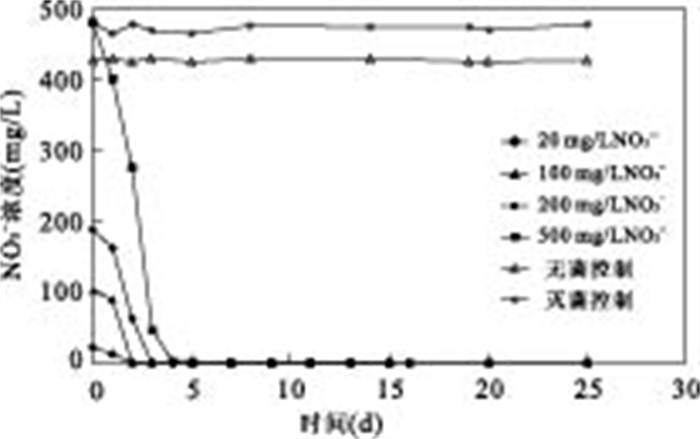
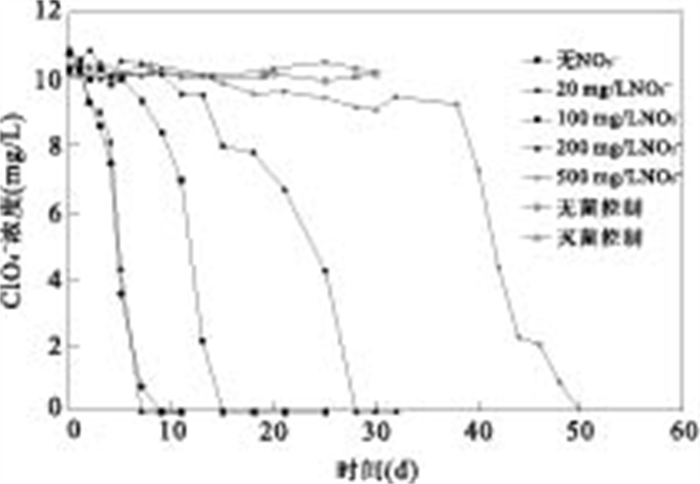
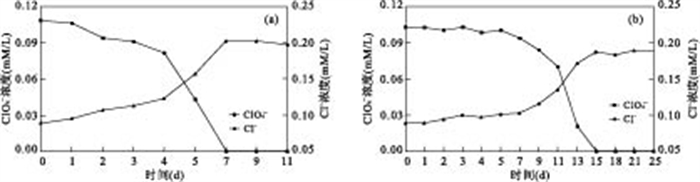
|
Bardiya, N., Bae, J.H., Nusslein, K.R., et al., 2005. Bioremediation potential of a perchlorate-enriched sewage sludge consortium. Chemosphere, 58(1): 83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.09.001 |
|
Cai, Y.Q., Shi, Y.L., Zhang, P., et al., 2006. Perchlorate related environmental problems. Progress in Chemistry, 18(11): 1554-1564 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HXJZ200611017.htm |
|
Dasgupta, P.K., Martinelango, P.K., Jachson, W.A., et al., 2005. The origin of naturally occurring perchlorate: the role of atmospheric processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 39(6): 1569-1575. doi: 10.1021/es048612x |
|
Dudley, M., Salamone, A., Nerenberg, R., 2008. Kinetics of a chlorate-accumulating, perchlorate-reducing bacterium. Water Res. , 42(10-11): 2403-2410. doi: 10.1016/ j.watres.2008.01.009 |
|
Farhan, Y.H., Hatzinger, P.B., 2009. Modeling the biodegradation kinetics of perchlorate in the presence of oxygen and nitrate as competing electron acceptors. Biorem. J. , 13(2): 2, 65-78. doi: 10.1080/10889860902902016 |
|
Furdui, V.I., Tomassini, F., 2010. Trends and sources of perchlorate in Arctic snow. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 44(2): 588-592. doi: 10.1021/es902243b |
|
Gal, H., Ronen, Z., Weisbrod, N., et al., 2008. Perchlorate biodegradation in contaminated soils and the deep unsaturated zone. Soil Biol. Biochem. , 40(7): 1751-1757. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbil.2008.02.015 |
|
Jackson, W.A., Bohlke, J.K., Gu, B.H., et al., 2010. Isotopic composition and origin of indigenous natural perchlorate and co-occurring nitrate in the southwestern United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 44(13): 4869-4876. doi: 10.1021/es903802j |
|
Jin, Z.F., Li, W.T., Pan, Z.Y., et al., 2006. Methods for nitrate removal from underground water. Technology of Water Treatment, 32(8): 34-37 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=22497484 |
|
Ju, X.M., Sierra-Alvarez, R., Field, J.A., et al., 2008. Microbial perchlorate reduction with elemental sulfur and other inorganic electron donors. Chemosphere, 71(1): 114-122. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.09.045 |
|
Lee, J.W., Lee, K.H., Park, K.Y., et al., 2010. Hydrogenotrophic denitrification in a packed bed reactor: effects of hydrogen-to-water flow rate ratio. Bioresour. Technol. , 101(11): 3940-3946. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.022 |
|
Nerenberg, R., Kawagoshi, Y., Rittnann, B.E., 2006. Kinetics of a hydrogen-oxidizing, perchorate-reducing bacterium. Water. Res. , 40(17): 3290-3296. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.035 |
|
Nozawa-Inoue, M., Scow, K.M., Rolston, D.E., 2005. Reduction of perchlorate and nitrate by microbial communities in vadose soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. , 71(7): 3928-3934. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.7.3928-3934.2005 |
|
Qian, H.J., Xi, S.L., He, P., et al., 2009. Biological reduction of perchlorate and optimization. Environmental Science, 30(5): 1402-1407 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/19558109 |
|
Sahu, A.K., Conneely, T., Nusslein, K.R., et al., 2009. Biological perchlorate reduction in packed bed reactors using elemental sulfur. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 43(12): 4466-4471. doi: 10.1021/es900563f |
|
Shrout, J.D., Parkin, G.F., 2006. Influence of electron donor, oxygen, and redox potential on bacterial perchlorate degradation. Water Res. , 40(6): 1191-1199. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.01.035 |
|
Son, A., Lee, J., Chiu, P.C., et al., 2006. Microbial reduction of perchlorate with zero-valent iron. Water. Res. , 40(10): 2027-2032. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.03.027 |
|
Srinivasan, A., Viraraghavan, T., 2009. Perchlorate: health effects and technologies for its removal from water resources. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 6(4): 1418-1442. doi: 10.3390/ijerph6041418 |
|
Tan, K., Anderson, T.A., Jackson, W.A., 2004. Degradation kinetics of perchlorate in sediments and soils. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. , 151(1-4): 245-259. doi: 10.1023/B:WATE.0000009904.23410.89 |
|
Wang, D.M., Shah, S.I., Chen, J.G., et al., 2008. Catalytic reduction of perchlorate by H2 gas in dilute aqueous solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. , 60(1): 14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2007.07.039 |
|
Wang, H.C., Sun, C., 2009. Inorganic and analytical chemistry experiment. Chemical Industry Publishing House, Beijing, 1-134 (in Chinese). |
|
Wu, D.L., He, P., Xu, X.H., et al., 2008. The effect of various reaction parameters on bioremediation of perchlorate-contamiated water. J. Hazard. Mater. , 150(2): 419-423. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.124 |
|
Xu, J., Trimble, J.J., Steinberg, L., et al., 2004. Chlorate and nitrate reduction pathways are separately induced in the perchlorate-respiring bacterium Dechlorosoma sp. KJ and chlorate-respiring bacterium Pseudomonas sp. PDA. Water Res. , 38(3): 673-680. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.20083.10.017 |
|
Yu, X.Y., Amrhein, C., Deshusses, M.A., et al., 2007. Perchlorate reduction by autotrophic bacteria attached to zero-valent iron in a flow-through reactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. , 41(3): 990-997. doi: 10.1021/es061959a |
|
Ziv-EI, M.C., Rittmann, B.E., 2009. Systematic evaluation of nitrate and perchlorate bioreduction kinetics in groundwater using a hydrogen-based membrane biofilm reactor. Water Res. , 43(1): 173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.09.035 |
|
蔡亚岐, 史亚利, 张萍, 等, 2006. 高氯酸盐的环境污染问题. 化学进展, 18(11): 1554-1564. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-281X.2006.11.018 |
|
金赞芳, 李文腾, 潘志彦, 等, 2006. 地下水硝酸盐去除方法. 水处理技术, 32(8): 34-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2006.08.009 |
|
钱慧静, 奚胜兰, 何平, 等, 2009. 生物法降解高氯酸盐及其优化研究. 环境科学, 30(5): 1402-1407. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.05.025 |
|
王和才, 孙成, 2009. 无机及分析化学实验. 北京: 化学工业出版社. |










 下载:
下载: