Lunar Mineral Abundance Inversion of Sinus Iridum Considering Space Weathering Effect
-
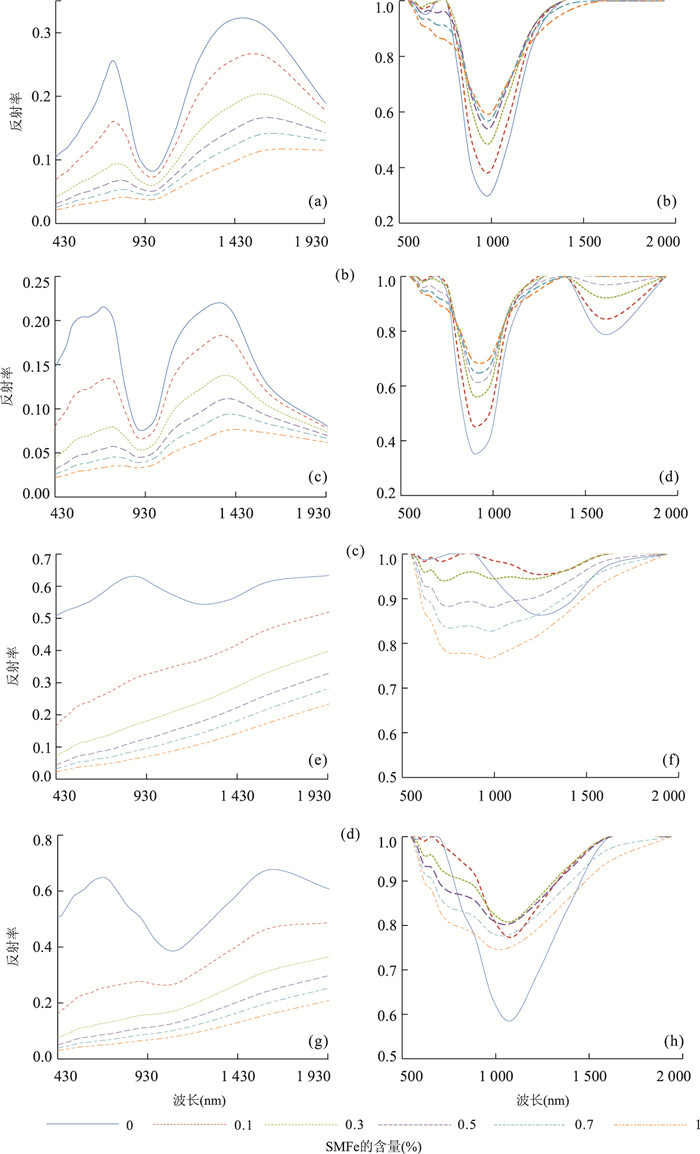
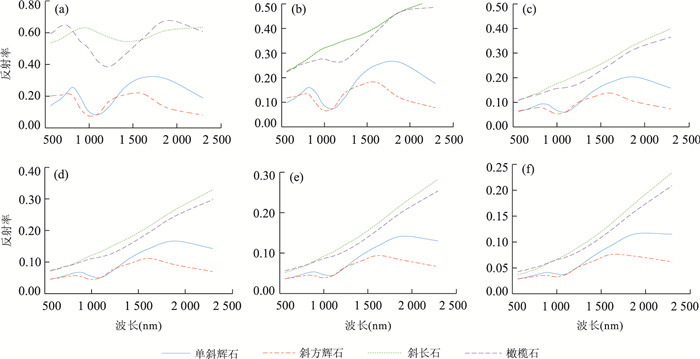
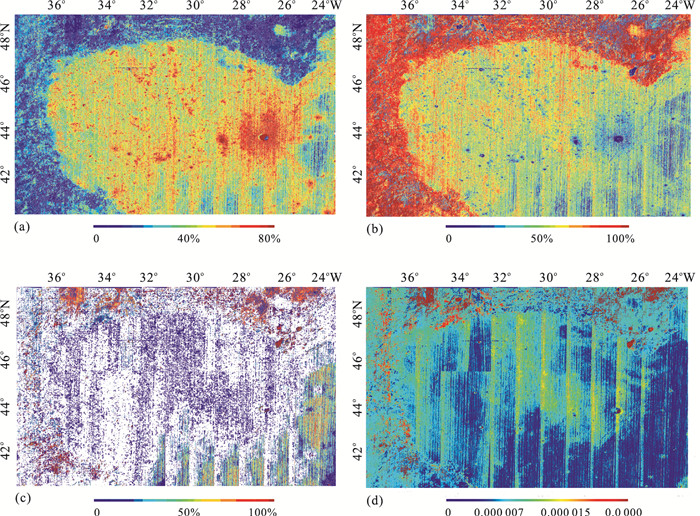
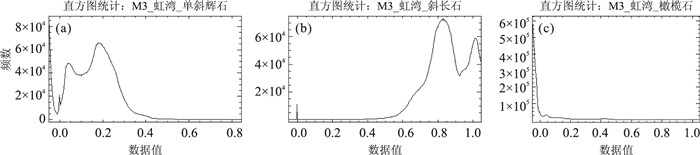
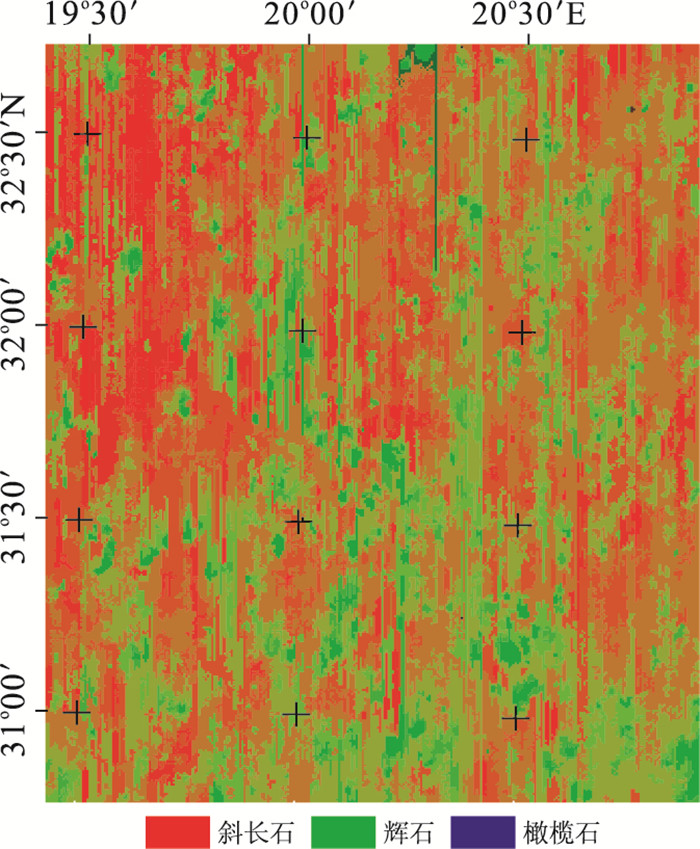
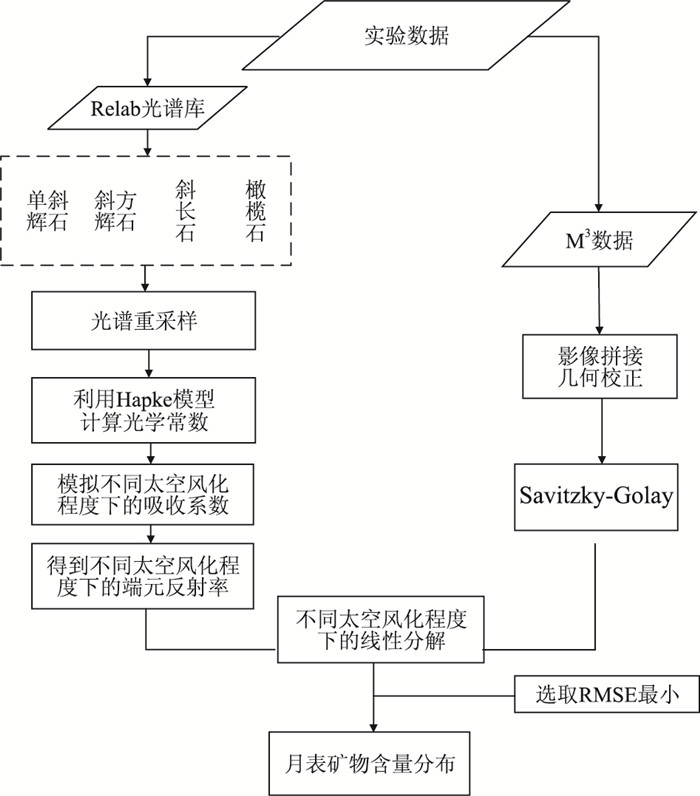
摘要: 月表矿物含量反演是研究月球地质起源和演化的关键.太空风化作用普遍发生在月球表面,对矿物纯净光谱造成了不可忽视的影响,它弱化光谱吸收特征, 降低反射率,影响矿物含量遥感反演精度.基于Relab光谱库和Hapke辐射传输模型,将月表 4种矿物(单斜辉石、斜方辉石、斜长石、橄榄石)的二向性反射率转换成同向性的单次散射反照率,然后计算矿物的光学常数;再根据亚微观金属铁SMFe(submicroscopic metallic iron)的质量分数模拟6种不同程度太空风化效应,得到端元矿物的反射率光谱;最后基于上述方法,利用多端元线性分解方法和M3(moon mineralogy mapper,月球矿物绘图仪)高光谱数据反演不同风化程度下的矿物含量,得到月表虹湾地区辉石、斜长石、橄榄石3种矿物的含量分布.实验表明,利用多端元线性分解可以有效模拟太空风化效应对矿物光谱的影响,是研究太空风化效应影响下矿物识别及含量反演的一种行之有效的方法.Abstract: The inversion of lunar minerals is critical to study the Moon's geological origin and evolution. Space weathering generally occurs on the surface of the Moon with an assignable influence on the pure mineral spectra, which obscures the reflectance spectra feature of minerals and reduces the overall reflectance. The effect of space weathering should be removed when accurately investigating the lunar minerals using remote sensing technology. The level of the space weathering is proportional to the mass fraction of submicroscopic metallic iron (SMFe). In this paper, the authors firstly transform the bidirectional reflectance into the isotropic single scattering albedo of four endmember minerals (clinopyroxene, orthopyroxene, plagioclase and olivine) in the Relab spectral library based on Hapke radiative transfer model, secondly, calculate the optical constants and absorption coefficient of each mineral, then simulate the reflectance spectra of these minerals under six space weathering levels according to SMFe mass fraction, thus we obtain endmember mineral reflectance under different space weathering levels. Finally we inverse mineral abundance with six multi-endmember linear unmixing models and the M3 (moon mineralogy mapper) hyperspectral data and obtain the inversion abundance and distribution of pyroxene, plagioclase and olivine in Lunar Sinus Iridum. The results show that using multi-endmember linear unmixing method can effectively simulate the effects of space weathering on mineral spectra, and it is an useful way of mineral identification and abundance inversion with hyperspectral under the space weathering.
-
Key words:
- space weathering /
- Hapke model /
- Sinus Iridum /
- minerals /
- inversion
-
表 1 M3主要技术和性能指标
Table 1. Main index and performance parameter of M3
视场(km) 光谱范围(nm) 采样间隔(nm) 空间分辨率(m/pixel) 波段数(个) 光谱分辨率(nm) Target模式 40 430~3 000 5 70 261 10 Global模式 40 430~3 000 5 140 85 20/40 表 2 Relab光谱库端元矿物光学常数信息
Table 2. Optical constant information of endmember minerals in Relab spectral library
矿物类别 样本编号 光谱范围(nm) DU(μm) DL(μm) < D >(μm) n 区域 单斜辉石 LS-CMP-009 350~2 600 250 5 20 1.727 Apollo 12 斜方辉石 LS-CMP-012 350~2 600 250 5 20 1.768 Apollo 17 斜长石 LS-CMP-011 350~2 600 500 5 23 1.560 Apollo 15 橄榄石 LR-CMP-014 300~2 600 45 5 11 1.827 Apollo 17 表 3 Apollo 17矿物实测含量与分解含量对比
Table 3. Comparison between mineral abundances inversed and measured in Apollo 17
Apollo 17 实测含量(%) 分解含量(%) 众数(%) 辉石 30.1 38.0 38.10 斜长石 34.1 61.9 62.30 橄榄石 0.2 0.4 0.11 钛铁矿 12.8 - 玻璃 21.9 - 其他 0.7 - 总计 99.9 100.3 -
Combe, J.P., Mccord, T.B., Kramer, G.Y., et al., 2010.Mixing of Surface Materials Investigated by Spectral Mixture Analysis with the Moon Mineralogy Mapper.Advances in Food & Nutrition Research, 59:167-213. http://phys.scichina.com:8083/sciG/EN/abstract/abstract512594.shtml Fu, X.H., Zou, Y.L., Zheng, Y.C., et al., 2011.Space Weathering Processes and Effects on the Moon.Chin.J.Space Sci., 31(6):705-715 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255486094_Space_weathering_processes_and_effects_on_the_Moon Gaffey, M.J., 2010.Space Weathering and the Interpretation of Asteroid Reflectance Spectra.Icarus, 209(2):564-574.doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2010.05.006 Hapke, B., 1981.Bidirectional Reflectance Spectroscopy:1.Theory.Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 86(B4):3039-3054.doi: 10.1029/jb086ib04p03039 Hapke, B., 1993.Theory of Reflectance and Emittance Spectroscopy.Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.doi: 10.1017/cbo9780511524998 Hapke, B., 2001.Space Weathering from Mercury to the Asteroid Belt.Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets, 106(E5):10039-10073.doi: 10.1029/2000je001338 Heiken, G., Vaniman, D., French, B.M., 1991.Lunar Sourcebook:A User's Guide to the Moon.Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. Huang, S., Chen, S.B., Zha, F.L., et al., 2015.Inversion and Geological Significance of Minerals in Dark Matter of Craters of Oceanus Procellarum of Lunar Surface.Earth Science, 40(12):2103-2109 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228369793_Lunar_regolith_thermal_behavior_revealed_by_Chang'E-1_microwave_brightness_temperature_data Johnson, P., Christy, R., 1974.Optical Constants of Transition Metals:Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Pd.Physical Review B, 9(12):5056-5070.doi: 10.1103/physrevb.9.5056 Li, C., Liu, F.J., Zheng, X.P., et al., 2013.Lunar Pyroxene and Olivine Abundance Analysis of Sinus Iridum.Sci.Sin-Phys.Mech.Astron., 43:1387-1394 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/132013-294 Li, L., Lucey, P.G., 2009.Use of Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis and Radiative Transfer Model to Derive Lunar Mineral Abundance Maps.40th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Texas. Li, S., Li, L., 2011.Radiative Transfer Modeling for Quantifying Lunar Surface Minerals, Particle Size, and Submicroscopic Metallic Fe.Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(E9):86.doi: 10.1029/2011je003837 Lucey, P.G., 1998.Model Near-Infrared Optical Constants of Olivine and Pyroxene as a Function of Iron Content.Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets, 103(E1):1703-1713.doi: 10.1029/97je03145 Lucey, P.G., 2004.Mineral Maps of the Moon.Geophysical Research Letters, 31(8):289-291.doi: 10.1029/2003gl019406 Mustard, J.F., Pieters, C.M., 1989.Photometric Phase Functions of Common Geologic Minerals and Applications to Quantitative Analysis of Mineral Mixture Reflectance Spectra.Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 94(B10):13619-13634.doi: 10.1029/jb094ib10p13619 Ouyang, Z.Y., 2005.Introduction to Lunar Science.China Astronautic Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Pieters, C.M., 1998.Lunar Materials from the Visible to Mid-Infrared:The Effects of Space Weathering.International Geology Review, 40(11):981-989.doi: 10.1080/00206819809465249 Quinn, D.P., Gillisdavis, J.J., Lucey, P.G.2010.Using Microsoft Excel for Hapke Modeling:A Technique to Simplify Calculations of Optical Constants and Reflectance Spectra.41th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Texas. Roberts, D.A., Gardner, M., Church, R., et al., 1998.Mapping Chaparral in the Santa Monica Mountains Using Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Models.Remote Sensing of Environment, 65(3):267-279.doi: 10.1016/s0034-4257(98)00037-6 Shuai, T., Zhang, X., Zhang L.F., et al., 2013.Mapping Global Lunar Abundance of Plagioclase, Clinopyroxene and Olivine with Interference Imaging Spectrometer Hyperspectral Data Considering Space Weathering Effect.Icarus, 222(1):401-410.doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2012.11.027 Taylor, L.A., Pieters, C.M., Keller, L.P., et al., 2001.Lunar Mare Soils:Space Weathering and the Major Effects of Surface-Correlated Nanophase Fe.Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets, 106(E11):27985-27999.doi: 10.1029/2000je001402 Weider, S.Z., Kellett, B.J., Swinyard, B.M., et al., 2012.The Chandrayaan-1 X-Ray Spectrometer:First Results.Planetary and Space Science, 60(1):217-228.doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2011.08.014 Wu, Y.Z., Zheng, Y.C., Zou, Y.L., et al., 2010.Research of the Optical Effects of Space Weathering on Lunar Regolith Based on the Nonlinear Mixing Model.Chin.J.Space Sci., 30(2):154-159 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4688456_Optical_Effects_of_Space_Weathering_The_Role_of_the_Finest_Fraction Yan B.K., Wang R.S., Gan F.P., et al., 2010.Minerals Mapping of the Lunar Surface with Clementine UVVIS/NIR Data Based on Spectra Unmixing Method and Hapke Model.Icarus, 208(1):11-19.doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2010.01.030 Yan, B.K., Gan, F.P., Wang, R.S., et al., 2009, .Mineral Mapping of the Lunars Surface Using Clementine UV/VIS/NIR Data Based on of Unmixing Spectral.Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, (4):19-24 (in Chinese with English abstract). 付晓辉, 邹永廖, 郑永春, 等, 2011.月球表面太空风化作用及其效应.空间科学学报, 31(6): 705-715. doi: 10.11728/cjss2011.06.705 黄爽, 陈圣波, 查逢丽, 等, 2015.月球风暴洋火山口暗物质矿物反演及地质意义.地球科学, 40(12): 2103-2109. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3212 李婵, 刘福江, 郑小坡, 等, 2013.月表虹湾地区辉石及橄榄石含量反演.中国科学:物理学力学天文学, (11): 1387-1394. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGXK201311004.htm 欧阳自远, 2005.月球科学概论.北京:中国宇航出版社. 吴昀昭, 郑永春, 邹永廖, 等, 2010.基于非线性混合模型研究太空风化对月壤光谱的影响.空间科学学报, 30(2): 154-159. doi: 10.11728/cjss2010.02.154 闫柏琨, 甘甫平, 王润生, 等, 2009.基于光谱分解的Clementine UV/VIS/NIR数据月表矿物填图.国土资源遥感, 21(4): 19-24. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2009.04.04 -









 下载:
下载: