REE Geochemistry in the Laterite Crusts Derived from Ultramafic Rocks: Comparative Study of Two Laterite Profiles under Different Climate Condition
-
摘要: 选择印度尼西亚苏拉威西岛Kolonodale地区和中国云南省元江地区的2个超基性岩红土风化壳为研究对象,对比研究不同气候环境下超基性岩在红土风化过程中REE的地球化学特征及其演化机制.研究发现,印尼Kolonodale和中国元江剖面的REE分布型式具有一定的共性规律,都表现出显著的REE表生富集效应(相对于基岩的最大富集系数分别达44.21和236.19)、不均一的轻重稀土分异(分异程度随剖面深度加大而降低)以及剧烈的Ce异常正负转换现象(风化壳上部是正Ce异常,风化壳下部是负Ce异常).2个剖面中REE最大富集段的产出位置明显错位,表现在Kolonodale剖面中REE最大富集段出现在腐岩层,而在元江剖面中REE最大富集段出现在红土层.质量平衡计算指示,REE在超基性岩红土化过程中发生了显著的迁移和分异现象,其地球化学行为受红土剖面pH值环境与有机质(O.M.)含量的制约.案例对比分析表明,气候环境对超基性岩红土化过程中REE的地球化学演化具有重要影响.在热带雨林环境的印尼Kolonodale剖面中,风化壳中REE主要继承于基岩,在高强度的红土化作用下,REE经历了强烈的重新分配和垂向分异.而在亚热带季风气候环境的中国元江剖面中,风化壳中的REE具有更复杂的物源背景,除继承基岩外还可能叠加了风尘沉积物的影响.元江剖面的红土化程度偏弱,导致REE在表生演化中未发生强烈的淋滤和次生富集作用.Abstract: To understand the characteristics and evolution of REE during the process of the ultramafic laterization under different climate conditions, two outcrops Kolonodale in Indonesia and Yuanjiang in China are chosen for comparision. It is found that the contents of REE from the laterite crusts are higher than those from the bed rocks in both places (enrichment factor being 44.21 and 236.19 respectively).The indices of differentiation between the LREE and HREE decrease with profile downward toward, and the indice of Ce anomaly shows a shift from the positive Ce anomaly in the upper segment to negative Ce anomaly in the lower part. The difference between the two profiles lies in the distribution of the highest REE enriched segment. The laterite layer represent the most REE enriched for the Yuanjiang, whereas the saprolite layer for the Kolonodale. The evaluation of the mass balance shows remarkable migration and differentiation of REE in the ultramafic laterization process, which were constrained effectively by the pH environmentand organic matter (O.M.). The results indicate that climate have had great influence on the geochemical evolution of REE during the ultramafic laterization. Under the rainforest climate condition, the REE from the Kolonodale originates mainly from the basal rocks and has experienced intensive redistribution during the laterization; whereas the REE from the Yuanjiang has a mixed source stemming from both the parent rock and aeolian sediment, and it has been through only slight redistribution during the laterization.
-
Key words:
- rare earth element /
- laterite crust /
- ultramafic rock /
- climate condition /
- geochemistry
-
表 1 Kolonodale剖面中稀土元素、pH及有机质含量分析结果
Table 1. The contents of REE, pH and O.M. of the Kolonodale laterite profile
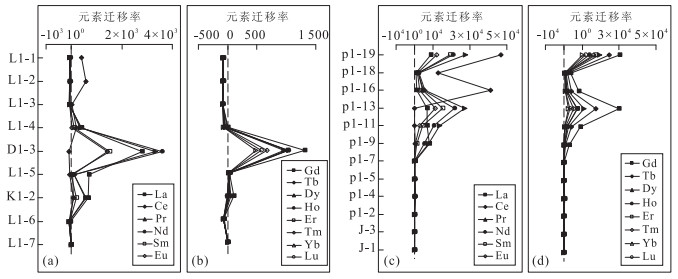
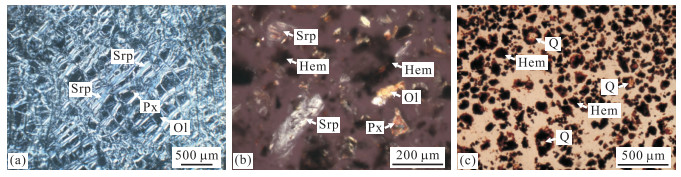
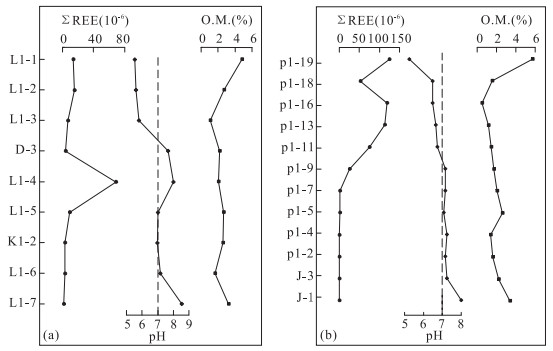
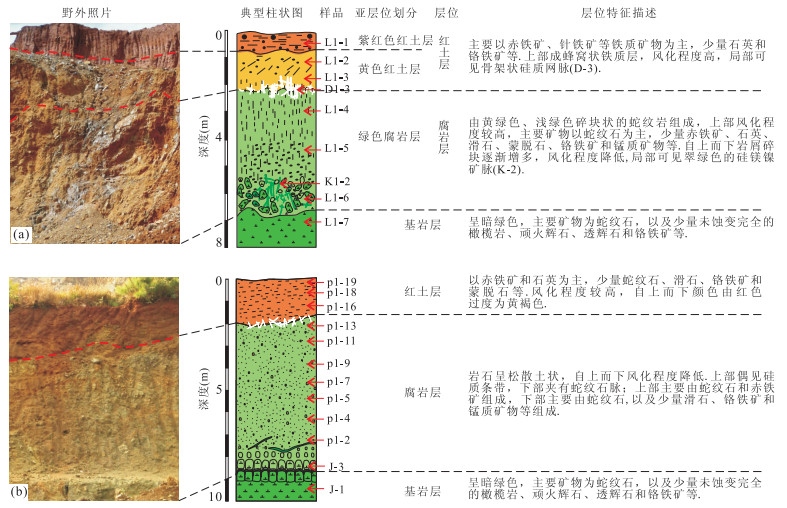
层位 紫红色红土层 黄色红土层 腐岩层 基岩层 编号 L1-1 L1-2 L1-3 D1-3 L1-4 L1-5 K1-2 L1-6 L1-7 La 1.165 1.265 0.561 1.144 17.090 4.531 0.996 0.751 0.219 Ce 7.879 9.741 2.193 0.388 0.062 0.096 0.130 0.063 0.120 Pr 0.321 0.323 0.202 0.269 4.865 0.286 0.209 0.050 0.053 Nd 1.261 1.227 0.988 0.914 18.920 1.011 0.739 0.235 0.191 Sm 0.404 0.363 0.425 0.187 3.456 0.198 0.142 0.122 0.080 Eu 0.106 0.090 0.106 0.030 0.932 0.084 0.023 0.047 0.023 Gd 0.438 0.415 0.417 0.177 5.845 0.527 0.189 0.245 0.155 Tb 0.078 0.077 0.085 0.029 0.888 0.095 0.027 0.053 0.030 Dy 0.548 0.515 0.570 0.161 6.037 0.708 0.154 0.417 0.213 Ho 0.127 0.120 0.128 0.031 1.637 0.195 0.034 0.103 0.054 Er 0.382 0.389 0.392 0.071 4.599 0.582 0.099 0.322 0.153 Tm 0.071 0.069 0.074 0.011 0.573 0.086 0.014 0.053 0.028 Yb 0.584 0.579 0.548 0.056 3.059 0.588 0.114 0.404 0.198 Lu 0.091 0.095 0.087 0.010 0.558 0.095 0.023 0.061 0.031 Y 2.833 2.952 2.462 0.734 64.92 9.624 1.176 2.750 1.328 ∑REE 13.46 15.27 6.78 3.48 68.52 9.08 2.89 2.93 1.55 LREE 11.14 13.01 4.48 2.93 45.33 6.21 2.24 1.27 0.69 HREE 2.32 2.26 2.30 0.55 23.20 2.88 0.65 1.66 0.86 LREE/HREE 4.80 5.76 1.94 5.37 1.95 2.16 3.42 0.76 0.80 LaN/YbN 1.43 1.57 0.73 14.65 4.01 5.53 6.27 1.33 0.79 δEu 0.77 0.71 0.76 0.50 0.63 0.75 0.43 0.81 0.62 δCe 3.100 3.640 1.590 0.170 0.001 0.010 0.070 0.060 0.260 pH 5.56 5.61 5.80 7.66 8.03 7.03 6.98 7.19 8.56 O.M.(%) 4.82 2.74 1.11 2.22 2.11 2.70 2.67 1.75 3.36 注:REE单位为10-6;REE、pH和O.M.送样测试:黄小荣. 表 2 元江剖面稀土元素、pH及有机质含量分析结果
Table 2. The contents of REE, pH and O.M. in YuanJiang laterite profile
层位 红土层 腐岩层 基岩层 编号 p1-19 p1-18 p1-16 p1-13 p1-11 p1-9 p1-7 p1-5 p1-4 p1-2 J-3 J-1 La 25.120 5.812 7.746 36.500 40.210 18.430 1.095 0.419 0.079 0.068 0.026 0.237 Ce 53.360 35.970 92.210 0.324 0.262 0.324 0.186 0.440 0.065 0.108 0.071 0.096 Pr 5.948 1.412 2.419 11.020 5.991 1.377 0.037 0.058 0.011 0.017 0.007 0.018 Nd 21.720 5.458 9.879 42.180 21.600 4.530 0.123 0.223 0.046 0.056 0.033 0.087 Sm 3.935 1.026 1.741 5.867 1.867 0.209 0.023 0.039 0.007 0.009 0.010 0.017 Eu 0.726 0.222 0.340 1.267 0.335 0.031 0.001 0.007 <0.001 0.001 <0.001 0.005 Gd 3.236 0.992 1.678 6.011 1.942 0.265 0.019 0.039 0.004 0.013 0.010 0.009 Tb 0.593 0.139 0.192 0.777 0.197 0.019 0.003 0.006 0.001 0.003 0.003 0.002 Dy 3.949 0.752 0.993 4.179 0.971 0.093 0.026 0.040 0.008 0.021 0.018 0.017 Ho 0.822 0.146 0.200 0.850 0.226 0.028 0.007 0.010 0.003 0.006 0.004 0.005 Er 2.507 0.364 0.462 2.041 0.498 0.065 0.023 0.032 0.008 0.021 0.015 0.012 Tm 0.387 0.054 0.070 0.239 0.049 0.007 0.004 0.004 0.001 0.004 0.002 0.002 Yb 2.461 0.349 0.421 1.205 0.203 0.050 0.043 0.045 0.009 0.032 0.019 0.020 Lu 0.419 0.055 0.072 0.222 0.040 0.010 0.007 0.007 <0.001 0.003 0.003 0.003 Y 20.310 3.490 5.513 26.49 13.500 4.384 0.312 0.297 0.055 0.148 0.111 0.107 ∑REE 125.18 52.75 118.42 112.68 74.39 25.44 1.60 1.37 0.24 0.36 0.22 0.53 LREE 110.81 49.90 114.34 97.16 70.27 24.90 1.47 1.19 0.21 0.26 0.15 0.46 HREE 14.37 2.85 4.09 15.52 4.13 0.54 0.13 0.18 0.04 0.10 0.07 0.07 LREE/HREE 7.71 17.50 27.97 6.26 17.03 46.37 11.10 6.48 5.97 2.51 1.99 6.57 LaN/YbN 7.32 11.95 13.20 21.73 142.08 264.40 18.27 6.68 6.30 1.52 0.98 8.50 δEu 0.60 0.66 0.60 0.65 0.53 0.40 0.14 0.54 0.53 0.28 0.30 1.11 δCe 1.030 0 2.980 0 5.180 0 0.003 9 0.003 7 0.010 0 0.120 0 0.600 0 0.470 0 0.760 0 1.270 0 0.260 0 pH 5.25 6.48 6.48 6.65 6.75 7.15 7.15 7.07 7.24 7.15 7.24 8.00 O.M.(%) 4.70 1.57 0.49 1.17 1.43 1.71 2.04 2.63 1.41 1.62 2.25 3.37 注:REE单位为10-6;表中<0.001的计算过程中按0.001计算;REE、pH和O.M.送样测试:黄小荣. 表 3 Kolonodale剖面稀土元素质量平衡评价(10-6)
Table 3. The mass balance count of REE in the Kolonodale laterite profile
编号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu L1-1 -58.77 408.93 -53.05 -48.83 -60.86 -64.28 -78.10 -79.85 -80.06 -81.77 -80.65 -80.35 -77.14 -77.25 L1-2 -51.86 576.57 -49.21 -46.46 -62.18 -67.39 -77.68 -78.61 -79.85 -81.48 -78.81 -79.46 -75.63 -74.46 L1-3 -83.82 15.45 -75.92 -67.32 -66.44 -70.89 -83.00 -82.10 -83.09 -85.03 -83.81 -83.30 -82.52 -82.27 D1-3 395.32 206.59 381.26 353.75 121.64 23.68 8.28 -8.34 -28.33 -45.57 -56.00 -62.75 -73.18 -69.41 L1-4 2 812.63 -80.72 3 326.05 3 597.21 1 512.39 1 412.43 1 307.47 1 004.79 957.86 1 031.47 1 021.91 663.81 476.64 571.83 L1-5 683.48 -69.71 104.35 100.44 -6.28 38.30 28.75 19.92 25.87 36.75 44.05 16.31 12.46 16.05 K1-2 678.56 85.46 575.07 562.35 203.86 71.19 108.74 54.07 23.77 7.79 10.77 -14.41 -1.44 27.01 L1-6 -42.97 -91.27 -84.31 -79.54 -74.64 -66.02 -73.71 -70.62 -67.44 -68.28 -65.00 -68.52 -66.07 -67.28 表 4 元江剖面稀土元素质量平衡评价(10-6)
Table 4. The mass balance count of REE in the Yuanjiang laterite profile
编号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu p1-19 8 809.60 46 623.09 27 677.00 20 885.90 19 357.31 12 105.44 30 124.07 24 823.65 19 426.53 13 719.39 17 461.44 16 165.52 10 243.53 11 640.31 p1-18 732.55 12 620.51 2 563.16 2 029.85 1 948.96 1 407.36 3 642.00 2 259.50 1 401.77 891.33 929.81 816.64 492.42 522.41 p1-16 1 308.59 4 1296.26 5 691.85 4 793.82 4 313.71 2 830.65 7 935.33 4 037.38 2 417.41 1 623.91 1 559.26 1 408.42 807.21 934.35 p1-13 6 764.93 50.44 27 189.81 21 511.19 15 283.62 11 195.31 29 671.15 17 217.39 10 857.58 7 477.75 7 481.46 5 226.71 2 585.64 3 198.55 p1-11 6 978.58 13.87 13 786.32 10 258.45 4 482.01 2 695.34 8 902.58 4 009.57 2 283.04 1 785.81 1 631.44 922.18 323.47 456.29 p1-9 7 898.64 247.15 7 768.66 5 255.73 1 164.55 537.72 2 928.61 877.15 462.70 476.01 457.15 260.00 157.15 242.86 p1-7 260.79 51.30 60.51 10.40 5.65 -84.38 64.85 17.13 19.43 9.32 49.67 56.18 67.89 82.21 p1-5 17.78 205.35 114.67 70.77 52.84 -6.73 188.70 99.87 56.76 33.24 77.66 33.24 49.90 55.45 p1-4 142.78 393.15 345.10 285.10 199.90 45.67 223.71 264.17 242.75 337.00 385.56 264.17 227.75 142.78 p1-2 -60.50 54.86 30.01 -11.40 -27.13 -72.47 98.83 106.48 70.04 65.18 140.89 175.30 120.24 37.65 J-3 -91.04 -39.56 -68.22 -69.00 -51.93 -83.66 -9.20 22.58 -13.48 -34.63 2.15 -18.28 -22.37 -18.28 -
Allen, D.E., Seyfried, W.E., 2005. REE Controls in Ultramafic Hosted MOR Hydrothermal Systems: An Experimental Study at Elevated Temperature and Pressure. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(3): 675-683. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.07.016 Bao, Z.W., Zhao, Z.H., 2008. Geochemistry of Mineralization with Exchangeable REY in the Weathering Crusts of Granitic Rocks in South China. Ore Geology Reviews, 33(3): 519-535. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.03.005 Braun, J.J., Ngoupayou, J.R.N., Viers, J., et al., 2005. Present Weathering Rates in a Humid Tropical Watershed: Nsimi, South Cameroon. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(2): 357-387. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.06.022 Braun, J.J., Pagel, M., 1994. U, Th and REE in the Akongo Lateritic Prole (SW Cameroon). Chemical Geology, 84(1-5): 357-359. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(90)90265-9 Braun, J.J., Pagel, M., Herbilln, A., et al., 1993. Mobilization and Redistribution of REEs and Thorium in a Syenitic Lateritic Profile: A Mass Balance Study. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 57(18): 4419-4434. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90492-F Braun, J.J., Pagel, M., Muller, J.P., et al., 1990. Cerium Anomalies in Lateritic Profiles. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 54(3): 781-795. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90373-S Braun, J.J., Viers, J., Dupré, B., et al., 1998. Solid/Liquid REE Fractionation in the Lateritic System of Goyoum, East Cameroon: The Implication for the Present Dynamics of the Soil Covers of the Humid Tropical Regions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62(2): 273-299. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00344-X Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Yunnan Province, 1990. Regional Geology of Yunnan Province. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Brimhall, G.H., Dietrich, W.E., 1987. Constitutive Mass Balance Relations between Chemical Composition, Volume, Density, Porosity, and Strain in Metasomatic Hydrochemical Systems: Results on Weathering and Pedogenesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 51(3): 567-587. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90070-6 Brookins, D.G., 1989. Aqueous Geochemistry of Rare Earth Elements. In: Lipin, B.R., Mckay, G.A., eds., Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Rare Earth Elements, Reviews in Mineralogy, Vol. 21. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C., 201-225. Brown, D.J., Helmke, P.A., Clayton, M.K., 2003. Robust Geochemical Indices for Redox and Weathering on a Granitic Laterite Landscape in Central Uganda. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(15): 2711-2723. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00104-2 Chen, J., 2012. Progress of Aeolian Sediments and Dust Geochemistry in Asia in the New Century. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 31(5): 433-446 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201205003.htm Chen, J., Wang, H.T., Lu, H.Y., 1996. Behaviours of REE and Other Trace Elements during Pedological Weathering—Evidence from Chemical Leaching of Loess and Paleosol from the Luochuan Section in Central China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 70(1): 61-72 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=DZXW199603005 Chen, Z.C., Chen, D.H., Yu, S.Y., et al., 1994. A Preliminary Study on the Role of Organic Matter in Dissolution, Migration and Concentration of Rare Earth Elements in Weathering Crust of Granites from South China. Geochimica, 23(2): 168-178 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX402.008.htm Chen, Z.C., Yu, S.J., Fu, Q.C., et al., 1997. Study on the Organic Metallogenic Mechanism of Weathering Crust REE Deposits. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 15(3): 244-251 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288029452_Study_on_the_organic_metallogenic_mechanism_of_weathering_crust_REE_deposits Chi, R.A., Xu, J.M., He, P.J., et al., 1995. REE Geochemistry of Granitoid Weathering Crust and Properties of Ores in Southern China. Geochimica, 24(3): 261-269 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX503.006.htm Condie, K.C., Dengate, J., Cullers, R.L., 1995. Behavior of Rare Earth Elements in a Paleoweathering Profile on Granodiorite in the Front Range, Colorado, USA. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(2): 279-294. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)00280-Y Coppin, F., Berger, G., Bauer, A., et al., 2002. Sorption of Lanthanides on Smectite and Kaolinite. Chemical Geology, 182(1): 57-68. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00283-2 Fang, W.X., Hu, R.Z., Xie, G.Q., et al., 2001. Research and Analysis on Ore-Controlling Factors for Mojiang-Yuanjiang Nickel-Gold Deposits in Yunnan, China. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 21(1): 80-88 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200101013.htm Fu, W., Niu, H.J., Chen, Y.R., et al., 2012. Supergene Enrichment and Mineralization Texture of Nickel in Laterite Weathered Crust from Ultrabasic Rocks: A Case Study of Kolonodale Ore District in Sulawesi Island, Indonesia. Mineral Deposits, 31(2): 229-240 (in Chinese with English abstract). Fu, W., Zhou, Y.Z., Chen, Y.R., et al., 2010. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics of Laterite Nickel Deposit and Ore Genesis—A Case Study of Kolonodale Deposit in Indonesia Sulawesi, Southeast Asia. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(2): 127-139 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002018.htm Garnier, J., Quantin, C., Guimares, E., et al., 2008. Can Chromite Weathering be a Source of Cr in Soils. Mineralogical Magazine, 72(1): 49-53. doi: 10.1180/minmag.2008.072.1.49 Garnier, J., Quantin, C., Guimares, E., et al., 2009. Understanding the Genesis of Ultramafic Soils and Catena Dynamics in Niquelndia, Brazil. Geoderma, 151(3): 204-214. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.04.020 Gleeson, S.A., Herrington, R.J., Durango, J., et al., 2004. The Mineralogy and Geochemistry of the Cerro Matoso SA Ni Laterite Deposit, Montelíbano, Colombia. Economic Geology, 99(6): 1197-1213. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.99.6.1197 Golightly, J.P., 1979. Geology of the Soroako Nickeliferous Laterite Deposits. In: Evans, D.J.I., Shoemaker, R.S., Veltman, H., eds., International Laterite Symposium: New York, American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers, 38-56. Gong, Q.J., Zhang, G.X., Zhang, J., et al., 2010. Behavior of REE Fractionation during Weathering of Dolomite Regolith Prole in Southwest China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(6): 1447-1469. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2010.00339.x Gosselin, D.C., Smith, M.R., Lepel, E.A., et al., 1992. Rare Earth Elements in Chloride-Rich Groundwater, Palo Duro Basin, Texas, USA. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 56(4): 1495-1505. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(92)90219-9 Guo, S., Ye, K., Chen, Y., et al., 2013. Introduction of Mass-Balance Calculation Method for Component Transfer during the Opening of a Geological System. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(5): 1486-1498 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huang, C.M., Gong, Z.T., 2001. Geochemical Implication of Rare Earth Elements in Process of Soil Development. Journal of Rare Earth, 19(1): 57-62. Huang, X.R., Fu, W., Niu, H.J., et al., 2012. The Vertical Structure and Mineral Composition of Yuanjiang Laterite Nickel Deposit, Yunnan. Mineral Deposits, 31(S): 1127-1128 (in Chinese). Ji, H.B., Wang, S.J., Ouyang, Z.Y., et al., 2004. Geochemistry of Red Residua Underlying Dolomites in Karst Terrains of Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau Ⅱ. The Mobility of Rare Earth Elements during Weathering. Chemical Geology, 203(1): 29-50. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.08.013 Johannesson, K.H., Stetzenbach, K.J., Hodge, V.F., 1995. Speciation of the Rare Earth Element Neodymium in Groundwaters of the Nevada Test Site and Yucca Mountain and Implications for Actinide Solubility. Applied Geochemistry, 10(5): 565-572. doi: 10.1016/0883-2927(95)00028-3 Kadatusmana, A., Miyashitab, S., Maruyamaa, S., et al., 2004. Petrology, Geochemistry and Paleogeographic Reconstruction of the East Sulawesi Ophiolite, Indonesia. Tectonophysics, 392(1): 55-83. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2004.04.008 Laveuf, C., Cornu, S., 2009. A Review on the Potentiality of Rare Earth Elements to Trace Pedogenetic Processes. Geoderma, 154(1): 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.10.002 Li, J.J., Zhang, L.Y., Deng, Y.X., et al., 1983. Mount Lu Quaternary Environmental Evolution and Landscape Development. Science in China (Series B), 13(8): 734-745 (in Chinese). Lin, C.X., Zheng, Z.P., 1994. Experimental Studies on Metallogenetic Mechanism of Weathering Crust-Leaching REE Deposits in Southern China. Geochimica, 23(2): 189-198 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX402.010.htm Liu, C.Q., Wu, J.H., Yu, W.H., 2001. Ferric Hydroxide Colloid/Water Interface and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements in Surface Water—Experimental Study of pH Control Mechanism. Science in China (Series D), 31(10): 873-880 (in Chinese). Liu, Y., Liu, H.C., Li, X.H., 1996. Simultaneous and Precise Determination of 40 Trace Elements in Rock Samples Using ICP-MS. Geochimica, 25(6): 552-558 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/303067662_Simultaneous_precise_determination_of_40_trace_elements_in_rock_samples_using_ICP-MS Lottermoster, B.G., 1990. Rare-Earth Element Mineralization within the Mt Weld Carbonatite Laterite, Westen Australia. Lithos, 24(2): 151-167. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(90)90022-S Ma, Y.J., Huo, R.K., Xu Z.F., et al., 2004. REE Behavior and Influence Factors during Chemical Weathering. Advance in Earth Sciences, 19(1): 87-94 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285839688_REE_behavior_and_influence_factors_during_chemical_weathering Ma, Y.J., Liu C.Q., 1999. Chemical Weathering of Trace Element Geochemistry—Take the Case of Jiangxi Longnan Biotite Granite Weathering Crust as an Example. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44(22): 2433-2437 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1999-44-22-2433 Marker, A., de Oliveira, J.J., 1994. Climatic and Morphological Control of Rare Earth Element Distribution in Weathering Mantles on Alkaline Rocks. Catena, 21(2): 179-193. doi: 10.1016/0341-8162(94)90011-6 Mo, X.X., Pan, G.T., 2006. From the Tethys to the Formation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Constrained by Tectono-Magmatic Events. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(6): 43-51 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/303494314_From_the_Tethys_to_the_Formation_of_the_Qinghai-Tibet_Plateau_Constrained_by_Tectono-Magmatic_Event Morteani, G., Preinfalk, C., 1995. REE Distribution and REE Carriers in Laterites Formed on the Alkaline Complexes of Araxá and Catalo (Brazil). In: Jones, A.P., Wall, F., Williams, C.T., eds., Rare Earth Minerals. Chemistry, Orign and Ore Deposits. Chapman & Hall, London, 227-255. Murakami, H., Ishihara, S., 2008. REE Mineralization of Weathered Crust and Clay Sediment on Granitic Rocks in the Sanyo Belt, SW Japan and Southern Jiangxi Province. China. Resource Geology, 58(4): 373-401. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-3928.2008.00071.x Ndjigui, P.D., Bilong, P., Bitom, D., 2009. Negative Cerium Anomalies in the Saprolite Zone of Serpentinite Lateritic Proles in the Lomié Ultramafic Complex, South-East Cameroon. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 53(1): 59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2008.09.002 Ndjigui, P.D., Bilong, P., Bitom, D., et al., 2008. Mobilization and Distribution of Major and Trace Elements in Two Weathering Proles Developed on Serpentinites in the Lomié Ultramafic Complex, South-East Cameroon. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 50(5): 305-328. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2007.10.006 Nesbitt, H.W., 1979. Mobility and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements during Weathering of a Granodiorite. Nature, 279: 206-210. doi: 10.1038/279206a0 Nesbitt H.W., Markovics, G., 1997. Weathering of Granodioritic Crust, Long-Term Storage of Elements in Weathering Profiles, and Petrogenesis of Siliciclastic Sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(8): 1653-1670. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00031-8 Ohta, A., Kawabe, I., 2001. REE (Ⅲ) Adsorption onto Mn Dioxide (σ-MnO2) and Fe Oxyhydroxide: Ce (Ⅲ) Oxidation by σ-MnO2. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(5): 695-703. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00578-0 Oliva, P., Viers, J., Dupré, B., et al., 1999. The Effect of Organic Matter on Chemical Weathering: Study of a Small Tropical Watershed: Nsimi-Zoétélé Site, Cameroon. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(23): 4013-4035. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00306-3 Patino, L.C., Velbel, M.A., Price, J.R., et al., 2003. Trace Element Mobility during Spheroidal Weathering of Basalts and Andesites in Hawaii and Guatemala. Chemical Geology, 202(3): 343-364. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.01.002 Qiao, F.G., Zhu, J.Y., Tian, Y.L., et al., 2005. Nickel Resources Distribution in the World and Nickel Resources of Yunnan. Yunnan Geology, 24(4): 395-401 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD200504008.htm Ran, Y., Liu, Z., 1992. Specific Adsorption of Rare Earth Elements by Soil and Oxides and the Mechanism. Chinese Science Bulletin, 37(18): 1705-1709 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1992-37-18-1705 Sanematsu, K., Moriyama, T., Sotouky, L., et al., 2011. Mobility of Rare Earth Elements in Basalt-Derived Laterite at the Bolaven Plateau, Southern Laos. Resource Geology, 61(2): 140-158. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-3928.2011.00155.x Schellmann, W., 1981. Considerations on the Definition and Classification of Laterites. In: Laterisation Processes. Proceedings of the International Seminar on Lateritisation Processes. Trivandrum, Indian, 1979. Balkema, Rotterdam, 1-10. Schellmann W., 1989. Composition and Origin of Lateritic Nickel Ore at Tagaung Taung, Burma. Mineralium Deposita, 24(3): 161-168. doi: 10.1007/BF00206438 Song, Y.H., Shen, L.P., 1986. REE Geochemistry of the Weathered Crust of Acid Volcanic Rocks—An Experimental Study. Geochimica, 15(3): 225-234 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQHB198702005.htm Sun, C.X., Wang, S.J., Ji, H.B., 2002. Formation Mechanism of the Superhigh Concentration of REE and the Strong Negative Ce Anomalies in the Carbonate Rock Weathering Profiles in Guizhou Province, China. Geochimica, 31(2): 119-128 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200202002.htm Sun, S.S., McDonough, W.F., 1989. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. In: Saunders, A.D., Norry M.J., eds., Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society Sepical Publication 42, London, 313-345. Tang, S.L., Sun, J.X., Tu, S.D., et al., 1980. Rare Earth Elements in Some Soils from Guangzhou. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 17(4): 299-307 (in Chinese with English abstract). Taylor, S.R., McLennan, S.M., 1985. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution. Blackwell Scientific Publication, London. Wang, S.J., Ji, H.B., Ouyang, Z.Y., et al., 1999. A Preliminary Study of Carbonate Rock Weathering Pedogenesis. Science in China (Series D), 29(5): 441-449 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1007/BF02877784 Wang, Z.G., Yu, X.Y., Zhao, Z.H., et al., 1989. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Science Press, Beijing, 133-359 (in Chinese). Wood, S.A., 1990. The Aqueous Geochemistry of the Rare-Earth Elements and Yttrium: Review of Available Low-Temperature Data for Inorganic Complexes and the Inorganic REE Speciation of Natural Waters. Chemical Geology, 82: 159-186. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(90)90080-Q Wu, C.Y., Huang, D.H., Guo, Z.X., 1989. REE Geochemistry in the Weathering Process of Granites in Longnan County, Jiangxi Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 63(4): 349-362, 387-388 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dzxe198904005.htm Yang, L.Q., Liu, J.T., Zhang, C., et al., 2010. Superimposed Orogenesis and Metallogenesis: An Example from the Orogenic Gold Deposits in Ailaoshan Gold Belt, Southwest China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(6): 1723-1739 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201006008.htm Yang, T., Zhu, Z.Y., Wu, Y., et al., 2010. Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry in Topsoils from the Eastern Part of China. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(3): 233-241 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_earth-science-frontiers_thesis/0201253152475.html Ye, W., Yang, L.H., Zhu, L.D., et al., 2008. Characteristics and Origin of Rare Earth Elements of Vermicular Red Earth in Middle Sub-Tropic Zone. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 28(1): 40-44 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95809X/200801/26692099.html Zhang, Q., Zhou, D.J., Li, X.Y., et al., 1995. Characteristics and Geneses of Shuanggou Ophiolites, Yunnan Province, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 11 (Suppl. ): 190-202 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/283922359_Characteristics_and_genesises_of_Shuanggou_ophiolites_Yunnan_Province_China Zhang, X.Q., Liu, J.L., Jiang, Y.M., et al., 2004. Determination of Trace REEs and Non-REEs Impurities in High Pure Lanthanum Oxide by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 25(4): 204-208 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZPXB200404002.htm 云南省地质矿产局, 1990. 云南省区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版杜. 陈骏, 2012. 新世纪亚洲风尘系统地球化学研究进展. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 31(5): 433-446. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2012.05.003 陈骏, 王洪涛, 鹿化煜, 1996. 陕西洛川黄土沉积物中稀土元素及其他微量元素的化学淋滤研究. 地质学报, 70(1): 61-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199601005.htm 陈志澄, 陈达慧, 俞受鋆, 等, 1994. 试论有机质在华南花岗岩风化壳REE溶出、迁移和富集中的作用. 地球化学, 23(2): 168-178. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1994.02.002 陈志澄, 俞受鋆, 符群策, 等, 1997. 风化壳稀土矿有机成矿机理研究. 中国稀土学报, 15(3): 244-251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTXB703.011.htm 池汝安, 徐景明, 何培炯, 等, 1995. 华南花岗岩风化壳中稀土元素地球化学及矿石性质研究. 地球化学, 24(3): 261-269. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1995.03.007 方维萱, 胡瑞忠, 谢桂青, 等, 2001. 云南墨江镍金矿床主要控矿因素分析与研究. 矿物学报, 21(1): 80-88. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2001.01.014 付伟, 牛虎杰, 陈远荣, 等, 2012. 超基性岩红土风化壳中镍的表生富集规律及矿化结构研究——以印尼苏拉威西岛Kolonodale矿区为例. 矿床地质, 31(2): 229-240. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2012.02.005 付伟, 周永章, 陈远荣, 等, 2010. 东南亚红土镍矿床地质地球化学特征及成因探讨——以印尼苏拉威西岛Kolonodale矿床为例. 地学前缘, 17(2): 127-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002018.htm 郭顺, 叶凯, 陈意, 等, 2013. 开放地质体系中物质迁移质量平衡计算方法介绍. 岩石学报, 29(5): 1486-1498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201305005.htm 黄小荣, 付伟, 牛虎杰, 等, 2012. 云南元江富镍红土风化壳的垂向结构及矿物组成. 矿床地质, 31(增刊): 1127-1128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2012S1569.htm 李吉均, 张林源, 邓养鑫, 等, 1983. 庐山第四纪环境演变和地貌发育问题. 中国科学(B辑), 13(8): 734-745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK198308006.htm 林传仙, 郑作平, 1994. 风化壳淋积型稀土矿床成矿机理的实验研究. 地球化学, 23(2): 189-198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1994.02.004 刘丛强, 吴佳红, 于文辉, 2001. 氢氧化铁胶体/水界面作用与地表水中稀土元素的分异——pH控制机理的实验研究. 中国科学(D辑), 31(10): 873-880. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200110011.htm 刘颖, 刘海臣, 李献华, 1996. 用ICP-MS准确测定岩石样品中的40余种微量元素. 地球化学, 25(6): 552-558. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1996.06.004 马英军, 霍润科, 徐志方, 等, 2004. 化学风化作用中的稀土元素行为及其影响因素. 地球科学进展, 19(1): 87-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200401012.htm 马英军, 刘丛强, 1999. 化学风化作用中的微量元素地球化学——以江西龙南黑云母花岗岩风化壳为例. 科学通报, 44(22): 2433-2437. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199922014.htm 莫宣学, 潘桂棠, 2006. 从特提斯到青藏高原形成: 构造-岩浆事件的约束. 地学前缘, 13(6): 43-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200606007.htm 乔富贵, 朱杰勇, 田毓龙, 等, 2005. 全球镍资源分布及云南镍矿床. 云南地质, 24(4): 395-401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD200504008.htm 冉勇, 刘铮, 1992. 土壤和氧化物对稀土元素的专性吸附及其机理. 科学通报, 37(18): 1705-1709. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199218021.htm 宋云华, 沈丽璞, 1986. 酸性火山岩类风化壳中稀土元素的地球化学实验研究. 地球化学, 15(3): 225-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX198603003.htm 孙承兴, 王世杰, 季宏兵, 2002. 碳酸盐岩风化成土过程中REE超常富集及Ce强烈亏损的地球化学机理. 地球化学, 31(2): 119-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200202002.htm 唐诵六, 孙景信, 屠树德, 等, 1980. 广州土壤中的稀土元素. 土壤学报, 17(4): 299-307. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB198004000.htm 王世杰, 季宏兵, 欧阳自远, 等, 1999. 碳酸盐岩风化成土作用的初步研究. 中国科学(D辑), 29 (5): 441-449. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199905007.htm 王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华, 等, 1989. 稀土元素地球化学. 北京: 科学出版社, 133-359. 吴澄宇, 黄典豪, 郭中勋, 1989. 江西龙南地区花岗岩风化壳中稀土元素的地球化学研究. 地质学报, 63(4): 349-362, 387-388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE198904005.htm 杨立强, 刘江涛, 张闯, 等, 2010. 哀牢山造山型金成矿系统: 复合造山构造演化与成矿作用初探. 岩石学报, 26(6): 1723-1739. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201006008.htm 杨恬, 朱照宇, 吴翼, 等, 2010. 中国东部地带表土稀土元素的地球化学特征. 地学前缘, 17(3): 233-241. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201003025.htm 叶玮, 杨立辉, 朱丽东, 等, 2008. 中亚热带网纹红土的稀土元素特征与成因分析. 地理科学, 28(1): 40-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX200801008.htm 张旗, 周德进, 李秀云, 等, 1995. 云南双沟蛇绿岩的特征和成因. 岩石学报, 11(增刊): 190-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB5S1.014.htm 章新泉, 刘晶磊, 姜玉梅, 等, 2004. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定高纯氧化镧中稀土和非稀土杂质. 质谱学报, 25(4): 204-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZPXB200404002.htm -









 下载:
下载: