Impact of Clay Mineral Formation in High-Temperature Geothermal System on Accuracy of Na-K and K-Mg Geothermometers
-
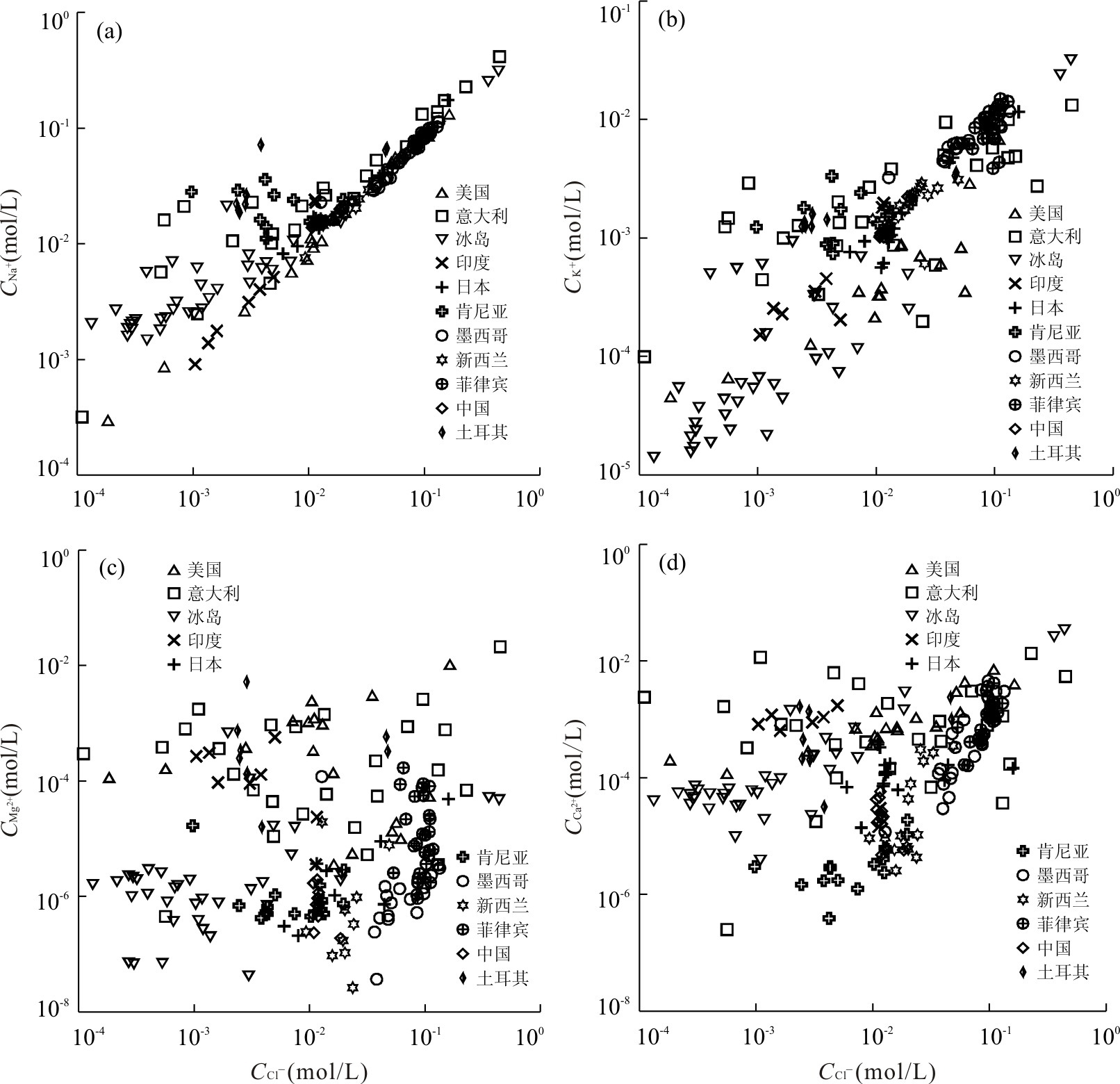
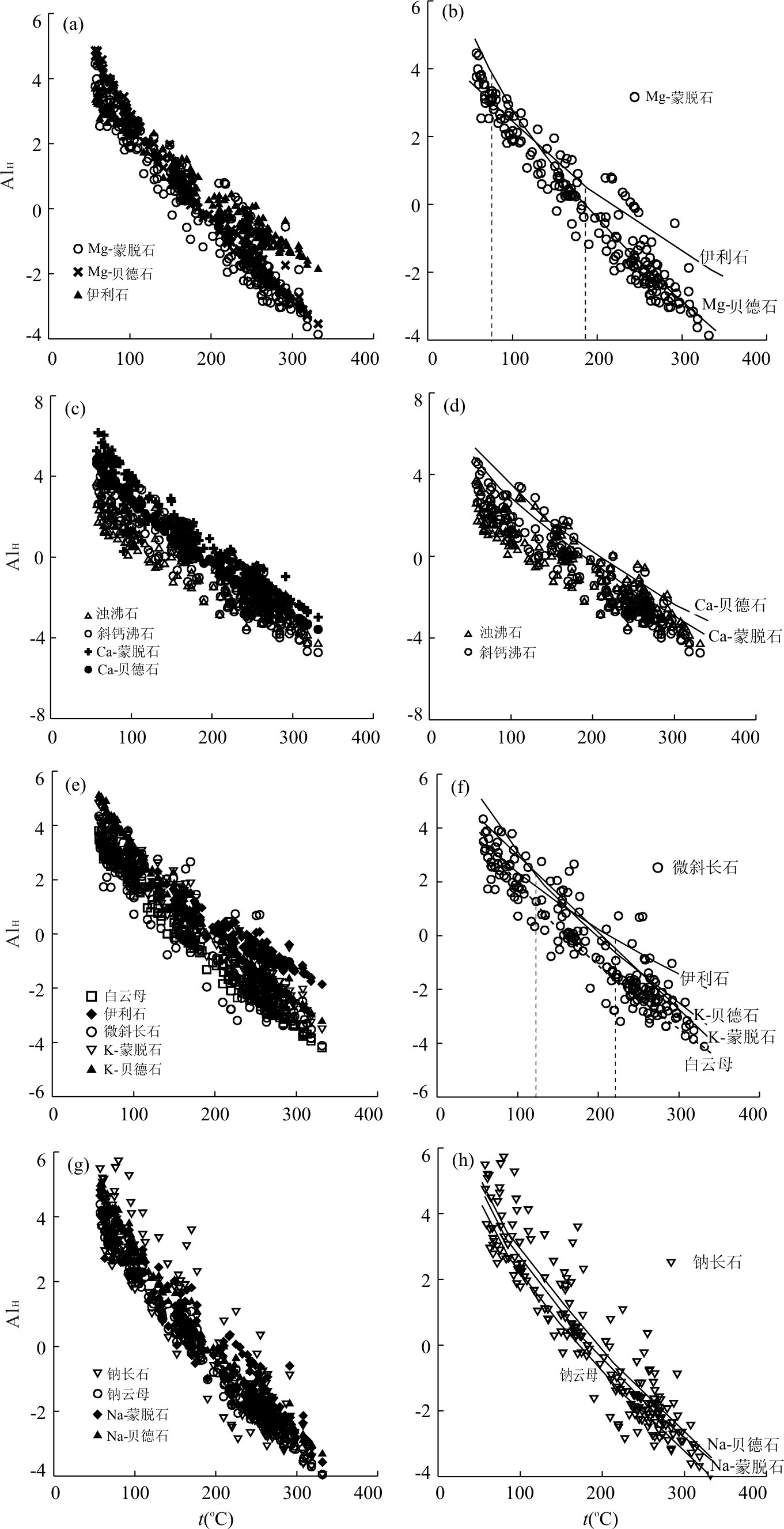
摘要: 传统地球化学温标在估算高温地热系统内浅层热储温度(一般为100~200℃)时存在局限性,其中应用广泛的Na-K温标和K-Mg温标出现误差的原因仍不清楚.在收集了全球代表性热田内采自地热井的201个流体样品的水文地球化学数据后,利用软件WATCH将井口流体地球化学数据还原为热储条件下的对应值;在此基础上,对Na-K温标和K-Mg温标进行了评价,发现钾长石和常见富钾双八面体粘土矿物均可能对浅层热储内地热流体中的钾含量产生影响,富镁双八面体粘土矿物也可达到与地热流体的平衡,而地热流体中钠含量则受水-岩相互作用的影响很小.因此,浅层地热流体的Na-K比值与热储温度不具有对应关系,而K-Mg温标在计算浅层热储温度时虽然具有一定指示意义,但仍无法得到足够准确的结果.Abstract: Traditional geochemical geothermometers have limitations when used to estimate the temperature of shallow reservoirs(100-200 ℃)in high-temperature geothermal systems, and it remains unclear about the cause of the error due to the widely used geothermometers of Na-K and K-Mg. In this study, the hydrogeochemical data of 201 water samples from geothermal wells in the typical hydrothermal areas across the world were collected, based on which the corresponding geochemical compositions of reservoir fluids are calculated using the code WATCH. An evaluation of Na-K and K-Mg geothermometers was further made. The results show that K-feldspar and common dioctahedral potassium-rich clay minerals are likely to control the content of potassium in geothermal fluid from shallow reservoirs and dioctahedral magnesium-rich clay minerals can be equilibrated with geothermal fluid as well, whereas the content of sodium in geothermal fluid is little affected by water-rock interactions. Hence, the Na-K ratio of shallow geothermal fluid doesn't match well with reservoir temperature. K-Mg geothermometer is capable of indicating shallow reservoir temperature to some degree, but still not accurate enough.
-
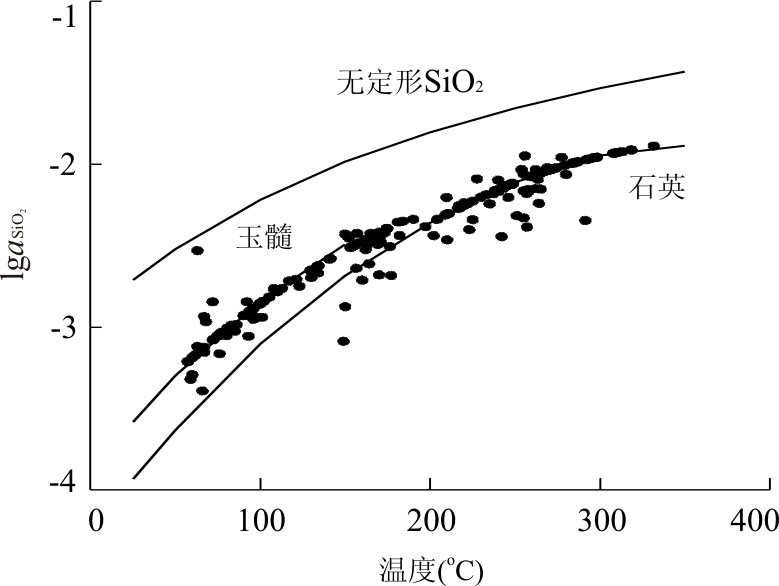
图 1 热储中玉髓和石英的饱和状态
据Stefánsson and Arnòrsson(2000)
Fig. 1. The saturated state of chalcedony and quartz in thermal reservoirs
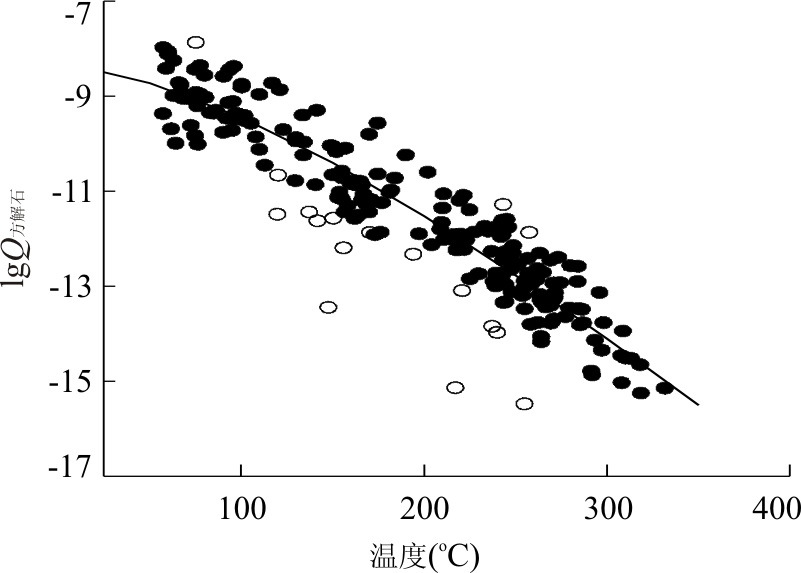
图 2 热储中方解石的饱和状态
据Stefánsson and Arnòrsson(2000)
Fig. 2. The saturated state of calcite in thermal reservoirs
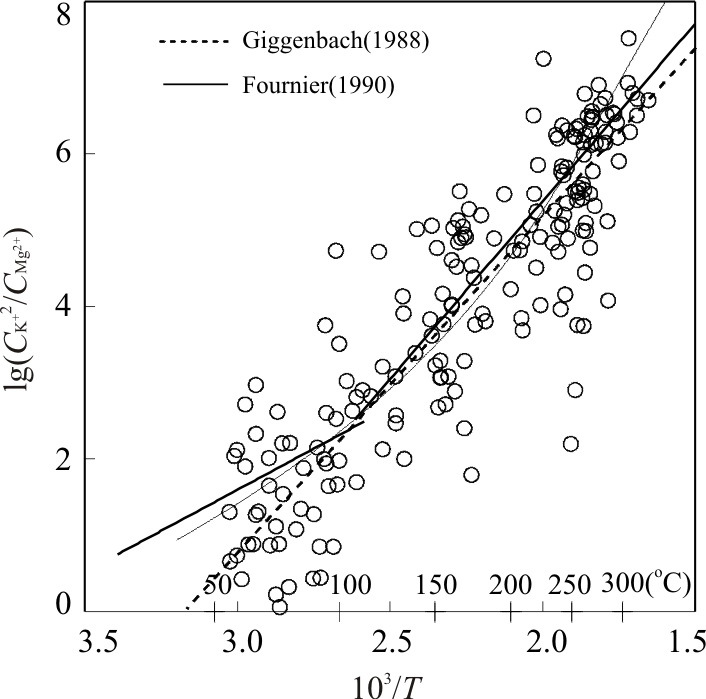
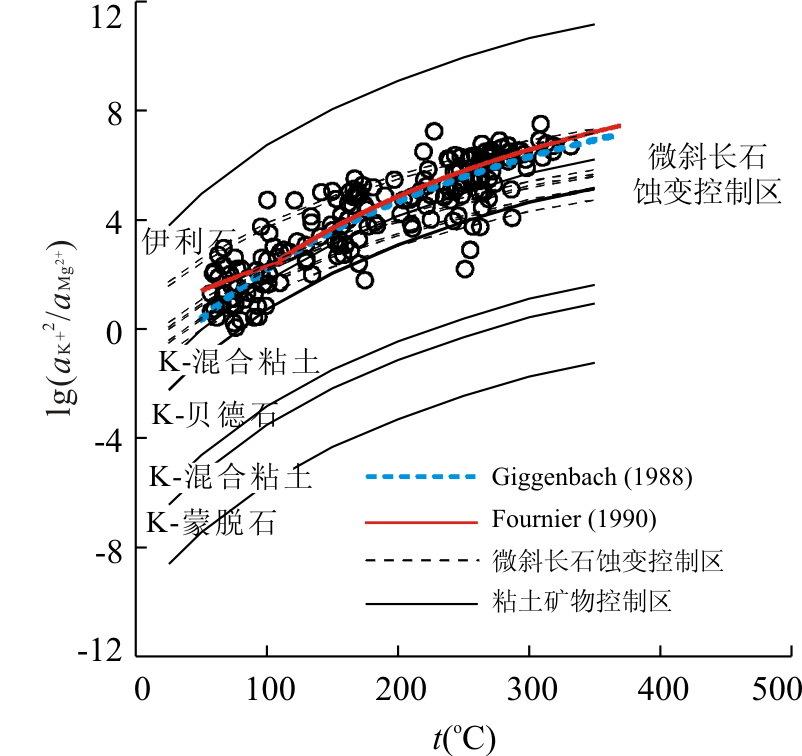
图 5 不同热储温度下CK+2/CMg2+的比值
Fig. 5. The value of CK+2/CMg2+ in different thermal reservoir temperature
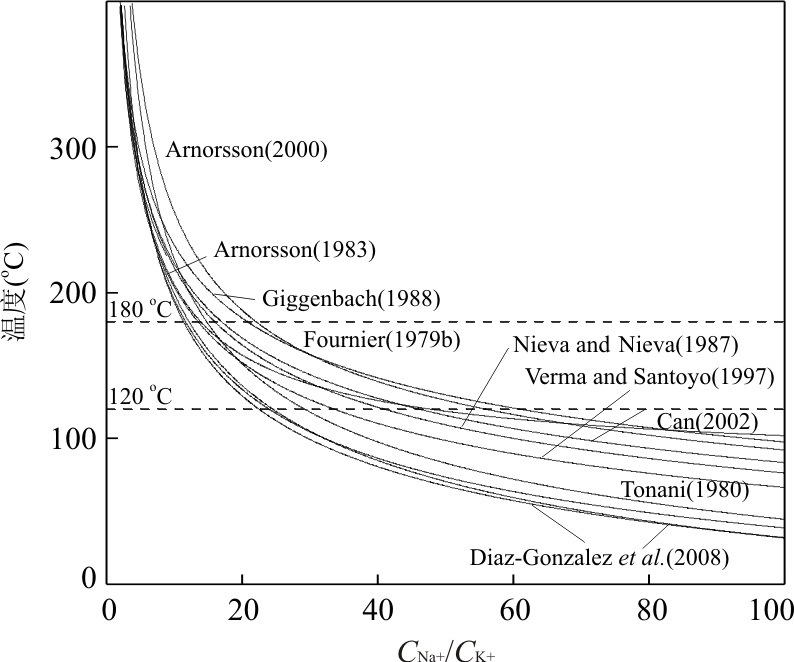
表 1 不同的Na-K温标表达式
Table 1. Different Na-K geothermometer expressions
Na-K温标表达式 参考文献 T=883/[lg(Na/K)+0.780]-273.15 Tonani(1980) T=933/[lg(Na/K)+0.993]-273.15 25~250℃,Arnòrsson et al.(1983) T=1319/[lg(Na/K)+1.699]-273.15 250~350℃,Arnòrsson et al.(1983) T=1217/[lg(Na/K)+1.483]-273.15 Fournier(1979) T=1178/[lg(Na/K)+1.470]-273.15 Nieva and Nieva(1987) T=1390/[lg(Na/K)+1.750]-273.15 Giggenbach(1988) T=(1289±76)/[(lg(Na/K)+1.615(±0.179)]-273.15 Verma and Santoyo(1997) T=733.6-770.511lg(Na/K)+378.189lg(Na/K)2-95.753lg(Na/K)3+9.544lg(Na/K)4 Arnòsson(2000) T=1052/{1+exp[1.714lg(Na/K)]+0.252}+76 Can(2002) T=1273.2tanh{[-0.4144lg(Na/K)]-0.5642}+1156.9 Díaz-González and Santoyo(2008) T=(883±15)/[(lg(Na/K)+0.894(±0.032)]-273.15 Díaz-González and Santoyo(2008) 注:Na/K为泉水中浓度的比值. -
Aagaard,P.,Helgeson,H.C.,1983.Activity/Composition Relations among Silicates and Aqueous Solutions:Ⅱ.Chemical and Thermodynamic Consequences of Ideal Mixing of Atoms on Homological Sites in Montmorillonites,Illites,and Mixed-Layer Clays.Clays and Clay Minerals,31(3):207-217.doi: 10.1346/ccmn.1983.0310306 Aja,S.U.,Rosenberg,P.E.,1992.The Thermodynamic Status of Compositionally-Variable Clay Minerals:A Discussion.Clays and Clay Minerals,40(3):292-299.doi: 10.1346/ccmn.1992.0400307 Arnòrsson,S.,1978.Precipitation of Calcite from Flashed Geothermal Waters in Iceland.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,66(1):21-28.doi: 10.1007/bf00376082 Arnòsson,S.,2000.The Quartz and Na/K Geothermometers.I.New Thermodynamic Calibration,Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress,Kyushu,929-934. Arnòrsson,S.,Gunnlaugsson,E.,Svavarsson,H.,1983.The Chemistry of Geothermal Waters in Iceland.II.Mineral Equilibria and Independent Variables Controlling Water Compositions.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,47(3):547-566.doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(83)90277-6 Browne,P.R.L.,1978.Hydrothermal Alteration in Active Geothermal Fields.Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,6(1):229-248.doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.06.050178.001305 Can,I.,2002.A New Improved Na/K Geothermometer by Artificial Neural Networks.Geothermics,31(6):751-760.doi: 10.1016/s0375-6505(02)00044-5 Capuano,R.M.,Cole,D.R.,1982.Fluid-Mineral Equilibria in a Hydrothermal System,Roosevelt Hot Springs,Utah.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,46(8):1353-1364.doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(82)90271-x Chiba,H.,1991.Attainment of Solution and Gas Equilibrium in Japanese Geothermal Systems.Geochemical Journal,25(4):335-355.doi: 10.2343/geochemj.25.335 Chiodini,G.,Cioni,R.,Guidi,M.,et al.,1991.Chemical Geothermometry and Geobarometry in Hydrothermal Aqueous Solutions:A Theoretical Investigation Based on a Mineral-Solution Equilibrium Model.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,55(10):2709-2727.doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(91)90438-b Díaz-González,L.,Santoyo,E.,2008.A New Precise Calibration of the Na/K Geothermometer Using a World Database of Geothermal Fluids and Improved Geochemometric Techniques.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,72(12):215. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=809cf904de82de0e990b510a81a738ff&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Duchi,V.,Minissale,A.,Manganelli,M.,1992.Chemical Composition of Natural Deep and Shallow Hydrothermal Fluids in the Larderello Geothermal Field.Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,49(3-4):313-328.doi: 10.1016/0377-0273(92)90020-e Eberl,D.D.,1980.Alkali Cation Selectivity and Fixation by Clay Minerals.Clays and Clay Minerals,28(3):161-172.doi: 10.1346/ccmn.1980.0280301 Ellis,A.J.,1979.Chemical Geothermometry in Geothermal Systems.Chemical Geology,25(3):219-226.doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(79)90143-8 Ellis,A.J.,Mahon,W.A.J.,1967.Natural Hydrothermal Systems and Experimental Hot Water/Rock Interactions (Part Ⅱ).Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,31(4):519-538.doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(67)90032-4 Fournier,R.O.,1979.A Revised Equation for the Na/K Geothermometer.Transactions-Geothermal Resources Council,3:221-224. Fournier,R.O.,1989.Lectures on Geochemical Interpretation of Hydrothermal Waters.Geothermal Training Programme,the United Nations University,Reykjavík,41-47. Fournier,R.O.,1990.Interpretation of Na-K-Mg Relations in Geothermal Waters.Transactions-Geothermal Resources Council,14:1421-1425. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f1cb23b155ade746f7d9ccbae83d7fb5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Gianelli,G.,Grassi,S.,2001.Water-Rock Interaction in the Active Geothermal System of Pantelleria,Italy.Chemical Geology,181(1-4):113-130.doi: 10.1016/s0009-2541(01)00276-5 Giggenbach,W.F.,1985.Construction of Thermodynamic Stability Diagrams Involving Dioctahedral Potassium Clay Minerals.Chemical Geology,49(1-3):231-242.doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(85)90158-5 Giggenbach,W.F.,1988.Geothermal Solute Equilibria.Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca Geoindicators.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,52(12):2749-2765.doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3 Giggenbach,W.F.,1995.Variations in the Chemical and Isotopic Composition of Fluids Discharged from the Taupo Volcanic Zone,New Zealand.Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,68(1-3):89-116.doi: 10.1016/0377-0273(95)00009-j Giggenbach,W.F.,Gonfiantini,R.,Jangi,B.L.,et al.,1983.Isotopic and Chemical Composition of Parbati Valley Geothermal Discharges,North-West Himalaya,India.Geothermics,12(2-3):199-222.doi: 10.1016/0375-6505(83)90030-5 González-Partida,E.,Carrillo-Chávez,A.,Levresse,G.,et al.,2005.Hydro-Geochemical and Isotopic Fluid Evolution of the Los Azufres Geothermal Field,Central Mexico.Applied Geochemistry,20(1):23-39.doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.07.006 Hoffman,J.,Hower,J.,1979.Clay Mineral Assemblages as Low Grade Metamorphic Geothermometers:Application to the Thrust Faulted Disturbed Belt of Montana,U.S.A..Special Publications,26:55-79.doi: 10.2110/pec.79.26.0055 Holland,T.J.B.,Powell,R.,1998.An Internally Consistent Thermodynamic Data Set for Phases of Petrological Interest.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,16(3):309-343.doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.1998.00140.x Inoue,A.,1995.Formation of Clay Minerals in Hydrothermal Environments.Origin and Mineralogy of Clays,268-329.doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-12648-6_7 Inoue,A.,Kohyama,N.,Kitagawa,R.,et al.,1987.Chemical and Morphological Evidence for the Conversion of Smectite to Illite.Clays and Clay Minerals,35(2):111-120.doi: 10.1346/ccmn.1987.0350203 Inoue,A.,Utada,M.,1983.Further Investigations of a Conversion Series of Dioctahedral Mica/Smectites in the Shinzan Hydrothermal Alteration Area,Northeast Japan.Clays and Clay Minerals,31(6):401-412.doi: 10.1346/ccmn.1983.0310601 Inoue,A.,Utada,M.,Wakita,K.,1992.Smectite-to-Illite Conversion in Natural Hydrothermal Systems.Applied Clay Science,7(1-3):131-145.doi: 10.1016/0169-1317(92)90035-l Japan International Collaboration Agency,Tibet Electric Power Company,2006.Final Report for the Development Program of the Geothermal Resource at Yangbajing.Tibet Electric Power Company,Tibet (in Chinese). Karingithi,C.W.,2000.Geochemical Characteristics of the Greater Olkaria Geothermal Field,Kenya.Geothermal Training Programme,the United Nations University,Reykjavík,165-188. Li,J.X.,Guo,Q.H.,Wang,Y.X.,2015.Evaluation of Temperature of Parent Geothermal Fluid and Its Cooling Processes during Ascent to Surface:A Case Study in Rehai Geothermal Field,Tengchong.Earth Science,40(9):1576-1584 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lutz,S.J.,Moore,J.N.,Copp,J.F.,1996.Integrated Mineralogical and Fluid Inclusion Study of the Coso Geothermal System,California.Proceedings of the Twenty-First Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering,Stanford University,Palo Alto,187-194. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4e740191473cfef9e6f3f62676a25558&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Mas,A.,Guisseau,D.,Mas,P.P.,et al.,2006.Clay Minerals Related to the Hydrothermal Activity of the Bouillante Geothermal Field (Guadeloupe).Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,158(3-4):380-400.doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2006.07.010 McMurtry,G.M.,Fan,P.F.,Coplen,T.B.,1977.Chemical and Isotopic Investigations of Groundwater in Potential Geothermal Areas in Hawaii.American Journal of Science,277(4):438-458.doi: 10.2475/ajs.277.4.438 Mutlu,H.,1998.Chemical Geothermometry and Fluid-Mineral Equilibria for the Ömer-Gecek Thermal Waters,Afyon Area,Turkey.Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,80(3-4):303-321.doi: 10.1016/s0377-0273(97)00051-6 Nathenson,M.,Urban,T.C.,Diment,W.H.,et al.,1980.Temperatures,Heat Flow,and Water Chemistry from Drill Holes in the Raft River Geothermal System,Cassia County,Idaho.Hydrothermal Systems.doi: 10.2172/5294453 Nicholson,K.,1993.Geothermal Fluids.Springer-Verlag,Berlin,72-73.doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77844-5 Nieva,D.,Nieva,R.,1987.Developments in Geothermal Energy in Mexico—Part Twelve.A Cationic Geothermometer for Prospecting of Geothermal Resources.Heat Recovery Systems and CHP,7(3):243-258.doi: 10.1016/0890-4332(87)90138-4 Pang,Z.H.,Reed,M.,1998.Theoretical Chemical Thermometry on Geothermal Waters:Problems and Methods.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,62(6):1083-1091.doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00037-4 Rae,A.J.,Cooke,D.R.,Brown,K.L.,2011.The Trace Metal Chemistry of Deep Geothermal Water,Palinpinon Geothermal Field,Negros Island,Philippines:Implications for Precious Metal Deposition in Epithermal Gold Deposits.Economic Geology,106(8):1425-1446.doi: 10.2113/econgeo.106.8.1425 Stefánsson,A.,Arnòrsson,S.,2000.Feldspar Saturation State in Natural Waters.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,64(15):2567-2584.doi: 10.1016/s0016-7037(00)00392-6 Steiner,A.,1968.Clay Minerals in Hydrothermally Altered Rocks at Wairakei,New Zealand.Clays and Clay Minerals,16(3):193-213.doi: 10.1346/ccmn.1968.0160302 Tarcan,G.,Filiz,S.,Gemici,U.,2000.Geology and Geochemistry of the Salihli Geothermal Fields,Turkey.Proceedings World Geothermal Congress,Kyushu-Tohoku,1829-1834. Tarcan,G.,Gemici,V.,Aksoy,N.,2005.Hydrogeological and Geochemical Assessments of the Gediz Graben Geothermal Areas,Western Anatolia,Turkey.Environmental Geology,47(4):523-534.doi: 10.1007/s00254-004-1174-1 Tonani,F.B.,1980.Some Remarks on the Application of Geochemical Techniques in Geothermal Exploration.Advances in European Geothermal Research,428-443.doi: 10.1007/978-94-009-9059-3_38 Truesdell,A.H.,Nathenson,M.,Rye,R.O.,1977.The Effects of Subsurface Boiling and Dilution on the Isotopic Compositions of Yellowstone Thermal Waters.Journal of Geophysical Research,82(26):3694-3704.doi: 10.1029/jb082i026p03694 Valentino,G.M.,Cortecci,G.,Franco,E.,et al.,1999.Chemical and Isotopic Compositions of Minerals and Waters from the Campi Flegrei Volcanic System,Naples,Italy.Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,91(2-4):329-344.doi: 10.1016/s0377-0273(99)00042-6 Verma,S.P.,Santoyo,E.,1997.New Improved Equations for Na/K,Na/Li and SiO2 Geothermometers by Outlier Detection and Rejection.Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,79(1-2):9-23.doi: 10.1016/s0377-0273(97)00024-3 Walshe,J.L.,1986.A Six-Component Chlorite Solid Solution Model and the Conditions of Chlorite Formation in Hydrothermal and Geothermal Systems.Economic Geology,81(3):681-703.doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.81.3.681 Weaver,C.E.,Pollard,L.D.,1973.The Chemistry of Clay Minerals.Developments in Sedimentology,15:213.doi: 10.1016/S0070-4571(09)70015-9 White,D.E.,1957.Thermal Waters of Volcanic Origin.Geological Society of America Bulletin,68(12):1637-1658.doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1957)682.0.co;2 Yan,Y.H.,Tillick,D.A.,Peacor,D.R.,et al.,2001.Genesis of Dioctahedral Phyllosilicates during Hydrothermal Alteration of Volcanic Rocks:Ⅱ.The Broadlands-Ohaaki Hydrothermal System,New Zealand.Clays and Clay Minerals,49(2):141-155.doi: 10.1346/ccmn.2001.0490204 Yang,K.,Browne,P.R.L.,Huntington,J.F.,et al.,2001.Characterising the Hydrothermal Alteration of the Broadlands-Ohaaki Geothermal System,New Zealand,Using Short-Wave Infrared Spectroscopy.Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,106(1-2):53-65.doi: 10.1016/s0377-0273(00)00264-x 日本国际协力机构, 中国西藏自治区电力工业局, 2006.中国人民共和国西藏羊八井地热资源开发计划调查最终报告.中国西藏自治区电力工业局, 西藏. 李洁祥, 郭清海, 王焰新, 2015.高温热田深部母地热流体的温度计算及其升流后经历的冷却过程: 以腾冲热海热田为例.地球科学, 40(9): 1576-1584. http://www.earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3161 -









 下载:
下载: