Cross Action of Mn-Cr (Ⅵ) in Water-Soil-Rock System
-
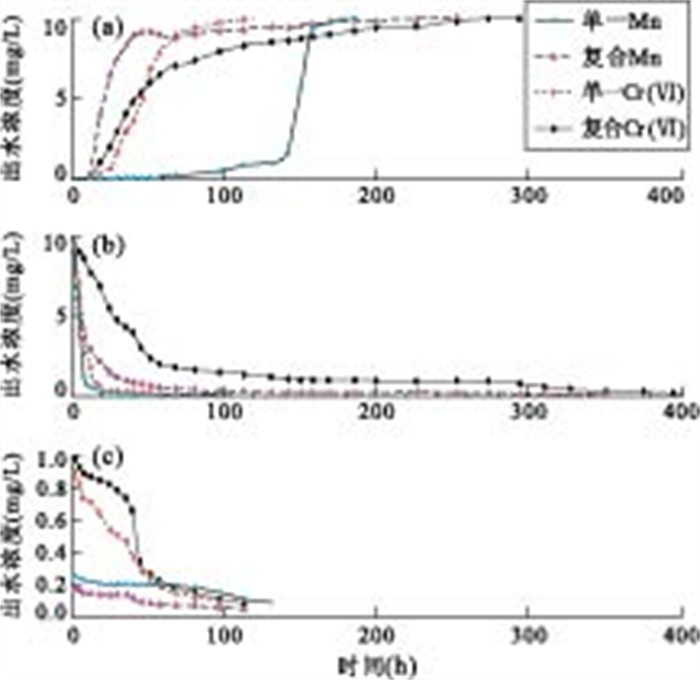
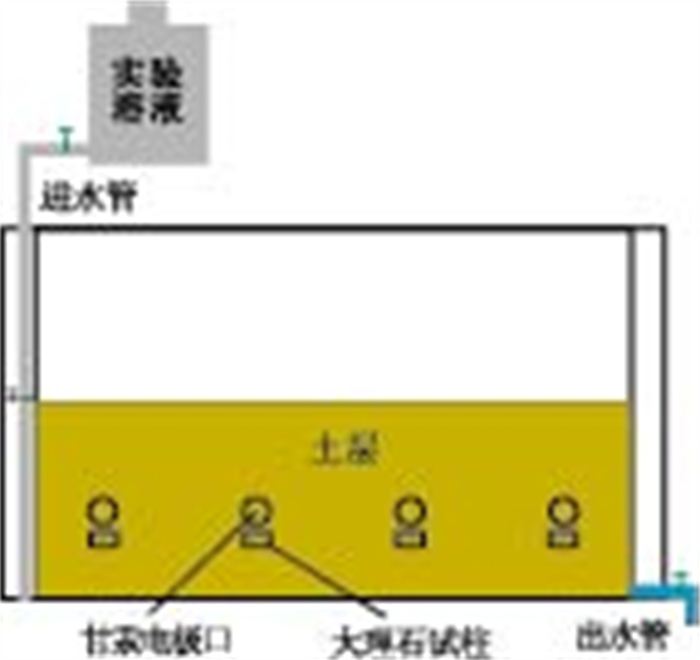
摘要: 采用窄缝槽实验装置, 分别模拟岩溶水系统内单一Mn、Cr(Ⅵ)以及Mn-Cr(Ⅵ)复合体系的动态吸附、物理解吸、化学解吸3个阶段的行为特征, 分析含锰、铬污水对地下水的污染规律及其相互作用.结果表明: 土壤对单一体系Mn的吸附率远大于Cr(Ⅵ), 但两者均以专性吸附为主, 不易活化、迁移; 在复合体系内均出现吸附率降低、解吸率升高, 表现为以物理吸附为主, 易活化、迁移, 从而引起水体重金属污染; 两者表现为显著的协同作用, 但Mn对Cr(Ⅵ)的影响远小于Cr(Ⅵ)对Mn的影响; 在酸性环境下, Mn对Cr(Ⅵ)的化学活性有轻微的抑制作用.Abstract: Using narrow-slit experimental plants, this paper simulates behavioral features of dynamic adsorption, physical desorption, chemical desorption of single Mn system, single Cr (Ⅵ) system and Mn-Cr (Ⅵ) complex system in karst groundwater system. The results indicate that: (1) Under a single system, soil absorption rate of Mn is much larger than that of Cr (Ⅵ); and the two are of specific-orientated adsorption, and difficult to be activated and migrate; (2) Under complex system, the two metals both show absorption rate reduction, desorption rate increase and easy to be activated, migrate; (3) the two metals both show synergistic action, however the effect of Mn to Cr (Ⅵ) is smaller than that of Cr (Ⅵ) to Mn.
-
Key words:
- heavy metals /
- cross action /
- karst area /
- water-soil-rock system /
- adsorption /
- desorption /
- hydrogeology /
- environmental engineering
-
表 1 土壤理化性质
Table 1. Physical and chemical properties of the soil
pH CEC(cmol/L) TOC(%) TN(%) Mn(μg/g) 总Cr(μg/g) 有效N(μg/g) 有效P(μg/g) 有效K(μg/g) Fe2O3(%) CaO(%) 7.73 28.09 0.30 0.050 80.5 <0.5 22.0 3.88 35.90 8.78 0.65 表 2 实验结果
Table 2. Test results
溶液类型 组分 动态吸附 物理解吸 化学解吸 时间(h) 吸附总量(mg)/吸附率(%) 时间(h) 解吸量(mg)/解吸率(%) 时间(h) 解吸量(mg)/解吸率(%) 单一体系 Mn 175 89.6/85.3 68 7.05/7.9 126 0.71/0.8 Cr(Ⅵ) 115 32.5/47.1 60 10.8/33.2 84 1.99/6.1 复合体系 Mn 225 21.4/15.9 320 11.19/52.3 45 0.48/2.2 Cr(Ⅵ) 250 49.8/33.2 400 31.53/63.3 100 2.79/5.6 -
Boik, J., Kirakosyan, A., Kaufman, P.B., et al., 2009. Interactions of bioactive plant metabolites: synergism, antagonism, and additivity. In: Kirakosyan, A., Kaufman, P.B., eds., Recent advances in plant biotechnology. Springer Science+Bussiness Media, LLC, New York, 213-230. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-0194-1_10 Fakayode, S.O., Onianwa, P.C., 2002. Heavy metal contamination of soil, and bioaccumulation in Guinea grass (Panicum maximum) around Ikeja industrial estate, Lagos, Nigeria. Environmental Geology, 43(1-2): 145-150. doi:10.1007/s00254- 002-0633-9 Huang, Q.Y., Tang, J.S., Shi, J., et al., 2008. Migration and conversion of Cr (Ⅵ) in Fe-Mn nodule. Guangxi Agriculture Science, 40(2): 184-189 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_journal-southern-agriculture_thesis/020122590626.html Li, G.H., Cao, Z.M., Lan, D.Z., et al., 2008. Variation of depositional environment and accumulation of heavy metals in West Harbour, Xiamen. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 13(2): 22-223 (in Chinese with English abstract). Luo, Y.P., Wu, X.F., Li, M.S., et al., 2007. Investigation of main plant species and assessment of soil heavy metal pollutions in manganese mine wastelands in North Guangxi. Ecology and Environment, 16(4): 1149-1153 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ200704018.htm Mingorance, M.D., Oliva, R.S., 2006. Heavy metals content in N. Oleander leaves As urban pollution assessment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 119(1-3): 57-68. doi: 10.1007/s10661-005-9004-9 Stehling, F., Kindorf, J., 1994. Interacting environmental influences: concepts of synergism, antagonism, and superposition. Annals of Operations Research, 54(1): 291-304. doi: 10.1007/BF02031739 Sun, T.H., Zhou, Q.X., 2002. Retrospect and prospect of pollution ecology. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 13(2): 221-223 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB200202026.htm Verma, S.R., Rani, S., Dalela, R.C., 1981. Synergism, antagonism, and additivity of phenol, pentachlorophenol, and dinitrophenol to a fish (Notopterus notopterus). Arch. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 10(3): 365-370. doi: 10.1007/BF01055638 Yi, X., Li, W.F., 2005. Studies on absorption and reduction dynamics of Cr (Ⅵ) in Loessial soil. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 19(3): 141-144 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH20050300Q.htm Yu, X.Y., Zou, S.Z., 2009. Research on absorption, desorption behavior of manganese in rock-soil medium. Groundwater, 31(3): 82-84 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU200903028.htm Zeng, Z.H., Cai, W.D., Zhang, Z.L., 2004. The migration enrichment of Mn element in groundwater and the controlling factor. Resources Environment & Engineering, 18(4): 39-42 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285874810_The_migration_enrichment_of_Mn_element_in_groundwater_and_the_controlling_factor Zhang, L., Song, F.B., 2005. Adsorption of heavy metals by soils and its affecting factors. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 36(4): 629-631 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB200504036.htm 黄琼瑶, 唐建生, 时坚, 等, 2009. 六价铬在铁锰结核中的迁移转化研究. 广西农业科学, 40(2): 184-189. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXNY200902018.htm 李桂海, 曹志敏, 蓝东兆, 等, 2008. 厦门西港沉积环境变化及重金属的污染累积. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 13(2): 22-223. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200801020.htm 罗亚平, 吴晓芙, 李明顺, 等, 2007. 桂北锰矿废弃地主要植物种类调查及土壤重金属污染评价. 生态环境, 16(4): 1149-1153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2007.04.016 孙铁珩, 周启星, 2002. 污染生态学研究的回顾与展望. 应用生态学报, 13(2): 22-223. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB200202026.htm 易秀, 李五福, 2005. 黄土性土壤对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附还原动力学研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 19(3): 141-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2005.03.027 于晓英, 邹胜章, 2009. 岩土介质中锰的吸附、解吸行为研究. 地下水, 31(3): 82-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2009.03.027 曾昭华, 蔡伟娣, 张志良, 2004. 地下水中锰元素的迁移富集及其控制因素. 资源环境与工程, 18(4): 39-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1211.2004.04.008 张磊, 宋凤斌, 2005. 土壤吸附重金属的影响因素研究现状及展望. 土壤通报, 36(4): 629-631. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB200504036.htm -









 下载:
下载: