Dielectric Constant of Lunar Soil Derived from Chang'E-2 Passive Microwave Radiometer Measurements
-
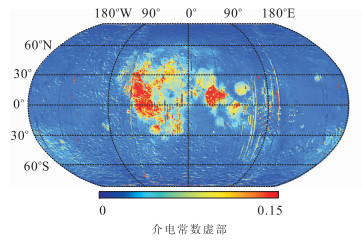
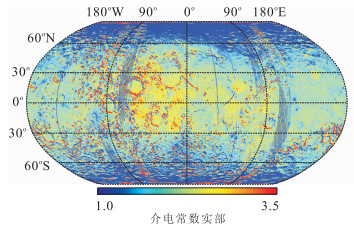
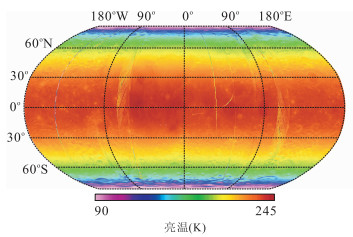
摘要: 月壤介电常数是当前月球微波遥感探测的基础, 是月壤厚度、成分等信息提取不可或缺的参数.为了实现全月介电常数反演, 通过对嫦娥二号卫星微波辐射计亮温数据进行时角校正, 得到同一时角的全月微波亮温图.全月微波亮温表现出随月球地形、月壤成分及纬度变化的特征.基于校正后的微波辐射亮温, 结合辐射传输模型, 通过解算相关参数, 反演得到3GHz频率下全月介电常数分布.其中, 月海地区的介电常数实部高于月陆地区, 且月球极地区域介电常数实部偏低; 而介电常数虚部则在月海区域和艾肯盆地较高.通过模拟月表介电常数实验对反演结果进行温度校正, 得到22℃下全月介电常数.将反演结果和月壤真实样品的介电常数测量值进行比较评价.结果表明介电常数实部相对误差都低于11%;虚部相对误差偏大, 但其差值最大仅为0.02.因此, 基于嫦娥二号卫星微波辐射计亮温数据反演月表介电常数的方法是可行的.Abstract: Dielectric constant of lunar soil is the basis of lunar microwave remote sensing detection and it is an indispensable parameter for information extraction of lunar regolith layer thickness and composition. With the aim to simulate dielectric constant for the whole moon, the correction of time angle on brightness temperature data captured by microwave radiometer on board of Chang'E-2 is carried out in the paper and the distribution map of the whole lunar surface microwave brightness temperature under the same time angle with various lunar terrains is obtained, soil compositions and latitudes is obtained. By applying the radiative transfer model to the corrected microwave temperature brightness, the distribution of dielectric constants for 3GHz channel in the whole moon is obtained. The real part of dielectric constant in the lunar mare region is higher than that in highland and this value is low in polar region. The imaginary part in lunar mare and Aitken basin are relatively higher. The dielectric constant data have been calibrated in the experiment to obtain dielectric constant temperature at 22℃. To compare the electric constant of real lunar soil samplings under normal temperature on Earth with inversed results, the results show as follows: the relative error of the real part of dielectric constant is less than 11%; the relative error of the imaginary part of dielectric constant is higher, but the maximum difference is below 0.02. So it is feasible to derive the dielectric constant inversion in the manner of utilizing brightness temperature data of microwave radiometer on board of Chang'E-2.
-
表 1 MRM反演结果与月壤真实样品测量结果比较
Table 1. Comparison between the experimental results from real lunar soil and MRM inversion results
月壤真实样品 MRM反演结果 相对误差(%) 差值(%) ε′ ε″ ε′ ε″ ε′ ε″ Apollo 11 2.530 0.0428 2.47 0.0560 2.55 -30.84 Apollo 12 2.280 0.0315 2.45 0.0336 -7.38 -6.80 Apollo 14 2.620 0.0220 2.40 0.0347 8.22 -57.73 Apollo 15 2.375 0.0196 2.48 0.0185 -4.30 5.61 Apollo 16 2.440 0.0076 2.18 0.0137 10.65 -80.26 Apollo 17 2.810 0.0158 2.94 0.0231 -4.62 -46.20 -
Berlin, G.L., Tarabzouni, M.A., Al-Naser, A.H., et al., 1986. SIR-B Subsurface Imaging of a Sand-Buried Landscape: Al Labbah Plateau, Saudi Arabia. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, GE-24(4): 595-602. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.1986.289676 Fa, W.Z., Jin, Y.Q., 2007. Quantitative Estimation of Helium-3 Spatial Distribution in the Lunar Regolith Layer. Icarus, 1990: 15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2007.03.014 Fa, W.Z., Jin, Y.Q., 2010. A Primary Analysis of Microwave Brightness Temperature of Lunar Surface from Chang-E 1 Multi-Channel Adiometer Observation and Inversion of Regolith Layer Thickness. Icarus, 207: 605-615. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2009.11.034 Jiang, J.S., Wang, Z.Z., Li, Y., 2008. Study on Theory and Application of CE-1 Micronave Sounding Lunar Surface. Engineering Sciences, 10(6): 16-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2008.06.003 Lawson, S.L., Jakosky, B.M., Park, H.S., 2000. Brightness Temperature of the Lunar Surface: Calibration and Global Analysis of the Clementine Long-Wave Infrared Camera Data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105: 4273-4290. doi: 10.1007/s11432-010-0020-1 Lucey, P.G., Blewett, D.T., Hawke, B.R., 1998. Mapping the FeO and TiO2 Content of the Lunar Surface with Multispectral Imagery. Journal of Geophysical Research, 103: 3679-3699. doi: 10.1029/97JE03019 Lucey, P.G., Blewett, D.T., Jollifff, B.L., 2000. Lunar Iron and Titanium Abundance Algorithms Based on Final Processing of Clementine Ultraviolet-Visible Images. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105: 20297-20305. doi: 10.1029/1999JE001117 Lucey, P.G., Taylor, G.J., Malaret, E., et al., 1995. Abundance and Distribution of Iron on the Moon. Science, 268: 1855-1858. doi: 10.1126/science.268.5214.1150 Matveev, Y.G., Suchkin, G.L., Troitskii, V.S., 1966. Change of Lunite Density with Depth in the Surface Layer. Soviet Astronomy, 9(4): 626-631. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1966SvA.....9..626M Meng, Z.G., 2008. Lunar Regolith Parameters Retrieval Using Radiative Transfer Simulation and Look-up Technique (Dissertation). Jilin University, Changchun (in Chinese with English abstract). Meng, Z.G., Chen, S.B., Du, X.J., et al., 2011a. Influence of Temperature and Frequency on Microwave Dielectric Properties of Lunar Regolith Stimulant. Chinese Geographical Science, 21(1): 94-101. doi: 10.1007/s11769-011-0443-7 Meng, Z.G., Chen, S.B., Liu, C., et al., 2008. Simulation on Passive Microwave Radiative Transfer in Inhomogeneous Lunar Regolith. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 38(6): 1070-1074 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200806028.htm Meng, Z.G., Chen, S.B., Lu, P., et al., 2011b. Research on the Distribution and Content of Water Ice in Lunar Pole Regions Using Clementine UVVIS Data. Journal of Earth Science, 22(5): 595-600. doi: 10.1007/s12583-011-0210-9 Shkuratov, Y.G., Bondarenko, N.V., 2001. Regolith Layer Thickness Mapping of the Moon by Radar and Optical Data. Icarus, 149: 329-338. doi: 10.1006/icar.2000.6545 Shkuratov, Y.G., Kaydash, V.G., Opanasenko, N.V., 1999. Iron and Titanium Abundance and Maturity Degree Distribution on the Lunar Nearside. Icarus, 137: 222-234. doi: 10.1006/icar.1999.6046 Tyler, G.L., 1968. Brewster Angle of the Lunar Crust. Nature, 219(B): 1243-1244. doi: 10.1038/2191243a0 Wang, Z.Z., Li, Y., Jiang, J.S., et al., 2009. Lunar Surface Dielectric Constant, Regolith Thickness and Helium-3 Abundance Distributions Retrieved from Microwave Brightness Temperatures of CE-1 Lunar Microwave Sounder. Science in China (Series D), 39(8): 1069-1084 (in Chinese). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313716035_Lunar_surface_dielectric_constant_regolith_thickness_and_helium-3_abundance_distributions_retrieved_from_microwave_brightness_temperatures_of_CE-1_Lunar_Microwave_Sounder Zheng, Y.C., Tsang, K.T., Chan, K.L., et al., 2012. First Microwave Map of the Moon with Chang'e-1 Data: The Role of Local Time in Global Imaging. Icarus, 219: 194-210. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2012.02.017 姜景山, 王振占, 李芸, 2008. 嫦娥1号卫星微波探月技术机理和应用研究. 中国工程科学, 10(6): 16-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2008.06.003 孟治国, 2008. 月壤参数的辐射传输模拟和查找反演技术研究(博士学位论文). 长春: 吉林大学. 孟治国, 陈圣波, 刘财, 等, 2008. 非均匀月壤介质中的被动微波辐射传输模拟. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 38(6): 1070-1074. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200806028.htm 王振占, 李芸, 姜景山, 等, 2009. 用"嫦娥一号"卫星微波探测仪亮温反演月壤厚度和3He资源量评估的方法及初步结果分析. 中国科学(D辑), 39(8): 1069-1084. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200908006.htm -









 下载:
下载: