Vegetation and Climate Changes around Celebes Sea during Holocene
-
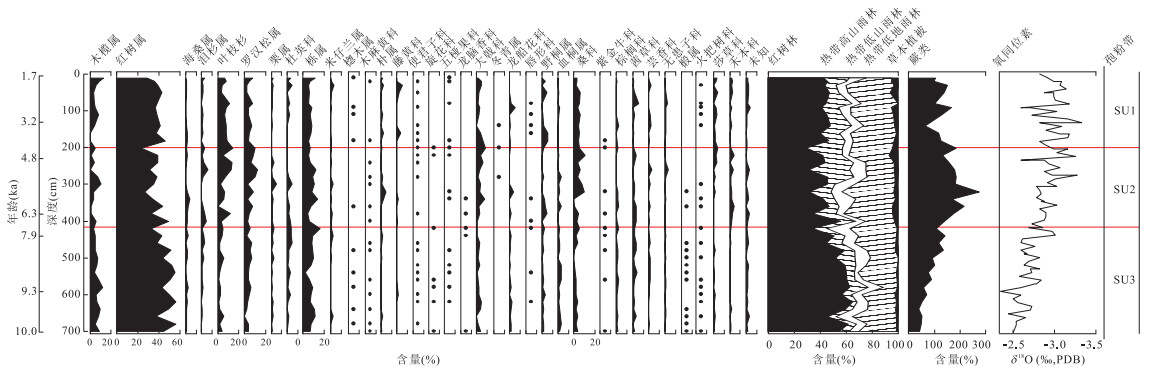
摘要: 全新世时期的环境和气候变化是全球气候模拟、预测中不可或缺的资料.对苏拉威西海西北部MD98-2178孔(3.6200°N,118.7000°E,水深1 984 m)全新世的样品进行孢粉分析和浮游有孔虫氧稳定同位素测试,重建全新世苏拉威西海周边地区植被演化和气候变化图景.根据孢粉记录得到:在全新世早期至7 ka BP时,各孢粉组合浓度剧烈下降,指示海平面处于上升阶段;在7~4 ka BP时,各孢粉组合浓度都处于低谷,体现为高海平面期;在4 ka BP之后,孢粉记录则显示海平面有小幅的下降.在全新世中期,即5~4 ka BP,热带高山雨林花粉含量明显上升,表明是温度低值期.蕨类孢子记录显示降雨量在全新世早期是持续增加的,但在全新世中期之后,降雨量有所减少,这与陆地孢粉记录和印尼石笋记录的结果相似,体现全新世该地区降雨量受海陆格局和太阳活动共同影响.Abstract: The environment and climate information during the Holocene is indispensable data for the global climate modeling and forecasting. Scenarios of regional vegetation and climate changes around the Celebes Sea during the Holocene are explored based on the alynological and oxygen isotope records of core MD98-2178 (3.6200°N, 118.7000°E; 1 984 m water depth) from the northwest Celebes Sea in this study. Sea-level changes are discussed since the marine pollen record of core MD98-2178 is considered as an indicator. The sharp decline in concentration of all pollen groups during the Early Holocene, ~10-7 ka BP, indicates a sea-level rise. All pollen groups at 7-4 ka BP suggest sustaining of a high sea-level. The marine pollen record after 4 ka BP shows a slight fall of sea-level. The significant increase in pollen percentage of the tropical montane forest during the Middle Holocene, 5-4 ka BP, suggests a much cold condition along the Celebes Sea at the time. It is suggested that precipitation along the Celebes Sea has been affected by variations of land-ocean distribution and solar activities. It is implied by fluctuation in fern spores record that precipitation was at a high level during the Early Holocene, but lowered after the Middle Holocene, which is in a similar pattern as indicated by the Indonesian stalagmite records.
-
Key words:
- Holocene /
- Celebes Sea /
- pollen analysis /
- sea-level change /
- temperature /
- precipitation /
- climate change /
- vegetation
-
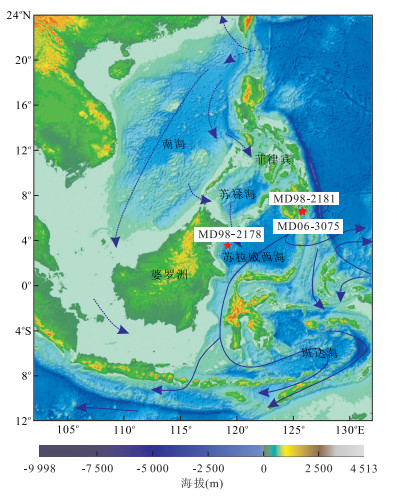
图 1 研究站位地理位置
图中红星为站位位置,虚线为南海穿越流,实线为印尼穿越流;修改自Gordon et al.(2012)
Fig. 1. General location of the study cores
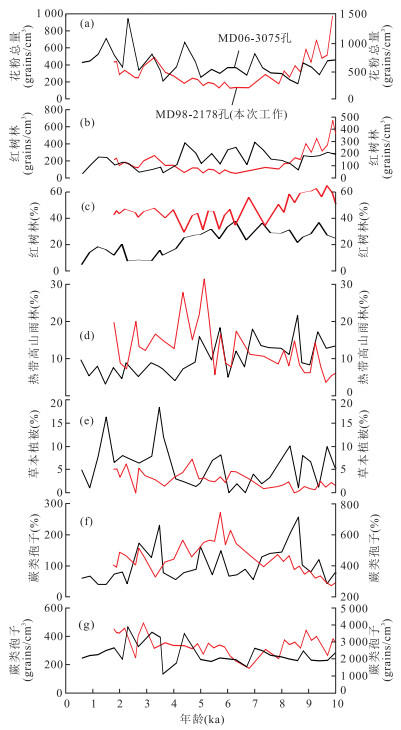
图 5 苏拉威西海西北部MD98-2178孔与菲律宾南部MD06-3075孔海洋孢粉记录对比
红色曲线以左侧坐标轴来度量;黑色曲线以右侧坐标轴来度量,据Bian et al.(2011);a.花粉总浓度;b.红树林花粉浓度;c.红树林花粉含量;d.热带高山雨林花粉含量;e.草本植被花粉含量;f.蕨类孢子含量;g.蕨类孢子浓度
Fig. 5. Comparison of pollen records of core MD98-2178 from northwest Celebes Sea and MD06-3075 from the southern Philippines
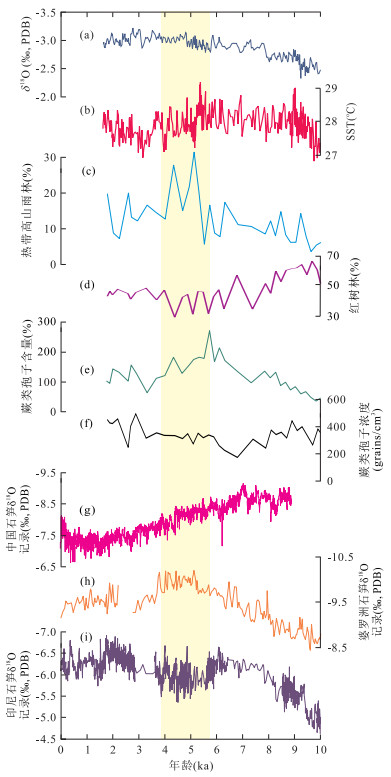
图 6 MD98-2178孔海洋孢粉记录和古海洋记录与石笋记录对比
黄色阴影区为全新世中期植被和气候突变期;a.浮游有孔虫氧同位素记录,据Fan et al.(2013);b.海水表层温度(SST),据Fan et al.(2013);c~e.热带高山雨林花粉含量、红树林花粉含量和蕨类孢子含量;f.蕨类孢子浓度;g.中国石笋δ18O记录,据Wang et al.(2005);h.婆罗洲石笋δ18O记录,据Partin et al.(2007);i.印度尼西亚石笋δ18O记录,据Griffiths et al.(2009)
Fig. 6. Comparison of marine pollen and palaeoceanographic records from core MD98-2178 with stalagmite records
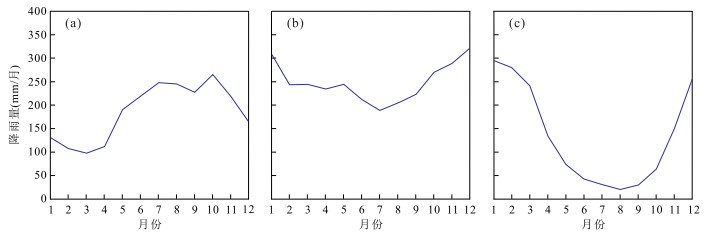
图 7 菲律宾南部棉兰老岛(a)、婆罗洲(b)以及印度尼西亚Flores岛的月平均降雨量变化(c)
降雨量资料来源于全球降水气候中心(Global Precipitation Climatology Centre,GPCC,http://gpcc.dwd.de);据Tierney et al.(2012)资料
Fig. 7. Observed monthly cycles of precipitation for the Mindanao in the southern Philippines (a), Borneo (b), and Flores in Indonesia (c)
-
Anhuf, D., Ledru, M.P., Behling, H., et al., 2006. Paleo-Environmental Change in Amazonian and African Rainforest during the LGM. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 239(3-4): 510-527. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.01.017 Anshari, G., Kershaw, A.P., van der Kaars, S., 2001. A Late Pleistocene and Holocene Pollen and Charcoal Record from Peat Swamp Forest, Lake Sentarum Wildlife Reserve, West Kalimantan, Indonesia. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 171(3-4): 213-228. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00246-2 Anshari, G., Kershaw, A.P., van der Kaars, S., et al., 2004. Environmental Change and Peatland Forest Dynamics in the Lake Sentarum Area, West Kalimantan, Indonesia. Journal of Quaternary Science, 19(7): 637-655. doi: 10.1002/jqs.879 Bian, Y.P., Jian, Z.M., Weng, C.Y., et al., 2011. A Palynological and Palaeoclimatological Record from the Southern Philippines since the Last Glacial Maximum. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56(22): 2359-2365. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4573-1 Bian, Y.P., Li, J.B., Jian, Z.M., et al., 2012. The Different Response of Marine Pollen Records to the Sea Level Change in the Low Latitude West Pacific since the Last Glacial Period. Quaternary Sciences, 32(6): 1078-1086 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201206005.htm Bird, M.I., Hope, G., Taylor, D., 2004. Polulating PEP Ⅱ: The Dispersal of Humans and Agriculture through Austral-Asia and Oceania. Quaternary International, 118-119: 145-163. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(03)00135-6 Bush, M., Flenley, J.R., Gosling, W., 2011. Tropical Rainforest Responses to Climatic Change. Praxis Publishing, Chichester. Chu, Z.H., 2011. Late Quaternary Responses of Upper Ocean Water to the Global Climate Changes in the Sulawesi Sea (Dissertation). Tongji University, Shanghai (in Chinese with English abstract). Dam, R.A.C., Fluin, J., Suparan, P., et al., 2001. Palaeoenvironmental Developments in the Lake Tondano Area (N. Sulawesi, Indonesia) since 33 000 B.P. . Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 171(3-4): 147-183. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00244-9 Fan, W.J., Jian, Z.M., Bassinot, F., et al., 2013. Holocene Centennial-Scale Changes of the Indonesian and South China Sea Throughflows: Evidences from the Makassar Strait. Global and Planetary Change, 111: 111-117. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2013.08.017 Grindrod, J., Moss, P., van der Kaars, S., 2002. Mangrove Palynology in Continental Shelf and Deep Sea Cores of the North Australian-Indonesian Region. In: Kershaw, P., David, B., Tapper, N., et al., eds., Bridging Wallace's Line: The Environmental and Cultural History and Dynamics of the SE-Asian-Australian Region. Catena-Verlag, Reiskirchen. Griffiths, M.L., Drysdale, R.N., Gagan, M.K., et al., 2009. Increasing Australian-Indonesian Monsoon Rainfall Linked to Early Holocene Sea-Level Rise. Nature Geoscience, 2(9): 636-639. doi: 10.1038/ngeo605 Gordon,A.L.,Huber,B.A.,Metzger,E.J.,et al.,2012.South China Sea Throughflow Impact on the Indonesian Throughflow.Geophysical Research Letters,39:L11602.doi: 10.1029/2012GL052021.doi:10.1029/2012GL052021,2012 Hill, R.D., 1979. South-East Asia: A Systematic Geography. Oxford University Press, Oxford. Hope, G., 2001. Environmental Change in the Late Pleistocene and Later Holocene at Wanda Site, Soroako, South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 171(3-4): 129-145. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00243-7 Hope, G., Kershaw, A.P., van der Kaars, S., et al., 2004. History of Vegetation and Habitat Change in the Austral-Asian Region. Quaternary International, 118-119: 103-126. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(03)00133-2 Kershaw, A.P., van der Kaars, S., Flenley, J.R., 2007. The Quaternary History of Far Eastern Rainforests. In: Bush, M.B., Flenley, J.R., eds., Tropical Rainforest Responses to Climatic Change. Praxis Publishing, Chichester, 77-115. Leduc, G., Vidal, L., Tachikawa, K., et al., 2007. Moisture Transport across Central America as a Positive Feedback on Abrupt Climatic Changes. Nature, 445(7130): 908-910. doi: 10.1038/nature05578 Lee, C.Y., Liew, P.M., 2010. Late Quaternary Vegetation and Climate Changes Inferred from a Pollen Record of Dongyuan Lake in Southern Taiwan. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 287(1-4): 58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.01.015 Li, X., Sun, X.J., 1999. Palynological Records since Last Glacial Maximum from a Deep Sea Core in Southern South China Sea. Quaternary Sciences, (6): 526-535(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1571012 Liu, Z., Harrison, S.P., Kutzbach, J., et al., 2004. Global Monsoons in the Mid-Holocene and Oceanic Feedback. Climate Dynamics, 22(2-3): 157-182. doi: 10.1007/s00382-003-0372-y MacKinnon, K., Hatta, G., Halim, H., et al., 1997. The Ecology of Kalimantan, Indonesia Borneo. Oxford University Press, Oxford. Maxwell, A.L., Liu, K.B., 2002. Late Quaternary Pollen and Associated Records from the Monsoonal Areas of Continental South and SE Asia. In: Kershaw, P., David, B., Tapper, N., et al., eds., Bridging Wallace's Line: The Environmental and Cultural History and Dynamics of the SE-Asian-Australian Region. Catena-Verlag, Reiskirchen. Mayewski, P.A., Rohling, E.E., Stager, J.C., et al., 2004. Holocene Climate Variability. Quaternary Research, 62(3): 243-255. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2004.07.001 Morley, R.J., 2002. Tertiary Vegetation History of Southeast Asia, with Emphasis on the Biogeographical Relationships with Australia. In: Kershaw, P., David, B., Tapper, N., et al., eds., Bridging Wallace's Line: The Environmental and Cultural History and Dynamics of the SE-Asian-Australian Region. Catena Verlag, Reiskirchen. Partin, J.W., Cobb, K.M., Adkins, J.F., et al., 2007. Millennial-Scale Trends in West Pacific Warm Pool Hydrology since the Last Glacial Maximum. Nature, 449(7161): 452-456. doi: 10.1038/nature06164 Steinke, S., Mohtadi, M., Prange, M., et al., 2014. Mid- to Late-Holocene Australian-Indonesian Summer Monsoon Variability. Quaternary Science Reviews, 93: 142-154. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.04.006 Stott, L., Cannariato, K., Thunell, R., et al., 2004. Decline of Surface Temperature and Salinity in the Western Tropical Pacific Ocean in the Holocene Epoch. Nature, 431(7004): 56-59. doi: 10.1038/nature02903 Stott, L., Poulsen, C., Lund, S., et al., 2002. Super ENSO and Global Climate Oscillations at Millennial Time Scales. Science, 297(5579): 222-226. doi: 10.1126/science.1071627 Sun, X.J., Luo, Y.L., Huang, F., et al., 2003. Deep-Sea Pollen from the South China Sea: Pleistocene Indicators of East Asian Monsoon. Marine Geology, 201(1-3): 97-118. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00211-1 Thevenon, F., Williamson, D., Bard, E., et al., 2010. Combining Charcoal and Elemental Black Carbon Analysis in Sedimentary Archives: Implications for Past Fire Regimes, the Pyrogenic Carbon Cycle, and the Human-Climate Interactions. Global and Planetary Change, 72(4): 381-389. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2010.01.014 Tierney,J.E.,Oppo,D.W.,LeGrande,A.N.,et al.,2012.The Influence of Indian Ocean Atmospheric Circulation on Warm Pool Hydroclimate during the Holocene Epoch.Journal of Geophysical Research,117(D19):D19108.doi: 10.1029/2012JD018060.doi:10.1029/2012JD018060 van der Kaars, S., De Deckker, P., 2003. Pollen Distribution in Marine Surface Sediments Offshore Western Australia. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 124(1-2): 113-129. doi: 10.1016/s0034-6667(02)00250-6 van der Kaars, S., Wang, X., Kershaw, P., et al., 2000. A Late Quaternary Palaeoecological Record from the Banda Sea, Indonesia: Patterns of Vegetation, Climate and Biomass Burning in Indonesia and Northern Australia. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 155(1-2): 135-143, 147-153. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(99)00098-X Wang, P.X., Li, Q.Y., 2009. The South China Sea, Paleoceanography and Sedimentology. Springer, Dordrecht. Wang, S.Y., Lü, H.Y., Liu, J.Q., 2007. The Early Holocene Optimum Inferred from a High-Resolution Pollen Record of Huguanyan Maar Lake in Southern China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(20): 2829-2836. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0419-2 Wang, Y.J., Cheng, H., Edwards, R.L., et al., 2005. The Holocene Asian Monsoon: Links to Solar Changes and North Atlantic Climate. Science, 308(5723): 854-857. doi: 10.1126/science.1106296 Whitmore, T.C., 1984. Tropical Rain Forests of the Far East. Clarendon Press, Oxford, 121-163. Xu, D.K., Lu, H.Y., Wu, N.Q., et al., 2010.30 000-Year Vegetation and Climate Change around the East China Sea Shelf Inferred from a High-Resolution Pollen Record. Quaternary International, 227(1): 53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2010.04.015 Yan, C.C., 1984. Types and Distribution Patterns of Vegetation in Southeastern Asia. Chinese Journal of Ecology, (5): 28-32(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-STXZ198405006.htm Zhou, W.J., Yu, X.F., Jull, A.J.T., et al., 2004. High-Resolution Evidence from Southern China of an Early Holocene Optimum and a Mid-Holocene Dry Event during the Past 18 000 Years. Quaternary Research, 62(1): 39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2004.05.004 边叶萍, 李家彪, 翦知湣, 等, 2012. 低纬西太平洋末次冰期以来海洋孢粉记录对海平面变化的不同响应. 第四纪研究, 32(6): 1078-1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.06.03 褚智慧, 2011. 苏拉威西海晚第四纪上层海水对全球气候变化的响应(硕士学位论文). 上海: 同济大学. 李逊, 孙湘君, 1999. 南海南部末次冰期以来的孢粉记录及其气候意义. 第四纪研究, 6: 526-535. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.06.005 严崇潮, 1984. 东南亚的植被类型和分布规律. 生态学杂志, (5): 28-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ198405006.htm -









 下载:
下载: