Thermal Evolution Modeling and Characteristic of Source Rock of Paleogene in Beitang Sag
-
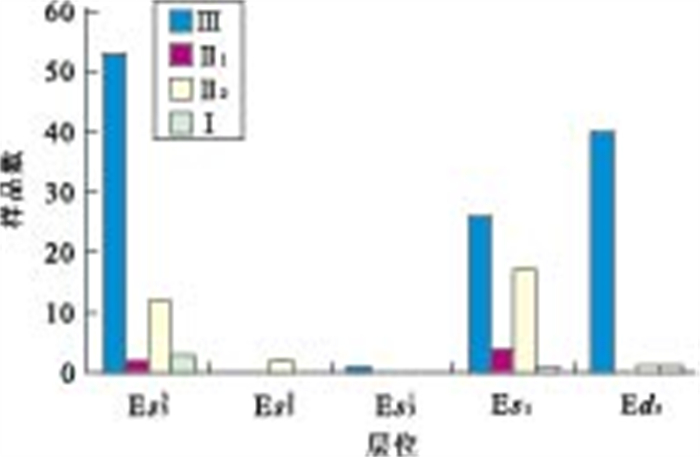
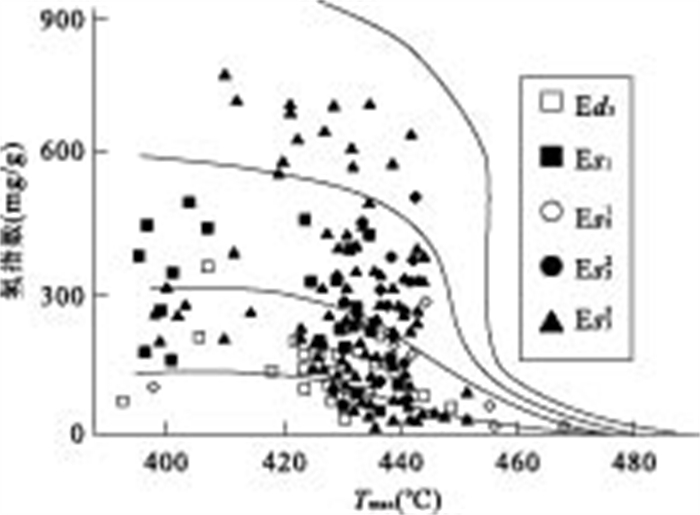
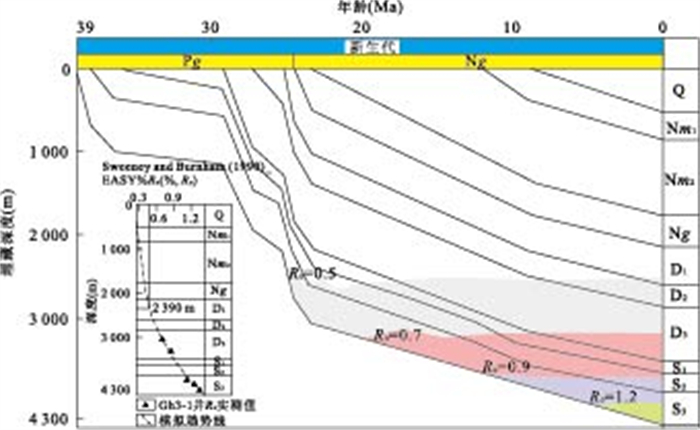
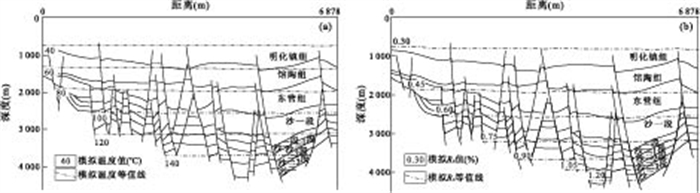
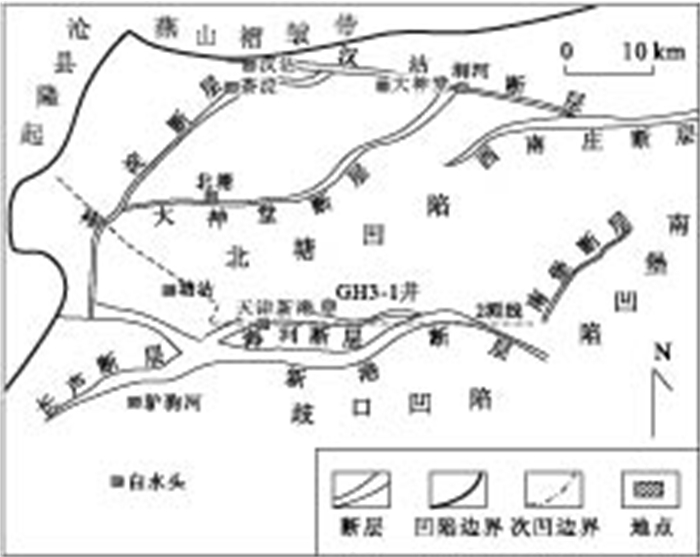
摘要: 根据大量的烃源岩地球化学数据, 分析了北塘凹陷古近系烃源岩的地球化学特征, 从有机碳含量(TOC)、氯仿沥青"A"、总烃含量、S1+S2、有机质类型和成熟度(Ro)等方面对古近系烃源岩进行了系统分析, 结果表明北塘凹陷东三段、沙一段和沙三段是本区的烃源岩层段, 其中沙三段烃源岩生烃指标最好, 是本区的主力烃源岩层段.烃源岩的模拟结果表明: (1)北塘凹陷的烃源岩门限深度为2 390 m, 门限温度为94.2℃, 进入生烃门限的时间约为25~28 Ma; (2)北塘凹陷沙三段的现今地层温度为140~160℃, Ro达0.9%~1.4%, 正处于生油高峰期; 沙一、二段的现今地层温度为100~140℃, Ro达到了0.75%~1.0%左右, 已进入中等成熟阶段; 东营组的现今地层温度为80~100℃, Ro为0.45%~0.75%, 处于低-中等成熟阶段.Abstract: Based on large quantity of organic geochemistry data, the geochemistry characteristics are systematically analyzed on organic carbonate content (TOC), chloroform bitumen "A", overall hydrocarbon content, S1+S2, organic matter types and maturity (Ro%) and so on. It shows that the Dong 3 Member, Sha 1 Member and Sha 3 Member are the main oil source beds of Beitang sag, especially, Sha 3 Member is the best in source rock quality. The model results indicate that (1) The depth of oil generative threshold is about 2 390 m, and the temperature is about 94.2℃, and the time entering on the oil generative threshold is from 25 Ma to 28 Ma in Beitang sag; (2) The present-day temperature of Sha 3 Layer is 140-160℃, the present-day Ro ranges between 0.9%-1.4%, It is in its peak of oil generation. The temperature of Sha 1+2 Layer is 100-140℃, the Ro ranged between 0.75%-1.0%, which suggests that it is in the middle-maturity at present. The present-day temperature of Dongying Layer is 80-100℃, the present-day Ro ranges between 0.45%-0.75%, which indicates that the present-day source rocks are in low maturation.
-
Key words:
- Beitang sag /
- Paleogene /
- source rock /
- thermal evolution history modeling /
- sedimentology
-
表 1 北塘凹陷古近系有机质丰度统计
Table 1. Abundance of organic of Paleogene in Beitang sag
层位 有机碳
(TOC, %)氯仿沥青“A”
(EOM, %)总烃
(10-6)生烃潜量
(S1+S2, mg/g)Ed3 $\frac{\text{0}\text{.52}\sim \text{1}\text{.03}}{\text{0}\text{.64(58)}}$ $\frac{\text{0}\text{.006}\sim \text{0}\text{.192}}{\text{0}\text{.023(15)}}$ $\frac{\text{55}\sim \text{151}}{\text{79(10)}}$ $\frac{\text{0}\text{.32}\sim \text{5}\text{.96}}{\text{2}\text{.91(8)}}$ Es1 $\frac{\text{0}\text{.64}\sim \text{1}\text{.22}}{\text{0}\text{.79(78)}}$ $\frac{\text{0}\text{.008}\sim \text{0}\text{.242}}{\text{0}\text{.032(8)}}$ $\frac{\text{75}\sim \text{224}}{\text{141(6)}}$ $\frac{\text{1}\text{.45}\sim \text{9}\text{.61}}{\text{4}\text{.42(6)}}$ Es31 $\frac{\text{0}\text{.63}\sim \text{2}\text{.65}}{\text{1}\text{.17(246)}}$ $\frac{\text{0}\text{.018}\sim \text{0}\text{.331}}{\text{0}\text{.062(58)}} $ $\frac{\text{175}\sim \text{325}}{\text{271(33)}}$ $\frac{\text{2}\text{.22}\sim \text{13}\text{.24}}{\text{5}\text{.33(150)}}$ Es32 $\frac{\text{0}\text{.74}\sim \text{2}\text{.01}}{\text{1}\text{.23(147)}}$ $\frac{\text{0}\text{.014}\sim \text{0}\text{.412}}{\text{0}\text{.112(57)}}$ $\frac{\text{478}\sim \text{1 032}}{\text{609(19)}}$ $\frac{\text{2}\text{.41}\sim \text{15}\text{.29}}{\text{6}\text{.59(112)}}$ Es33 $\frac{\text{0}\text{.70}\sim \text{9}\text{.73}}{\text{1}\text{.11(18)}}$ $\frac{\text{0}\text{.023}\sim \text{0}\text{.302}}{\text{0}\text{.076(9)}}$ $\frac{\text{152}\sim \text{778}}{\text{394(5)}}$ $\frac{\text{1}\text{.52}\sim \text{9}\text{.77}}{\text{6}\text{.32(205)}}$ 注:(1)表格中的数据含义$\frac{最小值\sim 最大值}{平均值(样品数)}$;(2)东三段和沙一段数据为1999年所测数据①,沙三1段、沙三2段、沙三3段三组数据中增加了2005年以来所测的数据. -
Bai, Y.F., Wang, Z.S., Wei, A.J., et al., 2008. Time and space distribution characteristics and material resource system of heavy minerals in Dongying Formation of Huanghua depression. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 27(2): 39-42 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK200802010.htm Bai, Y.F., Zhang, B., Wang, H., et al., 2006. Research on the source direction of Palaeogene Dongying Formation in Huanghua depression. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 28(3): 17-19 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX200603004.htm Burnham, A.K., Sweeney, J.J., 1989. A chemical kinetic model of vitrinite maturation and reflectance. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53(10): 2649-2656. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90136-1 Chen, R.S., 1994. Geology of oil and gas. China University of Geosciences Press, Wuhan, 121-126 (in Chinese). Deng, R.J., Chai, G.Q., Yang, H., et al., 2001. Forming conditions and distribution characteristics of Tertiary oil and gas pools in Beitang sag. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 28(1): 27-29 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SKYK200101008.htm Guo, Q.L., Mi, S.Y., Shi, G.R., et al., 1998. Pinciple and method of basin modeling. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing, 1-7(in Chinese). He, L.J., Xiong, L.P., Wang, J.Y., 1998. Effects on the tectonothermal modeling of extensional basins. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 33(2): 222-228 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX802.010.htm Hertle, M., Littke, R., 2000. Coalification pattern and thermal modeling of the Permo-Carbonifer ous Saar basin (SW-Germany). International Journal of Coal Geology, 42: 273-296. doi: 10.1016/S0166-5162(99)00043-9 Hu, J.Y., Huang, D.F., Xu, S.B., et al., 1991. The foundation of China's non-marine petroleum geology theory. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing, 167-222(in Chinese). Hu, S.B., Wang, J.Y., 1995. Principles and progresses on thermal regime of sedimentary basins—an overview. Earth Science Frontiers, 2(3-4): 171-180 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY504.008.htm Hu, S.B., Zhang, R.Y., Luo, Y.H., et al., 1999. Thermal history and tectonic-thermal evolution of Bohai basin, East China. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 42(6): 748-755 (in Chinese with English abstract). Makhous, M., Galushkin, Y.I., 2003. Burial history and thermal evolution of the southern and western Saharan basins: synthesis and comparison with the eastern and northern Saharan basins. AAPG Bulletin, 87(11): 1799-1822. doi: 10.1306/06180301123 Ren, Z.L., 1996. Research on the relations between geothermal history and oil-gas accumulation in the Ordos basin. Acta Petrolei. Sinica, 17(1): 17-24 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB601.002.htm Ren, Z.L., 1999. Research on geothermal history in sedimentary basins of the North China. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing(in Chinese). Ren, Z.L., Zhang, S.H., 1999. Research on the relations between geothermal history and oil-gas accumulation in sedimentary basins of the North China. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 20(Suppl. ): 489-494 (in Chinese with English abstract). Sachsenhofer, R.F., Privalov, V.A., Zhykalyak, M.V., et al., 2002. The Donets basin(Ukraine/Russia): coalification and thermal history. International Joural of Coal Geology, 49(11): 33-55. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166516201000635 Shi, Z.S., He, S., Yang, D.Q., 2005. A study of source rock thermal evolution modeling of Hetaoyuan Formation in Dongzhuang sag of Nanyang oilfield. Geological Science and Technology Information, 24(2): 85-89 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200502019.htm Suggate, R.P., 1998. Relations between depth of burial, vitrinite reflectance and geothermal gradient. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 21(1): 5-32. doi: 10.1306/BF9AB79C-0EB6-11D7-8643000102C1865D Sweeney, J.J., Burnham, A.K., 1990. Evaluation of a simple model of vitrinite reflectance based on chemical kinetics. AAPG Bulletin, 74(10): 1559-1570. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/255005110_Evaluation_of_a_simple_model_of_vitrinite_reflectance_based_on_Chemical_kinetics Tissot, B.P., Welte, D.H., 1984. Petroleum formation and occurrence: a new approach to oil and gas exploration. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg. Wang, J.A., Wang, J.Y., 1993. The geothermal character and oil-gas resource of sedimentary basin in China continent. In: Zhao, C.Y., ed., The research progresses of petroliferous basin geology. Northwest University Press, Xi'an, 227-234 (in Chinese). Wang, Z.S., Liu, Q.X., Tan, Z.H., et al., 2009. Comprehensive evaluation of source rock of Qinan sag, Huanghua depression. Natural Gas Geoscience, 20(6): 968-971 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200906023.htm Zhao, C.Y., Liu, C.Y., Ren, Z.L., 1990. Geology of petroliferous basins and their systematic engineering in research. Oil & Gas Geology, 11(1): 108-113 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199001017.htm 白云风, 王振升, 韦阿娟, 等, 2008. 黄骅坳陷东营组重矿物时空展布特征及物源体系分析. 大庆石油地质与开发, 27(2): 39-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3754.2008.02.011 白云风, 张兵, 王华, 等, 2006. 黄骅坳陷古近纪东营组物源方向研究. 石油天然气学报, 28(3): 17-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2006.03.005 陈荣书, 1994. 石油天然气地质学. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 121-126. 邓荣敬, 柴公权, 杨桦, 等, 2001. 北塘凹陷第三系油气藏形成条件与油气分布. 石油勘探与开发, 28(1): 27-29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2001.01.009 郭秋麟, 米石云, 石广仁, 等, 1998. 盆地模拟原理方法. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1-7. 何丽娟, 熊亮萍, 汪集旸, 1998. 拉张盆地构造热演化模拟的影响因素. 地质科学, 33(2): 222-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX802.010.htm 胡见义, 黄第藩, 徐树宝, 等, 1991. 中国陆相石油地质理论基础. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 167-222. 胡圣标, 汪集旸, 1995. 沉积盆地热体制研究的基本原理和进展. 地学前缘, 2(3-4): 171-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY504.008.htm 胡圣标, 张荣燕, 罗毓辉, 等, 1999. 渤海盆地热历史及构造—热演化特征. 地球物理学报, 42(6): 748-755. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1999.06.004 任战利, 1996. 鄂尔多斯盆地热演化史与油气关系的研究. 石油学报, 17(1): 17-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB601.002.htm 任战利, 1999. 中国北方沉积盆地构造热演化史研究. 北京: 石油工业出版社. 任战利, 张世焕, 1999. 中国北方沉积盆地构造热演化史与油气关系研究. 地球学报, 20(增刊): 489-494. 史忠生, 何生, 杨道庆, 2005. 南阳油田东庄次凹核桃园组烃源岩热演化史模拟研究. 地质科技情报, 24(2): 85-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2005.02.015 汪缉安, 汪集旸, 1993. 中国大陆沉积盆地地热特征及油气资源. 见: 赵重远编. 含油气盆地地质学研究进展. 西安: 西北大学出版社, 227-234. 王振升, 刘庆新, 谭振华, 等, 2009. 黄骅坳陷岐南凹陷烃源岩评价. 天然气地球科学, 20(6): 968-971. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200906023.htm 赵重远, 刘池洋, 任战利, 1990. 含油气盆地地质学及其研究中的系统工程. 石油与天然气地质学, 11(1): 108-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199001017.htm -









 下载:
下载: