Nitrogen Isotope Tracing of Sources of Nitrate Contamination in Groundwater from Wastewater Irrigated Area
-
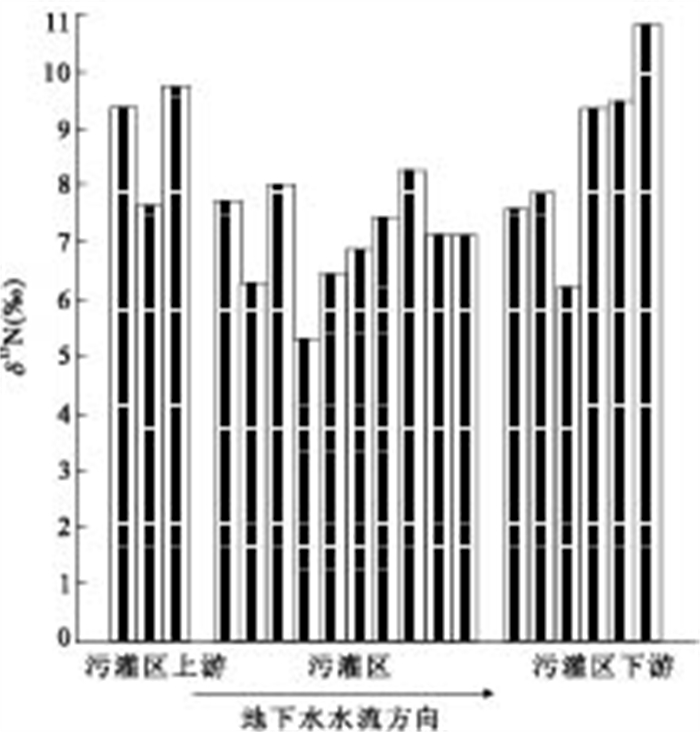
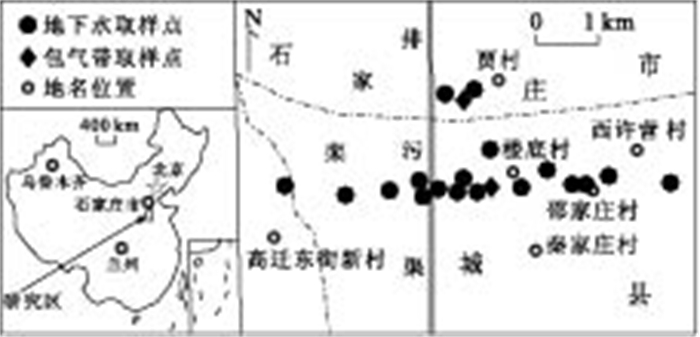
摘要: 为了识别石家庄市南部污灌区地下水硝酸盐污染来源, 采集5种潜在污染源和19组地下水样用于化学和氮同位素分析.灌溉污水NH4+的δ15N值较低(4.0‰), 施化肥土壤和粪堆下土壤NO3-的δ15N值分别为1.4‰和12.4‰; 仅施厩肥的蔬菜种植区下伏近30 m厚包气带沉积物NO3-的δ15N分布显示, 来自动物粪便的NO3-已运移到11.5 m以下包气带, 均值10.9‰; 污水灌溉农田下伏厚层包气带沉积物样品分析结果指示, 土壤层下伏包气带沉积物δ15N值变幅较小, 均值5.7‰.污灌区内除一深井外, 其他水井地下水硝酸盐浓度变化在52.6~124.5 mg/L之间, 均值79.72 mg/L, δ15N值变化在5.3‰~8.3‰之间, 均值7.0‰.污灌区地下水的δ15N值较污灌区土壤层下伏包气带沉积物的δ15N值高, 表明地下水NO3-除了来自灌溉的污水外, 还有δ15N值更高的其他来源, 这些来源主要是人和动物粪便.利用线性混合模型计算, 污灌区地下水NO3-来自灌溉的污水, 约占76%, 而来自人和动物粪便的NO3-约占24%.为控制污灌区地下水NO3-浓度进一步增长, 不仅要加强污水灌溉管理, 还要加强人和动物粪便的管理.Abstract: In order to identify sources of nitrate in groundwater from the wastewater irrigated area, the southern part of Shijiazhuang City, 5 soil/wastewater samples from potential contamination sources and 19 groundwater samples were collected for chemical and nitrogen isotopic analyses. Irrigation wastewater has relatively low δ15N value of 4.0‰, and soil applied with commercial fertilizer and beneath animal waste piles has δ15N values of 1.4‰ and 12.4‰, respectively. The distribution of δ15N values of sediment from about 30 m-thick vadose zone beneath the vegetable growth plot only applied with animal wastes shows that NO3- derived from animal wastes has transported to the lower vadose zone with the mean δ15N value of 10.9‰. Sediment samples collected from the thick vadose zone beneath the farmland only irrigated with wastewater indicates that the deep vadose zone below the soil layer has narrow range of δ15N values with the mean δ15N value of 5.7‰. Groundwater from the wastewater irrigated area has NO3- concentration ranging from 52.6 mg/L to 124.5 mg/L with a mean value of 79.72 mg/L, and δ15N values of NO3- ranging from 5.3 to 8.3‰ with a mean value of 7.0‰ except a sample from a deep well. δ15N values of groundwater from the wastewater irrigated area are higher than those from the deep vadose zone beneath the wastewater irrigated area, which indicates that other sources with higher δ15N values contribute to groundwater NO3-. The other sources are mainly human and animal wastes. NO3- in groundwater from the wastewater irrigated area are derived from irrigation wastewater accounting for about 76% and from human and animal wastes accounting for about 24%, respectively. Wastewater irrigation and human/animal wastes management should be strengthened to prevent groundwater NO3- contamination in the wastewater irrigated area.
-
表 1 潜在污染源氮同位素和无机氮分析结果
Table 1. Results of analyses of nitrogen isotopes and inorganic nitrogen for potential sources of contamination
样品类型 取样深度(m) δ15Ns/air(‰) NO3-(mg/kg) NH4+(mg/kg) 排污渠污水 +4.0 65 mg/L 粪堆下土壤 1.0 +12.4 134.50 施化肥土壤 1.0 +1.4 72.50 施厩肥菜地包气带沉积物 11.5~28.0 +10.9 66.21 污灌农田包气带沉积物 1.0~28.0 +5.7 43.96 表 2 地下水化学和氮同位素分析结果
Table 2. Results of chemical and nitrogen isotopic analyses
样品编号 取样日期 水井类型 井深(m) δ15Ni/air(‰) NO3-(mg/L) 溶解氧DO(mg/L) pH TDS(mg/L) Cl-(mg/L) n(NO3-)/n(Cl-) 污灌区上游 W09-1 2009-5-13 农灌井 50 9.4 39.92 / 7.06 609 172.70 0.13 W09-2 2009-5-13 农灌井 50 7.6 48.60 5.97 7.1 554 132.70 0.21 W09-3 2009-5-14 自备井 50 9.7 87.18 2.8 6.91 695 178.70 0.28 污灌区内 W09-4 2009-5-14 自备井 80 7.7 86.06 / 7.01 815 223.60 0.22 W09-17 2009-5-13 自备井 90 6.3 75.00 / 7.2 767 187.50 0.23 W09-5 2009-5-15 自备井 105 8.0 14.05 2.85 7.47 285 12.38 0.65 W09-6 2009-5-14 自备井 60 5.3 84.86 1.7 7.01 812 192.80 0.25 W09-7 2009-5-14 自备井 50 6.4 69.82 1.2 6.82 847 224.70 0.18 W09-8 2009-5-14 农灌井 60 6.8 82.60 2.83 7.02 807 192.80 0.25 W09-20 2009-5-15 自备井 60 7.5 124.50 3.34 7.14 809 232.50 0.31 W09-9 2009-5-14 村供水井 90 8.3 66.80 / 6.98 688 166.30 0.23 W09-15 2009-5-15 自备井 60 7.2 75.20 2.36 7 709 178.00 0.24 W09-16 2009-5-15 自备井 100 7.1 52.60 2.66 6.99 622 156.70 0.19 污灌区下游 W09-18 2009-5-15 自备井 50 7.6 80.00 1.87 7.08 615 182.20 0.25 W09-10 2009-5-14 自备井 60 7.9 51.19 / 7.17 581 157.50 0.19 W09-19 2009-5-15 村供水井 120 6.2 45.60 1.86 7.11 615 159.20 0.16 W09-11 2009-5-15 自备井 60 9.4 40.44 / 7.15 612 146.80 0.16 W09-12 2009-5-15 自备井 60 9.5 39.87 2.0 7.13 545 130.20 0.18 W09-13 2009-5-15 自备井 45 10.8 28.93 3.28 7.17 453 103.70 0.16 -
Chen, J.Y., Tang, C.Y., Yu, J.J., 2006. Use of 18O, 2H and 15N to identify nitrate contamination of groundwater in a wastewater irrigated field near the city of Shijiazhuang, China. J. Hydrol., 326(1-4): 367-378. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.11.007 Choi, W.J., Han, G.H., Lee, S.M., et al., 2007. Impact of land-use types on nitrate concentration and δ15N in unconfined groundwater in rural areas of Korea. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 120(2-4): 259-268. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2006.10.002 Delwiche, C.C., Steyn, P.L., 1970. Nitrogen isotope fractionation in soils and microbial reactions. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(11): 929-935. doi: 10.1021/es60046a004 Fogg, G.E., Rolston, D.E., Decker, D.L., et al., 1998. Spatial variation in nitrogen isotope values beneath nitrate contamination sources. Ground Water, 36(3): 418-426. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1998.tb02812.x Fryar, A.E., Macko, S.A., Mullican, Ⅲ, W.F., et al., 2000. Nitrate reduction during ground-water recharge, southern High Plains, Texas. J. Contam. Hydrol., 40(4): 335-363. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7722(99)00059-5 Heaton, T.H.E., 1986. Isotopic studies of nitrogen pollution in the hydrosphere and atmosphere: a review. Chem. Geol., 59: 87-102. doi: 10.1016/0168-9622(86)90059-X Herbei, M.J., Spalding, R.F., 1993. Vadose zone fertilizer-derived nitrate and δ15N extracts. Ground Water, 31(3): 376-382. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1993.tb01838.x Jiang, C.L., Xia, Z.Q., Liu, L., 1997. Impacts of wastewater irrigation on environmental factors of soil and groundwater either side of Kui River. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Science), 25(5): 114-116 (in Chinese with English abstract). Kass, A., Gavrieli, I., Yechieli, Y., et al., 2005. The impact of freshwater and wastewater irrigation on the chemistry of shallow groundwater: a case study from the Israeli coastal aquifer. Journal of Hydrology, 300: 314-331. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.06.013 Koba, K., Tokuchi, N., Wada, E., et al., 1997. Intermittent denitrification: the application of a 15N natural abundance method to a forested ecosystem. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 61(23): 5043-5050. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00284-6 Kreitler, C.W., Jones, D.C., 1975. Natural soil nitrate: the cause of the nitrate contamination of groundwater in Runnels County, Texas. Ground Water, 13(1): 53-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1975.tb03065.x Li, G.H., 1989. Research about "time effect" of sewage irrigation on groundwater pollution in Zhengzhou city. Journal of Changchun University of Earth Science, 19(4): 117-122 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ198904008.htm Mariotti, A., Germon, J.C., Hubert, P., et al., 1981. Experimental determination of nitrogen kinetic isotope fractionation: some principles; illustration for the denitrification and nitrification processes. Plant and Soil, 62(3): 413-430. doi: 10.1007/BF02374138 Qishlaqi, A., Moore, F., Forghani, G., 2008. Impact of untreated wastewater irrigation on soils and crops in Shiraz suburban area, SW Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 141: 257-273. doi:10.1007/ s10661-007-9893-x. Shao, Y.S., Ji, S., 1992. Using nitrogen isotope technique to study influence of irrigation with sewage on the pollution of groundwater. Geotechnical Investigation and Surveying, (4): 37-41 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC199204008.htm Sigman, D.M., Casciotti, K.L., Andreani, M., et al., 2001. A bacterial method for the nitrogen isotopic analysis of nitrate in seawater and freshwater. Anal. Chem., 73(17): 4145-4153. doi: 10.1021/ac010088e Spalding, R.F., U, Z.K., Hyun, S.W., et al., 2001. Source identification of nitrate on Cheju Island, South Korea. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 61: 237-246. doi: 10.1007/s10705-004-1476-4 Tang, C.Y., Chen, J.Y., Song, X.F., et al., 2006. Effects of wastewater irrigation on groundwater quantity and quality in the suburbs of Shijiazhuang city, China. Resources Science, 28(1): 102-109 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZRZY200601017.htm Xue, D.M., Botte, J., De Baets, B., et al., 2009. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface- and groundwater. Water Res., 43(5): 1159-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.048 Zeng, D.F., Zhu, W.B., 2004. Discussion on problems of sewage irrigation and countermeasures in China. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 22(4): 221-224 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GHDQ200404044.htm Zhang, C.Y., Zhang, J.X., Ma, L.N., et al., 2010. Nitrogen and oxygen isotopic analyses of nitrate in groundwater and sediments using the denitrifier method. In: Birkle, P., Torres-Alvarado, I.S., eds., Water-rock interaction, proceedings of the 13th international symposium on water-rock interaction, Guanajuato, Mexico, 16-20 August, 2010. Taylor & Francis, London, 319-322. Zhang, L., Altabet, M.A., Wu, T.X., et al., 2007. Sensitive measurement of NH4+15N/14N (δ15NH4+) at natural abundance levels in fresh and saltwaters. Analytical Chemsitry, 79(14): 5297-5303. doi: 10.1021/ac070106d 姜翠玲, 夏自强, 刘凌, 1997. 污灌对奎河两岸土壤和地下水环境要素的影响. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 25(5): 114-116. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1980.1997.05.021 李广贺, 1989. 郑州市污水灌溉对地下水污染的"时间效应" 研究. 长春地质学院学报, 19(4): 117-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ198904008.htm 邵益生, 纪衫, 1992. 应用氮同位素方法研究污灌对地下水氮污染的影响. 工程勘察, (4): 37-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC199204008.htm 唐常源, 陈建耀, 宋献方, 等, 2006. 农业污水灌溉对石家庄市近郊灌农业区地下水环境的影响. 资源科学, 28(1): 102-109. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2006.01.017 曾德付, 朱维斌, 2004. 我国污水灌溉存在问题和对策探讨. 干旱地区农业研究, 22(4): 221-224. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7601.2004.04.044 -









 下载:
下载: