Assessment and Prediction of the Combined Pollution Risk of Heavy Metals in the Sulfide Tailings of a Mining Area, Northern Guangxi, China
-
摘要: 对于硫化物尾矿重金属复合污染的评价采用以元素总量为主因子的单一方法(如Nemerom法)常难得到合理的结果.在桂北某矿区,运用地质累积指数、生态危害指数以及BCR酸提取等研究方法,并以近矿围岩风化壳的元素丰度作为参比值,对尾矿Pb、Zn、Cd及As复合污染进行综合评价预测.结果表明,(1)该区尾矿中Cd(生态危害性高、迁移性强)和As(污染程度高、生态危害性也较高)为主要污染因子,应重点预防和控制;而Zn(生态危害性较低)和Pb(污染程度、生态危害性及迁移性均较低)则相对次要;(2)尾矿中元素活性酸提取态分量(为产生环境效应的主因),与其元素总含量之间存在着不同程度或不一致的相关关系,这是元素总量因子评价法的问题之一.Abstract: It may be hard to make a reasonable assessment on the combined pollution risk of heavy metals in the sulfide tailings merely by using a single method (e.g. Nemerom index) based on element total content. This paper carries out the comprehensive assessment of the combined pollution risk of Pb, Zn, Cd and As in the sulfide tailings in a mine (northern Guangxi, China), integrating methods such as the geological accumulative index, the potential ecological risk evaluation, and BCR acid extraction procedure. The reference value is taken from the element abundance of the weathering crust of carbonate country rock nearby LTS ore body in the mine. The results display that: (1) Cadmium (strongest ecological risk and mobility in the four elements) and Arsenic (highest pollution level and stronger ecological risk) are major pollution factors in the mine, and should be prevented and controlled; while Zinc (weak ecological risk), and Pb (low pollution level, weak ecological risk and mobility) may be relatively minor. (2) The elements active-acid-extractable content, which is one of the main causes inducing environment damages, correlates variously or inconsistently with its total content. That may be one reason for the problems existing in the assessment methods only based on the factor of element total content.
-
表 1 尾矿及风化壳样品分析测试结果及其对比
Table 1. Analysis and measurement results of the tailings and the weathered crust samples, and comparison
采样地点 样品编号 样品产状(采样深度,cm) Pb(%) Zn(%) Cd(%) As(%) S(%) Paste pH BL尾矿库 G001-0 中褐色,胶结硬层(表层) 0.830 2.080 0.019 0 7.000 22.90 3.12 G001-1 中褐色,胶结硬层(50) 0.420 2.350 0.020 0 9.630 17.97 2.88 G001 深灰色,尾砂(120) 0.350 1.720 0.014 0 11.110 23.00 7.51 G002 深灰色,尾砂(140) 0.280 3.110 0.016 0 8.600 21.35 7.4 G003 深灰色,尾砂(160) 0.280 1.530 0.013 0 11.210 18.61 7.74 G004 深灰色,尾砂(180) 0.091 1.700 0.014 0 0.930 8.80 7.61 G005 深灰色,尾砂(200) 0.150 2.580 0.020 0 3.730 15.73 7.81 G006 深灰色,尾砂(220) 0.062 1.200 0.010 0 0.380 5.81 7.89 G007 深灰色,尾砂(240) 0.150 1.110 0.008 7 1.930 9.42 7.64 7号尾矿库 7#-3 浅褐色,胶结硬层(表层) 0.290 4.550 0.023 0 0.590 12.82 6.82 73009 灰色,尾砂(20) 0.450 2.500 0.019 0 0.570 11.85 7.44 73010 中灰色,尾砂(40) 0.270 3.010 0.023 0 0.230 8.68 7.58 73011 中灰色,尾砂(60) 0.260 2.200 0.017 0 0.750 8.57 7.84 73012 灰色,尾砂(80) 0.270 2.200 0.016 0 0.580 7.09 7.89 CH尾矿库 C003-1 中黄褐色,尾砂(表层) 0.046 0.320 0.002 0 0.450 5.00 7.37 C003-2 深灰色,尾砂(20) 0.110 0.830 0.006 1 1.040 9.25 7.46 C003-3 深灰色,尾砂(40) 0.092 0.750 0.004 9 0.620 7.74 7.53 C003-4 灰橙色,尾砂(60) 0.076 0.490 0.003 4 0.680 7.36 7.42 C003-5 深灰色,尾砂(80) 0.048 0.290 0.001 7 0.300 3.94 7.61 CH2001 中褐色,胶结硬层(表层) 0.230 0.780 0.005 6 3.940 24.20 5.78 CH2002 深黄褐色,尾砂(20) 0.170 0.710 0.005 2 2.480 15.50 6.66 CH2003 中灰色,尾砂(40) 0.093 0.470 0.003 8 0.800 8.70 6.93 CH2004 中灰色,尾砂(60) 0.051 0.300 0.002 2 0.360 4.00 7.37 CHN007 中灰色,新鲜尾砂(表层) 0.190 0.680 0.005 2 3.600 10.26 8.78 TC尾矿堆 T1004 中黄褐色,胶结硬层(表层) 0.420 0.270 0.001 7 5.980 15.25 2.22 T1005 深灰色,尾砂(20) 0.520 0.880 0.006 4 1.300 7.16 7.33 LTS碳酸盐岩风化壳 GF1001 深灰色,土壤(近地表) 0.600 0.230 0.005 4 0.180 0.80 4.11 GF1002 浅黄橙色,土壤(20) 0.072 0.085 0.000 5 0.050 0.11 4.17 GF1003 深黄橙色,土壤(40) 0.054 0.051 0.000 3 0.030 0.10 4.21 GF1004 灰橙色,土壤(60) 0.055 0.056 0.000 3 0.036 0.12 4.19 GF1005 灰橙色,土壤(80) 0.140 0.028 0.000 2 0.084 0.12 4.15 研究区尾矿统计 平均值 0.238 1.485 0.0108 3.030 11.96 6.91 中值 0.210 1.160 0.009 4 0.990 9.34 7.45 方差 0.182 1.092 0.007 2 3.585 6.19 1.63 变化系数 0.764 0.735 0.6703 1.183 0.52 0.24 LTS风化壳统计 平均值 0.184 0.090 0.001 3 0.076 0.25 4.17 中值 0.072 0.056 0.000 3 0.050 0.12 4.17 方差 0.235 0.081 0.002 3 0.062 0.31 0.04 变化系数 1.276 0.898 1.695 7 0.813 1.23 0.01 研究区旱地土壤均值(张新英等,2008) 0.110 0.140 0.005 0 0.130 研究区泥盆系(张国林和蔡宏渊,1987) 0.355×10-2 0.885×10-2 0.390×10-4① 0.167×10-2 0.40 泰勒克拉克值 0.125×10-2 0.700×10-2 0.200×10-4 0.018×10-2 0.03 注:①据李晓峰等,2010. 表 2 尾矿元素及pH值的Pearson相关系数矩阵
Table 2. Pearson correlation matrix of the elements and pH values of the tailings
Pb Zn Cd As S pH Pb 1.000 Zn 0.382 1.000 Cd 0.479① 0.940② 1.000 As 0.481① 0.175 0.250 1.000 S 0.572② 0.334 0.372 0.821② 1.000 pH 0.600② 0.003 -0.062 -0.422 -0.478 1.000 注:标注"①"表示在0.05置信水平显著相关(双尾);标注"②"表示在0.01置信水平显著相关(双尾). 表 3 尾矿样品地质累积指数(Igeo)计算结果统计
Table 3. Statistics results of the geological accumulation index (Igeo) of the tailings
重金属污染评价指标 矿区尾矿样品的Igeo值统计分布(%) 污染程度分级 Igeo值域 Pb Zn Cd As 无污染 ﹤0 65.40 0.00 0.0 0.0 无-中度污染 0~1 30.80 0.00 23.1 0.0 中度污染 1~2 3.85 23.10 23.1 19.2 中-强污染 2~3 0.00 23.10 19.2 26.9 强污染 3~4 0.00 23.10 34.6 11.5 强-极强污染 4~5 0.00 26.90 0.0 11.5 极强污染 ﹥5 0.00 3.85 0.0 30.8 注:重金属污染评价指标的数据据Muller et al.(1969). 表 4 尾矿样品Eri和RI值计算结果统计
Table 4. Statistics results of Eri and RI values of the tailings
重金属生态危害评价指标 尾矿样品Eri计算值统计(%) 尾矿样品RI计算值统计(%) 危害分级 Eri值域 RI值域 Pb Zn Cd As A.轻微 <30 <135 100.0 88.5 0.0 0.00 11.5 B.中等 30~60 135~265 0.0 11.5 15.4 19.20 11.5 C.强 60~120 265~525 0.0 0.0 19.2 26.90 30.8 D.很强 120~240 >525 0.0 0.0 19.2 7.69 46.2 E.极强 >2 400 0 46.2 46.2 注:重金属生态危害评价指标数据据Hakanson,1980. 表 5 BL尾矿元素总量(T)、元素酸提取态分量(AES)及pH值测试结果
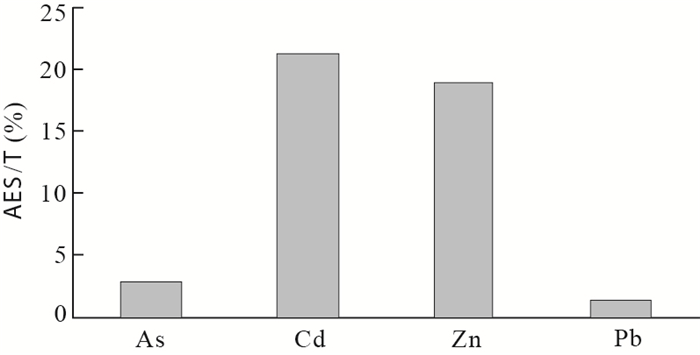
Table 5. Measurement results of the elements total contents (T), the elements acid extractable speciation (AES) and pH value of BL tailings
样品编号 As(10-2) Cd(10-2) Zn(10-2) Pb(10-2) pH T AES T AES T AES T AES G001-0 7.00 0.250 0.019 0.009 8 2.080 1.010 0.830 0.002 5 3.120 G001-1 9.63 0.270 0.020 0.009 2 2.350 1.100 0.420 0.001 0 2.880 G001 11.11 0.320 0.014 0.001 3 1.720 0.170 0.350 0.005 4 7.510 G002 8.60 0.240 0.016 0.001 3 3.110 0.170 0.280 0.003 7 7.400 G003 11.21 0.270 0.013 0.000 9 1.530 0.120 0.280 0.005 5 7.740 G004 0.93 0.024 0.014 0.000 9 1.700 0.100 0.090 0.003 6 7.610 G005 3.73 0.087 0.020 0.001 6 2.580 0.190 0.150 0.010 4 7.810 平均值 7.46 0.208 0.017 0.004 0 2.153 0.410 0.343 0.005 0 6.296 中值 8.60 0.250 0.016 0.001 3 2.080 0.170 0.280 0.003 7 7.510 标准差 3.87 0.109 0.003 0.004 1 0.570 0.443 0.240 0.003 0 2.260 变化系数 0.52 0.524 0.180 1.145 7 0.260 1.080 0.700 0.655 6 0.360 注:样品产状见表 1. -
Chen, Z.Q., Su, L., Yang, B.J., 2005. Geological Characteristics and Mineral Resources of Artificial Ore Deposits in Tailing Dams off Nonfero-Metal Mines in Nandan Area, Guangxi. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 20(Suppl. ): 139-144(in Chinese with English abstract). Dudka, S., Ponce-Hernandez, R., Tate, G., et al., 1996. Forms of Cu, Ni and Zn in Soils of Sudbury, Ontario and the Metal Concentrations in Plants. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 90(3-4): 531-542. doi: 10.1007/BF00282667 Favas, P.J.C., Pratas, J., Gomes, M.E.P., et al., 2011. Selective Chemical Extraction of Heavy Metals in Tailings and Soils Contaminated by Mining Activity: Environmental Implications. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 111(3): 160-171. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.04.009 Gómez-Álvarez, A., Valenzuela-García, L.J., Meza-Figueroa, D., et al., 2011. Impact of Mining Activities on Sediments in a Semi-Arid Environment: San Pedro River, Sonora, Mexico. Applied Geochemistry, 26(12): 2101-2112. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.07008 Gowda, S.S., Reddy, M.R., Govil, P.K., 2010. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soils at Jajmau (Kanpur) and Unnao Industrial Areas of the Ganga Plain, Uttar Pradesh, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174(1-3): 113-121. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.024 Hakanson, L., 1980. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control, a Sedimentological Approach. Water Research, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 Kubová, J., Matúš, P., Bujdoš, M., et al., 2008. Utilization of Optimized BCR Three-Step Sequential and Dilute HCl Single Extraction Procedures for Soil-Plant Metal Transfer Predictions in Contaminated Lands. Talanta, 75(4): 1110-1122. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2008.01.002 Lei, D.M., Duan, C.Q., Wang, M., 2007. Soil Fertility and Heavy Metal Contamination in Abandoned Regions of Different Mine Tailings in Yunnan Province. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 26(2): 612-616(in Chinese with English abstract). Lei, L.Q., Song, C.A., Wang, F., et al., 2010. The Neutralization Capacity and Acidification Potential of the Carbonate-Type Tailings in North Guangxi and Its Adjacent Areas, South China. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 30(4): 106-113(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285955119_The_neutralization_capacity_and_acidification_potential_of_the_carbonate-type_tailings_in_north_guangxi_and_its_adjacent_areas_South_China Lei, L.Q., Song, C.A., Xie, X.L., et al., 2011. Acidification Characteristics and Mechanism of Carbonate-Type Tailings of Bali Tailings Storage, the Dachang Tin-Polymetallic Orefield, Guangxi. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 30(1): 141-149(in Chinese with English abstract). Lei, L.Q., Zeng, Y.F., 1993. Hydrothermal Sedimentation and Magma-Pneumatolyto-Hydrothermal Superimposition in Relation with the Dachang Superlarge Sn-Polymetallic Ore Deposit. Geochimica, (3): 252-260(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199303005.htm Li, J.C., Yin, R.Z., Luo, Y.P., et al., 2010. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Soils in Daxin Manganese Mine, Guangxi. Environmental Science & Technology, 33(7): 183-185, 190(in Chinese with English abstract). Li, J.Y., Zhu, L.J., 2004. Modern Weathering Crust and Palaeo-Weathering Crust of Carbonate Rock. Carsologica Sinica, 23(1): 56-62(in Chinese with English abstract). Li, L., Zhang, G.P., Liu, H., et al., 2009. Antimony and Arsenic Migration and Environmental Impacts on River Draining in The Dachang Multi-Metalliferous Mine Area in Guangxi, China. Research of Environmental Sciences, 22(6): 682-687(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20093192439.html Li, X.F., Yang, F., Chen, Z.Y., et al., 2010. A Tentative Discussion on Geochemistry and Genesis of Indium in Dachang Tin Ore District, Guangxi. Mineral Deposits, 29(5): 903-914 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liao, G.L., Wu, C., 2005. Polluted Characteristics of Zn, Pb, Cd, Cu and As in Soil of Different Mining Activity Zones. Environmental Science, 26(2): 612-616(in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, H.Y., Probst, A., Liao, B.H., 2005. Metal Contamination of Soils and Crops Affected by the Chenzhou Lead/Zinc Mine Spill (Hunan, China). Science of the Total Environment, 339(1-3): 153-166. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.07.030 Louriño-Cabanaa, B., Lesvena, L., Charriaua, A., et al., 2011. Potential Risks of Metal Toxicity in Contaminated Sediments of Deûle River in Northern France. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186(2-3): 2129-2137. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.124 Ji, Y., Feng, Y., Wu, J., et al., 2008. Using Geoaccumulation Index to Study Source Profiles of Soil Dust in China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 20(5): 571-578. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62096-3 Pueyo, M., Mateu, J., Rigol, A., et al., 2008. Use of the Modified BCR Three-Step Sequential Extraction Procedure for the Study of Trace Element Dynamics in Contaminated Soils. Environmental Pollution, 152(2): 330-341. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.020 Wang, Y., Zhao, Q., Hu, Y., et al., 2011. Survey and Contamination Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil and Plants around the Pb/Zn Mine in Shangyu, Zhejiang Province. Environmental Chemistry, 30(7): 1354-1360 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201107024.htm Xiong, Z.F., Gong, Y.M., 2006. Geochemical Characteristics and Climatic-Environmental Significance of the Red Weathering Crusts in the Beidaihe Coast, North China. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(6): 177-186 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/296800809_Geochemical_characteristics_and_climatic-environmental_significance_of_the_red_weathering_crusts_in_the_Beidaihe_Coast_North_China Zhai, L.M., Chen, T.B., Liao, X.Y., et al., 2008. Pollution of Agricultural Soils Resulting from a Tailing Spill at a Pb-Zn Mine: A Case Study in Huanjiang, Guangxi Province. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 28(6): 1206-1211(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, G.L., Cai, H.Y., 1987. Genesis for the Dachang Tin-Polymetallic Deposit, Guangxi. Geological Review, 33(5): 426-436(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, X.Y., Zhao, C.L., Wu, H.D., et al., 2008. Situation of Heavy Metal Contamination in a Typical Mining Town of Guangxi, South China. Environmental Monitoring in China, 24(4): 79-83(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-IAOB200804020.htm 陈志强, 苏亮, 杨保疆, 2005. 广西南丹地区有色金属尾砂型人工矿床地质特征及其资源化. 地质找矿论丛, 20(增刊): 139-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK2005S1036.htm 雷冬梅, 段昌群, 王明, 2007. 云南不同矿区废弃地土壤肥力与重金属污染评价. 农业环境科学学报, 26(2): 612- 616. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2007.02.040 雷良奇, 宋慈安, 王飞, 等, 2010. 桂北及邻区碳酸盐型尾矿的酸中和能力及酸化潜力. 矿物岩石, 30(4): 106-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2010.04.018 雷良奇, 宋慈安, 谢襄漓, 等, 2011. 广西大厂巴里碳酸盐型尾矿的酸化特征及机理. 岩石矿物学杂志, 30(1): 141-149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.01.014 雷良奇, 曾允孚, 1993. 热水沉积和岩浆气液叠加与大厂超大型锡-多金属矿床. 地球化学, (3): 252-260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1993.03.006 李金城, 尹仁湛, 罗亚平, 等, 2010. 广西大新锰矿区土壤重金属污染评价. 环境科学与技术, 33(7): 183-185, 190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201007042.htm 李景阳, 朱立军, 2004. 论碳酸盐岩现代风化壳和古风化壳. 中国岩溶, 23(1): 56-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2004.01.010 李玲, 张国平, 刘虹, 等, 2009. 广西大厂多金属矿区河流中Sb和As的迁移及环境影响. 环境科学研究, 22(6): 682-687. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200906010.htm 李晓峰, 杨锋, 陈振宇, 等, 2010. 广西大厂锡矿铟的地球化学特征及成因机制初探. 矿床地质, 29(5): 903-914. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.05.012 廖国礼, 吴超, 2005. 矿山不同片区土壤中Zn、Pb、Cd、Cu和As的污染特征. 环境科学, 26(3): 157-161. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2005.03.032 王莹, 赵全利, 胡莹, 等, 2011. 上虞某铅锌矿区周边土壤植物重金属含量及其污染评价. 环境化学, 30(7): 1354-1360. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201107024.htm 熊志方, 龚一鸣, 2006. 北戴河红色风化壳地球化学特征及气候环境意义. 地学前缘, 13(6): 177-186. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.06.021 翟丽梅, 陈同斌, 廖晓勇, 等, 2008. 广西环江铅锌矿尾砂坝坍塌对农田土壤的污染及其特征. 环境科学学报, 28(6): 1206-1211. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.06.028 张国林, 蔡宏渊, 1987. 广西大厂锡多金属矿床成因探讨. 地质论评, 33(5): 426-436. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1987.05.005 张新英, 赵才流, 吴浩东, 等, 2008. 广西一个典型矿业镇环境中重金属污染分析. 中国环境监测, 24(4): 79-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2008.04.021 -









 下载:
下载:


