Adsorption Kinetics of As (III) from Groundwater by Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron
-
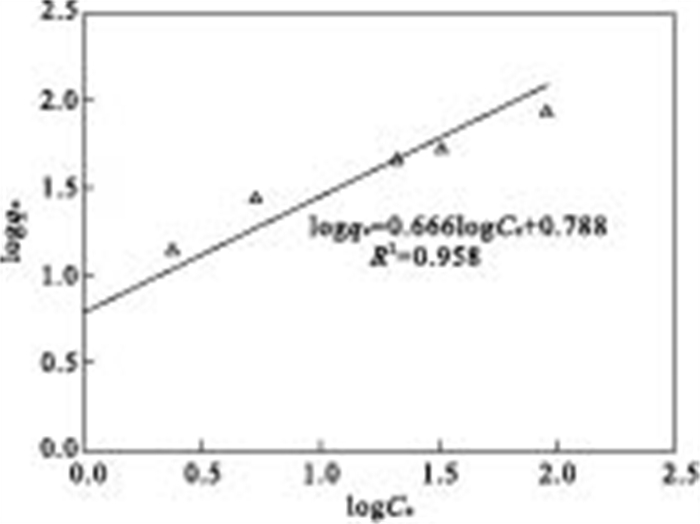
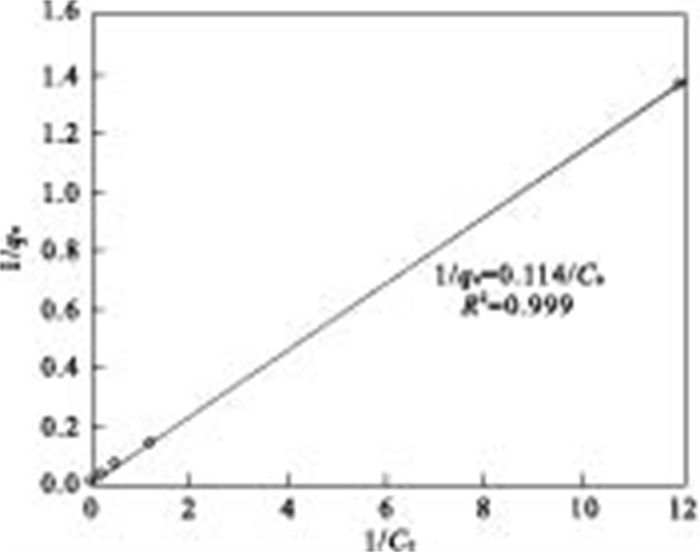
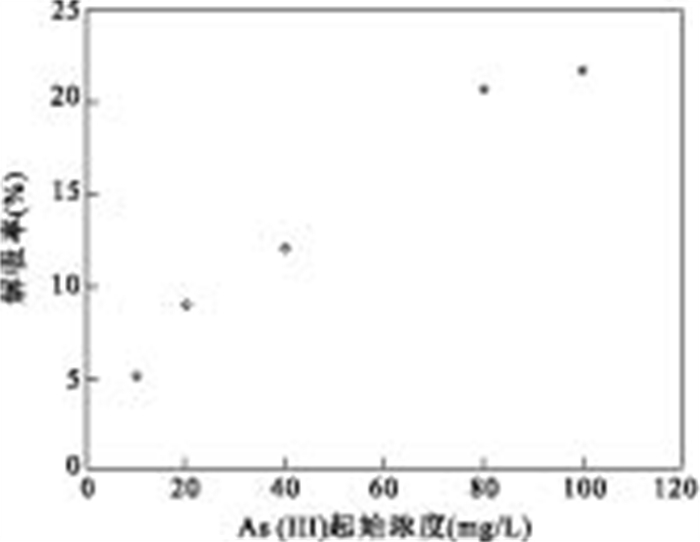
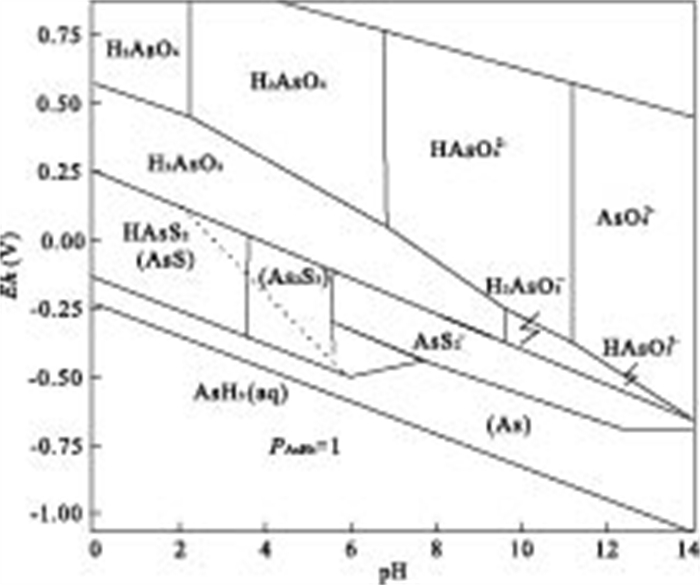
摘要: 实验室合成制得的纳米铁BET比表面积为49.16 m2/g, 直径范围为20~40 nm.通过批实验考察纳米铁对As(Ⅲ)吸附动力学情况.结果表明, 在20℃、pH为7时, 纳米铁能够快速地去除As(Ⅲ), 在60 min内, 0.1 g纳米铁对起始浓度为910 μg/L溶液As(Ⅲ)去除率大于99%.反应遵循准一级反应动力学方程, 标准化后的As(Ⅲ)速率常数kSA为2.6 mL/(m2·min).纳米铁对As(Ⅲ)的吸附等温曲线能够很好地满足Langmuir和Freundlich方程, 相关系数R2>0.95, 由Langmuir模型获得单层纳米铁的最大吸附量为76.3 mg/g.0.1 mol/L NaOH对吸附在纳米零价铁(NZVI)的As(Ⅲ)解吸率为21%.在竞争阴离子中, SiO32-和H2PO4-对As(Ⅲ)的去除有明显阻碍作用, 而其他离子基本上没有影响.纳米铁对As(Ⅲ)的去除机理主要是吸附和共沉淀.Abstract: Artificial synthesized nanoscale zero-valent iron (NZVI) was used in the laboratory for the removal of As(Ⅲ). The average BET surface area of particles was 49.16 m2/g, with a diameter in the range of 20-40 nm. Batch experiments were carried out to study the efficiency of inorganic arsenic removal and adsorption kinetics by NZVI. The results show that As (Ⅲ) can be removed efficiently by NZVI at pH 7, 20℃. The removal rate for As (Ⅲ) is over 99% within 60 minutes by reacting 910 μg/L As (Ⅲ) with 0.1 g NZVI. The As (Ⅲ) adsorption process follows the pseudo-first-order kinetic expression. The surface-area-normalized rate coefficient kSA is 2.6 mL·m-2·min-1 for As (Ⅲ). The equilibrium adsorption data fit Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption model well, with values of the constants at the regression coefficient (R2 > 0.95) for both models. The monolayer adsorption capacity of the sorbent, as obtained from the Langmuir isotherm, 76.3 mg/g is of NZVI. 21% As (Ⅲ) adsorpted on NZVI was found to desorption by sodium hydroxide solution (0.1 M). The effect of competing anions shows SiO32- and H2PO4- markedly decrease with the removal of As (III), while the effect of other anions is insignificant. The mechanism of As removal is adsorption and coprecipitation.
-
表 1 共存离子对As(III)去除率的影响
Table 1. Effect of coexisting ions on arsenic removal by NZVI
共存离子浓度(mM) HCO3- SO42- Br- CO32- NO3- H2PO4- SiO32- 20 99.8 99.8 99.8 99.8 97.5 66.5 28.8 200 99.8 99.8 99.8 95.5 98.9 18.5 0.0 表 2 NZVI表面各元素含量
Table 2. Element amount of NZVI
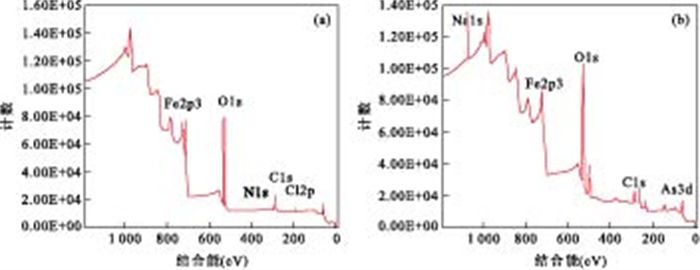
元素 特征能谱(eV) 反应前含量(At. %) 反应后含量(At. %) C1s 284.8 29.81 17.94 O1s 530.7 55.93 56.04 Fe2p3 711.2 11.51 10.65 As3d 44.9 0 3.25 Na1s 1 071.6 0 12.11 -
Bang, S., Johnson, M.D., Korfiatis, G.P., et al., 2005a. Chemical reactions between arsenic and zero-valent iron in water. Water Res. , 39(5): 763-770. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2004.12.022 Bang, S., Korfiatis, G.P., Meng, X.G., 2005b. Removal of arsenic from water by zero-valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. , 121(1-3): 61-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.01.030 Boddu, V.M., Abburi, K., Talbott, J.L., et al., 2008. Removal of arsenic (III) and arsenic (V) from aqueous medium using chitosan-coated biosorbent. Water Res. , 42(3): 633-642. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.08.014 Cumbal, L., Greenleaf, J., Leun, D., et al., 2003. Polymer supported inorganic nanoparticles: characterization and environmental applications. React. Funct. Polym. , 54(1-3): 167-180. doi: 10.1016/S1381-5148(02)00192-X Diamadopoulos, E., Ioanidis, S., Sakellaropoulos, G.P., 1993. As (V) removal from aqueous solutions by fly ash. Water Res. , 27(12): 1773-1777. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(93)90116-Y Farquhar, M.L., Charnock, J.M., Livens, F.R., et al., 2002. Mechanisms of arsenic uptake from aqueous solution by interaction with goethite, lpidocrocite, mackinawite, and pyrite: an X-ray absorption spectroscopy study. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 36(8): 1757-1762. doi: 10.1021/es010216g Farrell, J., Wang, J.P., O'Day, P., et al., 2001. Electrochemical and spectroscopic study of arsenate removal from water using zero-valent iron media. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 35(10): 2026-2032. doi: 10.1021/es0016710 Giménez, J., Martinez, M., de Pablo, J., et al., 2007. Arsenic sorption on to natural hematite, magnetite and goethite. J. Hazard. Mater. , 141(3): 575-580. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.07.020 Guo, H.M., Stüben, D., Berner, Z., 2007. Adsorption of arsenic (III) and arsenic (V) from groundwater using natural siderite as the adsorbent. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 315(1): 47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2007.06.035 Guo, X., Chen, F., 2005. Removal of arsenic by bead cellulose loaded with iron oxyhydroxide from groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 39(17): 6808-6818. doi: 10.1021/es048080k Huang, Y.Y., Liu, D.D., Liu, F., 2009a. Arsenic (III) removal from drinking water by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 18(1): 83-87 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huang, Y.Y., Qin, Z., Liu, F., 2009b. Removal of As (Ⅲ) and As (V) from drinking water by nanoscale zero valent iron. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 28(6): 529-534 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1109/CESCE.2010.232 Huang, C.P., Fu, P.L., 1984. Treatment of arsenic(V)-containing water by activated carbon process. Journal Water Pollution Control Federation, 56(3): 233-242. Kanel, S.R., Manning, B., Charlet, L., et al., 2005. Removal of arsenic (III) from groundwater by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 39(5): 1291-1298. doi: 10.1021/es048991u Korte, N.E., Fernando, Q., 1991. A review of arsenic (III) in groundwater. Critical Reviews in Environmental Control, 21(1): 1-39. doi: 10.1080/10643389109388408 Kundu, S., Gupta, A.K., 2006. Arsenic adsorption onto iron oxide-coated cement (IOCC): regression analysis of equilibrium data with several isotherm models and their optimization. Chem. Eng. J. , 122 (1-2): 93-106. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2006.06.002 Lien, H.L., Wilkin, R., 2005. High-level arsenite removal from groundwater by zero-valent iron. Chemosphere, 59(3): 377-386. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.055 Lumsdon, D.O., Evans, L.J., 1994, Surface complexation model parameters for goethite (α-FeOOH). J. Colloid Interface Sci. , 164 (1): 119-125. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1994.1150 Manning, B.A., Hunt, M.L., Amrhein, C., et al., 2002. Arsenic (III) and arsenic (V) reactions with zerovalent iron corrosion products. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 36(24): 5455-5461. doi: 10.1021/es0206846 Masscheleyn, P.H., DeLaune, R.D., Patrick, W.H., 1991. Effect of redox potential and pH on arsenic speciation and solubility in a contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 25(8): 1414-1419. doi: 10.1021/es00020a008 Melitas, N., Wang, J., Conklin, M., et al., 2002. Understanding soluble arsenate removal kinetics by zerovalent iron media. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 36(9), 2074-2081. doi: 10.1021/es011250y Mohan, D., Pittman, C.U. Jr., 2007. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. , 142(1-2): 1-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.006 Pokhrel, D., Viraraghavan, T., 2006. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by a modified fungal biomass. Water Res. , 40(3): 549-552. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2005.11.040 Pratap, C., Shigeru, K., Toshinori, K., et al., 2009. Arsenic adsorption from aqueous solution on synthetic zeolites. J. Hazard. Mater. , 162: 440-447. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.061 Su, C.M., Puls, R.W., 2001. Arsenate and arsenite removal by zerovalent iron: kinetics, redox transformation, and implications for in situ groundwater remediantion. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 35(7): 1487-1492. doi: 10.1021/es001607i Sun, H., Wang, L., Zhang, R., et al., 2006. Treatment of groundwater polluted by arsenic compounds by zero valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. , B129: 297-303. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.026 Sylvester, P., Westerhoff, P., Moller, T., et al., 2007. A hybrid sorbent utilizing nanoparticles of hydrous iron oxide for arsenic removal from drinking water. Environ. Eng. Sci. , 24(1): 104-112 doi: 10.1089/ees.2007.24.104 U.S. EPA., 2001. National primary drinking water regulations: arsenic and clarifications to compliance and new source contaminants monitoring: final rule. Federal Register, 66(14): 69-76. Welch, A.H., Lico, M.S., Hughes, J.L., 1988. Arsenic in ground water of the western United States. Ground Water, 26(3): 333-347. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584 Wilkie, J.A., Hering, J.G., 1998. Rapid oxidation of geothermal arsenic (III) in stream waters of the eastern Sierra Nevada. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 32(5): 657-662. doi: 10.1021/es970637r Zhang, W.X., Wang, C.B., Lien, H.L., 1998. Treatment of chlorinated organic contaminants with nanoscale bimetallic particles. Catalysis Today, 40(4): 387-395. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00067-4 Zhu, H.J., Jia, Y.F., Wu, X., et al., 2009. Removal of arsenic from water by supported nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. , 172: 1591-1596. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.031 Zhu, H.J., Jia, Y.F., Yao, S.H., et al., 2009. Removal of arsenate from drinking water by activated carbon supported nano zero-valent iron. Environmental Science, 30(12): 3562-3567 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/20187387 黄园英, 刘丹丹, 刘菲, 2009a. 纳米铁用于饮用水中As(III)去除效果. 生态环境学报, 18(1): 83-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ200901019.htm 黄园英, 秦臻, 刘菲, 2009b. 纳米铁去除饮用水中As(III)和As(V). 岩矿测试, 28(6): 529-534. 朱慧杰, 贾永锋, 姚淑华, 等, 2009. 负载型纳米铁吸附剂去除饮用水中As(Ⅴ) 的研究. 环境科学, 30(12): 3562-3567. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.12.019 -










 下载:
下载: