Control Factors of Enrichment and Producibility of Shale Oil: A Case Study of Biyang Depression
-
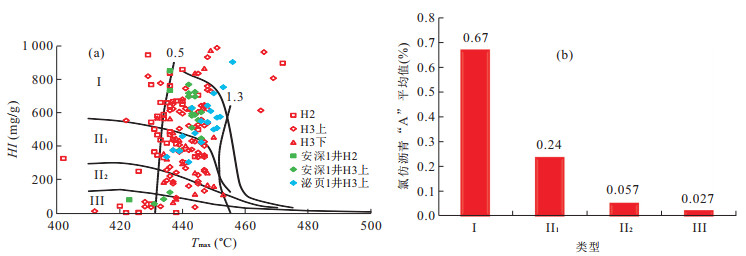
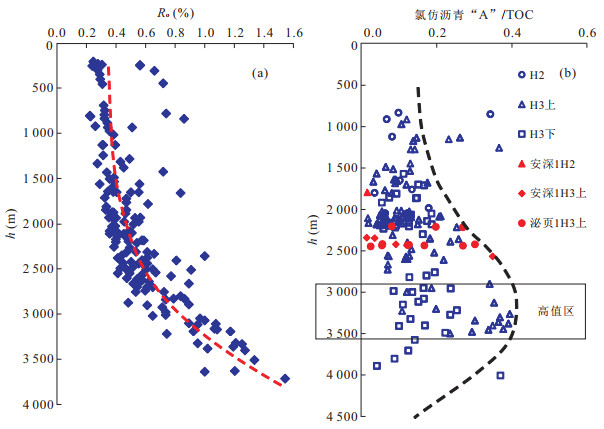
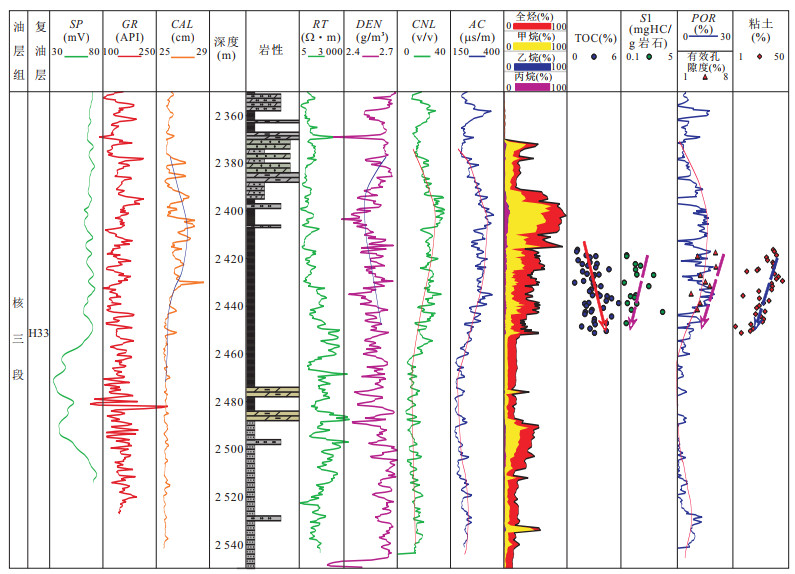
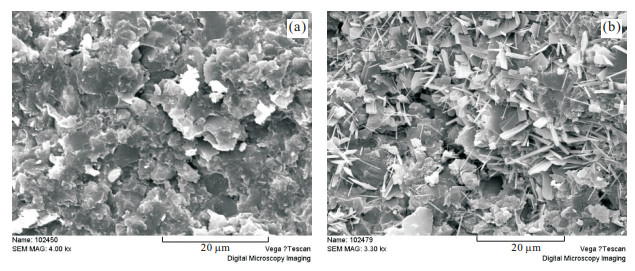
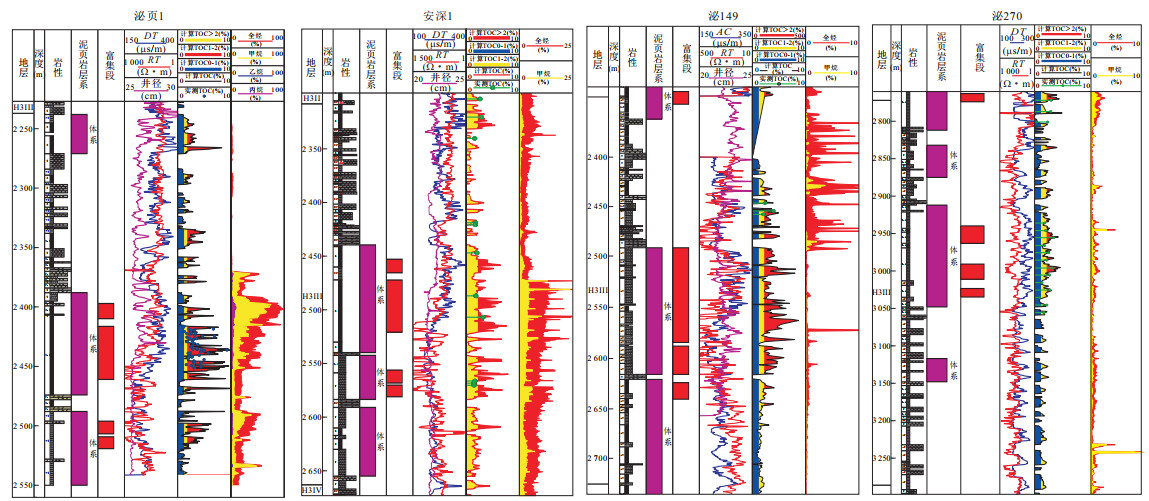
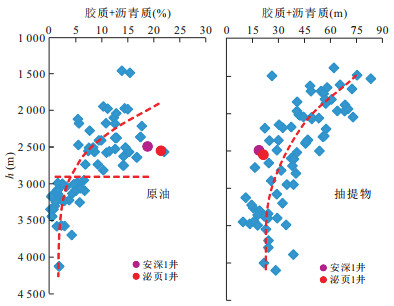
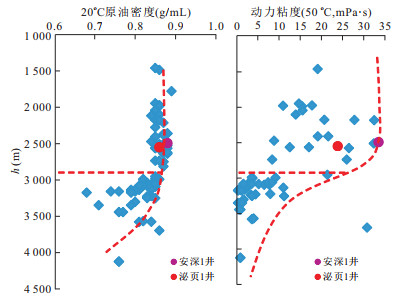
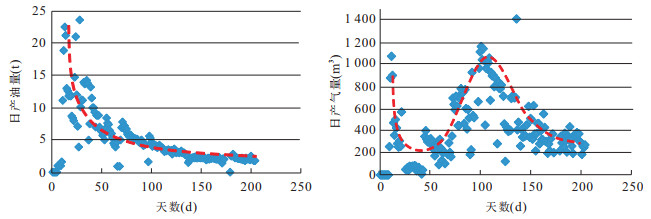
摘要: 页岩油能否有效聚集并具可采性主要受控于6个方面因素, 即生烃基础、存储空间、保存条件、储层改造条件、原油物性和开发方式.目前已取得页岩油突破的安深1井、泌页1井开发层段有机质丰度高、有机质类型好, 页理、纹理及构造裂缝发育, 脆性矿物含量较高等有利条件, 但其泥页岩有机质成熟度较低, 在影响泥页岩含油率的同时, 对原油的物性也有较大影响, 且保存条件不佳, 地层无超压, 能量较低, 不利于页岩油的产出.今后, 泥页岩埋深较大的东南部地区可能是下步页岩油勘探开发的有利区.另外, 考虑到原油溶解气量对其物性的影响以及低渗储层的应力敏感性, 生产方面应尽量延缓储层压力的降低.Abstract: This paper discusses the key control factors of shale oil enrichment and producibility. It is found that whether shale oil can effectively accumulate and has producibility is mainly controlled by six factors, namely, hydrocarbon generation amount, porosity, preservation condition, reservoir reconstruction condition, crude oil property and development scheme. A break-through of shale oil development has been made in Anshen-1 Well and Biye-1 Well due to their advantages for shale oil enrichment and producibility, including high organic matter abundance, excellent organic matter type and high brittle mineral content, good development of lamellation, structural fracture. But there are also disadvantages. Firstly, maturity of organic matter is low, which influences oil content of shale and physical property of crude oil. Secondly, there is no overpressure in Biyang depression, indicating the preservation condition of shale oil is not good and the stratum energy is low. So the southeast area where the shale has higher depth can be the favorable area for shale oil exploration and exploitation. It is concluded that the decrease of reservoir pressure shall be delayed during production due to the influence of dissolved gas amount on physical property of crude oil and the stress sensitivity of low permeability reservoir.
-
Key words:
- shale oil /
- enrichment /
- producibility /
- control factor /
- Biyang depression /
- petroleum geology
-
表 1 不同丰度、类型和成熟度有机质理论生烃量
Table 1. Hydrocarbon generation in the theory of organic matter with different abundance, type, and maturity
TOC(%) 生烃潜力(mg/g·TOC) 生烃转化率(%) 生油量(%) 生气量(m3/t岩石) 1 300 30 0.05 1.22 1 300 60 0.09 2.37 1 500 30 0.13 2.04 1 500 60 0.25 3.95 2 300 30 0.09 2.44 2 300 60 0.18 4.74 2 500 30 0.25 4.07 2 500 60 0.50 7.90 -
Cardott, B.J., 2012. Thermal Maturity of Woodford Shale Gas and Oil Plays, Oklahoma, USA. International Journal of Coal Geology, 103: 109-119. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2012.06.004 Chen, X., Wang, M., Yan, Y.X., et al., 2011. Accumulation Conditions for Continental Shale Oil and Gas in the Biyang Depression. Oil & Gas Geology, 32(4): 568-576(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/298104748_Accumulation_conditions_for_continental_shale_oil_and_gas_in_the_Biyang_Depression Ding, W.L., Zhang, B.W., Li, T.M., 2003. Formation of Non-Tectonic Fractures in Mudstones in Gulong Depression. Oil & Gas Geology, 24(1): 50-54(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313564266_Formation_of_non-tectonic_fractures_in_mudstones_in_Gulong_Depression Guo, X., Wu, Y., 2007. Influence of Start-up Pressure Gradient and Stress Sensitivity on Productivity of Low-Permeability Gas Reservoirs. Oil & Gas Geology, 28(4): 539-543(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200704022.htm Jarvie, D.M., 2008. Unconventional Shale Resource Plays: Shale-Gas and Shale-Oil Opportunities. Fort Worth Business Press Meeting, Fort Worth. Li, C.L., 2009. Stress Sensitivity Influence on Oil Well Productivity. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 31(1): 170-172(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/293257570_Stress_sensitivity_influence_on_oil_well_productivity Lu, S.F., Huang, W.B., Chen, F.W., et al., 2012. Classification and Evaluation Criteria of Shale Oil and Gas Resources: Discussion and Application. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 39(2): 268-276. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(12)60042-1 Luo, C.X., 2011. Shale Oil Development may Change the Landscape in the World's Oil Market. Sino-Global Energy, 16(12): 22-26(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SYZW201112006.htm Ma, Y.S., Feng, J.H., Mu, Z.H., et al., 2012. The Potential and Exploring Progress of Unconventional Hydrocarbon Resources in SINOPEC. Engineering Sciences, 14(6): 22-29(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/303362081_The_potential_and_exploring_progress_of_unconventional_hydrocarbon_resources_in_SINOPEC Mu, X.S., Yuan, X.R., Jia, Y.F., et al., 2003. The Formation Conditions and the Distribution Characteristics of the Oil Pools in the Fractures of the Shales in Dongpu Depression. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 10(1): 12-14(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT200301004.htm Pu, B.L., 2008. Analysis of the Reservoir-Forming Conditions of Shale Gas Potential in Sichuan Basin. China University of Petroleum (East China) (Disstertation), Dongying, 1-7(in Chinese). Ross, D.J.K., Bustin, R.M., 2007. Impact of Mass Balance Calculations on Adsorption Capacities in Microporous Shale Gas Reservoirs. Fuel, 86: 2696-2706. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2007.02.036 Ross, D.J.K., Bustin, R.M., 2009. The Importance of Shale Composition and Pore Structure upon Gas Storage Potential of Shale Gas Reservoirs. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 26: 916-927. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.06.004 Sheng, J.J., Chen, K., 2014. Evaluation of the EOR Potential of Gas and Water Injection in Shale Oil Reservoirs. Journal of Unconventional Oil and Gas Resources, 5: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.juogr.2013.12.001 Tran, T., Sinurat, P., Wattenbarger, R.A., 2011. Production Characteristics of the Bakken Shale Oil. SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver, Colorado, USA. doi: 10.2118/145684-MS Wu, C.F., Wang, C., Jiang, W., 2014. Abnormal High-Pressure Formation Mechanism in Coal Reservoir of Bide-Santang Basin, Western Guizhou Province. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 39(1): 73-78(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.007 Xiang, L.H., 2008. Quantitatively Analyze the Main Controlling Factors of Mudstone Fracture in Jiyang Depression. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 15(5): 31-33, 37 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YQCS200805011.htm Xu, F.G., Li, Q., Kang, R.H., et al., 2003. The Characteristics of Fractured Shale Reservoir in Zhanhua Depression. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 23(1): 74-76(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279596042_The_characteristics_of_fractured_shale_reservoir_of_in_Zhanhua_depression Xu, H.J., Fan, G.M., Kang, Z., et al., 2008. A Productivity Prediction Equation Considering Rock Permeability Stress-Sensitivity in Low-Permeability Gas Reservoirs. Natural Gas Geoscience, 19(1): 145-147(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97226X/200801/26657015.html Yang, Y.X., He, S., He, Z.L., et al., 2014. Sealing Mechanism of Overpressured Top Seal in Well Jianshen 1 Silurian Formation of Shizhu Synclinorium. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 39(1): 64-72(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.006 Zhang, G.Y., Chen, Q.M., Liu, L.M., 1993. A Discussion on the Characteristics of Fractured Reservoir of Mudstone in Nanyang Depression and the Mechanism of Its Formation. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 20(1): 18-26(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK199301004.htm Zhang, J.C., Lin, L.M., Li, Y.X., et al., 2012. Classification and Evaluation of Shale Oil. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(5): 322-331(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876380412600421 Zou, C.N., Yang, Z, Cui, J.W., et al., 2013. Formation Mechanism, Geological Characteristics and Development Strategy of Nonmarine Shale Oil in China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40(1): 14-26(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876380413600026 陈祥, 王敏, 严永新, 等, 2011. 泌阳凹陷陆相页岩油气成藏条件. 石油与天然气地质, 32(4): 568-576. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201104013.htm 丁文龙, 张博闻, 李泰明, 2003. 古龙凹陷泥岩非构造裂缝的形成. 石油与天然气地质, 24(1): 50-54. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2003.01.012 郭肖, 伍勇, 2007. 启动压力梯度和应力敏感效应对低渗透气藏水平井产能的影响. 石油与天然气地质, 28(4): 539-543. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2007.04.017 李传亮, 2009. 应力敏感对油井产能的影响. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 31(1): 170-172. doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2009.01.041 罗承先, 2011. 页岩油开发可能改变世界石油形势. 中外能源, 16(12): 22-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZW201112006.htm 马永生, 冯建辉, 牟泽辉, 等, 2012. 中国石化非常规油气资源潜力及勘探进展. 中国工程科学, 14(6): 22-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2012.06.004 慕小水, 苑晓荣, 贾贻芳, 等, 2003. 东濮凹陷泥岩裂缝油气藏形成条件及分布特点. 断块油气田, 10(1): 12-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8907.2003.01.004 蒲泊伶, 2008. 四川盆地页岩气成藏条件分析(学位论文). 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 1-7. 吴财芳, 王聪, 姜玮, 2014. 黔西比德-三塘盆地煤储层异常高压形成机制. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 39(1): 73-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201401008.htm 向立宏, 2008. 济阳坳陷泥岩裂缝主控因素定量分析. 油气地质与采收率, 15(5): 31-33, 37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2008.05.009 徐福刚, 李琦, 康仁华, 等, 2003. 沾化凹陷泥岩裂缝油气藏研究. 矿物岩石, 23(1): 74-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2003.01.015 胥洪俊, 范明国, 康征, 等, 2008. 考虑渗透率应力敏感的低渗气藏产能预测公式. 天然气地球科学, 19(1): 145-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200801035.htm 杨兴业, 何生, 何治亮, 等, 2014. 石柱地区建深1井志留系超压顶封层的封闭机制. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 39(1): 64-72. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.006 张光亚, 陈全茂, 刘来民, 1993. 南阳凹陷泥岩裂缝油气藏特征及其形成机制探讨. 石油勘探与开发, 20(1): 18-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1993.01.016 张金川, 林腊梅, 李玉喜, 等, 2012. 页岩油分类与评价. 地学前缘, 19(5): 322-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205032.htm 邹才能, 杨智, 崔景伟, 等, 2013. 页岩油形成机制、地质特征及发展对策. 石油勘探与开发, 40(1): 14-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201301003.htm -










 下载:
下载: