Magnetic Properties of Middle-Late Permian Carbonates in South China and Their Environmental Significances
-
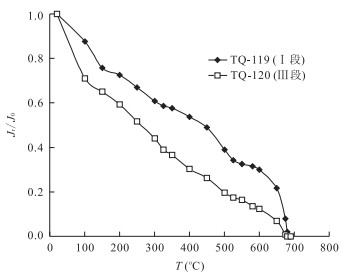
摘要: 磁学参数作为可靠的古气候和古环境指标, 能为全球环境变化、气候过程研究提供有价值的资料.对广西来宾铁桥剖面瓜德鲁普-乐平统界线地层进行详细岩石磁学研究, 结果表明, 铁桥剖面样品中主要磁性矿物是顺磁性矿物以及少量磁铁矿、赤铁矿.在瓜德鲁普-乐平统界线附近, 岩石磁学特征发生显著变化, 磁化率先增大再减小, 携磁矿物成分呈硬磁性矿物(赤铁矿)→软磁性矿物(磁铁矿)→硬磁性矿物(赤铁矿)的变化趋势, 这些转变仅在界线上下大约4m的岩层内完成, 与中二叠世晚期的海平面变化、古海水温度变化同步.中-晚二叠世之交碳酸盐岩磁学参数的变化显著, 反映磁性矿物在各圈层之间的运移和转换发生了转变, 这一转变起因于当时的气候环境变化.瓜德鲁普世晚期和乐平世早期, 海平面较高, 来宾地区物源少, 铁桥剖面的携磁矿物主要来自粉尘赤铁矿; 中-晚二叠世之交短暂的大规模海退作用使华南古陆面积大幅度增加, 同时陆生植物大规模灭绝, 地表侵蚀加剧, 来宾地区物源增多, 此时, 铁桥剖面的携磁矿物主要来源于河流输入的磁铁矿.Abstract: As a reliable proxy for paleoclimate and paleoenvironment, magnetic parameter could provide valuable data for the research of global environmental changes and climatic processes. A detailed study has been carried out on rock magnetism in order to reveal the change of climate and environment and its reasons across Guadalupian-Lopingian (G-L) boundary at Tieqiao section in Laibin area, Guangxi, China. The results show that the dominant magnetic minerals from Tieqiao section are paramagnetic minerals with a small amount of magnetite and hematite as well. There is a remarkable change in the properties of rock magnetism near the G-L boundary. Magnetic susceptibility increases first and then decreases. Magnetic carriers show the trend of being transformed from hard magnetic minerals (hematite) to soft magnetic mineral (magnetite) and then turning to hard magnetic minerals (hematite). All of these changes occur within 4m-thick strata interval above and below the G-L boundary, and synchronize with the fluctuation of sea-level and ancient seawater temperature during late Middle Permian. The significant changes in magnetic parameters for Middle-Late Permian carbonates suggest that the migration and conversion of magnetic minerals between different spheres in earth system has shifted, which resulted from the climatic and environmental changes. High sea-level during Late Guadalupian and Early Lopingian resulted in the decrease in terrigenous supply in South China. Therefore, the magnetic carriers in Tieqiao section mainly are hematite through aeolian transportation during this period. However, pronounced regression during the Middle-Late Permian transition led to the expansion of exposed land area. Meanwhile, land plants experienced widespread extinction, which led to increased sediment source. The magnetic carriers in contemporaneous sediments of Tieqiao section are mainly fluvial magnetite.
-
Key words:
- South China /
- Tieqiao section /
- Guadalupian-Lopingian /
- rock magnetism /
- regression /
- sediment /
- paleoenvironment
-
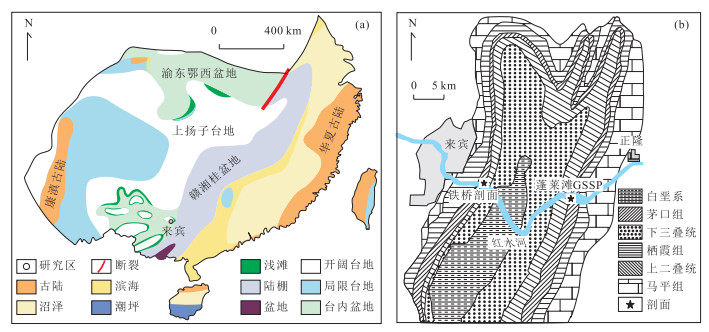
图 1 研究区中二叠世晚期古地理(a)及剖面位置(b)
图a据郑和荣和胡宗全(2010)修改;图b据Jin et al.(1998)修改
Fig. 1. Paleogeography (a) of late Middle Permian in South China and locations of sections in this study area (b)
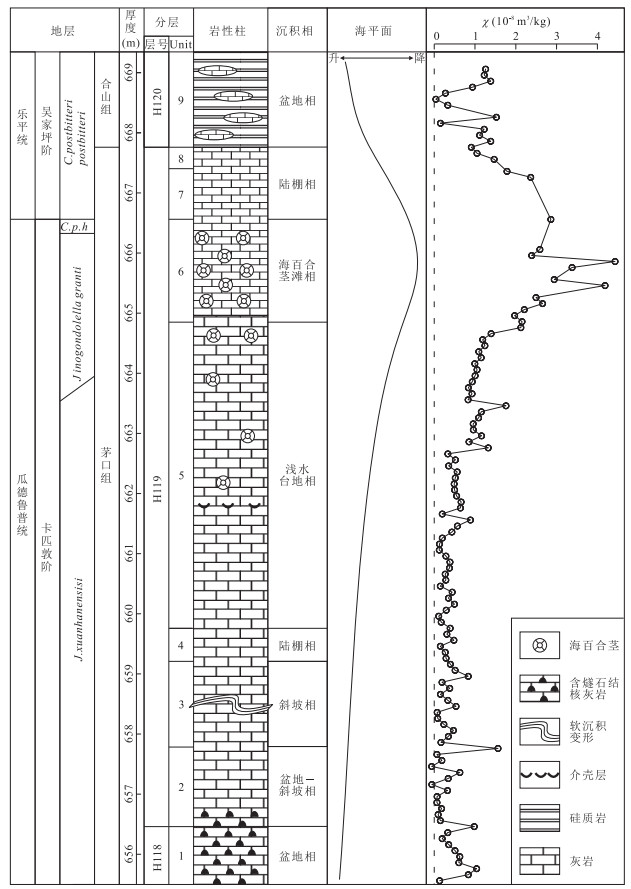
图 2 广西来宾铁桥剖面瓜德鲁普-乐平统界线地层柱状图
牙形石带与分层据Jin et al.(2001, 2006);C.p.h代表Clarkina postbitteri hongshuiensis
Fig. 2. Stratigraphic column across the Guadalupian-Lopingian boundary at Tieqiao section in Laibin, Guangxi, South China
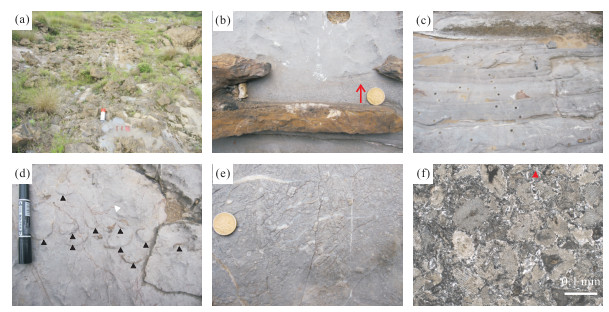
图 3 广西来宾铁桥剖面瓜德鲁普-乐平统界线地层野外及镜下特征
a.H118层,硅质岩夹灰岩透镜体;b.H119层(来宾灰岩)Unit 2的野外特征,红色箭头指示正粒序;c.来宾灰岩Unit 3中发育重力滑塌形成的软沉积变形构造;d.来宾灰岩Unit 5中发育介壳层和缝合线,黑色箭头指示腕足介壳,白色箭头指示缝合线;e.来宾灰岩Unit 6野外特征,层面见大小混杂的海百合茎板;f.来宾灰岩Unit 6显微镜下特征,生物碎屑90%以上为海百合茎碎片,少量介形虫(红色箭头所指),海百合茎分选差,指示原地埋藏,单偏光×25倍
Fig. 3. Field pictures of sedimentological features and microphotographs of carbonate fabrics of the Guadalupian-Lopingian boundary strata at Tieqiao section in Laibin, Guangxi, South China
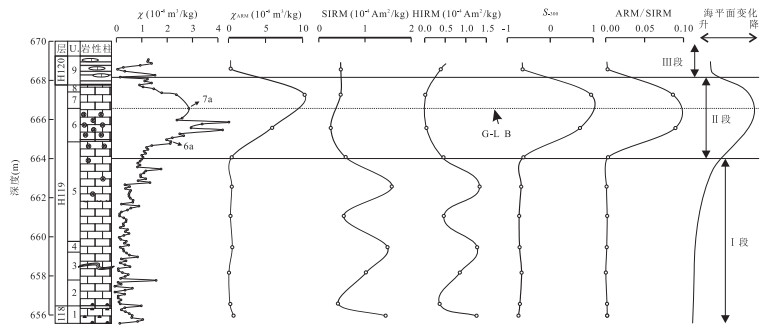
图 4 广西来宾铁桥剖面瓜德鲁普-乐平统界线地层磁学特征及海平面变化
U.代表Unit;岩性图例同图 2
Fig. 4. Magnetic characteristics and sea-level changes across the Guadalupian-Lopingian boundary at Tieqiao section in Laibin, Guangxi, South China
-
Ali, J.R., Thompson, G.M., Song, X.Y., et al., 2002. Emeishan Basalts (SW China) and the 'End-Guadalupian' Crisis: Magnetobiostratigraphic Constraints. Journal of the Geological Society, 159(1): 21-29. doi: 10.1144/0016-764901086 Bond, D.P.G., Hilton, J., Wignall, P.B., et al., 2010a. The Middle Permian (Capitanian) Mass Extinction on Land and in the Oceans. Earth-Science Reviews, 102(1-2): 100-116. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.07.004 Bond, D.P.G., Wignall, P.B., Wang, W., et al., 2010b. The Mid-Capitanian (Middle Permian) Mass Extinction and Carbon Isotope Record of South China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 292(1-2): 282-294. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.03.056 Borradaile, G.J., 1988. Magnetic Susceptibility, Petrofabrics and Strain. Tectonophysics, 156(1-2): 1-20. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(88)90279-X Chen, B., Joachimski, M.M., Sun, Y.D., et al., 2011. Carbon and Conodont Apatite Oxygen Isotope Records of Guadalupian-Lopingian Boundary Sections: Climatic or Sea-Level Signal? Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 311(3-4): 145-153. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2011.08.016 Chen, J.Y. Feng, Q.L., 2011. Rock-Magnetic Characteristics of the Permo-Triassic Boundary Section of Dongpan, Southwestern Guangxi, South China: Implications for Paleoclimate. Progress in Geophysics, 26(2): 529-539 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2011.02.018 Chen, X., Zhang, W.G., Yu, L.Z., 2009. The Dependence of Magnetic Parameters on the Mixing Proportion of Hematite and Magnetite. Progress in Geophysics, 24(1): 82-88 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200901008.htm Chen, Z.Q., George, A.D., Yang, W.R., 2009. Effects of Middle-Late Permian Sea-Level Changes and Mass Extinction on the Formation of the Tieqiao Skeletal Mound in the Laibin Area, South China. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 56(6): 745-763. doi: 10.1080/08120090903002581 Crick, R.E., Ellwood, B.B., El Hassani, A., et al., 1997. Magnetosusceptibility Event and Cyclostratigraphy (MSEC) of the Eifelian-Givetian GSSP and Associated Boundary Sequences in North Africa and Europe. Episodes, 20(3): 167-175. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/1997/v20i3/004 Deng, C.L., Yuan, B.Y., Hu, S.Y., et al., 2000. Environmental Magnetism: A Review. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 20(2): 93-101 (in Chinese with English abstract). Dunlop, D.J., Özdemir, Ö., 1997. Rock Magnetism: Fundamentals and Frontiers. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. Ellwood, B.B., Brett, C.E., MacDonald, W.D., 2007. Magnetostratigraphy Susceptibility of the Upper Ordovician Kope Formation, Northern Kentucky. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 243(1-2): 42-54. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.07.003 Ellwood, B.B., Crick, R.E., El Hassani, A., et al., 2000. Magnetosusceptibility Event and Cyclostratigraphy Method Applied to Marine Rocks: Detrital Input versus Carbonate Productivity. Geology, 28(12): 1135-1138. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<1135:MEACMA>2.0.CO;2 Evans, M.E., Heller, F., 2003. Environmental Magnetism: Principles and Applications of Enviromagnetics. Academic Press, London. Fu, C.F., Song Y.G., Qiang X.K., et al., 2009. Environmental Magnetism and Its Application Progress in Paleoclimatic and Paleoenvironmental Changes. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 31(3): 312-322 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX200903017.htm He, B., Xu, Y.G., Huang, X.L., et al., 2007. Age and Duration of the Emeishan Flood Volcanism, SW China: Geochemistry and SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Dating of Silicic Ignimbrites, Post-Volcanic Xuanwei Formation and Clay Tuff at the Chaotian Section. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 255(3-4): 306-323. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.12.021 He, B., Xu, Y.G., Wang, Y.M., et al., 2005. Nature of Dongwu Movement and Its Temporal and Spatial Evolution. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 30(1): 89-96 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_dqkx200501012.aspx Hrouda, F., 1994. A Technique for the Measurement of Thermal Changes of Magnetic Susceptibility of Weakly Magnetic Rocks by the CS-2 Apparatus and KLY-2 Kappabridge. Geophysical Journal International, 118(3): 604-612. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1994.tb03987.x Itambi, A.C., von Dobeneck, T., Mulitza, S., et al., 2009. Millennial-Scale Northwest African Droughts Related to Heinrich Events and Dansgaard-Oeschger Cycles: Evidence in Marine Sediments from Offshore Senegal. Paleoceanography, 24: PA1205. doi: 10.1029/2007PA001570 Jin, Y.G., Henderson, C.M., Wardlaw, B.R., et al., 2001. Proposal for the Global Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) for the Guadalupian-Lopingian Boundary. Permophiles, 39: 32-42. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285222479_Proposal_for_the_Global_Stratotype_Section_and_Point_GSSP_for_the_Guadalupian-Lopingian_boundary Jin, Y.G., Mei, S.L., Wang, W., et al., 1998. On the Lopingian Series of the Permian System. Palaeoworld, 9: 1-18. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285492190_On_the_Lopingian_Series_of_the_Permian_System Jin, Y., Shen, S.Z., Henderson, C.M., et al., 2006. The Global Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) for the Boundary between the Capitanian and Wuchiapingian Stage (Permian). Episodes, 29(4): 253-262. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/2006/v29i4/003 Kasuya, A., Isozaki, Y., Igo, H., 2012. Constraining Paleo-Latitude of a Biogeographic Boundary in Mid-Panthalassa: Fusuline Province Shift on the Late Guadalupian (Permian) Migrating Seamount. Gondwana Research, 21(2-3): 611-623. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.06.001 Liu, Q.S., Deng, C.L., 2009. Magnetic Susceptibility and Its Environmental Significances. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(4): 1041-1048 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.04.021 Liu, Q.S., Deng, C.L., Yu, Y., et al., 2005. Temperature Dependence of Magnetic Susceptibility in an Argon Environment: Implications for Pedogenesis of Chinese Loess/Palaeosols. Geophysical Journal International, 161(1): 102-112. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02564.x Maher, B.A., 1988. Magnetic Properties of Some Synthetic Sub-Micron Magnetites. Geophysical Journal, 94(1): 83-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1988.tb03429.x Maher, B.A., 2011. The Magnetic Properties of Quaternary Aeolian Dusts and Sediments, and Their Palaeoclimatic Significance. Aeolian Research, 3(2): 87-144. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2011.01.005 Mei, S.L., Jin, Y.G., Wardlaw, B.R., 1998. Conodont Succession of the Guadalupian-Lopingian Boundary Strata in Laibin of Guangxi, China and West Texas, USA. Palaeoworld, 9: 53-57. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284054146_Conodont_succession_of_the_Guadalupian-Lopingian_boundary_strata_in_Laibin_of_Guangxi_China_and_West_Texas_USA Meng, Q.Y., Li, A.C., 2008. Brief Reviews on Environment Magnetism in Marine Sediment. Marine Environmental Science, 27(1): 86-90(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HYHJ200801023.htm Oldfield, F., 1991. Environmental Magnetism—A Personal Perspective. Quaternary Science Reviews, 10(1): 73-85. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(91)90031-O Peck, J.A., King, J.W., Colman, S.M., et al., 1994. A Rock-Magnetic Record from Lake Baikal, Siberia: Evidence for Late Quaternary Climate Change. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 122(1-2): 221-238. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90062-0 Qiao, Q.Q., Zhang, C.X., Li. J., et al., 2011. Magnetic Properties and Indicator of Concentration of Pollution of Atmospheric Dust in Chaoyang, Beijing. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(1): 151-162 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.01.016 Qiu, Z., Wang, Q.C., 2010. Middle and Upper Permian Sedimentary Microfacies in the Tieqiao Section in Laibin, Guangxi, China. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 28(5): 1020-1036 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference_7450373.aspx Qiu, Z., Wang, Q.C., Zou, C.N., et al., 2014. Transgressive-Regressive Sequences on the Slope of an Isolated Carbonate Platform (Middle-Late Permian, Laibin, South China). Facies, 60(1): 327-345. doi: 10.1007/s10347-012-0359-4 Racki, G., Racka, M., Matyja, H., et al., 2002. The Frasnian/Famennian Boundary Interval in the South Polish-Moravian Shelf Basins: Integrated Event-Stratigraphical Approach. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 181(1-3): 251-297. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00481-3 Sha, Q.A., Wu, W.S., Fu J.M., 1990. An Integrated Investigation on the Permian System of Qian-Gui Areas, with Discussion on the Hydrocarbon Potential. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Shen, S.Z., Wang, Y., Henderson, C.M., et al., 2007. Biostratigraphy and Lithofacies of the Permian System in the Laibin-Heshan Area of Guangxi, South China. Palaeoworld, 16(1-3): 120-139. doi: 10.1016/j.palwor.2007.05.005 Sun, Y.D., Lai, X.L., Jiang, H.S., et al., 2008. Guadalupian (Middle Permian) Conodont Faunas at Shangsi Section, Northeast Sichuan Province. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 19(5): 451-460. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0705(08)60050-3 Sun, Y.D., Lai, X.L., Wignall, P.B., et al., 2010. Dating the Onset and Nature of the Middle Permian Emeishan Large Igneous Province Eruptions in SW China Using Conodont Biostratigraphy and Its Bearing on Mantle Plume Uplift Models. Lithos, 119(1-2): 20-33. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.05.012 Thompson, R., Oldfield, F., 1986. Environmental Magnetism. Allen & Unwin, London. Wang, H.P., Kent, D.V., Jackson, M.J., 2013. Evidence for Abundant Isolated Magnetic Nanoparticles at the Paleocene-Eocene Boundary. PNAS, 110(2): 425-430. doi: 10.7916/D84M92HF Wang, W., Cao, C.Q., Wang, Y., 2004. The Carbon Isotope Excursion on GSSP Candidate Section of Lopingian-Guadalupian Boundary. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 220(1-2): 57-67. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00033-0 Wang, Y., Jin, Y.G., 2000. Permian Palaeogeographic Evolution of the Jiangnan Basin, South China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 160(1-2): 35-44. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(00)00043-2 Wignall, P.B., 2001. Large Igneous Provinces and Mass Extinctions. Earth-Science Reviews, 53(1-2): 1-33. doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(00)00037-4 Wignall, P.B., Bond, D.P.G., Haas, J., et al., 2012. Capitanian (Middle Permian) Mass Extinction and Recovery in Western Tethys: A Fossil, Facies, and δ13C Study from Hungary and Hydra Island (Greece). Palaios, 27(2): 78-89. doi: 10.2110/palo.2011.p11-058r Wignall, P.B., Sun, Y., Bond, D.P.G., et al., 2009a. Volcanism, Mass Extinction, and Carbon Isotope Fluctuations in the Middle Permian of China. Science, 324(5931): 1179-1182. doi: 10.1126/science.1171956 Wignall, P.B., Védrine, S., Bond, D.P.G., et al., 2009b. Facies Analysis and Sea-Level Change at the Guadalupian-Lopingian Global Stratotype (Laibin, South China), and Its Bearing on the End-Guadalupian Mass Extinction. Journal of the Geological Society, 166(4): 655-666. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492008-118 Yamazaki, T., 2009. Environmental Magnetism of Pleistocene Sediments in the North Pacific and Ontong-Java Plaeau: Temporal Variations of Detrital and Biogenic Components. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 10(7): Q07Z04. doi: 10.1029/2009GC002413 Yao, Y., Yan, J.X., Li, A.Z., 2012. Sedimentary Features and Evolution of Mid-Permian Carbonates from Laibin of Guangxi. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 37(Suppl. 2): 184-194 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2012.S2.019 Zhang, S.H., Wang, X.L., Zhu, H., 1999. Magnetic Susceptibility Variations of Carbonates Controlled by Sea-Level Changes—Example in Devonian to Carboniferous Strata in Southern Guizhou Province, China. Science China (Ser. D), 29(6): 558-566 (in Chinese). Zheng, H.R., Hu, Z.Q., 2010. Chinese Pre-Mesozoic Tectonic: Atlas of Lithofacies and Paleogeography. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Zheng, Y., Zhang, S.H., 2007. Magnetic Properties of Street Dust and Topsoil in Beijing and Its Environmental Implications. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(20): 2399-2406 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2007-52-20-2399 Zhou, M.F., Malpas, J., Song, X.Y., et al., 2002. A Temporal Link between the Emeishan Large Igneous Province (SW China) and the End-Guadalupian Mass Extinction. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 196(3-4): 113-122. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00608-2 Ziegler, A.M., Hulver, M.L., Rowley, D.B., 1997. Permian World Topography and Climate. In: Martini, I.P., ed., Late Glacial and Postglacial Environmental Changes—Quaternary, Carboniferous-Permian, and Proterozoic. Oxford University Press, New York, 111-146. 陈建业, 冯庆来, 2011. 广西东攀二叠-三叠系界线剖面磁学特征及古气候意义. 地球物理学进展, 26(2): 529-539. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2011.02.018 陈曦, 张卫国, 俞立中, 2009. 赤铁矿与磁铁矿混合比例对磁性参数的影响. 地球物理学进展, 24(1): 82-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200901008.htm 邓成龙, 袁宝印, 胡守云, 等, 2000. 环境磁学某些研究进展评述. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 20(2): 93-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200002018.htm 符超峰, 宋友桂, 强小科, 等, 2009. 环境磁学在古气候环境研究中的回顾与展望. 地球科学与环境学报, 31(3): 312-322. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2009.03.017 何斌, 徐义刚, 王雅玫, 等, 2005. 东吴运动性质的厘定及其时空演变规律. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 30(1): 89-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200501012.htm 刘青松, 邓成龙, 2009. 磁化率及其环境意义. 地球物理学报, 52(4): 1041-1048. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.04.021 孟庆勇, 李安春, 2008. 海洋沉积物的环境磁学研究简述. 海洋环境科学, 27(1): 86-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2008.01.023 乔庆庆, 张春霞, 李静, 等, 2011. 北京市朝阳区大气降尘磁学特征及对空气污染物浓度的指示. 地球物理学报, 54(1): 151-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.01.016 邱振, 王清晨, 2010. 广西来宾铁桥剖面中上二叠统沉积微相. 沉积学报, 28(5): 1020-1036. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201005021.htm 沙庆安, 吴望始, 傅家谟, 1990. 黔桂地区二叠系综合研究——兼论含油气性. 北京: 科学出版社. 姚尧, 颜佳新, 李傲竹, 2012. 广西来宾中二叠世碳酸盐岩沉积特征与孤立台地演化. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 37(S2): 184-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX2012S2025.htm 张世红, 王训练, 朱鸿, 1999. 碳酸盐岩磁化率与相对海平面变化的关系—黔南泥盆石炭系例析. 中国科学(D辑), 29(6): 558-566. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199906010.htm 郑和荣, 胡宗全, 2010. 中国前中生代构造-岩相古地理图集. 北京: 地质出版社. 郑妍, 张世红, 2007. 北京市区尘土与表土的磁学性质及其环境意义. 科学通报, 52(20): 2399-2406. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074x.2007.20.011 -









 下载:
下载: