The Paleogene-Neogene Paleoclimate Evolution in Western Sector of Northern Margin of Qaidam Basin
-
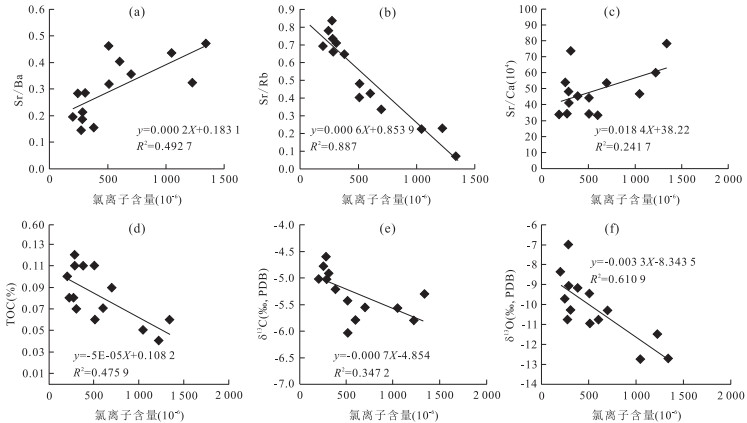
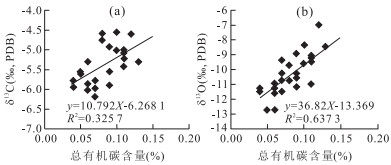
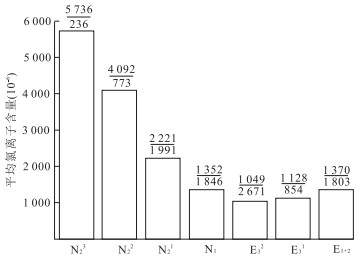
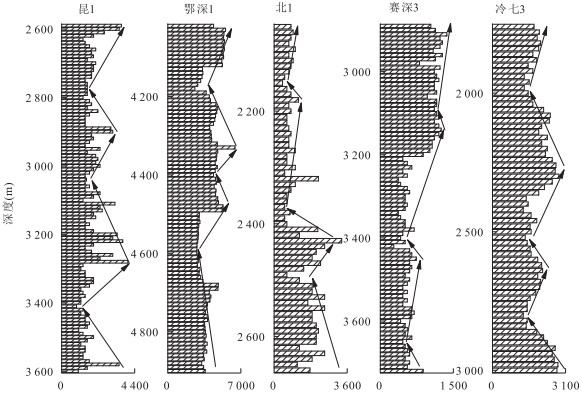
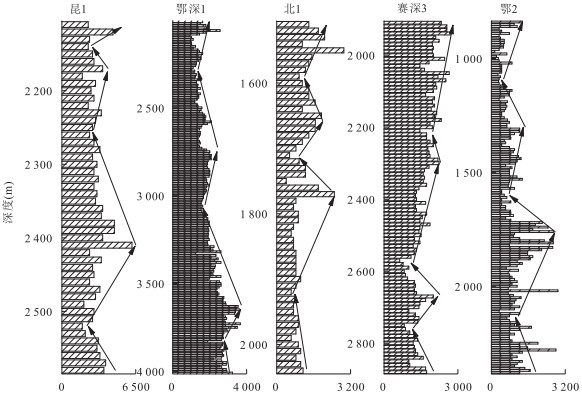
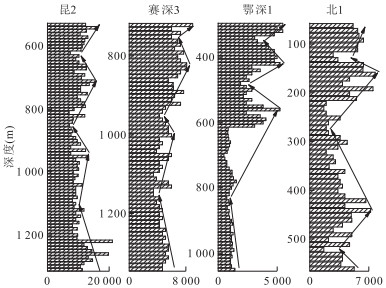
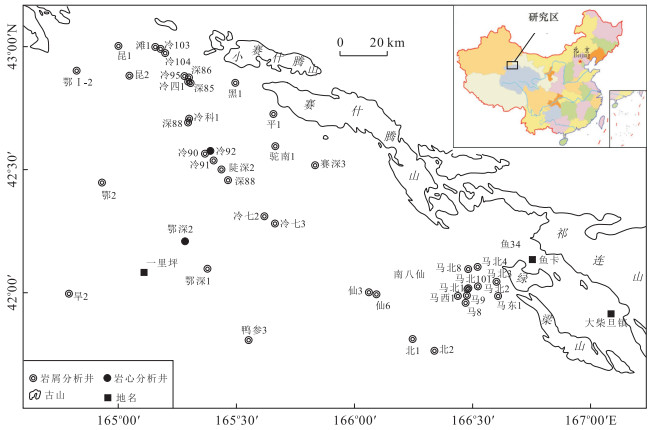
摘要: 古气候是陆相湖盆层序地层形成的主要沉积动力学因素之一.古-新近纪柴北缘西段及周边地区古气候演化过程复杂,目前就古气候演化过程还存在争议,利用地球化学方法对重点井的岩心和岩屑进行元素、TOC和碳氧稳定同位素测定.各古气候指标之间的相关性分析表明:Sr/Ba、Rb/Sr、Sr/Ca、TOC和氯离子含量可作为研究区恢复古气候的指标,δ13C与δ18O不能指示出该区的古气候演化过程.重点井全井段的岩屑氯离子含量分析表明:柴北缘西段古-新近纪古气候经历了干旱-潮湿-干旱的演化过程,从路乐河组到下干柴沟组上段沉积期古气候由干旱逐渐向潮湿的方向演化,呈现了7个旋回,湖盆水体盐度降低,总体来说气候潮湿,水体为微咸水;从上干柴沟组到狮子沟组沉积期古气候从潮湿向干旱方向演化,呈现了12个旋回,古水介质经历了微咸水至半咸水的演化过程.Abstract: Paleoclimate is one of the main sedimentary dynamic factors for the formation of sequence stratigraphy of continental basin. The Paleogene-Neogene paleoclimate evolution in western sector of northern margin of Qaidam basin and surrounding areas was complex, but now paleoclimate evolution remains controversial. The elements, TOC and C, O stable isotope content of key well cores and rock debris were measured by geochemical methods. Correlation analysis between paleoclimate indicators shows that: Sr/Ba, Rb/Sr, Sr/Ca, TOC and chloride ion content can be the paleoclimate recovery indicators, however, δ13C and δ18O can't indicate the paleoclimate evolution process in the study area. Analysis of rock debris chloride ion data of key wells shows that the paleoclimate evolution process in the study area is arid-humid-arid. From Lulehe Formation to upper Shangganchaigou Formation, the paleoclimate gradually evolved from arid to humid climate, including 7 cycles, and lake water salinity decreased, the climate was humid and water was brackish overall. From Shangganchaigou Formation to Shizigou Formation, the paleoclimate evolved from humid to arid, including 12 cycles, and brackish water changed to medium brackish water.
-
表 1 柴达木盆地古-新近纪泥岩氯度(10-6)与湖水类型关系
Table 1. The relationship of Paleogene-Neogene mudstone chlorine level (10-6) and water type of Qaidam basin
淡水 微咸水 半咸水 咸水 盐水 柴达木盆地湖水 0~200 200~1 650 1 650~12 800 12 800~28 500 大于28 500 海水 0~260 260~2 750 2 750~16 604 16 604~33 224 大于33 224 -
An, Z.S., Zhang, P.Z., Wang, E.C., et al., 2006. Changes of the Monsoon-Arid Environment in China and Growth of the Tibetan Plateau since the Miocene. Quaternary Sciences, 26(5): 678-693(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1571236 Andrea, B.R., Bojar, A.V., Franz, N., et al., 2009. Monitoring Cenozoic Climate Evolution of Northeastern Tibet: Stable Isotope Constraints from the Western Qaidam Basin, China. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(5): 1063-1075. doi: 10.1007/s00531-008-0304-5 Chen, H.D., Li, J., Zhang, C.G., et al., 2011. Discussion of Sedimentary Environment and Its Geological Enlightenment of Shanxi Formation in Ordos Basin. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(8): 2213-2229(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/ysxb98201108001 Chen, J.A., Zeng, Y., Wang, J.F., et al., 2013. The Geochemical Records of Rb and Sr of Different Forms in Lake Sediments. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 32(4): 408-417(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.04.004 Chen, L.X., Liu, J.P., Zhou, X.J., et al., 1999. Impact of Uplift of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and Change of Land-Ocean Distribution on Climate over Asia. Quaternary Sciences, 19(4): 314-329(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ199904003.htm Fang, X.M., Song, C.H., Dai, S., et al., 2007. Cenozoic Deformation and Uplift of the NE Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Evidence from High-Resolution Magnetostratigraphy and Basin Evolution. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(1): 230-242(in Chinese with English abstract). Fang, X.M., Wu, F.L., Han, W.X., et al., 2008. Plio-Pleistocene Drying Process of Asian Inland-Sporopollen and Salinity Records from Yahu Section in the Central Qaidam Basin. Quaternary Sciences, 28(5): 874-882(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97036X/20085/28351896.html Fritz, S.C., 1996. Paleolimnological Records of Climatic Change in North America. Limnology and Oceanography, 41(5): 882-889. doi: 10.4319/lo.1996.41.5.0882 Guo, Z.T., Ruddiman, W.F., Hao, Q.Z., et al., 2002. Onset of Asian Desertification by 22 Myr Ago Inferred from Loess Deposits in China. Nature, 416(6877): 159-163. doi: 10.1038/416159a Han, W.X., 2008. Climatic Records of Cenozoic Sediments from Qaidam Basin and Their Implieations on Drying of Asian Inland(Dissertation). Lanzhou University, Lanzhou (in Chinese with English abstract). Henderson, A.C.G., 2003. A Carbon- and Oxygen-Isotope Record of Recent Environmental Change from Qinghai Lake, NE Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(14): 1463. doi: 10.1360/02wd0272 Hu, S.H., Zhang, T., Gao, J.P., et al., 2012. The Miocene Climate Changes in Honggouzi Area of Western Qaidam Basin and Dominating Factors on Erosion Rate. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 30(6): 1106-1114(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201206012.htm Ji, L.M., Qiao, Z.Z., Zhang, H.Q., et al., 2007. Micropalaeontology of Eocene Lower Ganchaigou Formation in the Kunteyi Depression of the Northern Margin of the Qaidam Basin. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 24(1): 82-88(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2007.01.007 Jin, Z.D., Zhang, E.L., 2002. Paleoclimate Implication of Rb/Sr Ratios from Lake Sediments. Science Technology and Engineering, 2(3): 20-22(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS200203008.htm Kelts, K., Talbot, M., 1990. Lacustrine Carbonates as Geochemical Archives of Environmental Change and Biotic/Abiotic Interactions. In: Brock, T.D., ed., Brock/Springer Series in Contemporary Bioscience. Springer Berlin Heidelbery, Berlin, 288-315. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-84077-7_15 Kemp, J., Radke, L.C., Olley, J., et al., 2012. Holocene Lake Salinity Changes in the Wimmera, Southeastern Australia, Provide Evidence for Millennial-Scale Climate Variability. Quaternary Research, 77(1): 65-76. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2011.09.013 Lazar, B., Erez, J., 1992. Carbon Geochemistry of Marine-Derived Brines: I. 13C Depletions due to Intense Photosynthesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 56(1): 335-345. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(92)90137-8 Li, M.H., Kang, S.C., 2007. Responses of Lake Sediments to Paleoenvironmental and Paleoclimatic Changes in Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 15(1): 63-72 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YHYJ200701011.htm Li, M.J., Zheng, M.L., Cao, C.C., et al., 2005. Formation and Evolution of Qaidam Paleogene and Neogene Basin. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edition), 35(1): 87-90(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ20050100M.htm Liu, T.S., Zheng, M.P., Guo, Z.T., 1998. Initiation and Evolution of the Asian Monsoon System Timely Coupled with the Ice-Sheet Growth and the Tectonic Movements in Asia. Quaternary Sciences, 18(3): 194-204 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ199803001.htm Liu, H.N., Deng, L.L., Gong, Y.C., et al., 2008. Carbonate Cements from Xujiahe Sandstone and Its Forming Mechanism, West Sichuan Depression. Natural Gas Technology, 2(5): 24-27, 78. (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TRJJ200805013.htm Liu, Z.F., Wang, C.S., 1998. The Effects of Tibetan Plateau Uplift to Cenozoic Global Climate Change. Exploration of Nature, 17(3): 30-33(in Chinese). Ma, Y.Z., Li, J.J., Fang, X.M., 1998. The Records of Red Layer Palynoflora Aged 30.6-5.0 Ma and Climate Evolution in Linxia Area. Chinese Science Bulletin, 43(3): 301-304(in Chinese). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZWXB809.014.htm Matthews, M.B., Ayalon, A., Matthews, A., et al., 1996. Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Study of the Active Water-Carbonate System in a Karstic Mediterranean Caveimplication for Palaeoclimate Research in Semiarid Regions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60(2): 337-347. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00395-9 Miao, Y.F., Fang, X.M., Song, Z.C., et al., 2008. Eocene Sporopollen Records and Ancient Climate Change of Northern Tibetan Plateau. Science in China: Earth Sciences, 38(2): 187-196(in Chinese). Patrickson, S.J., Sack, D., Brunelle, A.R., et al., 2010. Late Pleistocene to Early Holocene Lake Level and Paleoclimate Insights from Stansbury Island, Bonneville Basin, Utah. Quaternary Research, 73(2): 237-246. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.12.006 Ramstein, G., Fluteau, F., Besse, J., et al., 1997. Effect of Orogeny, Plate Motion and Land-Sea Distribution on Eurasian Climate Change over the Past 30 Million Years. Nature, 386(6627): 788-795. doi: 10.1038/386788a0 Rea, D.K., Leinen, M., Janecek, T.R., 1985. Geologic Approach to the Long-Term History of Atmospheric Circulation. Science, 227(4688): 721-725. doi: 10.1126/science.227.4688.721 Shi, Y.F., Tang, M.C., Ma, Y.Z., 1998. Linkage between the Second Uplifting of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau and the Initiation of the Asian Monsoon System. Science in China: Earth Sciences, 28(3): 263-271(in Chinese). doi: 10.1007/bf02878967 Solotchina, E.P., Sklyarov, E.V., Solotchin, P.A., et al., 2014. Mineralogy and Crystal Chemistry of Carbonates from the Holocene Sediments of Lake Kiran (Western Transbaikalia): Connection with Paleoclimate. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 55(4): 472-482. doi: 10.1016/j.rgg.2014.03.005 Song, B.W., Xu, Y.D., Liang, Y.P., et al., 2014. Evolution of Cenozoic Sedimentary Basins in Western China. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 39(8): 1035-1051. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.093 Song, B.W., Zhang, K.X., Lu, J.F., et al., 2013. The Middle Eocene to Early Miocene Integrated Sedimentary Record in the Qaidam Basin and Its Implications for Paleoclimate and Early Tibetan Plateau Uplift. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 50(2): 183-196. doi: 10.1139/cjes-2012-0048 Song, C.H., Bai, J.F., Zhao, Y.D., et al., 2005. The Color of Lacustrine Sediments Recorded Climatic Changes from 13 to 4.5 Myr in Linxia Basin. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 23(3): 507-513(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.03.018 Stuiver, M., 1970. Oxygen and Carbon Isotope Ratios of Fresh-Water Carbonates as Climatic Indicators. Journal of Geophysical Research, 75(27): 5247-5257. doi: 10.1029/jc075i027p05247 Sun, Z.C., Cao, L., Zhang, H.Q., et al., 2003. Evolution of Ostracoda of the Great Ice Age of Last Glacial Stage in Qaidam Basin. Journal of Palaeogeography, 5(3): 365-377(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2003.03.009 Wang, C.W., Hong, H.L., Li, Z.H., et al., 2013. Climatic and Tectonic Evolution in the North Qaidam since the Cenozoic: Evidence from Sedimentology and Mineralogy. Journal of Earth Science, 24(3): 314-327. doi: 10.1007/s12583-013-0332-3 Wang, J., Wang, Y.J., Liu, Z.C., et al., 1999. Cenozoic Environmental Evolution of the Qaidam Basin and Its Implications for the Uplift of the Tibetan Plateau and the Drying of Central Asia. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 152(1-2): 37-47. doi: 10.1016/s0031-0182(99)00038-3 Wang, P.X., 2003. Evolution of the South China Sea and Monsoon History Revealed in Deep-Sea Records. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(23): 2549-2561. doi: 10.1360/03wd0156 Wang, Q., Hao, L.W., Chen, G.J., et al., 2010. Forming Mechanism of Carbonate Cements in Siliciclastic Sandstone of Zhuhai Formation in Baiyun Sag. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 31(4): 553-558, 565(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288271545_Forming_mechanism_of_carbonate_cements_in_siliciclastic_sandstone_of_Zhuhai_Formation_in_Baiyun_Sag Wang, X.Q., Wang, L.S., 2013. The Pollen and Spore Characteristics of the Diexi Ancient Dammed Lake on the Upstream of Minjiang River. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 38(5): 975-982. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2013.095 Wang, Y., Zhao, Z.H., Lin, J.X., 2004. Paleoclimate and Geochemical Composition of AK1 Core Sediments in Lop Nur, Xinjiang. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 25(6): 653-658(in Chinese with English abstract). Xiong, X.H., Xiao, J.F., 2011. Geochemical Indicators of Sedimentary Environments—A Summary. Earth and Environment, 39(3): 405-414(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201103021.htm Xu, L., Miao, Y.F., Fang, X.M., et al., 2009. Middle Eocene-Oligocene Climatic Changes Recorded by Sedimentary Colors in the Xining Basin, in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, NW China. Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Sciences), 45(1): 12-19(in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, Z.H., Hu, S.Y., Wang, Z.C., et al., 2011. Restoration of Paleoclimate and Its Geological Significance: As an Example from Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Sichuan Basin. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 29(2): 235-244(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201102005.htm Yi, H.S., Lin, J.H., Zhou, K.K., et al., 2007. Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Characteristics and Palaeoenvironmental Implication of the Cenozoic Lacustrine Carbonate Rocks in Northern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Palaeogeography, 9(3): 303-312(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2007.03.008 Yin, C.M., Li, W.M., Andrea, R., et al., 2007. Cenozoic Climate Changes in the Qaidam Basin, Western China: Evidenced from Carbon and Oxygen Stable Isotope. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 37(5): 901-907(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5888.2007.05.009 Zachos, J., 2001. Trends, Rhythms, and Aberrations in Global Climate 65 Ma to Present. Science, 292(5517): 686-693. doi: 10.1126/science.1059412 Zhang, H., Jin, H.L., Xiao, H.L., et al., 2004. Soluble Salt Sediments of East Juyan Lake and Its Indicating Palaeoclimate Environment Changes. Journal of Desert Research, 24(4): 409-415(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284617918_Soluble_salt_sediments_of_east_Juyan_Lake_and_its_indicating_palaeoclimate_environment_changes Zhang, R., Ji, Y.L., Sun, Y.E., 2011. A Study on PLC in Material of Automatic Sorting System. Coal Technology, 30(12): 119-120(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, S.C., Wang, R.L., Jin, Z.J., et al., 2006. The Relationship between the Cambrian-Ordovician High-TOC Source Rock Development and Paleoenvironment Variations in the Tariam Basin, Western China: Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Evidence. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(3): 459-466(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200603020.htm Zhao, J.F., Chen, X.H., Du, Y.B., 2004. The Tertiary Sedimentary Evolution of the Qaidam Basin, Northwest China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 31(3): 41-44(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200403010.htm Zhao, J.F., Chen, X.H., Jin, L., 2005. Application of Stable Isotope in Tertiary Saline Lake of Qaidam Basin. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edition), 35(3): 342-346(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XBDZ200503040.htm Zheng, R.C., Liu, M.Q., 1999. Study on Palaeosalinity of Chang-6 Oil Reservoir Set in Ordos Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 20(1): 20-25(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/291273288_Study_on_palaeosalinity_of_Chang_6_oil_reservoir_set_in_Ordos_Basin 安芷生, 张培震, 王二七, 等, 2006. 中新世以来我国季风-干旱环境演化与青藏高原的生长. 第四纪研究, 26(5): 678-693. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.05.002 陈洪德, 李洁, 张成弓, 等, 2011. 鄂尔多斯盆地山西组沉积环境讨论及其地质启示. 岩石学报, 27(8): 2213-2229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201108001.htm 陈敬安, 曾艳, 王敬富, 等, 2013. 湖泊沉积物不同赋存状态Rb、Sr地球化学记录研究. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 32(4): 408-417. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.04.004 陈隆勋, 刘骥平, 周秀骥, 等. 1999. 青藏高原隆起及海陆分布变化对亚洲大陆气候的影响. 第四纪研究, 19(4): 314-329. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.04.004 方小敏, 宋春晖, 戴霜, 等, 2007. 青藏高原东北部阶段性变形隆升: 西宁、贵德盆地高精度磁性地层和盆地演化记录. 地学前缘, 14(1): 230-242. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.01.022 方小敏, 吴福莉, 韩文霞, 等, 2008. 上新世-第四纪亚洲内陆干旱化过程——柴达木中部鸭湖剖面孢粉和盐类化学指标证据. 第四纪研究, 28(5): 874-882. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.05.010 韩文霞, 2008. 柴达木盆地新生代地层记录的亚洲内陆干旱气候演化(博士学位论文). 兰州: 兰州大学. 胡思虎, 张涛, 高军平, 等, 2012. 柴西红沟子地区中新世气候变化与侵蚀速率控制因素. 沉积学报, 30(6): 1106-1114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201206012.htm 吉利明, 乔子真, 张海泉, 等, 2007. 柴达木盆地北缘昆特依凹陷始新统下干柴沟组微体古生物研究. 微体古生物学报, 24(1): 82-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2007.01.007 金章东, 张恩楼, 2002. 湖泊沉积物Rb/Sr比值的古气候意义. 科学技术与工程, 2(3): 20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2002.03.009 李明慧, 康世昌. 2007. 青藏高原湖泊沉积物对古气候环境变化的响应. 盐湖研究, 15(1): 63-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-858X.2007.01.012 李明杰, 郑孟林, 曹春潮, 等, 2005. 柴达木古近纪-新近纪盆地的形成演化. 西北大学学报: 自然科学版, 35(1): 87-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ20050100M.htm 刘东生, 郑绵平, 郭正堂. 1998. 亚洲季风系统的起源和发展及其与两极冰盖和区域构造运动的时代耦合性. 第四纪研究, 18(3): 194-204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.03.002 刘昊年, 邓丽丽, 龚业超, 等. 2008. 川西坳陷须家河组砂岩中碳酸盐胶结物及形成机制. 天然气技术, 2(5): 24-27, 78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRJJ200805013.htm 刘志飞, 王成善. 1998. 青藏高原隆升对新生代全球气候变化的影响. 大自然探索, 17(3): 30-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZRT803.006.htm 马玉贞, 李吉均, 方小敏. 1998. 临夏地区30.6~5.0 Ma红层孢粉植物群与气候演化记录. 科学通报, 43(3): 301-304. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.03.019 苗运法, 方小敏, 宋之琛, 等. 2008. 青藏高原北部始新世孢粉记录与古环境变化. 中国科学: 地球科学, 38(2): 187-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200802005.htm 施雅风, 汤懋苍, 马玉贞. 1998. 青藏高原二期隆升与亚洲季风孕育关系探讨. 中国科学: 地球科学, 28(3): 263-271. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199803011.htm 宋博文, 徐亚东, 梁银平, 等, 2014. 中国西部新生代沉积盆地演化. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 39(8): 1035-1051. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201408008.htm 宋春晖, 白晋锋, 赵彦德, 等, 2005. 临夏盆地13~4.4 Ma湖相沉积物颜色记录的气候变化探讨. 沉积学报, 23(3): 507-513. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200503017.htm 孙镇城, 曹丽, 张海泉, 等, 2003. 柴达木盆地全球末次冰期介形类动物群的演变. 古地理学报, 5(3): 365-377. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200303008.htm 王琪, 郝乐伟, 陈国俊, 等, 2010. 白云凹陷珠海组砂岩中碳酸盐胶结物的形成机理. 石油学报, 31(4): 553-558, 565. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201004005.htm 王小群, 王兰生, 2013. 岷江叠溪古堰塞湖沉积物中孢粉特征. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 38(5): 975-982. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201305008.htm 王永, 赵振宏, 林景星, 2004. 罗布泊AK1孔沉积物地球化学组成与古气候. 地球学报, 25(6): 653-658. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2004.06.010 熊小辉, 肖加飞, 2011. 沉积环境的地球化学示踪. 地球与环境, 39(3): 405-414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201103021.htm 徐丽, 苗运法, 方小敏, 等, 2009. 青藏高原东北部西宁盆地中始新世-渐新世沉积物颜色与气候变化. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 45(1): 12-19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0455-2059.2009.01.003 徐兆辉, 胡素云, 汪泽成, 等, 2011. 古气候恢复及其对沉积的控制作用——以四川盆地上三叠统须家河组为例. 沉积学报, 29(2): 235-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201102005.htm 伊海生, 林金辉, 周恳恳, 等, 2007. 青藏高原北部新生代湖相碳酸盐岩碳氧同位素特征及古环境意义. 古地理学报, 9(3): 303-312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2007.03.008 尹成明, 李伟民, R. Andrea, 等, 2007. 柴达木盆地新生代以来的气候变化研究: 来自碳氧同位素的证据. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 37(5): 901-907. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200705008.htm 张洪, 靳鹤龄, 肖洪浪, 等, 2004. 东居延海易溶盐沉积与古气候环境变化. 中国沙漠, 24(4): 409-415. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2004.04.006 张锐, 纪友亮, 孙永娥, 2011. 柴达木盆地北缘马海凸起古近系-新近系层序地层格架. 煤炭技术, 30(12): 119-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJS201112059.htm 张水昌, Wang, R.L., 金之钧, 等, 2006. 塔里木盆地寒武纪-奥陶纪优质烃源岩沉积与古环境变化的关系: 碳氧同位素新证据. 地质学报, 80(3): 459-466. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.03.020 赵加凡, 陈小宏, 杜业波, 2004. 柴达木第三纪湖盆沉积演化史. 石油勘探与开发, 31(3): 41-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2004.03.011 赵加凡, 陈小宏, 金龙, 2005. 柴达木盆地第三纪盐湖沉积环境分析. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 35(3): 342-346. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-274X.2005.03.024 郑荣才, 柳梅青, 1999. 鄂尔多斯盆地长6油层组古盐度研究. 石油与天然气地质, 20(1): 20-25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.1999.01.005 -









 下载:
下载: