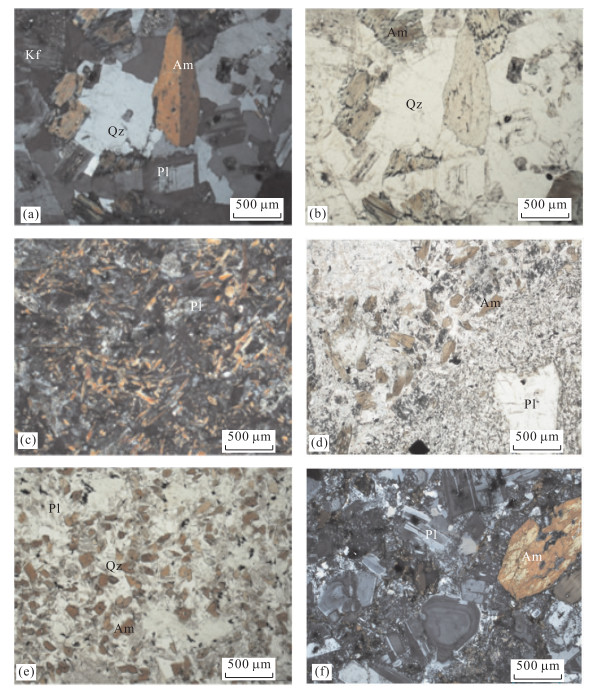
Geochronological, Geochemical and Petrogenesis of Bieluagaxi Granodioritic Pluton in Western Junggar
-
摘要: 为更深入了解西准噶尔晚古生代岩浆活动和构造背景,对位于西准噶尔中部的别鲁阿嘎希岩体开展了年代学、地球化学以及Sr-Nd同位素研究,讨论了岩石成因、源区性质和构造背景.别鲁阿嘎希花岗闪长岩为钙碱性系列岩石,岩浆锆石结晶年龄为318.7±3.3 Ma.其具相对高的MgO(Mg#=49~59)、Ni、Cr含量,富集大离子亲石元素(如K、Rb、Sr和Ba)、亏损高强场元素(如Nb、Ta、Ti),轻重稀土元素分异不明显.Sr-Nd同位素特征显示,其有较低的初始Sr比值(0.704 297~0.704 399),较高的εNd(t)值(5.8~6.5).通过综合分析,认为在晚石炭世早期,达尔布特洋壳(板片)俯冲至地幔楔下部,俯冲洋壳板片脱水所产生的流体在上升过程中与地幔楔共同作用,底侵加热由亏损地幔形成不久的年轻地壳(由洋壳和岛弧组成),使其部分熔融形成了别鲁阿嘎希分异I型花岗岩.Abstract: For a better understanding of the petrogenesis and tectonic environment of the acidic intrusive rocks in Western Junggar, a study is carried out on Bieluagaxi granodioritic pluton located in the Central part of West Junggar. Its petrogenesis, magma source, tectonics setting based on petrography, zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages, whole-rock major and trace elements, and Sr-Nd isotopic compositions are discussed in detail. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon data of the granodiorite give weighted ages of 318.7±3.3 Ma. Bieluagaxi granodiorite is calc-alkaline suite with high MgO(Mg#=49-59), Ni and Cr contents. Bieluagaxi granodiorite is strongly enriched in large ion lithophile elements (LILEs, e.g. K, Rb, Sr and Ba), but it displays depletion of high field strength elements (HFSEs, e.g. Nb, Ta and Ti). In terms of Sr-Nd isotopic compositions, granodiorite has low initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios (0.704 297-0.704 399) and high positive εNd(t) (5.8-6.5). Therefore, we suggest that the early Late Carboniferous Bieluagaxi granodioritic pluton has been generated in a subduction setting, the mantle wedge began to partially melt due to the upward fluid from the dehydration of subducting oceanic slab, resulting in the asthenospheric mafic magma underplating the lower crust. Then, the lower juvenile basaltic crust derived from the depleted mantle underwent partial melting to generate the I type granites of the Bieluagaxi granodioritic pluton.
-
Key words:
- Bieluagaxi granodioritic pluton /
- geochronology /
- geochemistry /
- Sr-Nd isotope /
- western Junggar /
- stratigraphy
-
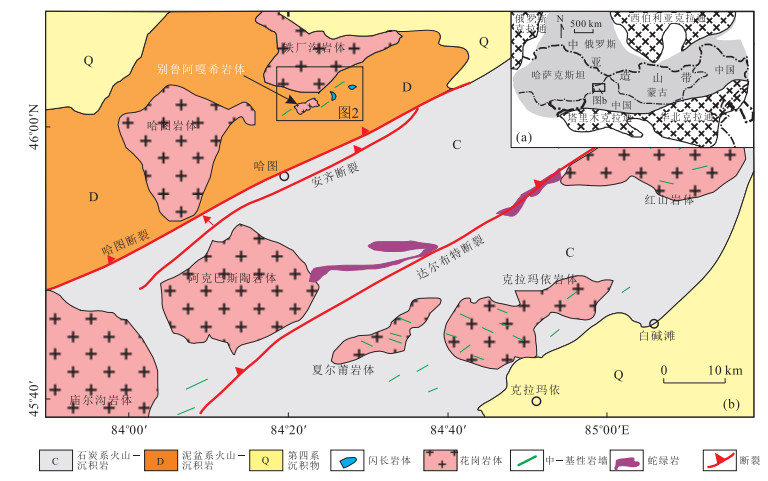
图 1 西准噶尔地区地质简图
据苏玉平等(2006)、安芳和朱永峰(2007)和尹继元等(2012)修改
Fig. 1. Geological sketch of the western Junggar region
图 2 别鲁阿嘎希岩体地质简图
1.库鲁木迪组上亚组上岩性段;2.库鲁木迪组上亚组中岩性段;3.库鲁木迪组上亚组下岩性段;4.花岗闪长岩;5.碱长花岗岩;6.岩墙;7.断层;8.采样点.据金成伟和徐永生(1997)以及尹继元等(2012)
Fig. 2. Geological sketch of the Bieluagaxi pluton
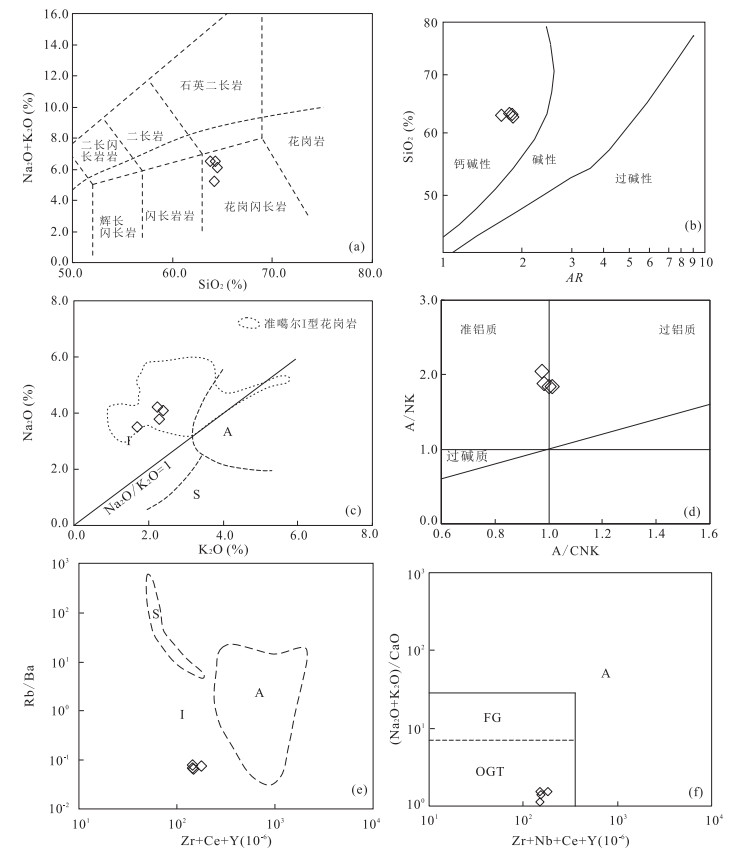
图 6 别鲁阿嘎希花岗闪长岩(Na2O+K2O)-SiO2、SiO2-AR、Na2O-K2O、A/NK-A/CNK、Rb/Ba-(Zr+Ce+Y)和(Na2O+K2O)/CaO-(Zr+Ce+Y)图解
数据来源:准噶尔I型花岗岩范围据Chen and Jahn(2004);图a底图据Middlemost(1994);图b底图据Peccerillo and Taylor(1976);图e和f底图据Whalen et al.(1987);I-I.I-I型花岗岩; S-S.S-S型花岗岩; A-A.A-A型花岗岩; FG.FG分异型I, S或M型花岗岩; OGT.OGT分异型I、S和M型花岗岩
Fig. 6. (Na2O+K2O)-SiO2, SiO2-AR, Na2O-K2O, A/NK-A/CNK, Rb/Ba-(Zr+Ce+Y) and (Na2O+K2O)/CaO-(Zr+Ce+Y) relationships of the Bieluagaxi granodiorite
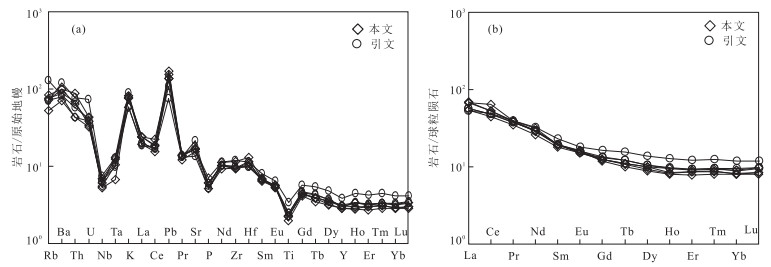
图 7 别鲁阿嘎希花岗闪长岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网(a)和球粒陨石标准化REE分布模式(b)
球粒陨石标准化值和原始地幔标准化值据Sun and McDonough(1989);引文据尹继元等(2012)
Fig. 7. Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram (a) and Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (b) for the Bieluagaxi granodiorite
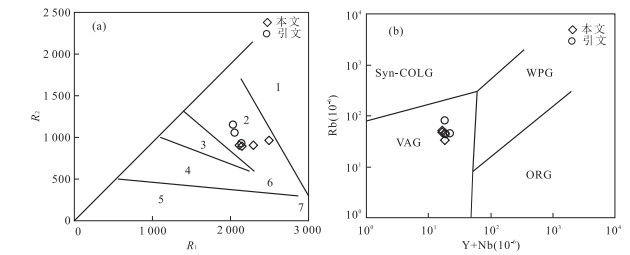
图 8 别鲁阿嘎希花岗闪长岩R2-R1(a)和Rb-Y+Nb(b)判别
图a底图据Bachelor and Bowden(1985); 图b底图据Pearce et al.(1984).1.地幔分异花岗岩; 2.碰撞前花岗岩; 3.碰撞后隆起花岗岩; 4.晚造山花岗岩; 5.非造山花岗岩; 6.同碰撞花岗岩; 7.后造山花岗岩.WPG.板内花岗岩; VAG.弧花岗岩; Syn-OLG.同碰撞花岗岩; ORG.洋脊花岗岩, 引文据尹继元等(2012)
Fig. 8. R2-R1 (a) and Rb-Y+Nb (b) discriminant diagrams of Bieluagaxi granodiorite
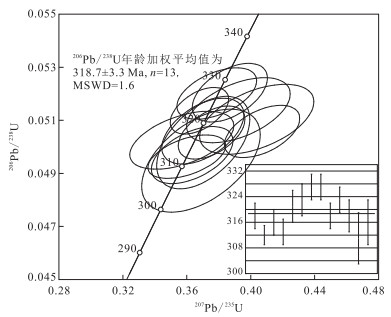
表 1 别鲁阿嘎希花岗闪长岩中锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年数据
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data for the Bieluagaxi granodiorite
测试点号 元素含量(10-6) Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U Pb Th U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ BL2.01 35 193 652 0.30 0.058 56 0.002 34 0.407 09 0.015 55 0.050 58 0.000 65 550 87 347 11 318 4 BL2.02 75 537 1 220 0.44 0.052 59 0.002 40 0.360 04 0.016 05 0.049 63 0.000 54 322 101 312 12 312 3 BL2.03 28 154 520 0.30 0.051 83 0.003 25 0.356 89 0.021 51 0.050 25 0.000 72 280 144 310 16 316 4 BL2.04 33 236 600 0.39 0.053 27 0.002 51 0.363 38 0.016 83 0.049 69 0.000 71 339 106 315 13 313 4 BL2.05 59 414 1 014 0.41 0.058 01 0.003 58 0.403 81 0.023 57 0.051 04 0.000 87 532 137 344 17 321 5 BL2.06 60 384 973 0.39 0.055 86 0.003 21 0.392 28 0.021 41 0.051 38 0.000 81 456 123 336 16 323 5 BL2.07 31 177 566 0.31 0.053 74 0.002 12 0.386 91 0.015 50 0.052 04 0.000 73 361 61 332 11 327 4 BL2.08 36 205 642 0.32 0.052 69 0.002 33 0.378 75 0.016 46 0.052 01 0.000 64 322 100 326 12 327 4 BL2.09 49 353 890 0.40 0.053 55 0.001 99 0.375 52 0.013 76 0.050 54 0.000 66 354 85 324 10 318 4 BL2.10 50 229 795 0.29 0.051 41 0.001 69 0.367 91 0.012 03 0.051 36 0.000 58 257 71 318 9 323 4 BL2.11 32 180 576 0.31 0.052 86 0.002 58 0.370 07 0.016 94 0.050 59 0.000 82 324 111 320 13 318 5 BL2.12 29 170 526 0.32 0.053 56 0.003 56 0.368 86 0.024 48 0.049 48 0.001 28 354 150 319 18 311 8 BL2.13 71 551 1 231 0.45 0.052 61 0.002 58 0.370 30 0.019 20 0.050 16 0.001 15 322 113 320 14 316 7 表 2 别鲁阿嘎希花岗闪长岩主量元素(%)和微量元素(10-6)组成
Table 2. Major (%) and trace elements (10-6) compositions for the Bieluagaxi granodiorite
样号 BL1 BL2 BL3 BL4 SiO2 64.2 64.3 64.5 63.8 TiO2 0.48 0.42 0.49 0.48 Al2O3 15.6 17.3 16.4 17.1 FeO 3.65 2.92 3.28 3.33 Fe2O3 0.50 0.51 0.48 0.62 MgO 3.34 1.84 2.25 2.28 MnO 0.09 0.07 0.09 0.09 CaO 4.61 4.22 4.39 4.28 K2O 1.70 2.25 2.29 2.39 Na2O 3.52 4.23 3.78 4.09 P2O5 0.11 0.13 0.13 0.15 H2O+ 1.96 1.43 1.49 1.19 CO2 0.06 0.24 0.24 0.08 Total 99.82 99.86 99.81 99.88 Mg# 59 49 52 51 AR 1.69 1.86 1.83 1.87 La 13.0 16.3 16.2 16.1 Ce 27.2 32.6 32.2 39.0 Pr 3.30 3.73 3.67 3.76 Nd 12.3 13.7 13.5 14.9 Sm 2.79 2.87 2.93 2.99 Eu 0.89 0.93 0.88 0.94 Gd 2.56 2.43 2.59 2.58 Tb 0.41 0.37 0.42 0.40 Dy 2.56 2.26 2.53 2.35 Ho 0.54 0.45 0.48 0.46 Er 1.49 1.28 1.42 1.42 Tm 0.24 0.21 0.22 0.23 Yb 1.56 1.36 1.40 1.37 Lu 0.25 0.21 0.22 0.22 Y 14.0 12.6 13.7 12.7 Zr 103 101 103 125 Nb 4.23 3.83 4.80 3.67 Ba 480 603 681 680 Hf 3.50 3.12 3.35 3.98 Ta 0.53 0.42 0.50 0.27 Li 25.5 18.7 23.8 29.3 Sc 14.60 9.86 11.90 10.80 Cr 102.0 46.2 56.4 54.8 Co 14.2 8.90 10.8 10.6 Ni 41.9 15.9 20.4 18.1 Rb 33.1 47.9 44.8 51.8 Cs 1.38 1.92 2.42 3.42 Pb 9.52 12.0 10.8 9.42 Th 3.65 5.72 7.25 5.40 U 0.66 0.71 0.89 0.79 Sr 319 357 341 348 V 84.1 37.0 51.6 46.6 ∑REE 83.03 91.35 92.27 99.45 LREE 61.99 72.60 71.93 80.26 HREE 21.05 18.75 20.34 19.19 LREE/HREE 2.95 3.87 3.54 4.18 (La/Yb)N 6.0 8.6 8.3 8.4 Nb/Ta 8 9 10 13 Zr/Hf 29 32 31 32 Rb/Sr 0.10 0.13 0.13 0.15 注:(La/Yb)N为La/Nb对球粒陨石标准化的值. 表 3 别鲁阿嘎希花岗闪长岩Sr-Nd同位素分析结果
Table 3. The Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of Bieluagaxi granodiorite
样号 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr±2σ 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd±2σ (87Sr/86Sr)i (143Nd/144Nd)i εNd(t) T2DM(Ma) BL2 0.388 537 0.706 161±8 0.126 689 0.512 787±5 0.704 399 0.512 523 5.8 610 BL4 0.431 488 0.706 254±4 0.121 195 0.512 814±5 0.704 297 0.512 561 6.5 550 注:误差为2σ;Nd和Sr同位素初始值根据318.7 Ma计算. -
An, F., Zhu, Y.F., 2007. Studies on Geology and Geochemistry of Alteration-Type Ore in Hatu Gold Deposit (Western Junggar), Xinjiang, NW China. Mineral Deposits, 26(6): 621-633(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200706005.htm Anderson, T., 2002. Correction of Common Lead in U-Pb Analyses that Do not Report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X Bachelor, R.A., Bowden, P., 1985. Petrographic Interpretation of Granitoid Rocks Series Using Multicationic Parameters. Chemical Geology, 48(1-4): 43-55. doi: 10.1016/0004-2541(85)90034-8 Barbarin, B., 1999. A Review of the Relationships between Granitoid Types, Their Origins and Their Geodynamic Environments. Lithos, 46(3): 605-626. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00085-1 Chappell, B.W., White, A.J.R., 1992. I- and S-Type Granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences, 83: 1-26. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300007720 Chen, B., Arakawa, Y., 2005. Elemental and Nd-Sr Isotopic Geochemistry of Granitoids from the West Junggar Foldbelt (NW China), with Implications for Phanerozoic Continental Growth. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(5): 1307-1320. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.09.019 Chen, B., Jahn, B.M., 2004. Genesis of Post-Collisional Granitoids and Basement Nature of the Junggar Terrane, NW China: Nd-Sr Isotope and Trace Element Evidence. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 23(5): 691-703. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00118-4 Chen, J.F., Han, B.F., Ji, J.Q., et al., 2010. Zircon U-Pb Ages and Tectonic Implications of Paleozoic Plutons in Northern West Junggar, North Xinjiang, China. Lithos, 115(1-4): 137-152. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.11.014 Chen, J.F., Han, B.F., Zhang, L., 2010. Geochemistry, Sr-Nd Isotopes and Tectonic Implications of Two Generations of Late Paleozoic Plutons in Northern West Junggar, Northwest China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(8): 2317-2335(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1474907 Faure, G., 1986. Principles of Isotope Geology. Second Edition. John Wiley and Sons, New, York, 589. Feng, Y., Coleman, R.G., Tilton, G., et al., 1989. Tectonic Evolution of the West Junggar Region, Xinjiang, China. Tectonics, 8(4): 729-752. doi: 10.1029/TC008i004p00729 Gao, R., Xiao, L., Pirajno, F., et al., 2014. Carboniferous-Permian Extensive Magmatism in the West Junggar, Xinjiang, Northwestern China: Its Geochemistry, Geochronology, and Petrogenesis. Lithos, 204: 125-143. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.05.028 Gao, R., Xiao, L., Wang, G.C., et al., 2013. Paleozoic Magmatism and Tectonic Setting in West Junggar. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(10): 3413-3434(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285747232_Paleozoic_Magmatism_and_Tectonic_Setting_in_West_Junggar Geng, H.Y., Sun, M., Yuan, C., et al., 2009. Geochemical, Sr-Nd and Zircon U-Pb-Hf Isotopic Studies of Late Carboniferous Magmatism in the West Junggar, Xinjiang: Implications for Ridge Subduction? Chemical Geology, 266(3-4): 364-389. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.07.001 Gill, J.B., 1981. Orogenic Andesites and Plate Tectonics. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. Green, T.H., 1982. Anatexis of Mafic Crust and High Pressure Crystallisation of Andesite. In: Thorpe, R.S., ed., Andesites. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 465-487. Han, B.F., Wang, S.G., Jahn, B.M., et al., 1997. Depleted-Mantle Source for the Ulungur River A-Type Granites from North Xinjiang, China: Geochemistry and Nd-Sr Isotopic Evidence, and Implications for Phanerozoic Crustal Growth. Chemical Geology, 138(3-4): 135-159. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00003-X Han, B.F., Ji, J.Q., Song. B., et al., 2006. Late Paleozoic Vertical Growth of Continental Crust around the Junggar Basin, Xinjiang, China(Part Ⅰ): Timing of Post-Collisional Plutonism. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5): 1077-1086(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1472627 Hoskin, P.W.O., Black, L.P., 2000. Metamorphic Zircon Formation by Solid-State Recrystallization of Protolith Igneous Zircon. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 18(4): 423-439. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2000.00266.x Hu, A.Q., Jahn, B.M., Zhang, G.X., et al., 2000. Crustal Evolution and Phanerozoic Crustal Growth in Northern Xinjiang: Nd Isotopic Evidence. Part Ⅰ. Isotopic Characterization of Basement Rocks. Tectonophysics, 328(1-2): 15-51. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00176-1 Jahn, B.M., 2004. The Central Asian Orogenic Belt and Growth of the Continental Crust in the Phanerozoic. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 226: 73-100. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2004.226.01.05 Jin, C.W., Xu, Y.S., 1997. Petrology and Genesis of the Bieluagaxi Granitoids in Tuoli, Xinjiang, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 13(4): 529-537(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/298288357_Petrology_and_genesis_of_the_bieluagaxi_granitoids_in_Tuoli_Xinjiang_China Jin, C.W., Zhang, X.Q., 1993. A Geochronology and Geneses of the Western Junggar Granitiods, Xinjiang, China. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 28(1): 28-36(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199301003.htm Koschek, G., 1993. Origin and Significance of the SEM Cathodoluminescence from Zircon. Journal of Microscopy, 171(3): 223-232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1993.tb03379.x Kwon, S.T., Tilton, G.R., Coleman, R.G., et al., 1989. Isotopic Studies Bearing on the Tectonics of the West Junggar Region, Xinjiang, China. Tectonics, 8(4): 719-727. doi: 10.1029/TC008i004p00719 Li, Z.H., Han, B.F., Li, X.Z., et al., 2004. Microgranular Dioritic Enclaves in Junggar Granites and Their Implications for the Origin and Evolution of Post-Collisional Granitic Magmatism in North Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 23(3): 214-226(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200403002.htm Ling, W.L., Duan, R.C., Xie, X.J., et al., 2009. Contrasting Geochemistry of the Cretaceous Volcanic Suites in Shandong Province and Its Implications for the Mesozoic Lower Crust Delamination in the Eastern North China Craton. Lithos, 113(3-4): 640-658. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.07.001 Liu, Y.S., Gao, S., Hu, Z.C., et al., 2010a. Continental and Oceanic Crust Recycling-Induced Melt-Peridotite Interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb Dating, Hf Isotopes and Trace Elements in Zircons from Mantle Xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537-571. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp082 Liu, Y.S., Hu, Z.C., Zong, K.Q., et al., 2010b. Reappraisement and Refinement of Zircon U-Pb Isotope and Trace Element Analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(15): 1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4 Liu, Y.S., Hu, Z.C., Gao, S., et al., 2008. In Situ Analysis of Major and Trace Elements of Anhydrous Minerals by LA-ICP-MS without Applying an Internal Standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 Ludwig, K.R., 2003. ISOPLOT 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, Berkeley. Ma, C., Xiao, W.J., Windley, B.F., et al. 2012. Tracing a Subducted Ridge-Transform System in a Late Carboniferous Accretionary Prism of the Southern Altaids: Orthogonal Sanukitoid Dyke Swarms in Western Junggar, NW China. Lithos, 140-141: 152-165. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.02.005 Middlemost, E.A.K., 1994. Naming Materials in the Magma/Igneous Rock System. Earth-Science Reviews, 37: 215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9 Miller, C.F., 1985. Are Strongly Peraluminous Magmas Derived from Pelitic Sedimentary Sources?The Journal of Geology, 93(6): 673-689. doi: 10.1086/628995 No. 11 Geological Party of Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources Exploration and Development. 1985.1∶50 000 Geological Survey Report. Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources Exploration and Development, Turpan (in Chinese). Pearce, J.A., Harris, N.B.W., Tindle, A.G., 1984. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 Peccerillo, A., Taylor, S.R., 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene Calc-Alkaline Volcanic Rocks from the Kastamonu Area, Northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745 Rapp, R.P., Watson, E.B., 1995. Dehydration Melting of Metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: Implications for Continental Growth and Crust-Mantle Recycling. Journal of Petrology, 36(4): 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891 Rapp, R.P., 1997. Heterogeneous Source Regions for Archean Granitoids. In: Wit, M.J., Ashwal, L.D., eds., Greenstone Belts. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 35-37. Sengör, A.M.C., Natal'In, B.A., Burtman, V.S., 1993. Evolution of the Altaid Tectonic Collage and Palaeozoic Crustal Growth in Eurasia. Nature, 364(6435): 299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0 Shen, P., Shen, Y.C., Li, X.H., et al., 2012. Northwestern Junggar Basin, Xiemisitai Mountains, China: A Geochemical and Geochronological Approach. Lithos, 140-141: 103-118. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.02.004 Su, Y.P., Tang, H. E, ,Hou, G.S., et al., 2006. Geochemistry of Aluminous A-Type Granites along Darabut Tectonic Belt in West Junggar, Xinjiang. Geochemica, 35(1): 55-67(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200601006.htm Sun, S.S., McDonough, W.F., 1989. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 Tang, G.J., Wang, Q., Wyman, D.A., et al., 2010. Ridge Subduction and Crustal Growth in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Evidence from Late Carboniferous Adakites and High-Mg Diorites in the Western Junggar Region, Northern Xinjiang (West China). Chemical Geology, 277(3-4): 281-300. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.08.012 Tatsumi, Y., Hamilton, D.L., Nesbitt, R.W., 1986. Chemical Characteristics of Fluid Phase Released from a Subducted Lithosphere and Origin of Arc Magmas: Evidence from High-Pressure Experiments and Natural Rocks. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 29(1-4): 293-309. doi: 10.1016/0377-0273(86)90049-1 Wang, R., Zhu, Y.F., 2007. Geology of the Baobei Gold Deposit in Western Junggar and Zircon SHRIMP Age of Its Wall-Rocks, Western Junggar (Xinjiang, NW China). Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(3): 590-602(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/267334888_Geology_of_Baobei_gold_deposit_in_western_Junggar_and_zircon_SHRIMP_age_of_its_wall-rock_Western_Junggar_Xinjiang_NW_China Whalen, J.B., Currie, K.L., Chappell. B.W., 1987. A-Type Granites: Geochemical Characteristics, Discrimination and Petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202 Wilson, M., 1989. Igneous Petrogenesis: A Global Tectonic Approach. Unwin Hyman, London, 466. Woodhead, J.D., Hergt, J.M., Davidson, J.P., et al., 2001. Hafnium Isotope Evidence for 'Conservative' Element Mobility during Subduction Zone Processes. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 192(3): 331-346. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00453-8 Wu, F.Y., Li, X.H., Yang, J.H., et al., 2007. Discussions on the Petrogenesis of Granites. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(6): 1217-1238 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279707410_Discussion_on_the_petrogenesis_of_granites Wu, F.Y., Jahn, B.M., Wilde, S.A., et al., 2003. Highly Fractionated I-Type Granites in NE China (I): Geochronology and Petrogenesis. Lithos, 66(3-4): 241-273. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00222-0 Xiao, L., Rapp, P.R., Xu, J.F., 2004. The Role of Deep Processes Controls on Variation of Compositions of Adakitic Rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(2): 219-228(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200402003.htm Xiao, W.J., Han, C.M., Yuan, C., et al., 2006. Unique Carboniferous-Permian Tectonic-Metallogenic Framework of Northern Xinjiang (NW China): Constraints for the Tectonics of the Southern Paleoasian Domain. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5): 1062-1076(in Chinese with English abstract). http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10026539172 Xiao, W.J., Kusky, T., 2009. Geodynamic Processes and Metallogenesis of the Central Asian and Related Orogenic Belts: Introduction. Gondwana Research, 16(2): 167-169. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2009.05.001 Xu, Q.Q., Ji, J.Q., Zhao, L., et al., 2013. Tectonic Evolution and Continental Crust Growth of Northern Xinjiang in Northwestern China: Remnant Ocean Model. Earth-Science Reviews, 126: 178-205. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.08.005 Yang, G.X., Li, Y.J., Gu, P.Y., et al., 2012. Geochronological and Geochemical Study of the Darbut Ophiolitic Complex in the West Junggar (NW China): Implications for Petrogenesis and Tectonic Evolution. Gondwana Research, 21(4): 1037-1049. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.07.029 Yin, J.Y., Chen, W., Yuan, C., et al., 2013. Ages and Tectonic Implication of Late Paleozoic Plutons in the West Junggar, North Xinjiang: Evidence from LA-ICP-MS Zircon Geochronology. Geochimica, 42(5): 414-429(in Chinese with English abstract). http://gsa.confex.com/gsa/2010AM/finalprogram/abstract_182664.htm Yin, J.Y., Yuan, C., Sun, M., et al., 2010. Late Carboniferous High-Mg Dioritic Dikes in Western Junggar, NW China: Geochemical Features, Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications. Gondwana Research, 17(1): 145-152. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2009.05.011 Yin, J.Y., Yuan, C., Sun, M., et al., 2012. Age, Geochemical Features and Possible Petrogenesis Mechanism of Early Permian Magnesian Diorite in Hatu, Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(7): 2171-2182(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/305535649_Age_geochemical_features_and_possible_petrogenesis_mechanism_of_Early_Permian_magnesian_diorite_in_Hatu_Xinjiang Yuan, C., Sun, M., Xiao, W.J., et al., 2008. Garnet-Bearing Tonalitic Porphyry from East Kunlun, Northeast Tibetan Plateau: Implications for Adakite and Magmas from the MASH Zone. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(6): 1489-1510. doi: 10.1007/s00531-008-0335-y Zhang, C., Huang, X., 1992. The Ages and Tectonic Settings of Ophiolites in West Junggar, Xinjiang. Geological Review, 38(6): 509-524(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/312462444_Age_and_tectonic_settings_of_ophiolites_in_west_Junggar_Xinjiang Zhang, J.E., Xiao, W.J., Han, C.M., et al., 2011. A Devonian to Carboniferous Intra-Oceanic Subduction System in Western Junggar, NW China. Lithos, 125(1-2), 592-606. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.03.013 Zhang, L.C., Wan, B., Jiao, X.J., et al., 2006. Characteristics and Geological Significance of Adakitic Rocks in Copper-Bearing Porphyry in Baogutu, Western Junggar. Geology in China, 33(3): 626-631(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi200603020 Zhao, Z.H., Wang, Q., Xiong, X.L., et al., 2006. Two Types of Adakites in North Xinjiang, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5): 1249-1265(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, T.F., Yuan, F., Fan, Y., et al., 2008. Granites in the Sawuer Region of the West Junggar, Xinjiang Province, China: Geochronological and Geochemical Characteristics and Their Geodynamic Significance. Lithos, 106(3-4): 191-206. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2008.06.014 安芳, 朱永峰, 2007. 新疆哈图金矿蚀变岩型矿体地质和地球化学研究. 矿床地质, 26(6): 621-633. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.06.004 陈家富, 韩宝福, 张磊, 2010. 西准噶尔北部晚古生代两期侵入岩的地球化学、Sr-Nd同位素特征及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 26(8): 2317-2335. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201008009.htm 高睿, 肖龙, 王国灿, 等, 2013. 西准噶尔晚古生代岩浆活动和构造背景. 岩石学报, 29(10): 3413-3434. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201310008.htm 韩宝福, 季建清, 宋彪, 等, 2006. 新疆准噶尔晚古生代陆壳垂向生长(Ⅰ)——后碰撞深成岩浆活动的时限. 岩石学报, 22(5): 1077-1086. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200605003.htm 金成伟, 徐永生, 1997. 新疆托里别鲁阿嘎希地区花岗岩类的岩石学和成因. 岩石学报, 13(4): 529-537. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1997.04.007 金成伟, 张秀棋, 1993. 新疆西准噶尔花岗岩类的时代及其成因. 地质科学, 28(1): 28-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199301003.htm 李宗怀, 韩宝福, 李辛子, 等, 2004. 新疆准噶尔地区花岗岩中微粒闪长质包体特征及后碰撞花岗质岩浆起源和演化. 岩石矿物学杂志, 23(3): 214-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2004.03.003 苏玉平, 唐红峰, 侯广顺, 等, 2006, 新疆西准噶尔达拉布特构造带铝质A型花岗岩的地球化学研究. 地球化学, 35(1): 55-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200601006.htm 王瑞, 朱永峰, 2007, 西准噶尔宝贝金矿地质与容矿火山岩的锆石SHRIMP年龄. 高校地质学报, 13(3): 590-602. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.027 新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产勘查开发局第十一地质大队, 1985.1∶50 000普查地质报告. 吐鲁番: 新疆地质矿产局. 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等, 2007. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题. 岩石学报, 23(6): 1217-1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.001 肖龙, Rapp, R.P., 许继峰, 2004. 深部过程对埃达克质岩石成分的制约. 岩石学报, 20(2): 219-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200402003.htm 肖文交, 韩春明, 袁超, 等, 2006. 新疆北部石炭纪-二叠纪独特的构造-成矿作用: 对古亚洲洋构造域南部大地构造演化的制约. 岩石学报, 22(5): 1062-1076. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200605002.htm 尹继元, 陈文, 袁超, 等, 2013. 新疆西准噶尔晚古生代侵入岩的年龄和构造意义: 来自锆石LA-ICP-MS定年的证据. 地球化学, 42(5): 414-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201305003.htm 尹继元, 袁超, 孙敏, 等, 2012. 新疆哈图早二叠世富镁闪长岩的时代, 地球化学特征和可能的成因机制. 岩石学报, 28(7): 2171-2182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201207019.htm 张弛, 黄萱, 1992. 新疆西准噶尔蛇绿岩形成时代和环境的探讨. 地质论评, 38(6): 509-524. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1992.06.009 张连昌, 万博, 焦学军, 等, 2006. 西准包古图含铜斑岩的埃达克岩特征及其地质意义. 中国地质, 33(3): 626-631. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.03.020 赵振华, 王强, 熊小林, 等, 2006. 新疆北部的两类埃达克岩. 岩石学报, 22(5): 1249-1265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200605016.htm -









 下载:
下载: