Formation, Modification and Analytical Techniques of Melt Inclusion, and Their Applications in Economic Geology
-
摘要: 熔体包裹体研究不仅广泛应用于火山岩和部分侵入岩系统,而且因其具有可以保存岩浆初始挥发分和金属组成的优势,近来也逐步应用于矿床学领域.在介绍熔体包裹体形成机制和捕获后成分改造的基础上,简要归纳了目前常用的熔体包裹体分析方法,以斑岩型Cu-(Mo-Au)和斑岩型Mo成矿系统为例,重点介绍熔体包裹体在矿床学领域的应用,包括成矿金属和挥发分含量的测定,以及熔体-流体分配系数测定等方面.然而,熔体包裹体在捕获后均会受到不同程度的成分改造,且对于大多数造岩矿物内的熔体包裹体,其成分改造的具体机制仍不明了,因此在实际应用过程中,需要对其组成进行具体分析和甄别.随着分析技术的改善和提高,熔体包裹体捕获后具体成分改造机制有待进一步查明,进而推动熔体包裹体的应用.现阶段熔体包裹体在斑岩型Cu-(Mo-Au)和斑岩型Mo成矿岩浆系统的成功应用表明,相比全岩地球化学研究,熔体包裹体已成为研究成矿岩浆体系内成矿金属和挥发分演化的重要手段.
-
关键词:
- 熔体包裹体 /
- 斑岩型Cu-(Mo-Au)矿床 /
- 斑岩型Mo矿床 /
- 电子探针 /
- 二次离子质谱 /
- 激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱
Abstract: Melt inclusion has been widely used in the research of volcanic and some magmatic systems, and now gradually applied to economic geology because of its absolute advantage over whole-rock analysis in preserving the primary metal and volatile composition of ore-forming magmas. In this paper, we firstly present melt inclusion formation and post-entrapment modification on its composition, then summarize the commonly used analytical techniques for melt inclusion studies, and finally take porphyry Cu-(Mo-Au) and porphyry Mo systems as examples to introduce its applications in economic geology, including determination of ore-forming metals, volatile composition, and fluid-melt partition coefficients. Considering the facts that most melt inclusions have been modified to a certain degrees after their entrapment, and that the modification mechanism for most rock-forming minerals has not been well understood, attention has to be paid to the melt inclusion data and associated interpretation.With the improvement of analytical methods, such ambiguous post-entrapment modification mechanism may be resolved in the near future, and in turn it can promote the applications of melt inclusion. The successful applications of melt inclusion in porphyry Cu-(Mo-Au) and porphyry Mo systems confirm that melt inclusion has been an important and powerful tool in studying ore-forming metals and volatile evolution in ore-forming magma systems in comparison with whole-rock study. -
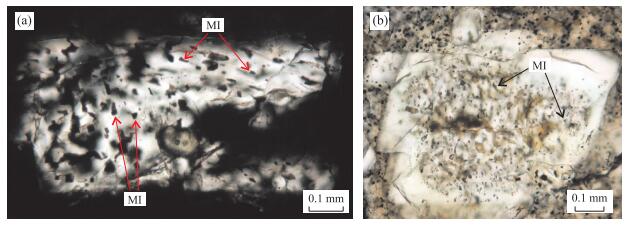
图 1 石英内不同类型熔体包裹体形成示意(a)及部分典型熔体包裹体显微照片(b~d)
a.熔体包裹体形成示意(据Audétat and Lowenstern, 2014),其中熔体包裹体A~D均为原生,E为假次生,F为次生,包裹体C和D代表捕获其他结晶相、不混溶熔体或流体相(白色部分);b.石英内随机分布原生熔体包裹体(MI);c.捕获锆石的玻璃质熔体包裹体,该情况较少见;d.石英内沿生长带分布熔体包裹体(MI)
Fig. 1. Schematic view showing the formation of different types of melt inclusions within quartz crystal (a), and microphotographs of typical melt inclusions (b-d)
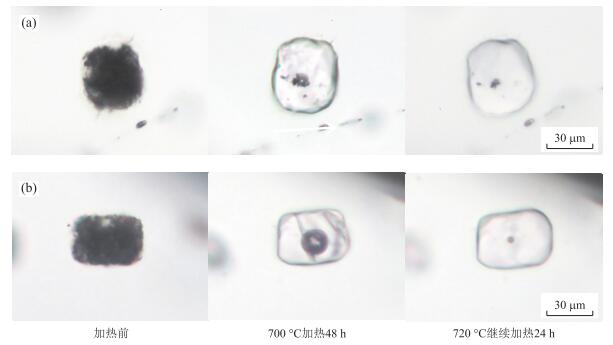
图 4 使用高压容器(Ar气压为2 GPa)加热均一石英内结晶熔体包裹体的前后变化
Fig. 4. Changes in the appearance of crystallized melt inclusions during stepwise homogenization at 2 GPa Ar confining pressure
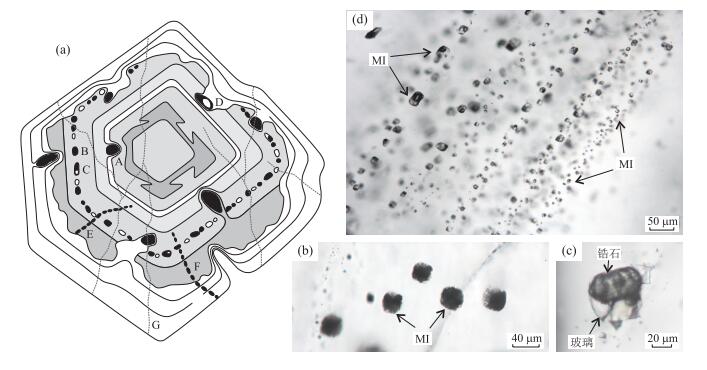
图 5 LA-ICP-MS分析橄榄石内结晶熔体包裹体剥蚀示意和对应信号
a.橄榄石内结晶熔体包裹体;b.激光剥蚀完整熔体包裹体示意(据Pettke, 2006);c.对应的LA-ICP-MS信号
Fig. 5. Schematic diagram of LA-ICP-MS analysis of a crystallized melt inclusion within olivine crystal, and corresponding transient signals
图 6 矿化与非矿化岩浆系统镁铁质端元熔体包裹体Cu(a)和S(b)含量对比
Fig. 6. Comparison of Cu (a) and S (b) concentrations in mafic melt inclusions from mineralized and barren systems
图 7 斑岩型Mo矿床、弱矿化和未矿化岩浆体系熔体包裹体Mo含量对比
据Audétat(2015);Henderson和Silver Creek数据引自Zhang and Audétat(2017b)
Fig. 7. Comparison of Mo concentrations from porphyry Mo-mineralized, sub-economically Mo-mineralized and barren systems
图 8 来自不同构造环境和斑岩型Mo矿床岩浆体系中流纹质熔体包裹体Rb与F含量变化关系
据Audétat(2015);Pine Grove数据引自Lowenstern(1994);Henderson和Silver Creek数据引自Zhang and Audétat(2017b)
Fig. 8. Rb vs. F diagram for rhyolitic melt inclusions from different tectonic settings and from porphyry Mo-mineralized systems
表 1 常用熔体包裹体成分分析技术方法的特点及优缺点对比
Table 1. Comparison among different characteristics of commonly used methods for analyzing melt inclusion composition, and their corresponding advantages and disadvantages
分析方法 包裹体要求 分析元素/同位素 空间分辨率(μm) 检测限(10-6) 优点 缺点 EPMA 均一、暴露至表面 主量和部分微量元素 1~20 500 非破坏性、同一包裹体可多次分析 分析元素少;Na丢失现象;样品准备工作繁琐;不适用于无法完全均一的包裹体 SIMS 均一、暴露至表面 微量元素、挥发分、稳定同位素、Pb同位素 10~30 <1 对同一包裹体进行多种分析 分析效率低;样品准备工作繁琐;不适用于无法完全均一的包裹体 LA-ICP-MS 包裹体埋深不能过大 主微量和稀土元素、Sr和Pb同位素 10~100 <1 无需均一化;分析元素范围广、效率高;样品准备工作简单 同一包裹体无法重复分析;无法测定挥发分;内标选择引入误差 注:据文献Kent (2008); Mason et al.(2008) ;Audétat and Lowenstern (2014)修改.表 2 斑岩型Mo成矿岩浆与未矿化岩浆Mo流体/熔体分配系数对比
Table 2. Comparison of fluid-melt partition coefficients of Mo from porphyry Mo-mineralized and barren magmas
岩体 样品 流体盐度(% NaClequiv.) 流体均一温度(℃) 流体包裹体Mo含量(10-6) 熔体包裹体Mo含量(10-6) DMo流体/熔体 数据来源 矿化 Cave Peak MC2A-GT 18.0 550~600 127±4 7.3±1.5 17.4±3.6 Audétat(2010) Cave Peak MC2A-GZ 19.0 550~600 106±11 5.3±1.7 19.8±6.7 Audétat(2010) 未矿化 Stronghold Stro 1A 5.9 412 46±9 3.2±2.2 14.4±10.3 Audétat et al.(2008) Rito del Medio Rtio5 last gz 4.9 420 133±6 9.3±2.4 14.3±3.7 Zajacz et al.(2008) Rito del Medio Rito5 2nd last gz 4.5 425 168±20 7.4±2.0 22.7±6.7 Zajacz et al.(2008) Huangshan HS8 4.7 389 75±14 3.6±0.5 20.8±4.8 未发表数据 注:据Audétat(2015)修改;流体盐度为质量百分含量. 表 3 不同斑岩型Mo成矿岩浆物理化学性质对比
Table 3. Comparison of physical and chemical properties of ore-forming magmas from porphyry Mo systems
Climax Henderson Pine Grove Silver Creek Mo(10-6) 5~7 10~15 ~2 3~4 F(%) 3.10~4.50 0.45~0.56 0.28~0.38 0.25~0.32 H2O(%) ~6.0 5.2~7.2 6.0~8.0 5.8~9.4 T(℃)1 710~730 740~780 710~720 780~800 log η(Pa·s)2 4.8~4.9 4.4~4.9 4.5~5.1 3.5~4.4 注:据Zhang and Audétat(2017b)修改;1.锆石饱和温度;2.岩浆粘度;F和H2O为质量百分含量. -
Anderson, A.T., 1974.Evidence for a Picritic, Volatile-Rich Magma beneath Mt Shasta, California.Journal of Petrology, 15(2):243-267.doi: 10.1093/petrology/15.2.243 Anderson, A.T., Wright, T.L., 1972.Phenocrysts and Glass Inclusions and Their Bearing on Oxidation and Mixing of Basaltic Magmas, Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii.American Mineralogist, 57:188-216. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284143492_Phenocrysts_and_glass_inclusions_and_their_bearing_on_oxidation_and_mixing_of_basaltic_magmas_Kilauea_Volcano_Hawaii Audétat, A., 2010.Source and Evolution of Molybdenum in the Porphyry Mo(-Nb) Deposit at Cave Peak, Texas.Journal of Petrology, 51(8):1739-1760.doi: 10.1093/petrology/egq037 Audétat, A., 2015.Compositional Evolution and Formation Conditions of Magmas and Fluids Related to Porphyry Mo Mineralization at Climax, Colorado.Journal of Petrology, 56(8):1519-1546.doi: 10.1093/petrology/egv044 Audétat, A., Dolejš, D., Lowenstern, J.B., 2011.Molybdenite Saturation in Silicic Magmas:Occurrence and Petrological Implications.Journal of Petrology, 52(5):891-904.doi: 10.1093/petrology/egr008 Audétat, A., Günther, D., Heinrich, C.A., 2000.Magmatic-Hydrothermal Evolution in a Fractionating Granite:A Microchemical Study of the Sn-W-F-Mineralized Mole Granite (Australia).Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 64(19):3373-3393.doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00428-2 Audétat, A., Lowenstern, J.B., 2014.Melt Inclusions.In:Scott, S.D., ed., Geochemistry of Mineral Deposits.Treatise on Geochemistry.Elsevier, London, 143-173. Audétat, A., Pettke, T., 2006.Evolution of a Porphyry-Cu Mineralized Magma System at Santa Rita, New Mexico (USA).Journal of Petrology, 47(10):2021-2046.doi: 10.1093/petrology/egl035 Audétat, A., Pettke, T., Dolejš, D., 2004.Magmatic Anhydrite and Calcite in the Ore-Forming Quartz-Monzodiorite Magma at Santa Rita, New Mexico (USA):Genetic Constraints on Porphyry-Cu Mineralization.Lithos, 72(3-4):147-161.doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2003.10.003 Audétat, A., Pettke, T., Heinrich, C.A., et al., 2008.The Composition of Magmatic-Hydrothermal Fluids in Barren and Mineralized Intrusions.Economic Geology, 103(5):877-908.doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.103.5.877 Audétat, A., Simon, A.C., 2012.Magmatic Controls on Porphyry Cu Genesis.In:Hedenquist, J.W., Harris, M., Camus, F., eds., Geology and Genesis of Major Copper Deposits and Districts of the World:A Tribute to Richard Sillitoe:SEG Special Publication 16, Society of Economic Geologists, Littleton. Baker, D.R., 2008.The Fidelity of Melt Inclusions as Records of Melt Composition.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 156(3):377-395.doi: 10.1007/s00410-008-0291-3 Blundy, J., Cashman, K., 2008.Petrologic Reconstruction of Magmatic System Variables and Processes.Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 69(1):179-239.doi: 10.2138/rmg.2008.69.6 Bodnar, R.J., Student, J.J., 2006.Melt Inclusions in Plutonic Rocks:Petrography and Microthermometry.In:Webster, J.D., ed., Melt Inclusions in Plutonic Rocks, Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Series.Mineralogical Association of Canada, Montreal, 1-25. Carten, R.B., Geraghty, E.P., Walker, B.M., et al., 1988.Cyclic Development of Igneous Features and Their Relationship to High-Temperature Hydrothermal Features in the Henderson Porphyry Molybdenum Deposit, Colorado.Economic Geology, 83(2):266-296.doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.2.266 Carten, R.B., White, W.H., Stein, H.J., 1993.High-Grade Granite-Related Molybdenum Systems:Classification and Origin.Geological Association of Canada Special Paper, 40:521-554. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279597436_High-grade_granite-related_molybdenum_systems_classification_and_origin Danyushevsky, L.V., Della-Pasqua, F.N., Sokolov, S., 2000.Re-Equilibration of Melt Inclusions Trapped by Magnesian Olivine Phenocrysts from Subduction-Related Magmatism:Petrological Implications.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 138(1):68-83.doi: 10.1007/PL00007664 Danyushevsky, L.V., McNeill, A.W., Sobolev, A.V., 2002.Experimental and Petrological Studies of Melt Inclusions in Phenocrysts from Mantle-Derived Magmas:An Overview of Techniques, Advantages and Complications.Chemical Geology, 183(1):5-24.doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00369-2 Devine, J.D., Gardner, J.E., Brack, H.P., et al., 1995.Comparison of Microanalytical Methods for Estimating H2O Contents of Silicic Volcanic Glasses.American Mineralogist, 80(3):319-328.doi: 10.2138/am-1995-3-413 Dietrich, A., Lehmann, B., Wallianos, A., 2000.Bulk Rock and Melt Inclusion Geochemistry of Bolivian Tin Porphyry Systems.Economic Geology, 95(2):313-326.doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.95.2.313 Ding, S., Tang, J.X., Zheng, W.B., et al., 2017.Geochronology and Geochemistry of Naruo Porphyry Cu (Au) Deposit in Duolong Ore-Concentrated Area, Tibet, and Their Geological Significance.Earth Science, 42(1):1-23(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284686858_Geochronology_and_geochemistry_of_the_Bolong_porphyry_Cu-Au_deposit_Tibet_and_its_mineralizing_significance Duan, X., Sun, H., Yang, W., et al., 2014.Melt-Peridotite Interaction in the Shallow Lithospheric Mantle of the North China Craton:Evidence from Melt Inclusions in the Quartz-Bearing Orthopyroxene-Rich Websterite from Hannuoba.International Geology Review, 56(4):448-472.doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.873357 Fu, L.B., Wei, J.H., Zhang, D.H., et al., 2015.A Review of LA-ICP-MS Analysis for Individual Fluid Inclusions and Its Applications in Ore Deposits.Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 46(10):3832-3840 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290319451_A_review_of_LA-ICPMS_analysis_for_individual_fluid_inclusions_and_its_applications_in_ore_deposits Gaetani, G.A., O'Leary, J.A., Schimizu, N., et al., 2012.Rapid Reequilibration of H2O and Oxygen Fugacity in Olivine-Hosted Melt Inclusions.Geology, 40(10):915-918.doi: 10.1130/G32992.1 Gaetani, G.A., Watson, E.B., 2002.Modeling the Major-Element Evolution of Olivine-Hosted Melt Inclusions.Chemical Geology, 183(1):25-41.doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00370-9 Giordano, D., Russell, J.K., Dingwell, D.B., 2008.Viscosity of Magmatic Liquids:A Model.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 271(1-4):123-134.doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.03.038 Halter, W.E., Heinrich, C.A., Pettke, T., 2005.Magma Evolution and the Formation of Porphyry Cu-Au Ore Fluids:Evidence from Silicate and Sulfide Melt Inclusions.Mineralium Deposita, 39(8):845-863.doi: 10.1007/s00126-004-0457-5 Halter, W.E., Pettke, T., Heinrich, C.A., et al., 2002.Major to Trace Element Analysis of Melt Inclusions by Laser-Ablation ICP-MS:Methods of Quantification.Chemical Geology, 183(1-4):63-86.doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00372-2 Halter, W.E., Pettke, T., Heinrich, C.A., 2004.Laser-Ablation ICP-MS Analysis of Silicate and Sulfide Melt Inclusions in an Andesitic Complex I:Analytical Approach and Data Evaluation.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 147(4):385-396.doi: 10.1007/s00410-004-0562-6 Hattori, K., 1993.High-Sulfur Magma, a Product of Fluid Discharge from Underlying Mafic Magma:Evidence from Mount Pinatubo, Philippines.Geology, 21(12):1083-1086.doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<1083:HSMAPO>2.3.CO;2 Heinrich, C.A., Pettke, T., Halter, W.E., et al., 2003.Quantitative Multi-Element Analysis of Minerals, Fluid and Melt Inclusions by Laser-Ablation Inductively-Coupled-Plasma Mass-Spectrometry.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(18):3473-3497.doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00084-X Hinton, R.W., 1995.Ion Microprobe Analysis in Geology.In:Potts, P.J., John, F.W., Stephen, J.B., et al., eds., Microprobe Techniques in the Earth Sciences.Chapman and Hall, London. Hou, Z.Q., Li, Q.Y., Gao, Y.F., et al., 2015.Lower-Crustal Magmatic Hornblendite in North China Craton:Insight into the Genesis of Porphyry Cu Deposits.Economic Geology, 110(7):1879-1904.doi: 10.2113/econgeo.110.7.1879 Hou, Z.Q., Meng, X.J., Qu, X.M., et al., 2005.Copper Ore Potential of Adakitic Intrusives in Gangdese Porphyry Copper Belt:Constrains from Rock Phase and Deep Melting Process.Mineral Deposits, 24(2):108-121(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200502002.htm Humphreys, M.C.S., Kearns, S.L., Blundy, J.D., 2006.SIMS Investigation of Electron-Beam Damage to Hydrous, Rhyolitic Glasses:Implications for Melt Inclusion Analysis.American Mineralogist, 91(4):667-679.doi: 10.2138/am.2006.1936 Layne, G., 2006.Applications of Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry to the Determination of Traditional and Non-Traditional Light Stable Isotopes in Silicate Melt Inclusions.In:Webster, J.D., ed., Melt Inclusions in Plutonic Rocks, Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Series.Mineralogical Association of Canada, Montreal. Lerchbaumer, L., Audétat, A., 2013.The Metal Content of Silicate Melts and Aqueous Fluids in Subeconomically Mo Mineralized Granites:Implications for Porphyry Mo Genesis.Economic Geology, 108(5):987-1013.doi: 10.2113/econgeo.108.5.987 Li, H.Y., Xu, Y.G., Ryan, J.G., et al., 2016.Olivine and Melt Inclusion Chemical Constraints on the Source of Intracontinental Basalts from the Eastern North China Craton:Discrimination of Contributions from the Subducted Pacific Slab.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 178:1-19.doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.12.032 Li, S.H., Li, J.K., Chou, I.M., et al., 2017.The Formation of the Yichun Ta-Nb Deposit, South China, through Fractional Crystallization of Magma Indicated by Fluid and Silicate Melt Inclusions.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 137:180-193.doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.11.016 Liu, J.Q., Ren, Z.Y., Nichols, A.R.L., et al., 2015.Petrogenesis of Late Cenozoic Basalts from North Hainan Island:Constraints from Melt Inclusions and Their Host Olivines.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 152:89-121.doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.12.023 Liu, Y.S., Hu, Z.C., Li, M., et al., 2013.Applications of LA-ICP-MS in the Elemental Analyses of Geological Samples.Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(36):3863-3878.doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5901-4 Loucks, R.R., 2014.Distinctive Composition of Copper-Ore-Forming Arc Magmas.Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 61(1):5-16.doi: 10.1080/08120099.2013.865676 Lowenstern, J.B., 1994.Dissolved Volatile Concentrations in an Ore-Forming Magma.Geology, 22(10):893-896.doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0893:DVCIAO>2.3.CO;2 Lowenstern, J.B.1995.Application of Silicate-Melt Inclusions to the Study of Magmatic Volatiles.In:Thompson, J.F.H., ed., Magmas, Fluids and Ore Deposition.Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Series.Mineralogical Association of Canada, Ottawa. Lu, H.Z., Fan, H.R., Ni, P., et al., 2004.Fluid Inclusions.Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Luhr, J.F., 2008.Primary Igneous Anhydrite:Progress since Its Recognition in the 1982 El Chichón Trachyandesite.Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 175(4):394-407.doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.02.016 Keith, J.D., Whitney, J.A., Hattori, K., et al., 1997.The Role of Magmatic Sulfides and Mafic Alkaline Magmas in the Bingham and Tintic Mining District, Utah.Journal of Petrology, 38(12):1679-1690.doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.12.1679 Kent, A.J.R., 2008.Melt Inclusions in Basaltic and Related Volcanic Rocks.Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 69(1):273-331.doi: 10.2138/rmg.2008.69.8 Kohut, E., Nielsen, R.L., 2004.Melt Inclusion Formation Mechanisms and Compositional Effects in High-An Feldspar and High-Fo Olivine in Anhydrous Mafic Silicate Liquids.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 147(6):684-704.doi: 10.1007/s00410-004-0576-0 Kuzmin, D.V., Sobolev, A.V., 2004.Boundary Layer Contribution to the Composition of Melt Inclusions in Olivine.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68:A544. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/283992803_Boundary_layer_contribution_to_the_composition_of_melt_inclusions_in_olivine Mason, P.R.D., Nikogosian, I.K., van Bergen, M.J., 2008.Major and Trace Element Analysis of Melt Inclusions by Laser Ablation ICP-MS.In:Sylvester, P.J., ed., Laser Ablation ICP-MS in the Earth Sciences; Current Practices and Outstanding Issues, Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Series.Mineralogical Association of Canada, Vancouver. Mercer, C.N., Hofstra, A.H., Todorov, T.I., et al., 2015.Pre-Eruptive Conditions of the Hideaway Park Topaz Rhyolite:Insights into Metal Source and Evolution of Magma Parental to the Henderson Porphyry Molybdenum Deposit, Colorado.Journal of Petrology, 56(4):645-679.doi: 10.1093/petrology/egv010 Metrich, N., Wallace, P.J., 2008.Volatile Abundances in Basaltic Magmas and Their Degassing Paths Tracked by Melt Inclusions.Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 69(1):363-402.doi: 10.2138/rmg.2008.69.10 Morgan, G.B., London, D., 2005.Effect of Current Density on the Electron Microprobe Analysis of Alkali Aluminosilicate Glasses.American Mineralogist, 90(7):1131-1138.doi: 10.2138/am.2005.1769 Mustard, R., Ulrich, T., Kamenetsky, V.S., et al., 2006.Gold and Metal Enrichment in Natural Granitic Melts during Fractional Crystallization.Geology, 34(2):85-88.doi: 10.1130/G22141.1 Naumov, V.B., Kamenetsky, V.S., 2006.Silicate and Salt Melts in the Genesis of the Industrial'noe Tin Deposit:Evidence from Inclusions in Minerals.Geochemistry International, 44(12):1181-1190.doi: 10.1134/S0016702906120032 Newcombe, M.E., Fabbrizio, A., Zhang, Y., et al., 2014.Chemical Zonation in Olivine-Hosted Melt Inclusions.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 168(1):1-26.doi: 10.1007/s00410-014-1030-6 Nielsen, R.L., Michael, P.J., Sours-Page, R., 1998.Chemical and Physical Indicators of Compromised Melt Inclusions.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62(5):831-839.doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00024-6 Pettke, T., 2006.In-Situ Laser-Ablation-ICP-MS Chemical Analysis of Melt Inclusion and Prospects for Constraining Subduction Zone Magmas.In:Webster, J.D., ed., Melt Inclusions in Plutonic Rocks, Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Series.Mineralogical Association of Canada, Montreal. Pettke, T., Halter, W.E., Webster, J.D., et al., 2004.Accurate Quantification of Melt Inclusion Chemistry by LA-ICP-MS:A Comparison with EMP and SIMS and Advantages and Possible Limitations of These Methods.Lithos, 78(4):333-361.doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.06.011 Portnyagin, M., Almeev, R., Matveev, S., et al., 2008.Experimental Evidence for Rapid Water Exchange between Melt Inclusions in Olivine and Host Magma.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 272(3-4):541-552.doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.05.020 Richards, J.P., 2005.Cumulative Factors in the Generation of Giant Calc-Alkaline Porphyry Cu Deposits.In:Porter, T.M., ed., Super Porphyry Copper and Gold Deposits:A Global Perspective.PGC Publishing, Adelaide. Roedder, E., 1979.Origin and Significance of Magmatic Inclusions.Bulletin de Mineralogie, 102(5-6):487-510. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB198500004.htm Schiano, P., Bourdon, B., 1999.On the Preservation of Mantle Information in Ultramafic Nodules:Glass Inclusions within Minerals versus Interstitial Glasses.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 169(1-2):173-188.doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00074-6 Severs, M.J., Azbej, T., Thomas, J.B., et al., 2007.Experimental Determination of H2O Loss from Melt Inclusions during Laboratory Heating:Evidence from Raman Spectroscopy.Chemical Geology, 237(3-4):358-371.doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.07.008 Shinohara, H., Kazahaya, K., Lowenstern, J.B., 1995.Volatile Transport in a Convecting Magma Column:Implications for Porphyry Mo Mineralization.Geology, 23(12):1091-1094.doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<1091:VTIACM>2.3.CO;2 Sillitoe, R.H., 2010.Porphyry Copper Systems.Economic Geology, 105(1):3-41.doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.105.1.3 Sorby, H.C., 1858.On the Microscopical, Structure of Crystals, Indicating the Origin of Minerals and Rocks.Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society, 14(1-2):453-500.doi: 10.1144/GSL.JGS.1858.014.01-02.44 Stavast, W.J.A., Keith, J.D., Christiansen, E.H., et al., 2006.The Fate of Magmatic Sulfides during Intrusion or Eruption, Bingham and Tintic Districts, Utah.Economic Geology, 101(2):329-345.doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.101.2.329 Steinberger, I., Hinks, D., Driesner, T., et al., 2013.Source Plutons Driving Porphyry Copper Ore Formation:Combining Geomagnetic Data, Thermal Constraints, and Chemical Mass Balance to Quantify the Magma Chamber beneath the Bingham Canyon Deposit.Economic Geology, 108(4):605-624.doi: 10.2113/econgeo.108.4.605 Stern, C.R., Funk, J.A., Skewes, M.A., et al., 2007.Magmatic Anhydrite in Plutonic Rocks at the El Teniente Cu-Mo Deposit, Chile, and the Role of Sulfurand Copper-Rich Magmas in Its Formation.Economic Geology, 102(7):1335-1344.doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.102.7.1335 Student, J.J., Bodnar, R.J., 1999.Synthetic Fluid Inclusions XIV:Coexisting Silicate Melt and Aqueous Fluid Inclusions in the Haplogranite-H2O-NaCl-KCl System.Journal of Petrology, 40(10):1509-1525.doi: 10.1093/petroj/40.10.1509 Student, J.J., Bodnar, R.J., 2004.Silicate Melt Inclusions in Porphyry Copper Deposits:Identification and Homogenization Behavior.Canadian Mineralogist, 42(5):1583-1599.doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.42.5.1583 Sun, H., Xiao, Y., Gao, Y., et al., 2013.Fluid and Melt Inclusions in the Mesozoic Fangcheng Basalt from North China Craton:Implications for Magma Evolution and Fluid/Melt-Peridotite Reaction.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 165(5):885-901.doi: 10.1007/s00410-012-0840-7 Thomas, R., Webster, J.D., Davidson, P., 2006a.Understanding Pegmatite Formation:The Melt and Fluid Inclusion Approach.In:Webster, J.D., ed., Melt Inclusions in Plutonic Rocks, Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Series.Mineralogical Association of Canada, Montreal. Thomas, R., Kamenetsky, V.S., Davidson, P., 2006b.Laser Raman Spectroscopic Measurements of Water in Unexposed Glass Inclusions.American Mineralogist, 91(2-3):467-470.doi: 10.2138/am.2006.2107 Vasyukova, O., Williams-Jones, A.E., 2014.Fluoride-Silicate Melt Immiscibility and Its Role in REE Ore Formation:Evidence from the Strange Lake Rare Metal Deposit, Québec-Labrador, Canada.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 139:110-130.doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.04.031 Vasyukova, O., Williams-Jones, A.E., 2016.The Evolution of Immiscible Silicate and Fluoride Melts:Implications for REE Ore-Genesis.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 172:205-224.doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.09.018 Wallace, P.J., Edmonds, M., 2011.The Sulfur Budget in Magmas:Evidence from Melt Inclusions, Submarine Glasses, and Volcanic Gas Emissions.Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 73(1):215-246.doi: 10.2138/rmg.2011.73.8 Xia, L.Q., 2002.Melt Inclusions in Magmatic Rocks.Earth Science Frontiers, 9(2):403-414 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200202031.htm Xiao, B., Qin, K.Z., Li, G.M., et al., 2012.Highly Oxidized Magma and Fluid Evolution of Miocene Qulong Giant Porphyry Cu-Mo Deposit, Southern Tibet, China.Resource Geology, 62(1):4-18.doi: 10.1111/j.1751-3928.2011.00177.x Zajacz, Z., Halter, W., 2007.LA-ICPMS Analyses of Silicate Melt Inclusions in Co-Precipitated Minerals:Quantification, Data Analysis and Mineral/Melt Partitioning.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(4):1021-1040.doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.11.001 Zajacz, Z., Halter, W.E., Pettke, T., et al., 2008.Determination of Fluid/Melt Partition Coefficients by LA-ICP-MS Analysis of Co-Existing Fluid and Silicate Melt Inclusions:Controls on Element Partitioning.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(8):2169-2197.doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.01.034 Zajacz, Z., Hanley, J.J., Heinrich, C.A., et al., 2009.Diffusive Reequilibration of Quartz-Hosted Silicate Melt and Fluid Inclusions:Are All Metal Concentrations Unmodified? Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(10):3013-3027.doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.02.023 Zhang, C.L., Liu, Y.S., Gao, S., et al., 2011.Chemical Compositions of Phenocryst-Hosted Melt Inclusions from the Sihetun Basalt:Implications for the Magma Evolution.Geochimica, 40(2):109-125 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285160417_Chemical_compositions_of_phenocryst-hosted_melt_inclusions_from_the_Sihetun_basalt_Implications_for_the_magma_evolution_in_Chinese Zhang, D.H., Audétat, A., 2017a.What Caused the Formation of the Giant Bingham Canyon Porphyry Cu-Mo-Au Deposit? Insights from Melt Inclusions and Magmatic Sulfides.Economic Geology, 112(2):221-244.doi: 10.2113/econgeo.112.2.221 Zhang, D.H., Audétat, A., 2017b.Chemistry, Mineralogy and Crystallization Conditions of Porphyry Mo-Forming Magmas at Urad-Henderson and Silver Creek, Colorado, USA.Journal of Petrology (in press). https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Daohan_Zhang Zhang, L., Audétat, A., 2016.Diffusional Modification of Cu Concentrations in Melt Inclusions.EMPG Abstract 2016, ETH Zürich. Zhang, L., Ren, Z.Y., Nichols, A.R.L., et al., 2014.Lead Isotope Analysis of Melt Inclusions by LA-MC-ICP-MS.Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 29:1393-1405.doi: 10.1039/C4JA00088A 丁帅, 唐菊兴, 郑文宝, 等, 2017.西藏拿若斑岩型铜(金)矿含矿岩体年代学、地球化学及地质意义.地球科学, 42(1):1-23. http://www.earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3409 付乐兵, 魏俊浩, 张道涵, 等, 2015.单个流体包裹体成分LA-ICP-MS分析与矿床学应用进展.中南大学学报(自然科学版), 46(10):3832-3840. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.10.037 侯增谦, 孟祥金, 曲晓明, 等, 2005.西藏冈底斯斑岩铜矿带埃达克质斑岩含矿性:源岩相变及深部过程约束.矿床地质, 24(2):108-121. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200502002.htm 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培, 等, 2004.流体包裹体.北京:科学出版社. 夏林圻, 2002.岩浆岩中的熔体包裹体.地学前缘, 9(2):403-414. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200202031.htm 张春来, 刘勇胜, 高山, 等, 2011.四合屯玄武岩斑晶中单个熔体包裹体元素组成及其对岩浆演化的指示.地球化学, 40(2):109-125. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201102001.htm -









 下载:
下载: