The Metal Element Information Extraction from Hyperion Data Based on the Vegetation Stress Spectra
-
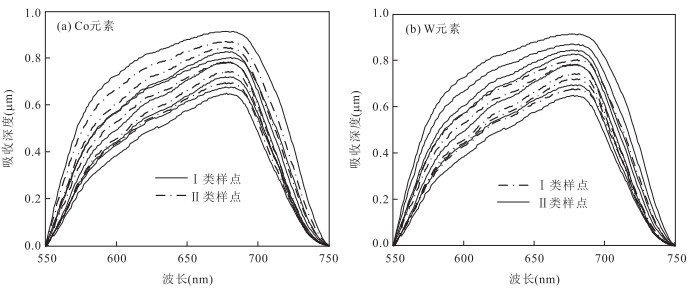
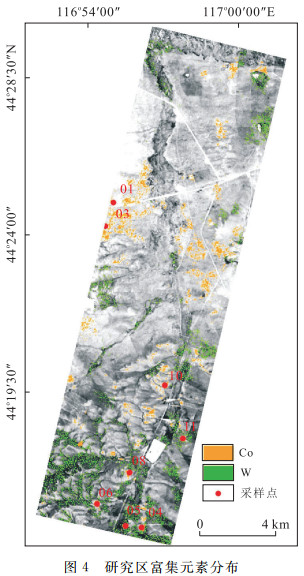
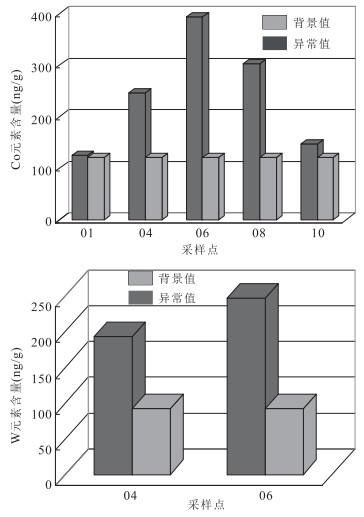
摘要: 含矿层中成矿元素的迁移富集可胁迫影响上覆植物光谱, 因此, 利用植物响应特征提取成矿元素富集信息可指示潜在的矿床位置.以内蒙古西乌旗草原覆盖区为例, 采集典型植物光谱并测试元素含量, 分析红边和吸收深度对不同成矿元素的敏感性, 并进行模型显著性参数检验, 建立了基于植物吸收深度的Co和W元素响应模型, 应用于示范区的Hyperion影像, 圈定了Co和W元素富集信息.结合野外实地采样验证, 富集点元素含量均高于背景值.该研究可为植被覆盖区的高光谱遥感地质调查提供新的思路.Abstract: The migration enrichment of metallogenic elements in the bearing bed can cause changes of the spectrum of overlying vegetation. Therefore, the metallogenic elements enrichment information which is extracted by using vegetation spectral response characteristics can be used to indicate the underlying mineral deposits. In this paper, Xi Ujimqin Qi grassland in Inner Mongolian was taken as an example. The spectra of the vegetation was collected and Nine metal elements in the vegetation were measured. The influence of red edge and absorption depth on the sensitivity of different metallogenic elements were analyzed. The significance of model parameters was verified and the element-response model based on absorption depth was established to detect W and Co elements, which was applied to hyperspectral data(Hyperion). Combined with the field work, the element contents of enriched samples are testified to be higher than the background values. This research shall provide new perspective for mineral investigation and prediction of hyperspectral remote sensing in vegetated area.
-
Key words:
- metallogenic elements /
- stress spectrum /
- red edge position /
- remote sensing /
- absorption depth
-
表 1 植被元素含量
Table 1. Elements content within vegetation
Au As Co Cu Hg Ni Pb W Zn NXV01-1 羊草 0.41 218.00 24.50 5 459.00 238.00 532.00 549.00 144.00 19 180.00 NXV01-2 糙隐子草 0.61 294.00 113.00 6 604.00 159.00 1 352.00 954.00 336.00 27 660.00 NXV01-3 大针茅 1.88 359.00 125.00 3 651.00 223.00 647.00 2 725.00 172.00 15 440.00 NXV03 大针茅 0.58 272.00 37.70 4 136.00 142.00 776.00 916.00 19.30 19 110.00 NXV04-1 大针茅 0.40 337.00 247.00 4 240.00 245.00 366.00 1 452.00 193.00 20 640.00 NXV05-1 大针茅 0.54 235.00 0.33 2 466.00 78.90 479.00 491.00 6.34 12 040.00 NXV05-2 糙隐子草 0.30 481.00 88.80 7 321.00 165.00 811.00 1 135.00 29.60 10 880.00 NXV06-2 糙隐子草 0.57 572.00 394.00 7 971.00 207.00 867.00 2 208.00 247.00 27 240.00 NXV08-1 大针茅 0.51 461.00 303.00 6 201.00 461.00 571.00 2 347.00 60.80 12 410.00 NXV08-2 羊草 0.67 249.00 33.80 4 069.00 536.00 170.00 346.00 22.50 15 690.00 NXV10-1 大针茅 0.69 469.00 148.00 4 129.00 281.00 551.00 2 883.00 86.50 9 603.00 NXV11-1 大针茅 0.38 430.00 236.00 7 885.00 215.00 1 010.00 1 282.00 24.10 24 250.00 均值 0.62 370.54 142.16 5 302.92 247.76 647.85 1 497.54 112.09 17 878.69 标准偏差 0.38 108.22 114.95 1 682.45 120.27 305.22 839.91 98.12 5 731.83 变异系数 61.90 29.20 80.90 31.70 48.50 47.10 56.10 87.50 32.10 注:植物含量单位:ng/g. 表 2 金属元素Co和W含量与光谱吸收深度拟合方程
Table 2. Regression equation between the absorption depths and the contents of Co and W
拟合方程 R2 R MCo=-2 543.752+1 200.211x1-14 161.749x2+12 005.275x3+ 3 038.511x4-89.022x5 0.996 0 0.997 9 MW=-972.878+1 908.580x1-11 395.301x2+8 814.099x3+1 886.741x4 0.949 9 0.974 6 注:x1、x2、x3、x4、x5、x6和x7分别表示(750-550)/(n-1)处的波段吸收深度值. -
Chen, S.B., Liu, Y.L., Yang, Q., et al., 2012a. Lithologic Classification from Hyperspectral Data in Dense Vegetation Cover Area. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 42(6): 1959-1965(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201206044.htm Chen, S.B., Zhou, C., Wang, J.N., 2012b. Vegetation Stress Spectra and Their Relation with the Contents of Metal Elements within the Plant Leaves in Metal Mines in Heilongjiang. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 32(5): 1310-1315(in Chinese with English abstract). Darvishzadeh, R., Skidmore, A., Schlerf, M., et al., 2008. LAI and Chlorophyll Estimation for a Heterogeneous Grassland Using Hyperspectral Measurements. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 63(4): 409-426. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2008.01.001 Gan, F.P., Liu, S.W., Zhou, Q., 2004. Identification of Mining Pollution Using Hyperion Data at Dexing Copper Mine Jiangxi Province, China. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 29(1): 119-126(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200401020.htm Gitelson, A.A., Merzlyak, M.N., Lichtenthaler, H.K., 1996. Detection of Red Edge Position and Chlorophyll Content by Reflectance Measurements Near 700 nm. Journal of Plant Physiology, 148(3-4): 501-508. doi: 10.1016/s0176-1617(96)80285-9 Gong, S.Q., Wang, X., Shen, R.P., et al., 2010. Study on Heavy Metal Element Content in the Coastal Saline Soil by Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 25(2): 169-177(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YGJS201002000.htm Houborg, R., Anderson, M., Daughtry, C., 2009. Utility of an Image-Based Canopy Reflectance Modeling Tool for Remote Estimation of LAI and Leaf Chlorophyll Content at the Field Scale. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(1): 259-274. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2008.09.014 Huang, Z., Turner, B.J., Dury, S.J., et al., 2004. Estimating Foliage Nitrogen Concentration from HYMAP Data Using Continuum Removal Analysis. Remote Sensing of Environment, 93(1-2): 18-29. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2004.06.008 Kruse, F.A., Boardman, J.W., Huntington, J.F., 2003. Comparison of Airborne Hyperspectral Data and EO-1 Hyperion for Mineral Mapping. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 41(6): 1388-1400. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2003.812908 Lin, F.F., Chen, Z.L., Wang, K., et al., 2009. Determination of Nitrogen in Rice Leaf Based on Ftir Spectra and siPLS-GA-PLS Algorithm. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 28(4): 277-280(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2009.00277 Rosso, P.H., Pushnik, J.C., Lay, M., et al., 2005. Reflectance Properties and Physiological Responses of Salicornia Virginica to Heavy Metal and Petroleum Contamination. Environmental Pollution, 137(2): 241-252. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.02.025 Sánchez-Azofeifa, G.A., Castro, K., Wright, S.J., et al., 2009. Differences in Leaf Traits, Leaf Internal Structure, and Spectral Reflectance between Two Communities of Lianas and Trees: Implications for Remote Sensing in Tropical Environments. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(10): 2076-2088. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2009.05.013 Xu, M.X., Wu, S.H., Zhou, S.L., et al., 2011. Hyperspectral Reflectance Models for Retrieving Heavy Metal Content: Application in the Archaeological Soil. J. Infrared Milli. Waves, 30(2): 109-114(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1598232 Zarco-Tejada, P.J., Miller, J.R., Morales, A., et al., 2004. Hyperspectral Indices and Model Simulation for Chlorophyll Estimation in Open-Canopy Tree Crops. Remote Sensing of Environment, 90(4): 463-476. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2004.01.017 Zhu, X.Y., Zhou, H., Yu, X.B., 2009. The Calculation Methods of Permeability Variation Coefficient-Taking Ningdong Oilflied in Mahuangshan West Block as An Example. Offshore Oil, 29(2): 23-27(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY200902006.htm Zhu, Y.Q., Qu Y.H., Liu S.H., et al., 2014. A Reflectance Spectra Model for Copper-Stressed Leaves: Advances in the PROSPECT Model through Addition of the Specific Absorption Coefficients of the Copper Ion. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35(4): 1356-1373. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2013.876123 陈圣波, 刘彦丽, 杨倩, 等, 2012a. 植被覆盖区卫星高光谱遥感岩性分类. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 42(6): 1959-1965. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201206044.htm 陈圣波, 周超, 王晋年, 2012b. 黑龙江多金属矿区植物胁迫光谱及其与金属元素含量关系研究. 光谱学与光谱分析, 32(5): 1310-1315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201205043.htm 甘甫平, 刘圣伟, 周强, 2004. 德兴铜矿矿山污染高光谱遥感直接识别研究. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 29(1): 119-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200401020.htm 龚绍琦, 王鑫, 沈润平, 等, 2010. 滨海盐土重金属含量高光谱遥感研究. 遥感技术与应用, 25(2): 169-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGJS201002000.htm 林芬芳, 陈祝炉, 王珂, 等, 2009. 基于傅里叶变换红外光谱和siPLS-GA-PLS的水稻叶片氮素含量预测研究. 红外与毫米波学报, 28(4): 277-280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYH200904008.htm 徐明星, 吴绍华, 周生路, 等, 2011. 重金属含量的高光谱建模反演: 考古土壤中的应用. 红外与毫米波学报, 30(2): 109-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYH201102004.htm 朱小影, 周红, 余训兵, 2009. 渗透率变异系数的几种计算方法——以麻黄山西区块宁东油田2, 3井区为例. 海洋石油, 29(2): 23-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY200902006.htm -









 下载:
下载: