Characteristics of Gravity Flow Deposits in Slope Basin of Nankai Trough and Their Responses to Subduction Tectonics
-
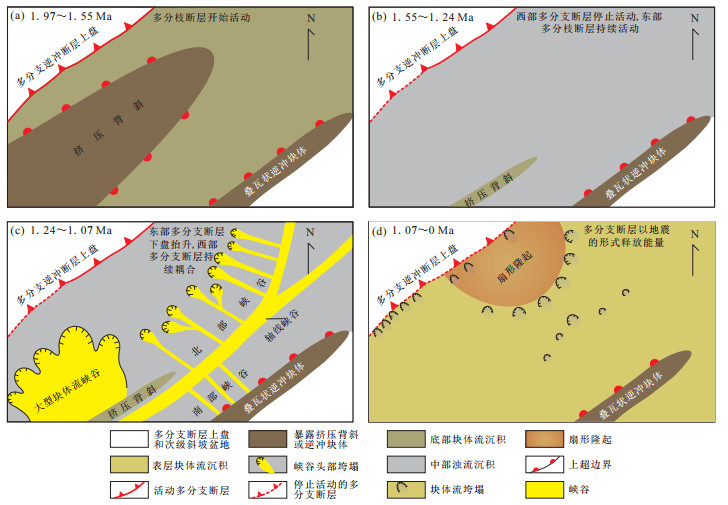
摘要: 南海海槽是全球大地震发生频率最高的地区之一,该地区增生楔上斜坡盆地内的重力流沉积记录了多分支断层及大地震活动历史.利用国际综合大洋钻探计划(IODP)314-316航次岩心-地震-综合测井资料,在详细分析南海海槽增生楔上斜坡盆地内重力流沉积特征基础上,阐明了其对多分支断层和大地震活动的响应机制.研究结果表明,南海海槽增生楔上斜坡盆地内依次充填了楔形块体流、峡谷和表层块体流沉积:楔形块体流形成于多分支断层活动早期,表现出北厚南薄的楔形特征,反映了多分支断层的持续活动的特征,沉积物中富含的粗颗粒泥质角砾岩反映了早期多分支断层剧烈活动的特征;峡谷系统由密集峡谷,大型块体流和轴向峡谷组成,主要受到多分支断层耦合造成斜坡变陡、区域地层孔隙流体压力增大和盆地不均衡抬升的影响;表层块体流位于盆地顶部,由多期次弱振幅块体流叠加组成,现今海底表面表现为大量“马蹄形”的垮塌地形,这些相对短期内广泛分布的块体流应该是由地震引起的地表震动触发的.斜坡盆地内重力流沉积特征反映了多分支断层活动历史以及大地震的发生过程:即1.95~1.55 Ma,多分支断层形成初期活动剧烈,逆冲活动造成了断层上盘沉积物垮塌,楔形块体流沉积在斜坡盆地底部;1.55~1.07 Ma,多分支断层西部耦合,导致斜坡盆地出现东高西低的构造格局以及盆地西部区域楔体和断层处能量的集聚;1.07 Ma至今,断层处能量间断释放,引发多次大地震.Abstract: Nankai trough is one of seismogenic zones known for massive earthquakes in the world. Gravity flow deposits in slope basin of Nankai trough accretionary prism record the active history of magesplay faults and the recurrences of great earthquakes. Based on the data of integrated ocean drilling program (IODP), this study explores the characteristics of gravity flow deposits in slope basin and illustrates their implications to the activities of magesplay faults and great earthquakes. The results show that the slope basin was filled successively with wedge-shaped mass transport deposits (MTDs), canyon system and superficial MTDs. Wedge-shaped MTDs developed in the initial stage of magesplay fault activity, which is wedge-shaped and mainly composed of muddy breccia, indicating continuous and strong activities of the magesplay faults at the initial stage. Canyon system consists of several kinds of canyons including slope canyons, great MTDs canyon and axial canyon, which are controlled by steepening slope, increasing regional interstitial fluid pressure and anisotropic uplifting. Superficial MTDs consist of stacking multi-stage low amplitude MTDs and represent as plenty of scars, which formed in a relatively short time, but extensively. It may be caused by the seafloor shaking during a great earthquake. These characteristics of gravity flow deposits record the history of magesplay fault activities and recurrences of great earthquakes as follows: 1.95-1.55 Ma, magesplay fault reactivated sharply at the initial stage which triggered slumps in the upper wall of magesplay fault; 1.55-1.07 Ma, coupling and activities of magesplay fault in the west domain caused strata compressed, deformed and energy assembled in the prism as well as in the magesplay fault; 1.07 Ma to now, energy in the mageplay fault was released discontinuously that resulted in multi great earthquakes.
-
Key words:
- Nankai trough /
- accretionary prism /
- gravity flow /
- magesplay fault /
- earthquake /
- sediment
-
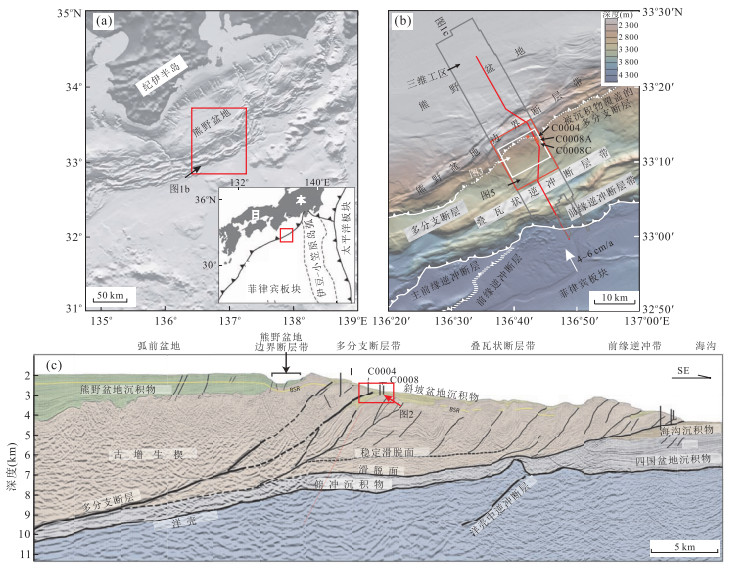
图 1 南海海槽增生楔区域地质背景(据Kimura et al., 2011, 修改)
a.南海海槽区域位置图;b.研究区位置及区域构造图;c.南海海槽增生楔构造及地层特征
Fig. 1. Geological setting and strata of Nankai trough accretionary prsim
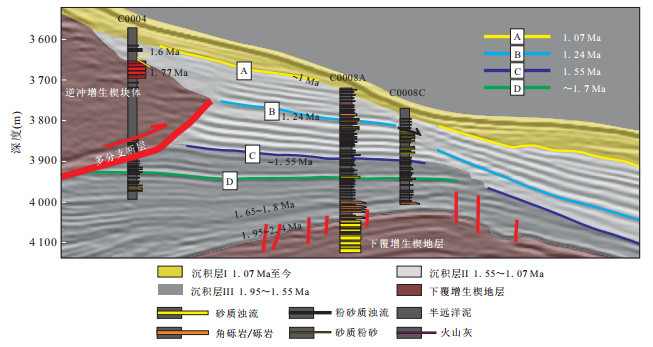
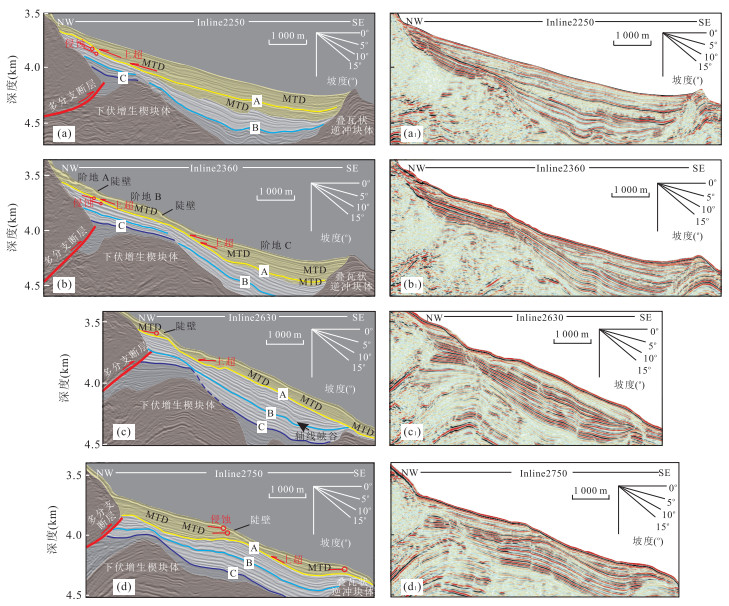
图 2 南海海槽增生楔斜坡盆地地层划分(剖面位置如图 1c所示)
Fig. 2. Stratigraphic classification in slope basin of Nankai trough accretionary prism
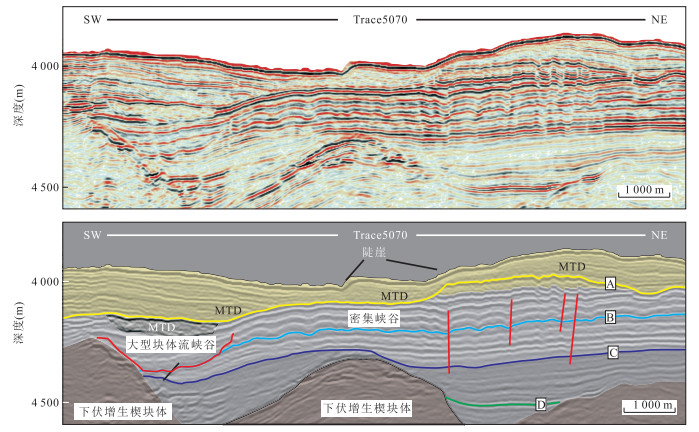
图 3 斜坡盆地密集峡谷及大型块体流峡谷剖面特征(剖面位置同图 4所示)
Fig. 3. Characteristics of serried canyons and great MTDs canyon in slope basin
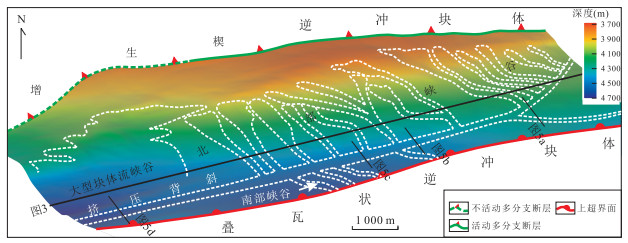
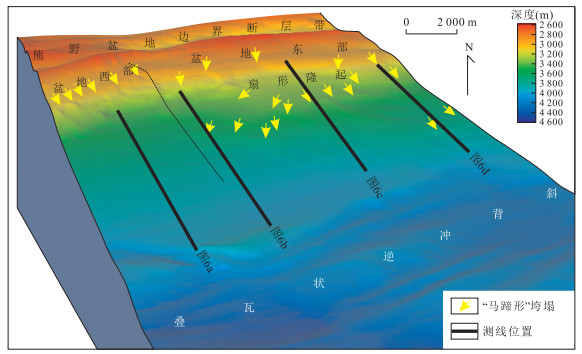
图 4 南海海槽增生楔斜坡盆地峡谷体系三维特征(位置同图 1b所示)
Fig. 4. 3D Characteristics of canyons system in slope basin of Nankai trough accretionary prism
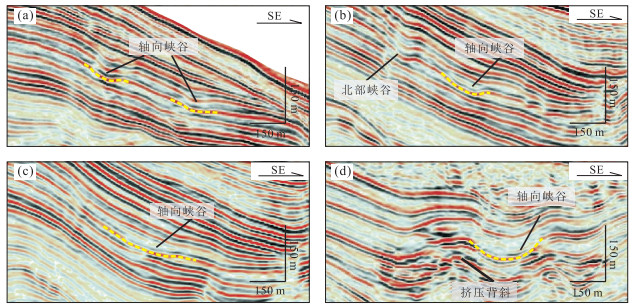
图 5 斜坡盆地轴向峡谷地震反射特征(位置同图 4所示)
Fig. 5. Characteristics of axis canyon in slope basin
图 6 斜坡盆地表层块体流平面特征(位置如图 1b所示)
Fig. 6. Characteristics of superficial MTDs on seafloor of slope basin
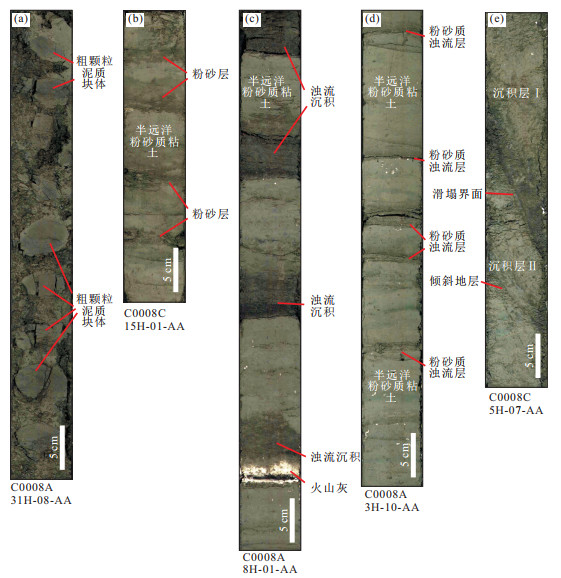
图 7 南海海槽增生楔斜坡盆地块体流沉积样式(剖面位置同图 6中所示)
Fig. 7. Depositional styles of superficial MTDs in slope basin of Nankai trough accretionary prism
-
Bouma, A.H., 1962. Sedimentology of Some Flysch Deposits: A Graphic Approach to Facies Interpretation. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 168. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/247468523_Sedimentology_of_Some_Flysch_Deposits_A_Graphic_Approach_To_Facies_Interpretation Bull, S., Cartwright, J., Huuse, M., 2009. A Review of Kinematic Indicators from Mass-Transport Complexes Using 3D Seismic Data. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 26(7): 1132-1151. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.09.011 Cochonat, P., Cadet, J.P., Lallemant, S.J., et al., 2002. Slope Instabilities and Gravity Processes in Fluid Migration and Tectonically Active Environment in the Eastern Nankai Accretionary Wedge (KAIKO-Tokai'96 Cruise). Marine Geology, 187(1): 193-202. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00266-9 Fergusson, C.L., 2003. Provenance of Miocene-Pleistocene Turbidite Sands and Sandstones, Nankai Trough, Ocean Drilling Program Leg 190. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 190(196): 1-28. doi: 10.2973/odp.proc.sr.190196.205.2003 Hampton, M.A., Lee, H.J., Locat, J., 1996. Submarine Landslides. Reviews of Geophysics, 34(1): 33-59. doi: 10.1029/95RG03287 Kimura, G., Moore, G.F., Strasser, M., et al., 2011. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of the Megasplay Fault in the Nankai Trough. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 12(3): Q0A008. doi: 10.1029/2010GC003335 Kimura, G., Screaton, E.J., Curewitz, D., et al., 2008. NanTroSEIZE Stage 1A: NanTroSEIZE Shallow Megasplay and Frontal Thrusts. IODP Prel. Rept., 316. doi: 10.2204/iodp.pr.316.2008 Lee, H.J., Locat, J., Desgagnés, P., et al., 2007. Submarine Mass Movements on Continental Margins. In: Nittrouer, C.A., Austin, J.A., Field, M.E., et al., eds., Continental Margin Sedimentation: From Sediment Transport to Sequence Stratigraphy, Int, Assoc. Sedimentol., Gent, 213-274. doi: 10.1002/9781444304398.ch5 Li, C.F., Su, X., Jiang, T., et al., 2010. Deformation at the Front of the Accretionary Prism of the Nankai Trough, Japan: Evidence from Core Samples. Advances in Earth Science, 25(2): 203-211 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201002015.htm Locat, J., Lee, H.J., 2002. Submarine Landslides: Advances and Challenges. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 39(1): 193-212. doi: 10.1139/T01-089 Lowe, D.R., 1982. Sediment Gravity Flows: Ⅱ. Depositional Models with Special Reference to the Deposits of High-Density Turbidity Currents. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 52(1): 279-297. Miyazaki, S., Heki, K., 2001. Crustal Velocity Field of Southwest Japan: Subduction and Arc-Arc Collision. Journal of Geophysical Research, 106(B3): 4305-4326. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900312 Moore, G.F., Bangs, N.L., Taira, A., et al., 2007. Three-Dimensional Splay Fault Geometry and Implications for Tsunami Generation. Science, 318(5853): 1128-1131. doi: 10.1126/science.1147195 Moore, G.F., Karig, D.E., Shipley, T.H., et al., 1991. Structural Framework of the ODP LEG 131 Area, Nankai Trough. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Initial Reports, 131: 15-20. doi: 10.2973/odp.proc.ir.131.102.1991 Moore, G.F., Park, J.O., Bangs, N.L., et al., 2009. Structural and Seismic Stratigraphic Framework of the NanTroSEIZE Stage 1 Transect. In: Kinoshita, M., Tobin, H., Ashi, J., et al., eds., Proceedings of IOOP, Integrated Ocean Drilling Program Management International, Inc., Texas, 314-316: 1-46. doi: 10.2204/iodp.proc.314315316.102.200 Moscardelli, L., Hornbach, M., Wood, L., 2010. Tsunamigenic Risks Associated with Mass Transport Complexes in Offshore Trinidad and Venezuela. Submarine Mass Movements and Their Consequences. Advances in Natural and Technological Hazards Research, 28: 733-744. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-3071-9_59 Mutti, E., Ricci Lucchi, F., 1972. Le Torbiditi Dell'Appennino Settentrionale: Introduzione All'analisi Di Facies. Memorie della Societa Geologica Italiana, 11(2): 161-199. Omura, A., Ikehara, K., 2010. Deep-Sea Sedimentation Controlled by Sea-Level Rise during the Last Deglaciation, an Example from the Kumano Trough, Japan. Marine Geology, 274(1): 177-186. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.04.002 Orange, D.L., Breen, N.A., 1992. The Effects of Fluid Escape on Accretionary Wedges 2. Seepage Force, Slope Failure, Headless Submarine Canyons, and Vents. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 97(B6): 9277-9295. doi: 10.1029/92JB00460 Palanques, A., Martín, J., Puig, P., et al., 2006. Evidence of Sediment Gravity Flows Induced by Trawling in the Palamos (Fonera) Submarine Canyon (Northwestern Mediterranean). Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ: Oceanographic Research Papers, 53(2): 201-214. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2005.10.003 Park, J., Moore, G.F., Tsuru, T., et al., 2004. A Subducted Oceanic Ridge Influencing the Nankai Megathrust Earthquake Rupture. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 217(1): 77-84. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00553-3 Pettingill, H.S., 1998. Turbidite Giants-Lessons from the World's 40 Largest Turbidite Discoveries. EAGE/AAPG 3rd Research Symposium-Developing and Managing Turbidite Reservoirs, Almeria. Pickering, K.T., Underwood, M.B., Taira, A., 1992. Open-Ocean to Trench Turbidity-Current Flow in the Nankai Trough: Flow Collapse and Reflection. Geology, 20(12): 1099-1102. doi: 10.2973/odp.proc.sr.131.104.1993 Puig, P., Ogston, A.S., Mullenbach, B.L., et al., 2004. Storm-Induced Sediment Gravity Flows at the Head of the Eel Submarine Canyon, Northern California Margin. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 109(C3): 1-10. doi: 10.1029/2003JC001918 Ratzov, G., Collot, J., Sosson, M., et al., 2010. Mass-Transport Deposits in the Northern Ecuador Subduction Trench: Result of Frontal Erosion over Multiple Seismic Cycles. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 296(1): 89-102. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.04.048 Sakaguchi, A., Kimura, G., Strasser, M., et al., 2011. Episodic Seafloor Mud Brecciation due to Great Subduction Zone Earthquakes. Geology, 39(10): 919-922. doi: 10.1130/G32043.1 Schnellmann, M., Anselmetti, F.S., Giardini, D., et al., 2002. Prehistoric Earthquake History Revealed by Lacustrine Slump Deposits. Geology, 30(12): 1131-1134. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1131:PEHRBL>2.0.CO;2 Seno, T., Stein, S., Gripp, A.E., 1993. A Model for the Motion of the Philippine Sea Plate Consistent with NUVEL-1 and Geological Data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 98(B10): 17941-17948. doi: 10.1029/93JB00782 Shanmugam, G., 2000.50 Years of the Turbidite Paradigm (1950s—1990s): Deep-Water Processes and Facies Models—A Critical Perspective. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 17(2): 285-342. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00011-2 Shiki, T., 1996. Reading of the Trigger Records of Sedimentary Events—A Problem for Future Studies. Sedimentary Geology, 104(1-4): 249-255. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(95)00132-8 Shiki, T., Cita, M.B., Gorsline, D.S., 2000. Sedimentary Features of Seismites, Seismo-Turbidites and Tsunamiites—An Introduction. Sedimentary Geology, 135(1-4): 7-9. doi: 10.1016/s0037-0738(00)00058-0 Shirai, M., Omura, A., Wakabayashi, T., et al., 2010. Depositional Age and Triggering Event of Turbidites in the Western Kumano Trough, Central Japan during the Last ca. 100 Years. Marine Geology, 271(3-4): 225-235. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.02.015 Stow, D.A., Mayall, M., 2000. Deep-Water Sedimentary Systems: New Models for the 21st Century. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 17(2): 125-135. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00064-1 Stow, D.A., Shanmugam, G., 1980. Sequence of Structures in Fine-Grained Turbidites: Comparison of Recent Deep-Sea and Ancient Flysch Sediments. Sedimentary Geology, 25(1-2): 23-42. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(80)90052-4 Strasser, M., Moore, G.F., Kimura, G., et al., 2009. Origin and Evolution of a Splay Fault in the Nankai Accretionary Wedge. Nature Geoscience, 2(9): 648-652. doi: 10.1038/NGEO609 Strasser, M., Moore, G.F., Kimura, G., et al., 2011. Slumping and Mass Transport Deposition in the Nankai Fore Arc: Evidence from IODP Drilling and 3-D Reflection Seismic Data. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 12(5): 1-24. doi: 10.1029/2010GC003431 Sultan, N., Cochonat, P., Canals, M., et al., 2004. Triggering Mechanisms of Slope Instability Processes and Sediment Failures on Continental Margins: A Geotechnical Approach. Marine Geology, 213(1-4): 291-321. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.10.011 Underwood, M.B., Moore, G.F., Taira, A., et al., 2003. Sedimentary and Tectonic Evolution of a Trench-Slope Basin in the Nankai Subduction Zone of Southwest Japan. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 73(4): 589-602. doi: 10.1306/092002730589 Underwood, M.B., Orr, R., Pickering, K.T., et al., 1993. Provenance and Dispersal Patterns of Sediments in the Turbidite Wedge of Nankai Trough. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program Leg 131, 131: 15-34. doi: 10.2973/odp.proc.sr.131.105.1993 Walker, R.G., 1978. Deep-water Sandstone Facies and Ancient Submarine Fans; Models for Exploration for Stratigraphic Traps. AAPG Bulletin, 62(6): 932-966. Wang, K., Hu, Y., 2006. Accretionary Prisms in Subduction Earthquake Cycles: The Theory of Dynamic Coulomb Wedge. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 111, B06410. doi: 10.1029/2005JB004094 Xu, J.R., Zhao, Z.X., Kono, Y., et al., 2003. Regional Characteristics of Stress Field and Its Dynamics in and around the Nankai Trough, Japan. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 46(4): 488-494 (in Chinese with English abstract). 李春峰, 苏新, 姜涛, 等, 2010. 日本南海海槽俯冲增生楔前缘的构造变形特征. 地球科学进展, 25(2): 203-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201002015.htm 徐纪人, 赵志新, 河野芳辉, 等, 2003. 日本南海海槽地震区域应力场及其板块构造动力学特征. 地球物理学报, 46(4): 488-494. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2003.04.010 -









 下载:
下载: