. 多宝山斑岩铜矿床. 北京: 地质出版社, 225-247. 侯增谦, 2004. 斑岩Cu-Mo-Au矿床: 新认识与新进展. 地学前缘, 11(1): 131-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200401014.htm 黄崇轲, 白冶, 朱裕生, 等, 2001. 中国铜矿床(上册). 北京: 地质出版社. 黄典豪, 吴澄宇, 杜安道, 等, 1994. 东秦岭地区钼矿床的铼-锇同位素年龄及其意义. 矿床地质, 13(3): 221-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ403.003.htm 李文昌, 潘桂棠, 侯增谦, 等, 2010. 西南"三江"多岛弧盆-碰撞造山成矿理论与勘查技术. 北京: 地质出版社. 曲晓明, 侯增谦, 黄卫, 2001. 冈底斯斑岩铜矿(化)带: 西藏第二条"玉龙"铜矿带. 矿床地质, 20(4): 355-366. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2001.04.009 芮宗瑶, 黄崇轲, 齐国明, 等, 1984. 中国斑岩铜(钼)矿床. 北京: 地质出版社, 242-272. 王登红, 陈毓川, 徐钰, 等, 2005. 中国新生代成矿作用(上). 北京: 地质出版社. 夏斌, 陈根文, 王核, 2002. 全球超大型斑岩铜矿床形成的构造背景分析. 中国科学(D辑), 32(增刊): 87-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2002S1009.htm 张玉泉, 谢应雯, 邱华宁, 等, 1998. 钾玄岩系列: 藏东玉龙铜矿带含矿斑岩Sr、Nd、Pb同位素组成. 地质科学, 33(3): 359-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX803.010.htm 赵鹏大, 2003. 非传统矿产资源概论. 北京: 地质出版社. 赵一鸣, 张德全, 1997. 大兴安岭及其邻区铜多金属矿床成矿规律与远景评价. 北京: 地震出版社. 郑明华, 等编著, 1993. 矿床地质原理. 成都: 成都科技大学出版社. -









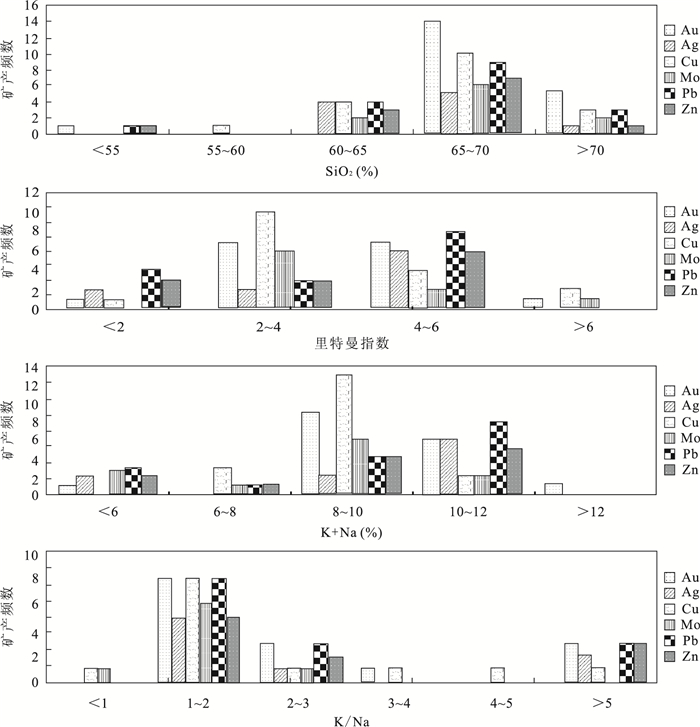
 下载:
下载:

