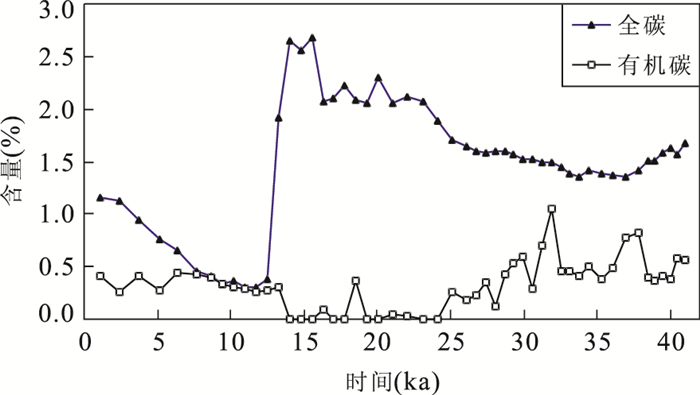
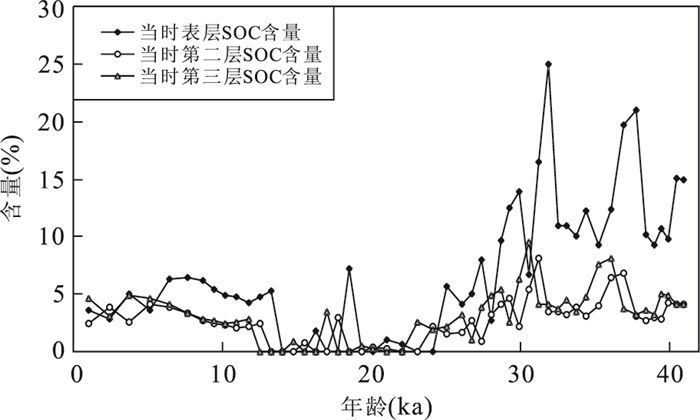
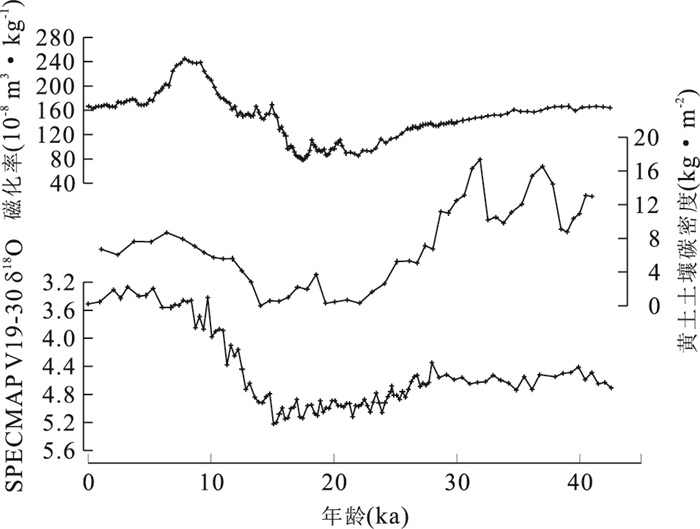
|
Batjes, N.H., 1996. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world. European Journal of Soil Science, 47: 151-163. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.1996.tb01386.x |
|
Dean, W.E., 1999. The carbon cycle and biogeochemical dynamics in lake sediments. Journal of Paleolimnology, 21(4): 375-393. doi: 10.1023/A:1008066118210 |
|
Ding, Z.L., Derbyshire, E., Yang, S.L., et al., 2002. Stacked 2.6 Ma grain size record from the Chinese loess based on five sections and correlation with the deep-sea δ18O record. Paleoceanography, 17(3): 1033. doi: 10.1029/2001PA000725 |
|
Fang, J.Y., Liu, G.H., Xu, S.L., 1996. Biomass and net production of forest vegetation in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 16(5): 497-508 (in China with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284688688_Biomass_and_net_production_of_forest_vegetation_in_China |
|
Feely, R.A., Sabine, C.L., Key, R.M., et al., 1999. CO2 survey synthesis results: estimating the anthropogenic carbon dioxide sink in the Pacific Ocean. U.S. JGOFS News, 9: 1-16. |
|
Guo, Z.T., Liu, D.S., An, Z.S., 1994. Paleosols of the last 0.15 Ma in the Weinan loess section and their paleoclimatic significance. Quaternary Sciences, (3): 256-269 (in China with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ199403006.htm |
|
Han, J.M., Jiang, W.Y., Liu, D.S., et al., 1996. The isotopic records in loess calcate of paleoclimate change. Science in China (Ser. D), 26: 399-404 (in Chinese). |
|
Hansen, J., Sato, M., Ruedy, R., et al., 2006. Global temperature change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(39): 14288-14293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606291103 |
|
Imbrie, J., Boyle, E.A., Clemens, S.C., et al., 1992. On the structure and origin of major glaciation cycles 1: linear responses to Milankovitch forcing. Paleoceanography, 7(6): 701-738. doi: 10.1029/92PA02253 |
|
IPCC, 2001. Climate change 2001: the science of climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. |
|
Jin, F., Yang, H., Cai, Z.C., et al., 2001. Calculation of density and reserve of organic carbon in soils. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 38(4): 522-528 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB200104009.htm |
|
King, A.W., Emanuel, W.R., Wullschleger, S.D., et al., 1995. A search of the missing carbon sink: a model of terrestrial biospheric response to land-use change and atmospheric CO2. Tellus, 47(4): 501-519. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0889.47.issue4.9.x |
|
Kukla, G., Heller, F., Liu, X.M., et al., 1988. Pleistocene climates in China dated by magnetic susceptibility. Geology, 16(9): 811-814. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0811:PCICDB>2.3.CO;2 |
|
Li, T.J., Zheng, Y.S., Wang, Y., 1983. Soil geography. Higher Education Press, Beijing, 59-95 (in Chinese). |
|
Liu, D.S., 1985. Loess and environment. Science Press, Beijing, 29-296 (in Chinese). |
|
Liu, J.Q., Chen, T.M., Nie, G.Z., et al., 1994. Datings and reconstruction of the high resolution time series in the Weinan loess section of the last 150 000 years. Quaternary Sciences, (3): 193-202 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/312662945_Dating_and_reconstruction_of_the_high_resolution_time_series_in_the_Weinan_loess_section_of_the_last_150000_years |
|
Liu, Z.W., Pan, K.W., 2005. Problems in Olson's litter decomposition model and its revision. Journal of Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry, 33(1): 69-70 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://europepmc.org/abstract/CBA/575422 |
|
Lü, H.Y., Liu, D.S., Wu, N.Q., et al., 1999. Phytolith record of vegetation succession in the southern loess plateau since Late Pleistocene. Quaternary Sciences, (4): 336-349 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284987929_Phytolith_record_of_vegetation_succession_in_the_southern_Loess_Plateau_since_Late_Pleistocene |
|
Morozova, T.D., Velichko, A.A., Dlussky, K.G., 1998. Organic carbon content in the Late Pleistocene and Holocene fossil soils (reconstruction for eastern Europe). Global and Planetary Change, 16-17: 131-151. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(98)00027-7 |
|
Post, W.M., Emanuel, W.R., Zinke, P.J., et al., 1982. Soil carbon pools and world life zones. Nature, 298: 156-159. doi: 10.1038/298156a0 |
|
Post, W.M., Peng, T.H., Emanuel, W.R., et al., 1990. The global carbon cycle. American Scientist, 78: 310-326. |
|
Qin, X.G., Cai, B.G., Liu, T.S., 2005. Loess record of the aerodynamic environment in the East Asia monsoon area since 60 000 years before present. Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth, 110(B01204): 16. doi: 10.1029/2004JB003131 |
|
Qin, X.G., Li, C.S., Cai, B.G., 2001. The sensitivity simulation of climate impact on C pools of loess. Quaternary Sciences, 21(2): 153-161 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284048269_The_sensitivity_simulation_of_climate_impact_on_C_pools_of_loess |
|
Schimel, D.S., House, J.I., Hibbard, K.A., et al., 2001. Recent patterns and mechanisms of carbon exchange by terrestrial ecosystems. Nature, 414(6860): 169-172. doi: 10.1038/35102500 |
|
Shi, P.L., Yu, G.R., Wang, S.Q., et al., 2003. Research of carbon cycle and carbon storage in Chinese terrestrial ecosystem. In: Yu, G.R., et al., eds., Global change, carbon cycle and storage in terrestrial system. Meteorological Press, Beijing, 396-442 (in Chinese). |
|
Starkel, L., 1998. Continental water cycle and carbon reservoirs and their relationships in the past. Global and Planetary Change, 16-17: 153-158. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(98)00028-9 |
|
Sun, X.J., Song, C.Q., Wang, B.Y., et al., 1995. The vegetation at south of Loess plateau at last 100 ka—the pollen records of Weinan section in Shaanxi. Science Bulletin, 40(13): 1222-1224 (in Chinese). |
|
Velichko, A.A., Zelikson, E.M., Borisova, O.K., 1999. Vegetation, phytomass and carbon storage in northern Eurasia during the last glacial-interglacial cycle and the Holocene. Chemical Geology, 159(1-4): 191-204. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00029-7 |
|
Wang, S.Q., Zhou, C.H., 1999. Estimating soil carbon reservior of terrestrial ecosystem in China. Geographical Research, 18(4): 349-356 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284651662_Estimating_soil_carbon_reservoir_of_terrestrial_ecosystem_in_China |
|
Wen, Q.Z., Diao, G.Y., Jia, R.F., et al., 1996. Geochemical indicators and their significance in paleoclimatic changes in Weinan loess section since the last interglacial. Geochimica, 25(6): 529-535 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/292016762_Geochemical_indicators_and_their_significance_in_paleoclimatic_changes_in_Weinan_loess_section_since_the_last_interglacial |
|
Wu, N.Q., Lü, H.Y., Sun, X.J., 1994. Climate transfer function from opal phytolith and its application in paleoclimate reconstruction of China loesspaleosol sequence. Quaternary Sciences, 3: 270-279 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ199403007.htm |
|
方精云, 刘国华, 徐嵩龄, 1996. 我国森林植被的生物量和净生产量. 生态学报, 16(5): 497-508. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB605.006.htm |
|
郭正堂, 刘东生, 安芷生, 1994. 渭南黄土沉积中十五万年来的古土壤及其形成时的古环境. 第四纪研究, (3): 256-269. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.03.007 |
|
韩家懋, 姜文英, 刘东生, 等, 1996. 黄土碳酸盐中古气候变化的同位素记录. 中国科学(D辑), 26(5): 399-404. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.1996.05.001 |
|
金峰, 杨浩, 蔡祖聪, 等, 2001. 土壤有机碳密度及储量的统计研究. 土壤学报, 38(4): 522-528. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2001.04.010 |
|
李天杰, 郑应顺, 王云, 1983. 土壤地理学. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 59-95. |
|
刘东生, 1985. 黄土与环境. 北京: 科学出版社, 29-296. |
|
刘嘉麒, 陈铁梅, 聂高众, 等, 1994. 渭南黄土剖面的年龄测定及十五万年来高分辨时间序列的建立. 第四纪研究, (3): 193-202. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.03.001 |
|
刘增文, 潘开文, 2005. Olson枯落物分解模型存在的问题与修正. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 33(1): 69-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-9387.2005.01.016 |
|
吕厚远, 刘东生, 吴乃琴, 等, 1999. 末次间冰期以来黄土高原南部植被演替的植物硅酸体记录. 第四纪研究, (4): 336-349. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.04.006 |
|
秦小光, 李长生, 蔡炳贵, 2001. 气候变化对黄土碳库效应影响的敏感性研究. 第四纪研究, 21(2): 153-161. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.02.008 |
|
石培礼, 于贵瑞, 王绍强, 等, 2003. 中国陆地生态系统碳循环与碳储量研究进展. 见: 于贵瑞, 等主编, 全球变化与陆地生态系统碳循环与碳蓄积. 北京: 气象出版社, 396-442. |
|
孙湘君, 宋长青, 王琫瑜, 等, 1995. 黄土高原南缘10万年以来的植被——陕西渭南黄土剖面的花粉记录. 科学通报, 40(13): 1222-1224. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.13.020 |
|
王绍强, 周成虎, 1999. 中国陆地土壤有机碳库的估算. 地理研究, 18(4): 349-356. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.1999.04.003 |
|
文启忠, 刁桂仪, 贾蓉芬, 等, 1996. 末次间冰期以来渭南黄土剖面地球化学指标所反映的古气候变化. 地球化学, 25(6): 529-535. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1996.06.001 |
|
吴乃琴, 吕厚远, 孙湘君, 等, 1994. 植物硅酸体-气候因子转换函数及其在渭南晚冰期以来古环境研究中的应用. 第四纪研究, 3: 270-279. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.03.008 |









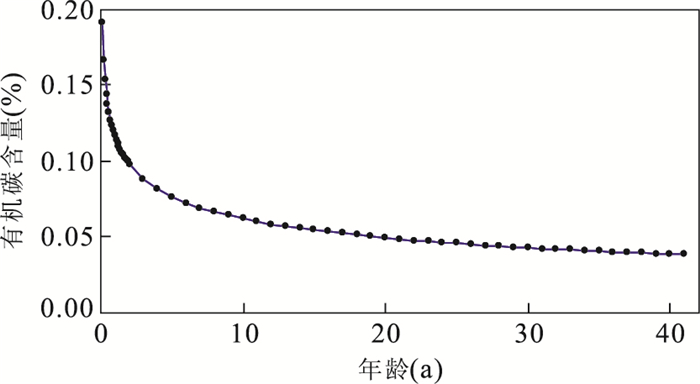
 下载:
下载: