River Terrace Extraction Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing
-
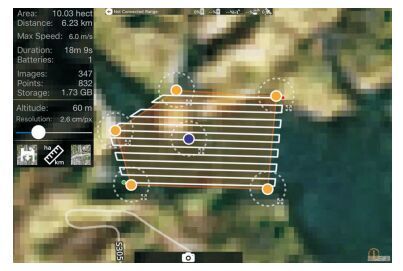
摘要: 河流阶地记录了河流演变过程中因构造抬升或气候变化引起的侵蚀基准面变化的信息,阶地的提取与划分对于新构造研究与古气候重建有着重要的意义,在分析传统阶地提取方法不足的基础上,提出了一种利用无人机遥感进行阶地提取的新方法.该方法利用无人机航拍影像和高精度地面控制点,通过基于计算机视觉的多视立体运动恢复结构(structure from motion with multi-view stereo, SfM-MVS)技术自动生成研究区高分辨率的正射影像和数字表面模型(digital surface model,DSM),在此基础上根据河流阶地的几何特征,利用高程、坡度及影像灰度等统计量实现阶地信息的提取.利用这一方法对汉江支流蛮河下游河段的阶地进行了提取试验.结果表明,该方法能够提取到两级河流阶地和一级河漫滩信息,提取结果与野外实测结果有较好的一致性.与传统阶地提取方法相比,该方法具有精度好、效率高、可视化效果全面直观等优势,显示出无人机遥感在河流地貌学研究中的巨大优势和广阔应用前景.Abstract: River terraces record the information of environmental changes in the process of river evolution. Proper identification and classification of terraces are of great importance to the paleo-environmental reconstruction and local tectonic evolution. Based on the analysis of drawbacks of the traditional approaches, a terrace extraction method using the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) remote sensing is proposed. In this paper, the UAV images and high precision ground control points are used to automatically generate the high resolution DSM (digital surface model) and orthophoto using computer vision-based structure from motion with multi-view stereo photogrammetry (SfM-MVS) techniques. On this basis, the geometric characteristics of river terraces, including the elevation, slope, and image textures are employed to delineate terraces. The proposed method is used to extract the river terraces in the lower reaches of Manhe River, a branch of Hanjiang River. The results show that the terraces extracted with the proposed method have a good agreement with those measured in the field. The proposed method has advantages of high precision and efficiency, and effective visualization for terrace representation. This method provides the technical support for the recognition of terraces, and reveals the potential of UAV remote sensing in geomorphology studies.
-
Key words:
- river terrace /
- unmanned aerial vehicle /
- remote sensing /
- digital surface model /
- Hanjiang River /
- hydrogeology
-
表 1 相机参数
Table 1. Camera parameters
焦距(mm) 主像点x (mm-1) 主像点y (mm-1) R1 R2 R3 T1 T2 初始值 3.722 3.159 2.369 -0.001 -0.002 0.000 -0.001 -0.001 校正值 3.417 3.180 2.296 -0.007 0.005 0.005 -0.001 0.000 注:R1,R2,R3.相机镜头径向畸变参数;T1,T2.相机镜头切向畸变参数. 表 2 检查点误差
Table 2. Errors of check points
编号 X(m) Y(m) Z(m) 1 0.086 9 -0.006 1 -0.198 7 2 0.065 7 -0.022 1 -0.093 8 3 0.004 3 -0.044 2 0.063 5 4 0.005 2 -0.021 7 0.096 8 5 -0.059 0 0.056 9 -0.055 6 6 -0.064 1 -0.010 0 0.146 8 7 -0.025 9 0.097 7 -0.095 5 RMSE(m) 0.053 7 0.047 6 0.116 7 表 3 阶地高度信息
Table 3. Statistics of extracted terraces
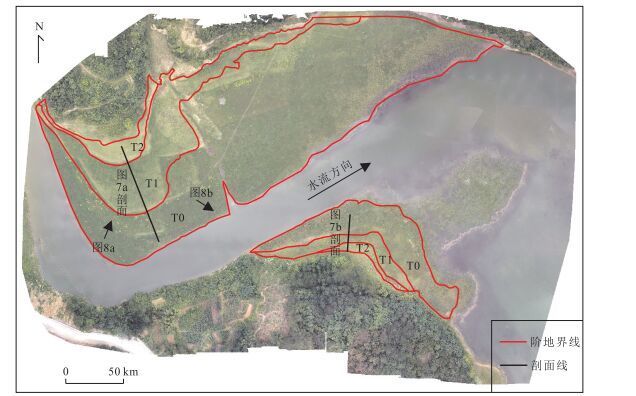
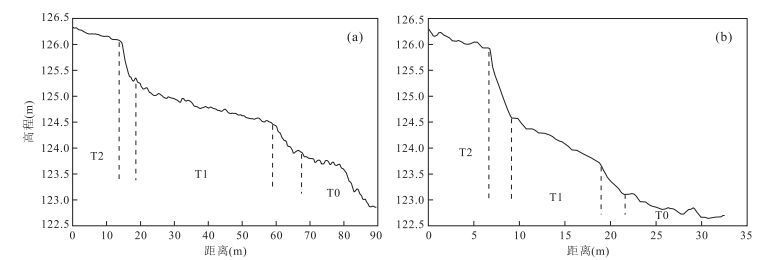
阶地 前缘高度(m) 后缘高度(m) 面积(m2) 左岸 右岸 左岸 右岸 左岸 右岸 T0 122.8 122.6 123.9 123.1 27 721.2 4 767.8 T1 124.5 123.8 125.3 124.6 7 373.2 1 422.0 T2 126.1 125.9 126.3 126.2 1 357.5 488.5 -
Del Val, M., Iriarte, E., Arriolabengoa, M., et al., 2015.An Automated Method to Extract Fluvial Terraces from LIDAR Based High Resolution Digital Elevation Models:The Oiartzun Valley, a Case Study in the Cantabrian Margin.Quaternary International, 364:35-43.doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.10.030 Demoulin, A., Bovy, B., Rixhon, G., et al., 2007.An Automated Method to Extract Fluvial Terraces from Digital Elevation Models:The Vesdre Valley, a Case Study in Eastern Belgium.Geomorphology, 91(1-2):51-64.doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.01.020 Diaz-Varela, R.A., Zarco-Tejada, P.J., Angileri, V., et al., 2014.Automatic Identification of Agricultural Terraces through Object-Oriented Analysis of very High Resolution DSMs and Multispectral Imagery Obtained from an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle.Journal of Environmental Management, 134(4):117-126.doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.01.006 Erlanger, E.D., Granger, D.E., Gibbon, R.J., 2012.Rock Uplift Rates in South Africa from Isochron Burial Dating of Fluvial and Marine Terraces.Geology, 40(11):1019-1022.doi: 10.1130/g33172.1 Gonalves, J.A., Henriques, R., 2015.UAV Photogrammetry for Topographic Monitoring of Coastal Areas.ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 104:101-111.doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.02.009 Gong, H.L., Ran, Y.K., 2015.Digital Terrain Analysis of Anning River Terraces Based on SPOT Image.North China Earthquake Sciences, 33(3):31-36(in Chinese with English abstract). Gong, H.L., Ran, Y.K., Chen, L.C., 2008.The Method of Terrace Analysis Based on Dem—A Case Study in Zimakua of Anninghe Fault.Seismology and Geology, 30(1):339-348 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286960856_The_method_of_terrace_analysis_based_on_DEM_-_A_case_study_in_Zimakua_of_Anninghe_Fault Han, F., Zhang, K.X., Wei, Y., et al., 2010.Sedimentary Sequences and Paleoclimate of Late Pleistocene in Xunhua Basin, Qinghai Province.Earth Science, 35(5):849-856(in Chinese with English abstract). Hu, X.F., Pan, B.T., Gao, H.S., et al., 2013.Development of Holocene Fluvial Terraces in the Eastern Qilianshan Mountain and Its Relationship with Climatic Changes.Quaternary Sciences, 33(4):723-736(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201304010.htm Jin, W., Ge, H.L., Du, H.Q., et al., 2009.A Review on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing and Its Application.Remote Sensing Information, (1):88-92(in Chinese with English abstract). Lewin, J., Gibbard, P.L., 2010.Quaternary River Terraces in England:Forms, Sediments and Processes.Geomorphology, 120(3-4):293-311.doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2010.04.002 Li, B., Liu, R.Y., Liu, S.H., et al., 2012.Monitoring Vegetation Coverage Variation of Winter Wheat by Low-Altitude UAV Remote Sensing System.Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 28(13):160-165(in Chinese with English abstract). Lowe, D.G., 2004.Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Key Points.International Journal of Computer Vision, 60(2):91-110.doi: 10.1023/b:visi.0000029664.99615.94 Pang, J.L., Huang, C.C., Zhou, Y.L., et al., 2014.Formation of the First River Terraces of Hanjiang River and Its Response to the East Asian Monsoon Change.Geological Review, 60(5):1076-1084(in Chinese with English abstract). Passaro, S., Ferranti, L., de Alteriis, G.D., 2011.The Use of High-Resolution Elevation Histograms for Mapping Submerged Terraces:Tests from the Eastern Tyrrhenian Sea and the Eastern Atlantic Ocean.Quaternary International, 232(1-2):238-249.doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2010.04.030 Schildgen, T.F., Cosentino, D., Bookhagen, B., et al., 2012.Multi-Phased Uplift of the Southern Margin of the Central Anatolian Plateau, Turkey:A Record of Tectonic and Upper Mantle Processes.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 317-318:85-95.doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2011.12.003 D'Oleireoltmanns, S., Marzolff, I., Peter, K.D., et al., 2012.Unmanned Aerial Vehicle(UAV) for Monitoring Soil Erosion in Morocco.Remote Sensing, 4(11):3390-3416. Smith, M.W., Carrivick, J.L., Quincey, D.J., 2015.Structure from Motion Photogrammetry in Physical Geography.Progress in Physical Geography, 40(2):247-275.doi: 10.1177/0309133315615805 Song, Z.Q., Zhang, J.L., Li, J.J., 2014.A Clustering Approach for Incorporation Spatial Dependence into the Automatic Fluvial Terrace Extraction from Digital Elevation Model:A Case Study from the Zhangla Basin along the Upstream of the Minjiang River.Seismology and Geology, 36(4):1029-1042 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tonkin, T.N., Midgley, N.G., Graham, D.J., et al., 2014.The Potential of Small Unmanned Aircraft Systems and Structure-from-Motion for Topographic Surveys:A Test of Emerging Integrated Approaches at Cwm Idwal, North Wales.Geomorphology, 226(1-2):35-43.doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.07.021 Turner, D., Lucieer, A., Watson, C., 2012.An Automated Technique for Generating Georectified Mosaics from Ultra-High Resolution Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Imagery, Based on Structure from Motion (SfM) Point Clouds.Remote Sensing, 4(12):1392-1410.doi: 10.3390/rs4051392 Wang, P.T., Shao, Y.X., Zhang, H.P., et al., 2016.The Application of sUAV Photogrammetry in Active Tectonics:Shanmagou Site of Haiyuan Fault, for Example.Quaternary Sciences, 36(2):433-442 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wei, Z.Y., Ramon, A., He, H.L., et al., 2015.Accuracy Analysis of Terrain Point Cloud Acquired by "Structure from Motion" Using Aerial Photos.Seismology and Geology, 37(2):636-648(in Chinese with English abstract). Xiang, F., Zhu, L.D., Wang, C.S., et al., 2005.Terrace Age Correlation and Its Significance in Research of Yangtze Three Gorges, China.Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition), 32(2):162-166(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Z.L., Wu, S.R., Tang, H.M., et al., 2015.Control Effect of Evolution Process of the Yellow River Terrace in Lanzhou on Landslide Activity.Earth Science, 40(9):1585-1597(in Chinese with English abstract). 宫会玲, 冉勇康, 2015.基于SPOT影像的安宁河阶地数字地形分析.华北地震科学, 33(3):31-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDKD201503008.htm 宫会玲, 冉勇康, 陈立春, 2008.基于DEM的阶地分析方法——以安宁河断裂紫马跨地区为例.地震地质, 30(1):339-348. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200801026.htm 韩芳, 张克信, 韦一, 等, 2010.青海循化盆地晚更新世沉积序列与古气候.地球科学, 35(5):849-856. http://www.earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=2029 胡小飞, 潘保田, 高红山, 等, 2013.祁连山东段全新世河流阶地发育及其与气候变化的关系研究.第四纪研究, 33(4):723-736. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201304010.htm 金伟, 葛宏立, 杜华强, 等, 2009.无人机遥感发展与应用概况.遥感信息, (1):88-92. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXX200901020.htm 李冰, 刘镕源, 刘素红, 等, 2012.基于低空无人机遥感的冬小麦覆盖度变化监测.农业工程学报, 28(13):160-165. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYGU201213027.htm 庞奖励, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等, 2014.汉江上游Ⅰ级河流阶地形成及对东亚季风变化的响应.地质论评, 60(5):1076-1084. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201405013.htm 宋卓沁, 张军龙, 李建军, 2014.基于模糊聚类和空间自相关性的河流阶地自动提取方法——以岷江上游漳腊盆地为例.地震地质, 36(4):1029-1042. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201404008.htm 王朋涛, 邵延秀, 张会平, 等, 2016.sUAV摄影技术在活动构造研究中的应用——以海原断裂骟马沟为例.第四纪研究, 36(2):433-442. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85402-1015543026.htm 魏占玉, Ramon, A., 何宏林, 等, 2015.基于SfM方法的高密度点云数据生成及精度分析.地震地质, 37(2):636-648. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201502024.htm 向芳, 朱利东, 王成善, 等, 2005.长江三峡阶地的年代对比法及其意义.成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 32(2):162-166. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG20050200A.htm 张泽林, 吴树仁, 唐辉明, 等, 2015.兰州黄河阶地演变过程对滑坡活动的控制效应.地球科学, 40(9):1585-1597. http://www.earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3162 -










 下载:
下载: