Singularity Modeling of Geo-Anomalies and Recognition of Anomalies Caused by Buried Sources
-
摘要: 以个旧锡多金属矿床为例,研究了致矿地质异常的非线性特征.从异常地质事件和成矿作用的奇异性出发,定量分析了地质异常的奇异性、不连续性、非平稳性、混沌性、自相似性、临界性等非线性特征.在此基础上,详细介绍了局部奇异性分析原理和方法,论述了奇异性指数对隐伏源异常的识别能力.结果表明,奇异性分析方法在个旧地区水系沉积物地球化学数据处理和隐伏源地球化学异常识别和圈定应用中是有效的.分析结果一定程度上消除了隐伏源深度的影响,所圈定的局部地球化学异常不仅在个旧东区较好地对应了已发现的大型锡矿床的分布,而且在其他低缓地球化学异常区也圈定了多处局部异常,为进一步开展锡矿勘查提供了重要靶区.奇异性理论和方法有望为深部矿产预测、隐伏矿预测、覆盖区矿产预测等特殊环境开展矿产预测提供了新的实用性理论和方法技术.Abstract: This paper investigates the nonlinear properties of geo-anomalies related to mineralization. It was demonstrated that geochemical anomalies in stream sediments in Gejiu mineral district caused by Sn mineralization can be modeled by fractal and multifractal models and they depict singularity, discontinuity, chaoticality, and indifferentiality. It was also shown that the singularity calculated from 2D geochemical landscape can reflect the causes of buried sources. The concepts and methods were validated using the concentration values of trace elements Sn, Cu, As, Pb, Zn and Cd in stream sediments. The results obtained using windows-based local singularity analysis method not only provide anomalies in general agreement with the locations of known mineral deposits in the eastern Gejiu district but also new anomalies delineated in the other areas of Gejiu that provide potential target areas for further mineral exploration for undiscovered Sn mineral deposits. It is anticipated that the singularity analysis method introduced in the paper will become a new powerful tool applicable for quantitative prediction of buried mineral deposits in covered terrain.
-
矿床是具有一定规模的天然形成的有用物质的富集体,是特殊的异常地质过程-成矿作用的产物.成矿作用能够导致有用物质在相对较小的时空范围内高度富集和堆积.与正常的区域性地质作用相比,成矿作用发生的时空范围均是局限的,对矿床的寻找和利用是困难的, 矿床的发现也常常表现为小概率事件.因此,矿产勘查和资源开发利用需要发展相应的先进理论和技术.由于矿床形成和分布的局限性和异常性,对矿床的寻找和勘探也自然要考虑矿床与地质异常的关系.地质异常成矿预测理论就强调了地质异常与矿床的形成以及时空分布的内在联系(赵鹏大,2001).地质异常矿产预测理论和方法已成为常用的矿产资源预测方法,被成功用于不同类型矿床的定量预测和评价,丰富了矿产定量预测学科内容,也对我国矿产资源勘查评价起到了重要作用.地质异常矿产预测理论的核心是强调求"异"的思想,尤其是在深部矿产、隐伏矿产、覆盖区矿产等非传统矿产预测中,相似类比准则会受到一定局限,求"异"显得尤为重要(赵鹏大,2007).成矿作用导致元素的超常富集机制以及矿床时空分布规律是矿产预测尤其是深部矿产预测的重要研究内容.新的预测思路和有效的方法技术是当前开展深部矿产预测、隐伏矿预测、覆盖区矿产预测等工作亟待解决的理论和方法技术难题.本文将地质异常理论与奇异性理论相结合,来探讨地质异常的非线性特征,包括地质异常的时间、空间、频率分布,其主要目的是寻求如何利用非线性动力学理论和非线性数据处理技术定量圈定和识别深部源致矿地质异常.通过对矿床时间-空间-频率分布规律的定量化研究,提高对难识别、难发现、难利用矿床的定量预测效果.
非线性固体地球科学领域近年来的研究结果表明,成矿作用与其他类型的灾害性地质过程(如地震、火山、洪水、降雨、台风、滑坡等)均受到地球内部非线性动力学机制的制约和地球内外环境的影响,这些过程都具有在较短的时间或空间间隔内产生巨量能量释放或物质的超常富集和堆积的特点(Cheng, 2007a).这些能量释放和物质富集的异常性可称之为奇异性(Cheng, 1999).因此,奇异性可能是异常地质事件导致的各种非线性和复杂性地质过程的基本属性,这些过程所产生的结果具有奇异性、自相似性、自组织临界性并可采用分形与多重分形模型进行度量和研究(Cheng, 2007b, 2007c; Cheng and Agterberg, 2009; Cheng and Zhao, 2011).
本文将从奇异性理论出发研究地质异常的非线性特征,首先探讨地质异常空间奇异性的几种度量模型,在此基础上重点研究如何利用这些非线性模型和方法进行隐伏矿定量预测.文章将以个旧地区锡多金属矿床预测为例介绍非线性矿产预测理论和方法原理以及应用效果.
1. 个旧锡多金属矿床的区域地质异常
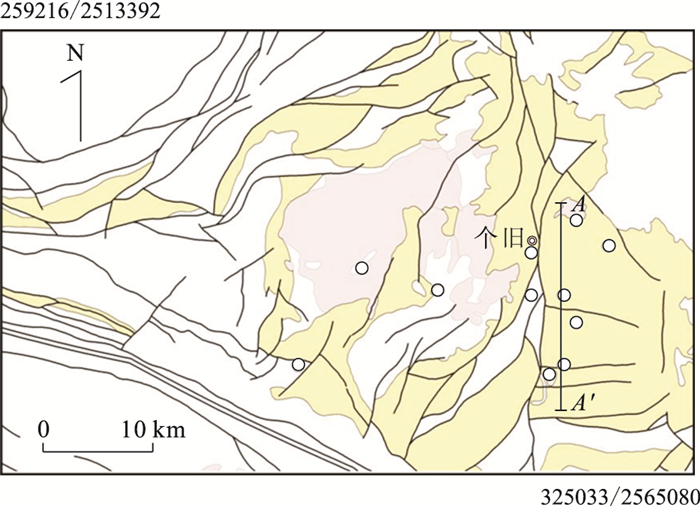
研究区位于云南省南部红河州的个旧锡多金属矿集区.个旧以发现世界级锡多金属矿床和具有重要的锡多金属矿产资源而闻名.为了定量研究个旧锡多金属矿床的区域地质异常及其非线性特征,本文选择了以个旧为中心大约1.5万km2的范围为研究示范区域(图 1).该地区的主要地质地层单元包括一套古生代-中生代沉积岩和火成岩.两组主要的火成岩包括:古生代火山岩和中生代侵入岩.前者主要是玄武岩,后者以花岗质侵入岩为主,岩性包括黑云母花岗岩、黑云母二长花岗岩和黑云母斜长花岗岩等.个旧杂岩体位于研究区中部,出露面积约450 km2,被认为是锡多金属矿床形成和分布的主要控矿要素之一.所发现的大型锡多金属矿床如老厂、卡房、马拉格、松树脚等矿床均分布在个旧岩体周围,主要矿体赋存在个旧组碳酸盐地层中(庄永秋等,1996).该区构造演化历史复杂,形成了不同规模和多组方向的断裂和褶皱构造(如图 1所示).这些构造是重要的控矿要素,如NNE方向断裂和褶皱构造控制了矿带展布方向,而NNE和EW向构造的交汇控制了多个矿田的分布,一系列次级EW、NE、NW、SN向构造多组相互交织控制了大型矿床的产出空间.人们普遍认为锡矿的形成与个旧组沉积岩、断裂构造以及岩浆活动等因素的耦合有关,它们构成了锡多金属致矿地质异常的主要地质要素,其空间叠加分布控制了锡多金属矿床的基本空间分布结构.比如,个旧锡多金属原生矿床按与岩体的空间位置关系可分为近接触带矽卡岩型硫化物矿和远离接触带的层间氧化矿两大类型.虽然岩浆期后热液成矿可能是主要的成矿类型,但其他多期次、多类型叠加成矿作用也可能是造就个旧特大型矿床的原因,更多关于矿床类型、成矿模式和成矿多样性的研究可供参考(秦德先等,2004;谈树成等,2004;夏庆霖等,2007;徐启东等,2009).
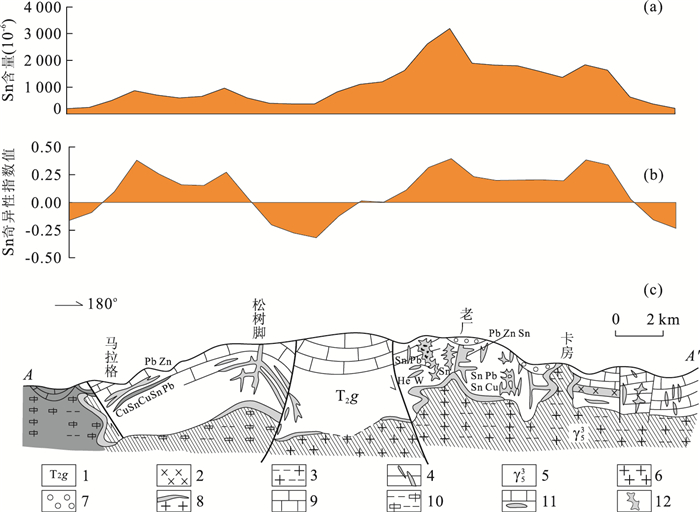
 图 1 个旧地区简化地质图紫红色多边形代表个旧岩体;黄色多边形代表个旧组碳酸盐地层;白色区域表示其他地层;黑色实线代表断裂构造;圆点代表锡矿床;箭头线A-A'表示剖面线(图 2c)的位置Fig. 1. Simplified geology of the Gejiu mineral district
图 1 个旧地区简化地质图紫红色多边形代表个旧岩体;黄色多边形代表个旧组碳酸盐地层;白色区域表示其他地层;黑色实线代表断裂构造;圆点代表锡矿床;箭头线A-A'表示剖面线(图 2c)的位置Fig. 1. Simplified geology of the Gejiu mineral district除了个旧岩基的主体分布外,在个旧岩基外围分布有一系列小岩珠和岩脉如老厂岩体.深部钻探和地球物理解释也均表明个旧岩体隐伏范围较大(熊光楚和石盛滕,1994),主要向东和向东南方向侧伏,侧伏范围覆盖整个个旧东矿区(成秋明等, 2009a, 2009b).岩体的隐伏深度在东矿区可以在地下200~1 000 m.受褶皱和断裂构造的控制,岩体往往形成若干局部凸、凹状接触面,锡矿床的分布往往与这些局部构造界面有关.为了解释隐伏岩体和矿床分布与地表地球化学异常的关系,本文引用了前人编制的个旧东区锡矿床与花岗质岩石接触关系剖面示意图(图 2c)(程彦博等,2008).
为了进一步研究个旧锡矿床区域地质异常的特征,我们采用的主要数据包括1∶20万地质与矿产图、地球物理(重磁图)和1∶20万比例尺水系沉积物地球化学数据.地球化学数据包括了3 800个水系沉积物样品的39种微量和常量元素含量,空间分辨率为2 km×2 km取样密度.本文利用了6种主要成矿微量元素(Sn, Cu, Pb, Zn, As和Cd).这些数据之前已经被用于锡矿异常的圈定,关于更多地球化学数据的应用可见文献(成秋明等, 2009a, 2009b).本文再次使用这些数据的主要目的是说明非线性预测理论和方法原理以及应用效果.
2. 个旧锡多金属矿床区域地质异常的奇异性分析
可以看出,在个旧东区非常有限的分布范围内产出了多个大型锡多金属矿床,表现出矿床集中分布、元素超常富集和堆积的现象.为了分析这种奇异性现象和定量度量元素超常富集程度,特别是希望通过揭示元素富集规律来帮助圈定未发现的特别是隐伏矿床的分布位置,我们将对地表地球化学数据进行处理和研究.
2.1 锡多金属矿床地质异常的广义自相似性
个旧矿区已经发现的锡多金属矿床集中分布在个旧岩体的东南侧.该致矿地质异常形成的主要因素包括个旧岩体的产出、个旧组碳酸盐地层、构造条件等地质要素的耦合,形成了三维地质异常.地质异常范围与周围环境不仅在岩石矿物成分、结构构造有明显不同,而且,在相应的地球化学场、地球物理场以及遥感图像上也表现出明显的异常差异.为了说明地质异常的奇异性,我们将采用水系沉积物中微量元素密度的空间分布来刻画地质异常的奇异性.当然,也可采用其他类型的场量,比如地球物理场、地球化学场、遥感图像、地层岩性变化、构造密度图、矿床分布概率图等来表征地质异常的奇异性.
首先采用2 km×2 km水系沉积物中微量元素含量原始数据绘制整个个旧地区的锡及相关元素含量空间分布图.为了避免数据插值对地球化学图的影响,我们选择空间分辨率为2 km,不对原始数据进行插值处理.然后采用密度-面积分形模型(C-A)(Cheng et al., 1994)检验该地区地质异常在地球化学场中的表现形式.密度-面积分形模型是用于度量和刻画地球化学场各向异性尺度不变性和广义自相似性的一种多重分形模型.该模型表明:地球化学元素浓度值(C)和由浓度等值线所圈定的面积(A[>C])服从幂律关系(Power-law)(Cheng et al., 1994):
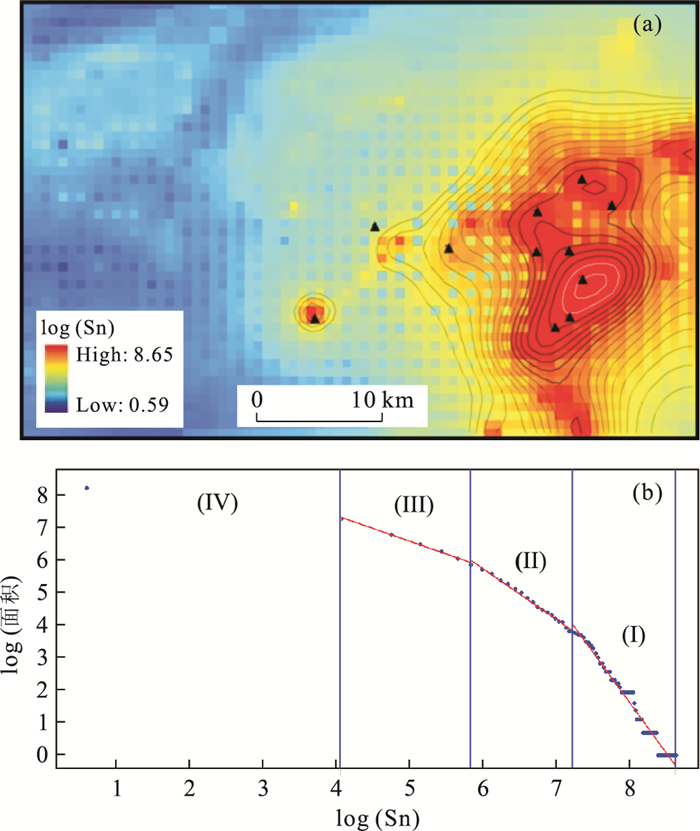
A[>C]=cC−β, (1) 这里,面积A是密度C的单调递减函数.随着元素密度等值线数值的提高,相应等值线所包含的面积将会减小,这种变化服从幂率关系(分形关系).这样的函数关系仅仅由2个参数(c和β)完全确定.一组参数值就确定了一个分形分布,反映了地球化学场的某种广义自相似规律,如果这些参数取多组不同的数值,就会对应多种分形分布或者多种广义自相似规律.图 3a中,我们给出了个旧地区水系沉积物地球化学锡元素密度分布图(元素密度单位为10-6).图中元素密度值是对数变换结果,其密度与面积关系见图 3b.由图 3b可以看出,随着元素密度的提高,等值线所圈定的范围不断缩小,而且逐渐集中到个旧东区的老厂和卡房矿化集中区.此外,随着密度的不断提高,等值线的形态也相应发生变化,由相对复杂变为相对简单的形态,矿化集中区以等轴状等值线为主.根据密度与面积的变化规律,可以将元素密度值分为4个区间(分别记为Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ).各区间的元素密度分界值分别为344×10-6、6×10-6、2×10-6.低于2×10-6的分布范围(Ⅳ)基本反映无显著矿化影响的背景区域,大于2×10-6的范围为受到矿化影响的区域.进一步,随着元素密度值从Ⅲ区间(2×10-6~6×10-6)到Ⅱ区间(6×10-6~344×10-6)再到Ⅰ区间(>344×10-6)的不断提高,元素密度与面积幂率关系也发生相应变化,其变化关系可以分别表示为A=10.6C-0.79,A=15.2C-1.57和A=26.6C-3.1.这些关系表明,面积随密度而缩小的速度不断增加.从图 3a可以看出,Ⅰ区内等值线为近圆形,2个大型锡矿床(老厂和卡房)均分布其中;Ⅱ区内等值线有两个浓集中心,图形较为复杂,有6个锡矿矿床位于该范围;此外还有2个矿床分布在Ⅲ区内.以上3个区域内元素空间变化模式(等值线形态)以及密度-面积关系的差异反映了该3个区域中元素分布的自相似性有所差异,这可能与地质异常的内部结构变化有关.比如说,Ⅰ区可能反映矿化集中区,Ⅰ+Ⅱ区基本对应个旧东矿区南北展布的锡矿带,而Ⅰ+Ⅱ+Ⅲ区基本圈定了个旧岩体东部的矿化范围.
 图 3 (a) 水系沉积物Sn含量图;(b)密度-面积关系图, 四段直线段由最小二乘法拟合a图中黑三角形表示锡矿床,等值线表示由图b中密度-面积关系确定的异常区间;白色等值线表示Sn>344×10-6(Ⅰ),黑粗等值线6×10-6<Sn≤344×10-6(Ⅱ),黑细等值线2×10-6<Sn≤6×10-6(Ⅲ)Fig. 3. (a) Distribution of log-transformed values (10-6) of Sn in stream sediment samples.; (b) C-A (concentration-area) plot showing the cumulative area (number of cells of 4 km2) versus the tin concentration value; the base of logarithms is e
图 3 (a) 水系沉积物Sn含量图;(b)密度-面积关系图, 四段直线段由最小二乘法拟合a图中黑三角形表示锡矿床,等值线表示由图b中密度-面积关系确定的异常区间;白色等值线表示Sn>344×10-6(Ⅰ),黑粗等值线6×10-6<Sn≤344×10-6(Ⅱ),黑细等值线2×10-6<Sn≤6×10-6(Ⅲ)Fig. 3. (a) Distribution of log-transformed values (10-6) of Sn in stream sediment samples.; (b) C-A (concentration-area) plot showing the cumulative area (number of cells of 4 km2) versus the tin concentration value; the base of logarithms is e应该指出的是,以上的分析是基于水系沉积物地球化学元素密度而进行的.由于地球化学密度含量反映了地表次生介质中元素总含量,元素的分布除了受到地表诸多因素包括一定的位移影响外,还会受到异常源埋藏深度的影响,因此,直接对元素含量的分析能够圈定露头矿引起的地球化学异常,如果不考虑隐伏源以及地表系统的影响就不可能有效圈定隐伏源引起的地球化学异常.作者曾经提出了能谱密度-面积模型(S-A),建立了在傅立叶空间进行异常和背景分解的分形滤波技术,克服了C-A模型在异常圈定中的不足(Cheng et al., 1999).以下将介绍局部奇异性原理和弱异常分析方法,该方法对圈定隐伏源引起的地球化学异常是有效的.
2.2 锡多金属矿床区域地质异常的奇异性
在C-A模型的基础上,作者曾提出了局部奇异性模型(Cheng, 1999).本文将重点说明该方法对隐伏源异常的识别能力.这里有必要简要介绍一下该方法的基本原理和计算方法.如果将C-A模型稍作修改并用于局部地球化学异常密度-面积关系度量,就可以得到以下元素密度(ρ)-面积(A)幂率统计关系:
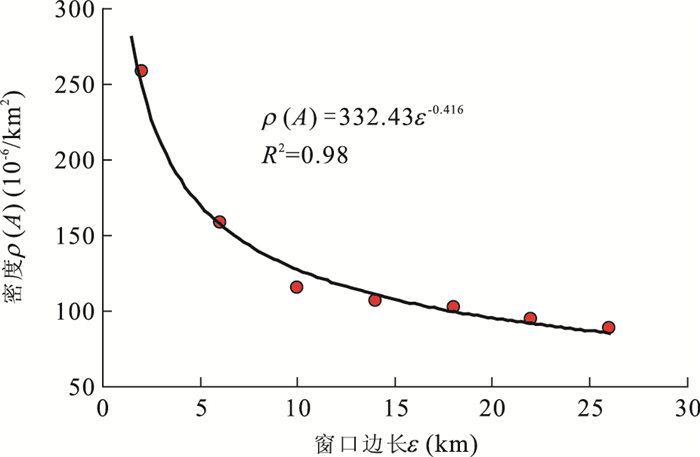
⟨ρ(A)⟩=c⟨√A⟩−Δα, (2) 该统计关系仍然为幂率关系并由两个参数确定,其中,参数$c = \langle \rho (A)\rangle {\langle \sqrt A \rangle ^{\Delta \alpha }}$代表分形密度(单位如10-6/cm1.5),参数Δα称之为奇异性指数,与分形密度的分形维数有关.称其为奇异性指数的原因之一是,当Δα>0时,元素密度随着面积的无限缩小将趋于无穷大.奇异性指数与元素密度的变化关系将在下面进行介绍.为了说明如何利用局部奇异性分析方法圈定地球化学异常,这里以As元素为例.在As地球化学图上选择某处来绘制元素密度与面积关系图.为了简单起见,这里采用了不同大小的正方形窗口作为面积来计算窗口中的元素平均密度,窗口的边长分别选为ε=2,6,10,…,26 km.计算的结果表达在了图 4上.图中,纵轴代表元素密度值(10-6/km2),水平轴代表的窗口边长尺度(km),圆点代表实际计算数据,实线代表最小二乘法拟合的幂律模型,其结果为ρ(A)=332.43ε-0.416,该估计的相关系数为R2=0.98.可见,在该位置上计算得两个参数值:c=332.43(分形密度)和Δα=0.416(局部奇异性指数).同样的方法可以计算整个地球化学图上每一点的局部奇异性指数值和分形密度.以下我们详细讨论局部奇异性指数α的性质和对隐伏源异常的识别能力.
 图 4 云南个旧东区某地水系沉积物As元素密度与面积关系(Cheng and Zhao, 2011)实线代表采用最小二乘法拟合的幂率模型Fig. 4. Relationship between the concentration density values (10-6/km2) of As and square windows with various window sizes
图 4 云南个旧东区某地水系沉积物As元素密度与面积关系(Cheng and Zhao, 2011)实线代表采用最小二乘法拟合的幂率模型Fig. 4. Relationship between the concentration density values (10-6/km2) of As and square windows with various window sizes局部奇异性计算模型(密度-面积模型)表明:当尺度非常小时(A接近零),密度有3种变化情况:当Δα>0时,密度值趋于无穷;当Δα<0时,密度接近于零;当Δα=0时,密度值保持不变.可见,局部奇异性指数刻画了元素富集、贫化、不变3种不同情况.从多重分形理论得知(Cheng, 1999),在成矿区带中的元素富集地段(即Δα>0)空间分布范围是局限的,其分形维数往往小于2,然而,元素密度相对不变或者贫化的地段(即Δα≤0)空间分布是广泛的,其分形维数往往接近于2.元素在岩石以及上覆介质中没有明显的富集的地段(Δα≤0)称为地球化学背景区.然而,当Δα>0,说明随着面积的减小元素密度急剧增加并趋于无穷,这样的元素富集区域称为地球化学异常区.因此,局部奇异指数值(Δα)可以用来定量刻画地球化学异常强度(Cheng, 2007c).
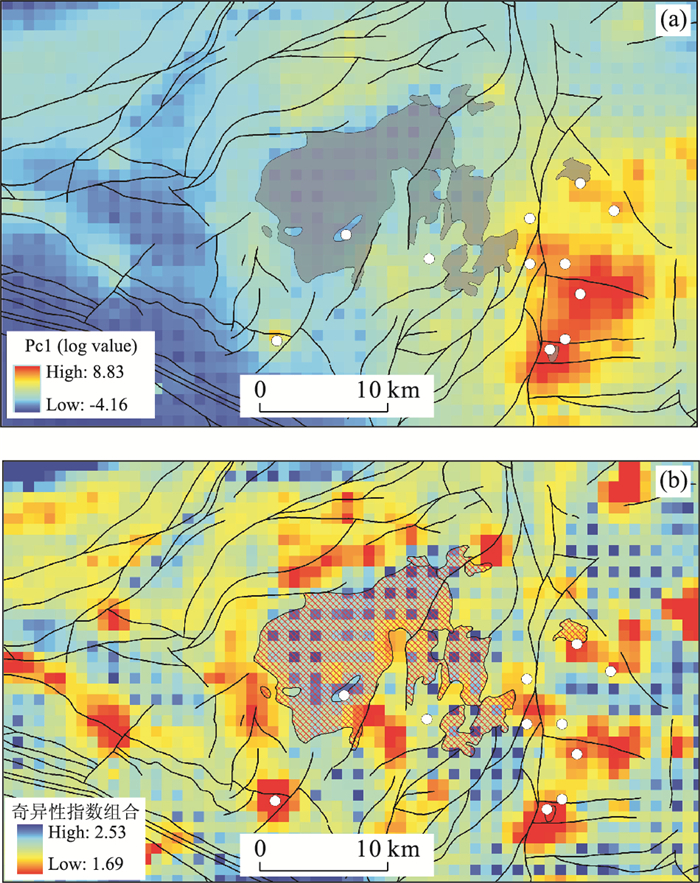
为了说明奇异性分析方法原理和应用,我们重新编制了Sn、Cu、As、Pb、Zn、Cd 6种元素组合地球化学异常图(成秋明等, 2009a, 2009b).应用主成分分析方法对这6种元素进行了组合,其中第一主成分反映了锡铜主成矿期相关元素组合.图 5a给出了6个元素在第一主成分上的得分图(可以理解为正规化的组合元素图).可以看出,组合异常的高值区主要分布在个旧东区,并与已经发现的主要大型矿床分布基本吻合,然而其他区域如个旧西区、南区和北区显示组合异常普遍较弱.这些含量较低异常较弱的原因除了其他各种原因外,异常源的埋深较大也许是原因之一(成秋明等, 2009a, 2009b).显然,这些组合元素异常并不能直接用来圈定东区以外的可能反映隐伏矿的地球化学异常.为了计算局部奇异性指数,我们对得分图做了向上平移变换,以保证变换后的主成分得分图不再有负值,微小的平移变换不会改变组合地球化学图的局部相对变化模式,不会显著改变局部奇异性指数值.同样,采用前面介绍过的多个正方形窗口的分析方法计算了局部奇异性指数值,正方形窗口的边长分别取为ε=2,6,…,26 km.图 5b中的计算结果表明,不仅东矿区内主要的大型矿床而且分布在其他地区的锡矿床如陡崖矿床均对应Sn、Cu、As、Pb、Zn、Cd组合元素奇异性指数高值区(Δα>0).在个旧岩体的周边圈出了多处相类似的组合异常,这些异常在今后的进一步矿产勘查中应该给予重视.
 图 5 (a) 由主成分分析方法所计算的地球化学组合元素(Sn、Cu、As、Pb、Zn and Cd)分布;(b) 采用局部奇异性分析方法所计算的奇异性指数值分布透明的多边形表示个旧岩体分布范围;白色的圆圈代表锡矿床;黑色线条代表断裂构造Fig. 5. (a) Scoring map of the first principle component showing the spatial distribution of multiple elements of Sn, Cu, As, Pb, Zn and Cd; (b) Singularity obtained from the anomalies in Fig. 5a, with a positive value of 5 added so that the map has positive values. Singularity was calculated with square windows sized within 26 km
图 5 (a) 由主成分分析方法所计算的地球化学组合元素(Sn、Cu、As、Pb、Zn and Cd)分布;(b) 采用局部奇异性分析方法所计算的奇异性指数值分布透明的多边形表示个旧岩体分布范围;白色的圆圈代表锡矿床;黑色线条代表断裂构造Fig. 5. (a) Scoring map of the first principle component showing the spatial distribution of multiple elements of Sn, Cu, As, Pb, Zn and Cd; (b) Singularity obtained from the anomalies in Fig. 5a, with a positive value of 5 added so that the map has positive values. Singularity was calculated with square windows sized within 26 km2.3 地质异常的不连续性、不光滑性、混沌性、非平稳性
以上讨论表明,局部奇异性指数可以度量元素富集或地球化学异常强度,以下将进一步讨论地质异常的其他非线性性质,如不连续性、不可微性、混沌性和非平稳性等基本性质.由关系(2)可以得到如下密度随面积的高阶导数关系:
dn⟨ρ(A)⟩dnA=(−1)n1/2Δα(1+1/2Δα)⋯(n+1/2Δα)An⟨ρ(A)⟩, (3) 可以看出,当面积等于零时,如果局部奇异指数值不等于零或者不等于负整数(如Δα>0或者Δα≠-整数),以上任何阶导数(n=0,1,…,n)都不存在.换句话说,当处于元素富集地段或异常地段(Δα>0),元素密度随面积变化的函数关系将不存在任何阶导数,说明异常地段的元素分布具有不连续性、奇异性、不光滑性.又由于不同位置上所对应的奇异性指数值的不同,说明密度具有非平稳性.实际上,对于一般的地球化学场而言,奇异性密度-面积模型(2)具有统计关系,而不具备点收敛的性质,只具有平均弱收敛性(Cheng and Agterberg, 2009).换句话说,模型(2)只在概率意义下是成立的.当面积很小时,面积内的元素密度将出现不收敛,或者振荡和混沌状态.因此对于异常地段只有通过一定的具有面积性意义的取样均值才有统计意义,否则将会出现"块金"效应,如在相同的位置重复取样也会得到不同的测量结果.不过,地质、地球化学、地球物理、遥感调查的结果往往是以一定空间分辨率的图像形式表达,每个样品或者象元实际上代表了所在位置上的某种平均值,这样的平均值是有意义的.然而,由于勘查数据的奇异性、不光滑性、不连续性、混沌性、非平稳性,这就使得传统的统计方法和许多空间分析方法不能直接用于对异常数据的信息处理.大多数传统的低阶矩统计方法和低阶矩地质统计学方法如克里格方法均要求数据具有连续性、光滑性、平稳性(Journal and Huijbregts, 1978).分形和多重分形理论的发展为研究奇异性地质事件和处理奇异性空间数据提供了有效的理论和方法(Cheng, 2007a).将奇异性原理与传统地质统计学相结合所提出的奇异性克立格模型就适用于奇异性数据的插值和异常分析工作(Cheng, 2007d).下面将进一步讨论奇异性方法对隐伏矿的预测能力和预测效果.
3. 奇异性分析方法与隐伏矿预测原理
如何预测隐伏矿床是当前成矿预测和矿产勘查领域所关心的重要科学问题.我国政府已把深部找矿和隐伏矿预测作为当前和今后地学研究的重要对象之一,地学工作者也对深部找矿和隐伏矿产预测表现了高度的研究热情,近几年来相继召开了各种深部找矿和隐伏矿找矿理论和方法研讨会.希望发展适应深部找矿和隐伏矿预测的新理论和有效的找矿技术.前人已经总结了大量的找矿经验和找矿方法,以及在深部找矿中的实践效果(编委会,2010).人们较为熟悉的深部找矿方法多数是地球物理方法.由于这些方法建立在电磁波、地震波、重力场等地球物理场论的基础上,因此这些地球物理测量方法具有对地观测的穿透性.在地表以及航空甚至卫星平台上获得的地球物理测量信号同样可以反映深部地质体物性差异.虽然矿体(或者其他与矿有关的地质体)的埋藏深度也会对地球物理信号产生衰减或者屏蔽作用,但是地质体之间的显著差异仍然会在这些地球物理信号有所反应.人们还可以通过研究信号的衰减规律进行地质解释,比如通过位场的转换和滤波运算达到压制噪声和去除背景从而突显有用信号的目的.关于深部找矿的其他方面的工作还很多,本文的目的也并非要综述该领域的进展,因此不做更多的介绍,有兴趣的读者可以参考其他参考文献.这里将要着重说明局部奇异性分析方法如何具有对深部成矿信息的获取功能.
幂律关系的独特性质是其具有尺度不变性或者自相似性,这一关系可以通过下面的分析给予说明.根据模型(2)我们可以得到在2个不同尺度上测量的元素密度值的转换关系:
⟨ρ(A1)⟩=(A1/A2)−Δα/2⟨ρ(A2)⟩, (4) 换言之,对于一个给定尺度上测量的元素密度值,可以通过尺度变换转换为另一尺度上测量的密度值(Cheng, 1999).同样的幂律关系在地球物理势场中也常见,比如重力场和磁场强度随探测仪器与地质体间距离或高度的变化呈现幂率关系并具有自相似性,如:
Z(h)∝1/hn, (5) 表示航磁强度随仪器距离地质体的距离(h)的变化规律.这里,n为衰减指数, 其数值变化范围0~3,并随地质体的形状而变化.对于较大的地质体而言,磁场强度衰减较慢,衰减指数较小.如水平无限延伸的全平面地质体衰减指数为0.反而当地质体规模较小,则磁场强度衰减较快,衰减指数值也较大.比如较小的球状地质体的衰减指数为3.因此,可以根据磁场向上延拓变换过程中不同规模的地质体所对应的磁场强度的衰减速度的差异进行低通滤波,以消除浅部地质体的影响,达到突出深部较大地质体磁场特征的目的.相反,可以采用对磁场进行微分处理的方法进行高通滤波,以达到去除较大地质体的影响,突出较小地质体或者浅部地质体的有效信噪比.
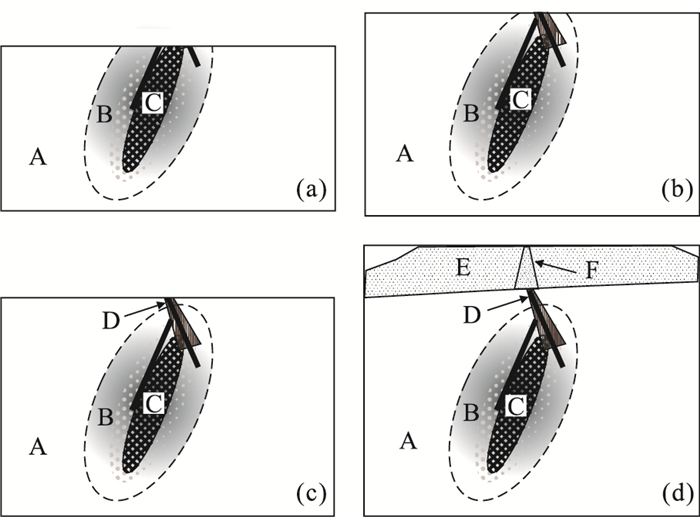
类似地,根据地球化学场的奇异性特征和自相似原理,可以建立起地球化学元素密度与面积(线段、面积、体积)之间的幂率关系.利用该幂率关系的尺度不变性和自相似性可以圈定隐伏源地球化学异常.我们用示意图(图 6)来说明深部源异常的识别情况和奇异性分析方法工作原理.假设由于热液作用使得赋存在岩石(A)中的矿体(C)周围形成了元素密度相对较高的矿体原生晕带(B).同时由于构造作用的影响,在矿体上方沿构造两侧形成了元素密度相对较高的构造原生晕带(D).由于在地表系统长期循环作用下,在构造晕分布的上覆盖层(E)中形成了元素密度相对较高的次生晕分布带(F).就找矿而言将至少有4种地质情况:(a)当矿体出露地表;(b)当矿体隐伏但矿体原生晕带出露地表;(c)当矿体和矿体原生晕均未出露地表,但与矿体或者矿体原生晕联通的断裂构造以及其两侧的原生晕带出露地表;(d)矿体、矿体原生晕、构造原生晕均被上覆盖层覆盖,但在长期经受地表系统的作用下,在矿体或者矿晕之上覆盖层中形成了元素富集带.一般来说,在矿体出露地表(a)情况下,在地表介质中所产生的地球化学异常较强,对这种异常的识别是较容易的.当矿体未出露地表并距离地表有一定距离,但矿体相关的原生晕带已经出露地表(b),地表介质中也会产生一定的地球化学异常,而且原生晕中的元素密度会随着矿体埋藏深度的加大而降低,在地表介质中所产生的元素密度也会逐渐减弱,相应地对异常的识别和圈定难度也会加大.矿体和矿体原生晕均未出露,但与矿体连通的构造周围所产生的原生晕带出露地表(c),在地表介质中会产生分布范围较小而强度较弱的异常,对这种异常的识别和圈定相对较难.当情况(d)发生,整个原生成矿系统均被上覆盖层掩埋,处于完全覆盖区.地球化学找矿难度较大.有些类型的覆盖层在长期的地表系统的作用下,下伏地层中所富集的成矿元素和微粒矿物质有可能随着地表水系统和地气的长期活动而在覆盖层中富集,形成弱异常.对这种类型弱异常的识别是非常困难的,必须选择合适的取样介质、采取高精度分析测试仪器和使用科学有效的信息提取技术.在地表水系统和地气系统的循环中,下伏成矿物质会以元素或者微颗粒形式在覆盖层中运移,并在运移过程中在合适的介质中以一定的相态形式沉淀富集.因此开展覆盖区地球化学调查工作,采样介质的研究和选择是非常关键的.同时由于盖层中元素含量较低,必须提高分析仪器的检测精度,这样才会得到有效的分析结果.这两方面均受到了勘查地球化学家们的普遍重视,并开展了各种取样介质和分析测试创新研究,如采用地气地球化学测量方法、地电地球化学方法等新的勘查地球化学方法.然而容易被忽视的是对测量数据的使用问题.由于覆盖层中的元素含量极低,在确定异常下限时必须考虑各种因素,特别是覆盖层类型和厚度等因素,避免采用简单的统计方法,否则将会漏掉微弱但有用的深部源致矿异常信息.除了图 6中给出的几种情况外,实际情况还会更加复杂,会有不同的组合情况,比如矿体出露在基岩表面但直接被上覆盖层所掩埋等.我们可以针对以上3种地球化学系统(矿体或矿体原生晕系统,构造原生晕系统,上覆盖层中元素富集系统)来讨论元素的空间变化规律,研究地表介质中的地球化学异常与隐伏源埋藏深度的关系.为此,我们必须做如下的假设:在以上3种系统中(矿体原生晕、构造原生晕或者覆盖层次生晕)均表现为围绕元素富集中心呈自相似性分布规律,具有以下元素密度与富集带体积之间的幂率关系:
⟨ρ(V)⟩=c⟨V1/3⟩−Δα, (6) 当然在不同的系统中,以上幂率关系的具体参数和等值面的自相似形式常常是不同的.比如围绕矿体的原生晕可以形成较宽和较复杂的元素密度等值面,而围绕构造的原生晕形成较为简单的元素密度等值面.元素在三维等值面上的分布可以表示为:
∂⟨ρ(V)⟩∂V=1/3cΔα⟨V⟩−Δα/3−1, (7) 从以上幂率关系可以看出,在不同等值面上幂率关系的分形密度随着远离中心而降低,但奇异性指数不变.奇异性指数反映了元素密度的变化率,与矿体的形态以及晕的形成是有关的.因此,可以通过识别和估计局部奇异性指数来识别致矿异常.以上幂率关系(6)还表明,元素密度分布具有三位空间的自相似性,因此在任一深度上与之相交的水平面上测量元素密度分布也应具有围绕密度中心的二维自相似性.通过该二维地球化学场可以估计局部奇异性指数.地表介质中元素密度分布模式一定意义上反映了三维地球化学场在地表的投影结果.随着深部异常源到地表投影面距离的加大,地表介质中测量的元素密度值的强度会显著降低.但地球化学场的自相似性和奇异性仍然存在.采用本文前面介绍过的二维局部奇异性分布方法就能估计和绘制二维奇异性指数分布图,从而达到增强深部源引起的地表地球化学异常强度的目的.作为应用实例,我们再来分析图 2a、2b中关于个旧东区地球化学异常与锡矿的分布关系.图 2分别给出了地质剖面图和水系沉积物地球化学元素密度的对比结果.可以看出,由南向北隐伏岩体的埋藏深度有所增大,地表地球化学元素密度强度也逐渐降低.如果直接根据元素密度的高低来定义异常,有些异常如马拉格和松树脚锡矿床所对应的地球化学异常将不易被发现.然而,在局部奇异性指数图上该情况得到了较大改善,反映了局部奇异性指数较好地克服了异常源埋藏深度的影响,强化了致矿地质异常.几个已发现的矿床上方如马拉格、松树脚、老厂、卡房等均有较好的局部奇异性异常反映.根据局部奇异性分析结果我们在研究区的其他范围也圈定了多处组合异常,这些异常很好地反映了岩体周边几组构造交汇等现象,应该在进一步勘查中给予重视.
4. 结论
成矿事件以及灾害性地质事件可以产生元素超常富集和巨量能量释放的异常性结果,这种现象和结果可以通过奇异性理论和多重分形模型进行定量刻画.本文采用奇异性原理和模型对致矿地质异常的研究表明,致矿地质异常所对应的地球化学异常具有奇异性、不连续性、混沌性、非平稳性等非线性特征.局部奇异性指数是度量元素富集强度的定量参数,其数值与元素密度的空间度量尺度无关.对于具有自相似的三维地球化学异常而言,奇异性指数与异常的分布范围大小独立,而与异常形态有关,因此当隐伏源距离地表较深时,地表异常强度显著降低,然而异常形态指数不变.因此,估计和绘制奇异性指数分布图有利于强化深部源引起的地球化学异常.奇异性分析对提取深部源引起的地球化学弱异常具有较好效果.在个旧地区圈定了水系沉积物地球化学弱异常.这些异常不仅与多数已发现的锡矿床相吻合,同时在未知区所圈出的弱异常也有进一步开展工作的意义.奇异性理论和方法通过进一步研究和广泛实践有望成为深部找矿、隐伏矿预测和覆盖区矿产预测的新的有效方法.文中关于地质异常奇异性的研究结果也预示了将现代非线性理论与地质异常研究相结合的良好的发展前景.
感谢: 本文是为庆祝赵鹏大院士80岁华诞和从事地球科学研究工作60年而撰写的.作者衷心祝愿赵先生身体健康,再创辉煌!作者感谢本刊特邀编辑陈永清教授、胡光道教授对撰写该论文的邀请,感谢学报主编王亨君教授的邀请和支持,感谢匿名评审专家对本论文所提的建设性意见. -
图 1 个旧地区简化地质图
紫红色多边形代表个旧岩体;黄色多边形代表个旧组碳酸盐地层;白色区域表示其他地层;黑色实线代表断裂构造;圆点代表锡矿床;箭头线A-A'表示剖面线(图 2c)的位置
Fig. 1. Simplified geology of the Gejiu mineral district
图 3 (a) 水系沉积物Sn含量图;(b)密度-面积关系图, 四段直线段由最小二乘法拟合
a图中黑三角形表示锡矿床,等值线表示由图b中密度-面积关系确定的异常区间;白色等值线表示Sn>344×10-6(Ⅰ),黑粗等值线6×10-6<Sn≤344×10-6(Ⅱ),黑细等值线2×10-6<Sn≤6×10-6(Ⅲ)
Fig. 3. (a) Distribution of log-transformed values (10-6) of Sn in stream sediment samples.; (b) C-A (concentration-area) plot showing the cumulative area (number of cells of 4 km2) versus the tin concentration value; the base of logarithms is e
图 4 云南个旧东区某地水系沉积物As元素密度与面积关系(Cheng and Zhao, 2011)
实线代表采用最小二乘法拟合的幂率模型
Fig. 4. Relationship between the concentration density values (10-6/km2) of As and square windows with various window sizes
图 5 (a) 由主成分分析方法所计算的地球化学组合元素(Sn、Cu、As、Pb、Zn and Cd)分布;(b) 采用局部奇异性分析方法所计算的奇异性指数值分布
透明的多边形表示个旧岩体分布范围;白色的圆圈代表锡矿床;黑色线条代表断裂构造
Fig. 5. (a) Scoring map of the first principle component showing the spatial distribution of multiple elements of Sn, Cu, As, Pb, Zn and Cd; (b) Singularity obtained from the anomalies in Fig. 5a, with a positive value of 5 added so that the map has positive values. Singularity was calculated with square windows sized within 26 km
-
Cheng, Q.M., 1999. Multifractality and spatial statistics. Computers & Geosciences, 25(10): 949-961. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300499000606 Cheng, Q.M., 2007a. Mapping singularities with stream sediment geochemical data for prediction of undiscovered mineral deposits in Gejiu, Yunnan Province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 32(1-2): 314-324. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2006.10.002 Cheng, Q.M., 2007b. Multifractal imaging filtering and decomposition methods in space, fourier frequency, and eigen domains. Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics, 14(3): 293-303. doi: 10.5194/npg-14-293-2007 Cheng, Q.M., 2007c. Singular mineralization processes and mineral resources quantitative prediction: new theories and methods. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(5): 42-53. Cheng, Q.M., 2007d. GIS based fractal/multifractal anomaly analysis for modeling and prediction of mineralization and mineral deposits. In: Harris, J., Wright, D., eds., GIS for geosciences. Geological Association of Canada, 285-296. Cheng, Q.M., Agterberg, F.P., 2009. Singularity analysis of ore-mineral and toxic trace elements in stream sediments. Computers & Geosciences, 35(2): 234-244. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300408002203 Cheng, Q.M., Agterberg, F.P., Ballantyne, S.B., 1994. The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods. J. Geochemical Exploration, 51(2): 109-130. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(94)90013-2 Cheng, Q.M., Xu, Y., Grunsky, E., 1999. Integrated spatial and spectral analysis for geochemical anomaly separation. In: Lippard, S.J., Naess, A., Sinding-Larsen, R., eds., Proceedings of the Firth Annual Conference of the International Association for Mathematical Geology, Trondheim, Norway 6-11th August, 1, 87-92. Cheng, Q.M., Zhao, P.D., 2011. Singularity theories and methods for characterizing mineralization processes and mapping geo-anomalies for mineral deposit prediction. Geoscience Frontiers, doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2010.12.003 Cheng, Q.M., Zhao, P.D., Chen, J.G., et al., 2009a. Application of singularity theory in prediction of tin and copper mineral deposits in Gejiu district, Yunnan, China: weak information extraction and mixing information decomposition. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 34(2): 232-242 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2009.021 Cheng, Q.M., Zhao. P.D., Zhang, S.Y., et al., 2009b. Application of singularity theory in prediction of tin and copper mineral deposits in Gejiu district, Yunnan, China: information integration and delineation of mineral exploration targets. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 34(2): 243-252 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2009.022 Cheng, Y.B., Mao, J.W., Xie, G.Q., et al., 2008. Petrogenesis of the Laochang-Kafang granite in the Gejiu area, Yunnan Province: constraints from geochemistry and zircon U-Pb dating. Acta Geologica Sinica, 82(11): 1478-1493 (in Chinese with English abstract). Editorial Board, 2010. Hand book of advanced technologies for geological (deep) mineral exploration (Vol. 4). Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Journel, A.G., Huijbregts, C.J., 1978. Mining Geostatistics. Academic Press, London, 600. Qing, D.X., Tan, S.C., Fan, Z.G., 2004. Geotectonic evolution and tin-polymetallic metallogenesis in Gejiu-Dachang area. Journal of Mineralogy, 24(2): 118-123 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=9972391 Tan, S.C., Qing, D.X., Chen, A.B., et al., 2004. Regional crust evolution and metallogenesis of Gejiu tin deposit—a discussion. Journal of Mineralogy, 24(2): 157-163 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200402011.htm Xia, Q.L., Zhang, S.T., Chen, S.Y., et al., 2007. The key problems for deep mineral potential assessment in Gejiu tin deposit, Yunnan, China. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 27(Suppl. ): 530-531 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xiong, G.C., Shi, S.T., 1994. Physico-geologic model of the Gejiu tin district and its application. Geological Review, 40(1): 19-27 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199401002.htm Xu, Q.D., Xia, Q.L., Cheng, Q.M., 2009. Tectono-magmatic evolution related to metallogenic system in the Gejiu ore area, southeastern Yunnan of China. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 34(2): 307-313 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2009.032 Zhao, P.D., 2001. Three component mineral resource quantitative prediction and assessment: quantitative mineral resource prediction theory and practice. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 27(5): 139-148 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, P.D., 2007. Quantitative mineral prediction and deep mineral exploration. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(5): 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285501491_Quantitative_mineral_prediction_and_deep_mineral_exploration Zhuang, Y.Q., Wang, R.Z., Yang, S.P., et al., 1996. Sn and Cu polymetallic mineral deposits in Gejiu. Seismology Press, Beijing, 124 (in Chinese). 编委会, 2010. 现代地质(深部)找矿新技术标准手册(第4卷). 北京: 地质出版社. 成秋明, 赵鹏大, 陈建国, 等, 2009a. 奇异性理论在个旧锡铜矿产资源预测中的应用: 成矿弱信息提取和复合信息分解. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 34(2): 232-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200902001.htm 成秋明, 赵鹏大, 张生元, 等, 2009b. 奇异性理论在个旧锡铜矿产资源预测中的应用: 综合信息集成与靶区圈定. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 34(2): 243-252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200902002.htm 程彦博, 毛景文, 谢桂青, 等, 2008. 云南个旧老厂-卡房花岗岩体成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学约束. 地质学报, 82(11): 1478-1493. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.11.003 秦德先, 谈树成, 范柱国, 等, 2004. 个旧-大厂地区地质构造演化及锡多金属成矿. 矿物学报, 24(2): 118-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200402004.htm 谈树成, 秦德先, 陈爱兵, 等, 2004. 个旧锡矿区域地壳演化与成矿探讨. 矿物学报, 24(2): 157-163. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2004.02.011 夏庆霖, 张寿庭, 陈守余, 等, 2007. 云南个旧锡矿深部资源潜力评价的几个关键问题. 矿物学报, 27(增刊): 530-531. 熊光楚, 石盛滕, 1994. 个旧锡矿区物理-地质模型及应用效果. 地质论评, 40(1): 19-27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1994.01.003 徐启东, 夏庆霖, 成秋明, 2009. 云南个旧矿集区区域构造-岩浆演化与锡铜多金属成矿系统. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 34(2): 307-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200902013.htm 赵鹏大, 2001. 三联式矿产资源定量预测与评价: 数值化矿产预测理论与实践. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 27(5): 139-148. 赵鹏大, 2007. 成矿定量预测与深部找矿. 地学前缘, 14(5): 1-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.05.001 庄永秋, 王任重, 杨树培, 等, 1996. 云南个旧锡铜多金属矿床. 北京: 地震出版社, 124. -










 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载: