GPS-Constrained Inversion of Slip Rate on Major Active Faults in the Northeastern Margin of Tibet Plateau
-
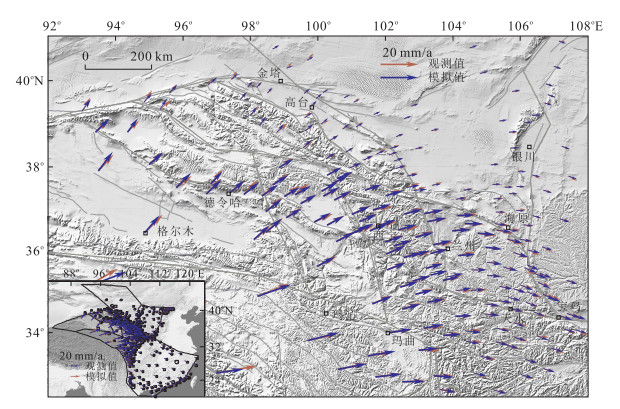
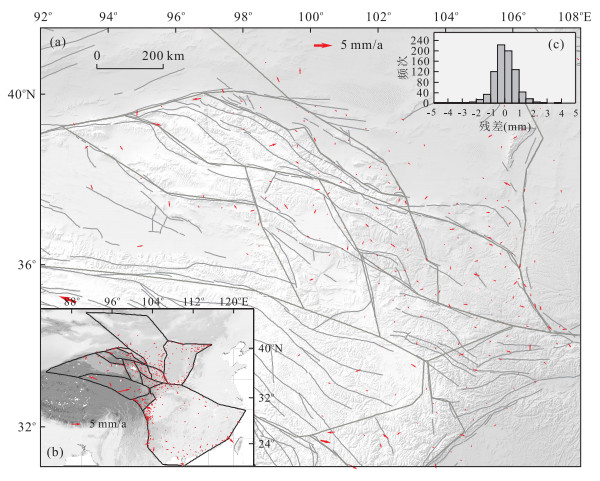
摘要: GPS测量可以提供高精度的时空图像, 但前任对比研究尚未深入.通过使用线性球面块体模型理论, 在前人针对活动块体研究的基础上, 建立青藏高原东北缘地区三维块体几何模型.以1999—2007年的GPS水平速度场数据作为约束, 反演得到青藏高原东北缘的主要活动断裂长期滑动速率和广义海原断裂带的空间亏损滑动分布及其耦合变化.上述结果为青藏高原东北缘现今运动变形的动力学和强震中-长期危险性预测研究提供了约束和参考.Abstract: GPS mwasurements can provide a high accuracy of spatio-temporal images, but there aren't enough study about it. We use the spherical linear block theory constrained by geodetic observations from Global Positioning System (GPS) stations to estimate fault slip rates on the Northeastern margin of Tibet plateau and spatially variable coupling on Haiyuan fault in abroad sense. The 3D geometric block model is based on the previous researches of active block. The result provides a new constraint and reference for the geodynamics of present crustal deformation and the middle-long term strong earthquake hazard study in this area.
-
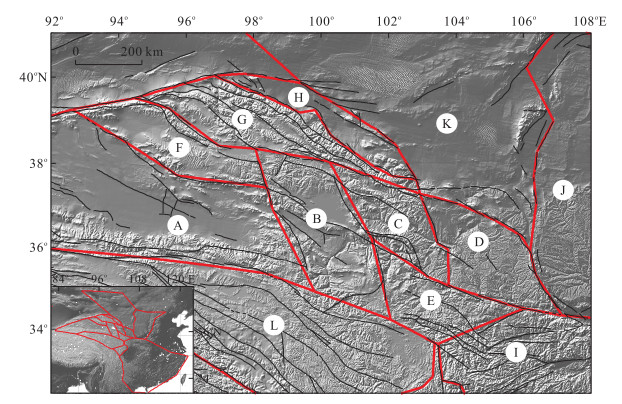
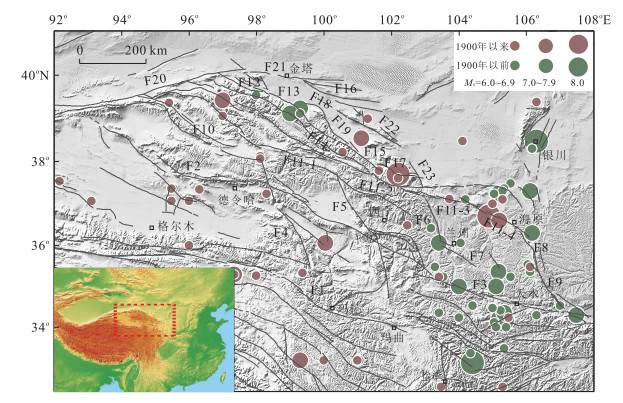
图 1 青藏高原东北缘主要活动断裂(黑线)分布
主要活动断裂据文献(袁道阳等,2004b),插图中红色虚线框表示研究区位置; F1.东昆仑断裂;F2.大柴旦-宗务隆山断裂;F3.西秦岭北缘断裂;F4.鄂拉山断裂;F5.日月山断裂;F6.庄浪河断裂;F7.马衔山断裂;F8.六盘山断裂;F9.陇县-宝鸡断裂;F10.党河-南山断裂;F11-1.海原断裂哈拉湖段;F11-2.海原断裂祁连段;F11-3.海原断裂毛毛山-老虎山段;F11-4.海原断裂海原段;F12.旱峡-大黄沟断裂;F13.佛洞庙-红崖子断裂;F14.肃南断裂;F15.民乐-永昌断裂;F16.合黎山南缘断裂;F17.昌马-俄博断裂;F18.榆木山北缘断裂;F19.榆木山东缘断裂;F20.阿尔金断裂;F21.金塔-花海断裂;F22.龙首山北缘断裂;F23.武威-天祝断裂
Fig. 1. Main active faults (black lines) in the northeastern margin of Tibet plateau
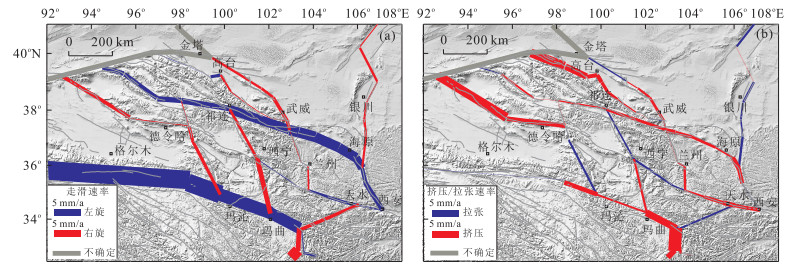
表 1 模拟主要断裂的滑动速率
Table 1. Predicted fault slip rates on major faults
断裂 分段 走滑速率①(mm/a) 挤压/拉张速率②(mm/a) 东昆仑断裂 北西西段 14.8±2.5 0.3±3.7 索托湖段 14.4±1.8 -3.6±5.2 玛沁段 10.2±2.6 -1.4±2.3 玛曲段 9.4±2.0 -5.5±2.6 祁连北缘断裂 旱峡-大黄沟 0.5±1.1 -7.0±3.8 佛洞沟-红崖子 0.2±1.2 -5.1±2.5 民乐-永昌 -0.6±1.3 -1.1±2.4 榆木山北缘断裂 2.6±1.3 -3.1±1.9 榆木山东缘断裂 -1.6±1.6 -3.2±1.5 昌马-俄博断裂 -0.5±1.2 0.7±3.6 党河-南山断裂 西段 3.6±2.7 1.0±3.9 中段 3.6±3.2 -1.4±2.6 东段 4.2±1.9 -0.2±3.8 海原断裂 哈拉湖段 4.5±2.4 -1.1±1.7 祁连段 7.5±1.4 -2.3±3.0 毛毛山-老虎山段 8.4±1.1 -2.6±1.3 海原段 7.8±0.9 -1.2±1.1 六盘山断裂 3.2±1.2 -3.2±0.8 陇县-宝鸡断裂 3.9±1.2 0.1±1.4 大柴旦-宗务 西段 -2.9±3.0 -7.3±2.5 隆山断裂 东段 -0.6±2.1 -3.7±4.1 西秦岭北缘断裂 漳县段 0.3±1.5 1.3±1.7 武山段 2.2±1.3 -1.4±1.1 天水段 2.5±1.3 -3.9±2.5 鄂拉山断裂 北段 -0.6±4.0 0 南段 -2.6±3.6 1.7±3.8 日月山断裂 北段 -2.1±1.8 1.2±1.8 南段 -3.9±2.5 -1.6±2.8 庄浪河断裂 -0.5±1.3 -0.1±1.4 马衔山断裂 -1.2±1.5 -1.8±1.1 合黎山南缘断裂 -2.0±0.9 1.0±1.5 武威-天祝断裂 -2.7±1.4 -2.1±2.1 注: ①正值代表左旋, 负值代表右旋; ②正值代表拉张, 负值代表挤压. -
Burchfiel B.C., Zhang P.Z., Wang Y.P., et al. 1991. Geology of the Haiyuan Fault Zone, Ningxia-Hui Autonomous Region, China, and Its Relation to the Evolution of the Northeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics, 10(6): 1091-1110. doi: 10.1029/90TC02685 Cui D.X., Hu Y.X., Wang W.P., et al. 2009. Coulomb Stress Accumulation along Haiyuan Fault Zone. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geoscience, 34(4): 641-650 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2009.070 Deng Q.D., Zhang P.Z., Ran Y.K., et al. 2003. Basic Characteristics of Active Tectonics of China. Science in China (Series D), 46(4): 356-372. doi: 10.1360/03yd9032 Ding G.Y., Tian Q.J., Kong F.C., et al. 1993. Segmentation of Active Faults-Principles, Methods and Applications. Seismological Press, Beijing, 1-5 (in Chinese with English abstract). England P., Molnar P., 2005. Late Quaternary to Decadal Velocity Fields in Asia. Journal of Geophysical Res., Earth: Solid Earth, 110(B12): 401. doi: 10.1029/2004JB003541 Gan W.J., Cheng P.G., Zhou D.M., et al. 2005. Observation of a GPS Profile across Main Faults on Northeast Margin of Tibetan Plateau and Data Analysis. Seismology and Geology, 27(2): 178-187 (in Chinese with English abstract). Guo S.M., Jiang Z.S., Zhang C.L., 2000. Division and Motion Status of Blocks for the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau in Late Quaternary. Seismology and Geology, 22(3): 219-231(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dzdz200003002.htm He W.G., Liu B.C., Lü, T.Y., et al. 1994. Study on the Segmentation of Laohushan Fault Zone. Northwestern Seismologic Journal, 16(3): 66-72 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZBDZ403.010.htm Jin S., Zhang L.T., Jin Y.J., et al. 2012. Crustal Electrical Structure along the Hezuo-Dajing Profile across the Northeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Geophysics Chinese J. Geophys. , 55(12): 3979-3990. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.010.(in Chinese with English abstract). Lasserre C., Morel P.H., Gaudemer Y., et al. 1999. Post Glacial Left Slip Rate and Past Occurrence of M≥8 Earthquakes on the Western Haiyuan Fault, Gansu, China. Journal of Geophysical Research, 144(B8): 17633-17652. doi: 10.1029/1998JB900082 Li C.X., Xu X.W., Wen X.Z., et al. 2011. Rupture Segmentation and Slip Partitioning of the Mid-Eastern Part of the Kunlun Fault, North Tibetan Plateau. Science in China (Series D), 54(11): 1730-1745. doi:10.1007/sl1430-011-4239-5 Li C.Y., 2005. Quantitative Studies on Major Active Fault Zones in Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (Dissertation). Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Loveless J.P., Meade B.J., 2010. Geodetic Imaging of Plate Motions, Slip Rates, and Partitioning of Deformation in Japan. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(B02): 410. doi: 10.1029/2008JB006248 Loveless J.P., Meade B.J., 2011. Stress Modulation on the San Andreas Fault by Inter-Seismic Fault System Interactions. Geological Society of America, 39(11): 1035-1038. doi: 10.1130/G32215.1 Mazzotti S., Le Pichon X. Le., Henry P., et al. 2000. Full Inter-Seismic Locking of the Nankai and Japan-West West Kurile Sub-Duction Zones: An Analysis of Uniform Elastic Strain Accumulation in Japan Constrained by Permanent GPS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 105(B6): 13159-13177. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900060 McCaffrey R., Qamar A.I., King R.W., et al. 2007. Fault Locking, Block Rotation and Crustal Deformation in the Pacific Northwest. Geophysical Journal International, 169(3): 1315-1340. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03371.x Meade B.J., Hager B.H., 2005. Block Models of Crustal Motion in Southern California Constrained by GPS Measurements. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 110 (B03): 403. doi: 10.1029/2004JB003209 Meade B.J., Loveless J.P., 2009. Block Modeling with Connected Fault-Network Geometries and a Linear Elastic Coupling Estimator in Spherical Coordinates Block Modeling with Multiple Fault Network Geometries and a Linear Elastic Coupling Estimator in Spherical Coordinates. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 99(6): 3124-3139. doi: 10.1785/0120090088 Meade B.J., 2007a. Present Day Kinematics at the India-Asia Collision Zone. Geology, 35(1): 81-84. doi: 10.1130/G22924A.1 Meade B.J., 2007b. Algorithms for the Calculation of Exact Displacements, Strains, and Stresses for Triangular Dislocation Elements in a Uniform Elastic Half Space. Computers & Geosciences, 33(8): 1064-1075. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2006.12.003 Niu Z.J., Ma Z.J., Chen X.L., et al. 2002. Crustal Movement Observation Network of China. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 22(3): 1-7(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB200203023.htm Okada Y., 1992. Internal Deformation Due to Shear and Tensile Faults in a Half-Space. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 82(2): 1018-1040. http://gji.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/ijlink?linkType=ABST&journalCode=ssabull&resid=75/4/1135 Pollitz F.F. , 2003. The Relationship between the Instantaneous Velocity Field and the Rate of Moment Release in the Lithosphere. Geophysical Journal International, 153(3): 595-608. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2003.01924.x Royden L.H., Burchfiel B.C., van Der Hilst R.D., 2008. The Geological Evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Science, 321(5892): 1054-1058, doi: 10.1126/science.1155371 Savage J.C., Burford R.O., 1973. Geodetic Determination of Relative Plate Motion in Central California. Journal of Geophysical Research, 78(5): 832-845. doi: 10.1029/JB078i005p00832 Tapponnier P., Xu Z.Q., Roger F., et al. 2001. Oblique Stepwise Rise an Growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science, 294(5547): 1671-1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978 Teng R.Z., Jin Y.Q., Li X.H., et al. 1994. Recent Activity Characteristics of the Recent Activity along the Fault Zone at the Northern Edge of Western Qinling Mt. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 16(2): 85-90(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZBDZ402.011.htm Thatcher W., 2007. Micro-Plate Model for the Present-day Day Deformation of Tibet. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 112(B01): 401. doi: 10.1029/2005JB004244 Wang H., Jin H.L., 2010. GPS-Constrained Constrained Inversion of Present-day Day Slip Rates along Major Faults in Chinese Mainland. Progress in Geophys. , 25(6): 1905-1916, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.06.004.(in Chinese with English abstract). Wang H., Liu M., Cao J., et al. 2011. Slip Rates and Seismic Moment Deficits on Major Active Faults in Mainland China, . Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 116(B02): 405. doi: 10.1029/2010JB007821 Wang H., Liu M., Shen X.H., et al. 2009. Balance of Seismic Moment in the Songpan-Ganze Region, Eastern Tibet: Implications for the 2008 Great Wenchuan Earthquake. Tectonophysics, 491(1-4): 154-164. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.09.022 Wang M., 2009. Analysis of GPS Data with High Precision Study on Present-day Day Crustal Deformation in China (Dissertation). Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing, 21-31(in Chinese with English abstract). Xiang H.F., Guo S.M., Zhang B.L., et al. 1998. Active Features of the Eastern Liupanshan Piedmont Reverse Fault Zone since Late Quaternary. Seismology and Geology, 20(4): 321-327(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ804.004.htm Xu X.W., Yu G.H., Chen G.H., et al. 2007. Near Near-Surface Character of Permanent Geologic Deformation across the Mega-Strike-Slip Faults in the Northern Tibetan Plateau. Seismology and Geology, 29(2): 201-217(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288595849_Near-surface_character_of_permanent_geologic_deformation_across_the_mega-strike-slip_faults_in_the_northern_Tibetan_Plateau Yang Z.X., Waldhauser F., Chen Y.T., et al. 2005. Double-Difference Difference Relocation of Earthquakes in Central-Western Western China, 1992—1999. Journal of Seismology, 9(2): 241-264. doi: 10.1007/s10950-005-3988-z Yuan D.Y., Liu X.L., Zhang P.Z., et al. 2003. Characteristics of the Modern Activity of the Reshui-Riyueshan Fault Zone in Qinghai Province. Seismology and Geology, 25(1): 155-165(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZDZ200301014.htm Yuan D.Y., Zhang P.Z., Liu X.L., et al. 2004a. The Tectonic Activity and Deformation Features During the Late Quaternary of Elashan Mountain Active Fault Zone in Qinghai Province and Its Implication for the Deformation of the Northeastern Margins of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(4): 393-403(in Chinese with English abstract). http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=DXQY200404007&dbcode=CJFD&year=2004&dflag=pdfdown Yuan D.Y., Zhang P.Z., Liu B.C., et al. 2004b. Geometrical Imagery and Tectonic Transformation of Late Quaternary Active Tectonics in Northeastern Margin of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 78(2): 270-278(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang G.M., Wang S.Y., Li L., et al. 2002. Focal Depth Research of Earthquakes in Mainland China: Implication for Tectonics. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(129): 663-668(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang P.Z., Deng Q.D., Zhang G.M., et al. 2003a. Active Tectonic Blocks and Strong Earthquakes Activities in the Continent of China. Science in China (Series D), 46(Suppl. 2): 13-24. doi: 10.1360/03dz0002 Zhang P.Z., Min W., Deng Q.D., et al. 2003b. Paleoearthquake Rupture Behavior and Recurrence of Great Earthquakes along the Haiyuan Fault, Northwestern China. Science in China (Series D), 48(3): 364-375. doi: 10.1360/02yd0464 Zhang P.Z., Zheng D.W., Yin G.M., et al. 2006. Discussion on Late Cenozoic Growth and Rise of Northeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Quaternary Sciences, 26(1): 5-13(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200601001.htm Zhang P.Z., Shen Z.K., Wang M., et al. 2004. Continuous Deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from Global Positioning System Data. Geology, 32(9): 809-812. doi: 10.1130/G20554.1 Zhang P.Z., 1987. Rate, Amount, and Style of Late Cenozoic Deformation of Southern Ningxia, Northeastern Margin of Tibetan Plateau (Ph. D. Dissertation). Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Massachusetts State, Massachusetts, 53-77. Zhang X., Wang S.X., Liu W.Y., et al. 2006. Characteristics of Recent Horizontal Crustal Movement and Tectonic Deformation Features in the Northwest China Region. Earthquake Research in China, 22(1): 43-55(in Chinese with English abstract). Zheng Y., Chen Y., Fu R.S., et al. 2007. Simulation of the Effects of Faults Movement on Stress and Deformation Fields of Tibetan Plateau by Discontinuous Movement Models. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 50(5): 1398-1408(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1568381 崔笃信, 胡亚轩, 王文萍, 等. 2009. 海原断裂带库仑应力积累. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 34(4): 641-650. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200904011.htm 邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 2002. 中国活动构造基本特征. 中国科学(D辑), 32(12): 1020-1030. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200212006.htm 丁国瑜, 田勤俭, 孔凡臣, 等. 1993. 活断层的分段-原则、方法及运用. 北京: 地震出版社, 1-5. 甘卫军, 程朋根, 周德敏, 等. 2005. 青藏高原东北缘主要活动断裂带GPS加密观测及结果分析. 地震地质, 27(2): 177-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2005.02.001 虢顺民, 江在森, 张崇立. 2000. 青藏高原东北缘晚第四纪块体划分与运动态势研究. 地震地质, 22(3): 219-231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.03.003 何文贵, 刘百篪, 吕太乙, 等. 1994. 老虎山断裂带的分段性研究. 西北地震学报, 16(3): 66-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ403.010.htm 金胜, 张乐天, 金永吉, 等. 2012. 青藏高原东北缘合作-大井剖面地壳电性结构研究. 地球物理学报, 55(12): 3979-3990. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.010 李陈侠, 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 等. 2011. 东昆仑断裂带中东部地震破裂分段性与走滑运动分解作用. 中国科学(D辑), 41(9): 1295-1310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201109008.htm 李传友. 2005. 青藏高原东北部几条主要断裂带的定量研究(博士论文). 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 1-5. 李延兴, 杨国华, 李智, 等. 2003. 中国大陆活动地块的运动与应变状态. 中国科学(D辑), 33(增刊): 65-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2003S1007.htm 牛之俊, 马宗晋, 陈鑫连, 等. 2002. 中国地壳运动观测网络. 大地测量与地球动力学, 22(3): 88-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB200203023.htm 滕瑞增, 金瑶泉, 李希候, 等. 1994. 西秦岭北缘断裂带新活动特征. 西北地震学报, 16(2): 85-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ402.011.htm 王辉, 金红林. 2010. 基于GPS资料反演中国大陆主要断裂现今活动速率. 地球物理学进展, 25(6): 1905-1916. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.06.004 王敏, 沈正康, 牛之俊, 等. 2003. 现今中国大陆地壳运动与活动块体模型. 中国科学(D辑), 33(增刊): 21-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2003S1002.htm 王敏. 2009. GPS观测结果的精化分析与中国大陆现今地壳形变场研究(博士论文). 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 21-31. 向宏发, 虢顺民, 张秉良, 等. 1998. 六盘山东麓活动逆断裂构造带晚第四纪以来的活动特征. 地震地质, 20(4): 321-327. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ804.004.htm 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 陈桂华, 等. 2007. 青藏高原北部大型走滑断裂带近地表地质变形带特征分析. 地震地质, 29(2): 201-217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.02.002 袁道阳, 刘小龙, 张培震, 等. 2003. 青海热水-日月山断裂带的新活动特征. 地震地质, 25(1): 155-165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2003.01.015 袁道阳, 张培震, 刘小龙, 等. 2004a. 青海鄂拉山断裂带晚第四纪构造活动及其所反映的青藏高原东北缘的变形机制. 地学前缘, 11(4): 393-403. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200404007.htm 袁道阳, 张培震, 刘百篪, 等. 2004b. 青藏高原东北缘晚第四纪活动构造的几何图像与构造转换. 地质学报, 78(2): 270-278. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200402016.htm 张国民, 汪素云, 李丽, 等. 2002. 中国大陆地震震源深度及其构造含义. 科学通报, 47(9): 663-668. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.09.004 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等. 2003a. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块. 中国科学(D辑), 33(增刊): 12-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2003S1001.htm 张培震, 闵伟, 邓起东, 等. 2003b. 海原活动断裂带的古地震与强震复发规律. 中国科学(D辑), 33(8): 705-713. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200308000.htm 张培震, 郑德文, 尹功明, 等. 2006. 有关青藏高原东北缘晚新生代扩展与隆升的讨论. 第四纪研究, 26(1): 5-13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.01.002 张希, 王双绪, 刘文义, 等. 2006. 西北地区近期地壳水平运动与构造变形特征. 中国地震, 22(1): 43-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2006.01.005 郑勇, 陈颠, 博容珊, 等. 2007. 应用非连续性模型模拟断层活动对青藏高原应力应变场的影响. 地球物理学报, 50(5): 1398-1408. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.05.015 -









 下载:
下载: