Basinal Groundwater Flow Patterns and Their Transformation and Dominant Factors
-
摘要:
Tóth(1963) 在复杂盆地给定上边界水头条件下, 推演出多级次地下水流系统.运用此方法探讨水流模式, 改变盆地介质或盆地深度等条件, 盆地水均衡会同步发生变化; 同时, 给定上边界水头也固化了盆地的势源与势汇的位置与数目, 这与实际条件不相符合, 也限制了地下水流模式的转化研究.在总结实验条件下多级水流系统特征的基础上, 提出了通量上边界的地下水流系统模拟方法(简称CUG-GWFS方法), 并进行了水流系统数值模拟.结果表明: (1)在多个可能势汇的盆地中, 可以发育5种地下水流模式, 即: 简单区域水流系统(RS)、局部+区域两级嵌套水流系统(LS+RS)、局部+中间+区域三级嵌套水流系统(LS+MS+RS)、局部+中间两级嵌套水流系统(LS+MS)和简单局部水流系统(LS).(2)盆地地下水流模式受盆地入渗强度、介质条件、盆地长度与深度比值, 以及盆地可能势汇的多少与位置的影响.(3)保持其他条件不变, 单独加大盆地入渗强度比Ric, 或加大盆地长深比Rld, 盆地水流模式按照上述5种模式呈现有序转化.Abstract: Tóth proposed hierarchical groundwater flow-systems in the complex basin based on given head upper-boundaries in the 1960's. However, when the flow patterns with the given head upper-boundary are dealt with (so called Tóth method), changes of hydraulic conductivities or basin geometry result in changes of water budget in a basin synchronously. At the same time, the number of potential sources and sinks and their positions are fixed by the given head upper-boundaries which are not consistent with the actual condition and may result in wrong groundwater flow patterns and their transformation. Based on summarizing the hierarchical characteristics of groundwater flow systems on sand-box experiments, we propose a numerical simulation of groundwater flow patterns using flux as upper-boundaries (so called CUG-GWFS method). The simulated results show that five sequential flow patterns may develop in the basin with several possible potential sources and sinks: (a) simple regional only, (b) nested local-regional, (c) nested local-intermediate-regional, (d) nested local-intermediate, and (e) just local flow systems. The basinal groundwater flow patterns are dominated by the infiltration intensity, hydraulic conductivities, the ratio of length to depth and the number of potential sources and sinks and their positions. The basinal flow patterns will transform orderly as the five patterns above with the increasing of the ratio of infiltration intensity to hydraulic conductivity Ric or the ratio of length to depth of a basin Rld while the rest conditions remain the same. -
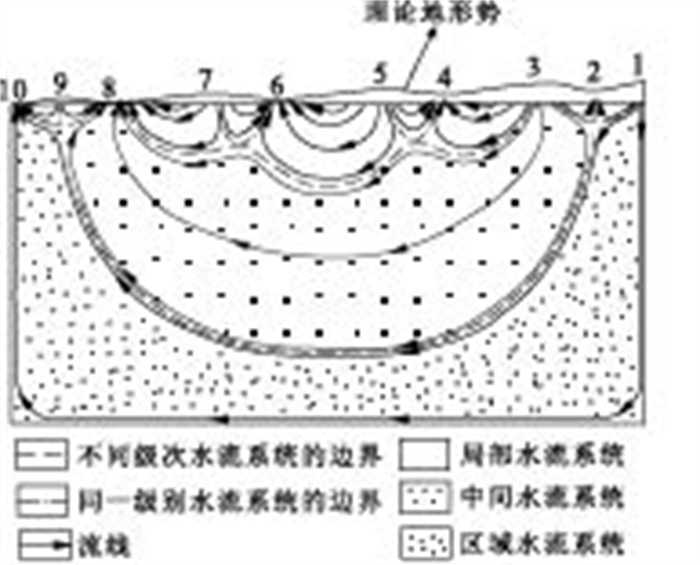
图 1 小型潜水盆地二维剖面数学模型图示(Tóth, 1963)
Fig. 1. Idealized cross-section of a drainage basin's valley flank of the sinusoidal water table
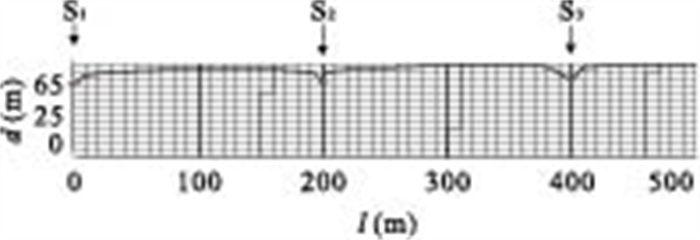
图 2 均质各向同性潜水盆地地下水流系统(Tóth, 1963;理论地形势垂向放大)
图中1、3、5、7、9代表地形势源区;2、4、6、8、10代表地形势汇区
Fig. 2. Theoretical flow pattern and boundaries between different flow systems
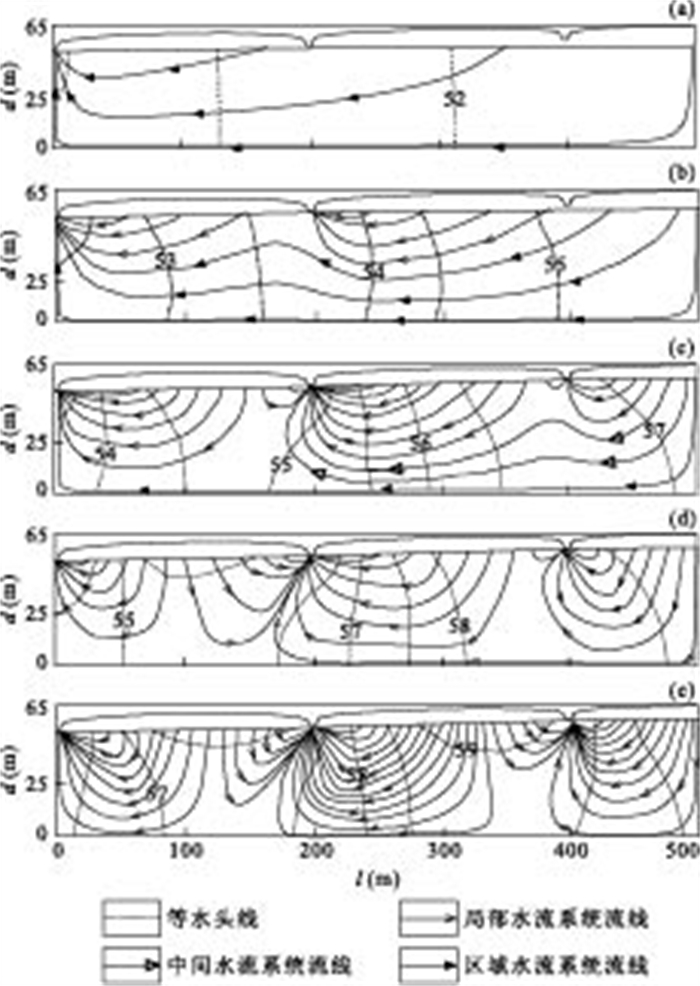
表 1 不同入渗强度比Ric的地下水流模拟结果
Table 1. Simulated results for different ratios of infiltration intensity to hydraulic conductivity
A类Ⅰ组 A类Ⅱ组 Ric(10-3) 地下水流模式 渗透系数K(m/d) 入渗强度ε(mm/d) 渗透系数K(m/d) 入渗强度ε(mm/d) AⅠ-a 0.1 0.05 AⅡ-a 1.00 0.5 0.5 一级RS AⅠ-b 0.1 0.20 AⅡ-b 0.25 0.5 2.0 二级RS+LS AⅠ-c 0.1 0.50 AⅡ-c 0.10 0.5 5.0 三级RS+MS+LS AⅠ-d 0.1 1.00 AⅡ-d 0.05 0.5 10.0 二级MS+LS AⅠ-e 0.1 1.25 AⅡ-e 0.04 0.5 12.5 一级LS 注:模拟的盆地长度与深度之比为10;Ric=ε/k 表 2 逐渐减小盆地深度的地下水流模拟结果
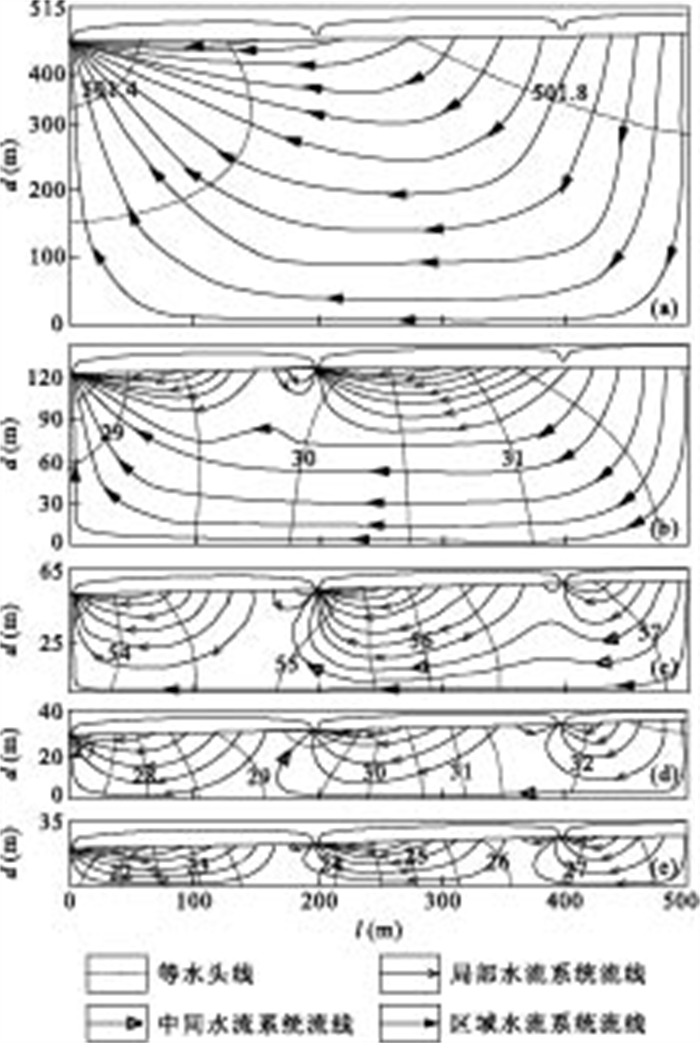
Table 2. Simulated results for different ratios of basin length to depth
B类 长度l(m) 深度d(m) S1坐标(x, z) S2坐标(x, z) S3坐标(x, z) Rld 地下水流模式 B-a 500 515 (0,500) (200,503) (400,506) 1 一级RS B-b 500 140 (0,125) (200,128) (400,131) 4 二级RS+LS B-c 500 65 (0,50) (200,53) (400,56) 10 三级RS+MS+LS B-d 500 40 (0,25) (200,28) (400,31) 20 二级MS+LS B-e 500 35 (0,20) (200,23) (400,26) 25 一级LS 表 3 入渗强度比Ric×长深比Rld相等时的水流模式
Table 3. Flow patterns for different Ric×Rld
A类改变入渗强度比Ric B类改变长深比Rld 地下水流模式 Rld Ric(10-3) Ric×Rld Ric(10-3) Rld Ric×Rld 10 0.5 5 5 1 5 一级RS 10 2.0 20 5 4 20 二级RS+LS 10 5.0 50 5 10 50 三级RS+MS+LS 10 10.0 100 5 20 100 二级MS+LS 10 12.5 125 5 25 125 一级LS -
Engelen, G.B., Jones, G.P., 1986. Developments in the analysis of groundwater flow sytems, No. 163. IAHS Publication, Wallingford. Engelen, G.B., Kloosterman, F.H., 1996. Hydrological systems analysis: methods and applications. Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht. Eótvós Loránd University. (ed. ), 2008. From the artesian paradigm to basin hydraulics—the contribution of József Tóth to hungarian hydrogeology. Publishing Company of Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Budapest. Freeze, R.A., Witherspoon, P.A., 1966. Theoretical analysis of regional groundwater flow: 1. analytical and numerical solutions to the mathematical model. Water Resource. Res., 2(4): 641-656. doi: 10.1029/WR002i004p00641 Freeze, R.A., Witherspoon, P.A., 1967. Theoretical analysis of regional groundwater flow: 2. effect of water-table configuration and subsurface permeability variations. Water Resource. Res., 3(2): 623-634. doi: 10.1029/WR003i002p00623 Freeze, R.A., Witherspoon, P.A., 1968. Theoretical analysis of regional groundwater flow: 3. quantitative interpretation. Water Resource. Res., 4: 581-590. doi: 10.1029/WR004i003p00581 Jiang, X.W., Wan, L., Cardenas, M.B., et al., 2010. Simultaneous rejuvenation and aging of groundwater in basins due to depth-decaying hydraulic conductivity and porosity. Geophysical Research Letters, 37(5): L05403, doi: 10.1029/2010GL042387 Jiang, X.W., Wan, L., Wang, X.S., et al., 2009. Effect of exponential decay in hydraulic conductivity with depth on regional groundwater flow. Geophysical Research Letters, 36(24): L24402. doi: 10.1029/2009GL041251 Liang, X. Liu, Y., Jin, M.G., et al., 2010. Direct observation of complex Tóthian groundwater flow systems in the laboratory. Hydrological Processes, 24: 3568-3573. doi: 10.1002/hyp.7758 Liang, X., Shen, Z.Z., Liu, Y., et al., 2008. A multi-level sub-groundwater flow system demonstrator, China. National utility model patent, 200820066726, 2009-01-14 (in Chinese). Liu, Y., Jia, J., 2009. Study of groundwater flow system simulation of small drainage basin based on matlab. Groundwater, 31(3): 1-3 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, Y., Liang, X., Dong, Q.J., et al., 2010. Experiment of groundwater flow patterns under changes of infiltration intensity. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(6): 111-116 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/el/18725791/2010/00000017/00000006/art00015 Tóth, J., 1963. Theoretical analysis of groundwater flow in small drainage basin. Journal of Geophysical Research, 67(11): 4375-4387. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/335339434_A_theoretical_analysis_of_groundwater_flow_in_small_drainage_basins Tóth, J., 1980. Cross-formation gravity flow of groundwater: a mechanism of the transport and accumulation of petroleum (The generalized hydraulic theory of petroleum migration). In: Robert Ⅲ, W., H., Cordell, R., J., eds., Problems of petroleum migration. AAPG Studies in Geology, 10: 121-167. Tóth, J., 1999. Groundwater as a geological agent: an overview of the cause, process, and manifestations. Hydrogeology Journal, 7(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2009.07.023 Tóth, J., 2009. Gravitational system of groundwater: theory, evaluation, utilization. Cambridge University Press, New York, 297. Zijl, W., 1999. Scale aspects of groundwater flow and transport systems. Hydrogeology Journal, 7(1): 139-150. doi: 10.1007/s100400050185 刘宇, 贾静, 2009. 基于Matlab小型潜水盆地地下水流动系统模拟研究. 地下水, 31(3): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU200903002.htm 刘彦, 梁杏, 权董杰, 等, 2010. 改变入渗强度的地下水流模式实验. 地学前缘, 17(6): 111-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201006015.htm 梁杏, 沈仲智, 刘宇, 等, 2008. 一种多级次地下水流系统演示仪. 中国国家实用新型专利, 200820066726, 2009-01-14. -









 下载:
下载: